11.2: Structure And Function Of The Respiratory System
Di: Jacob
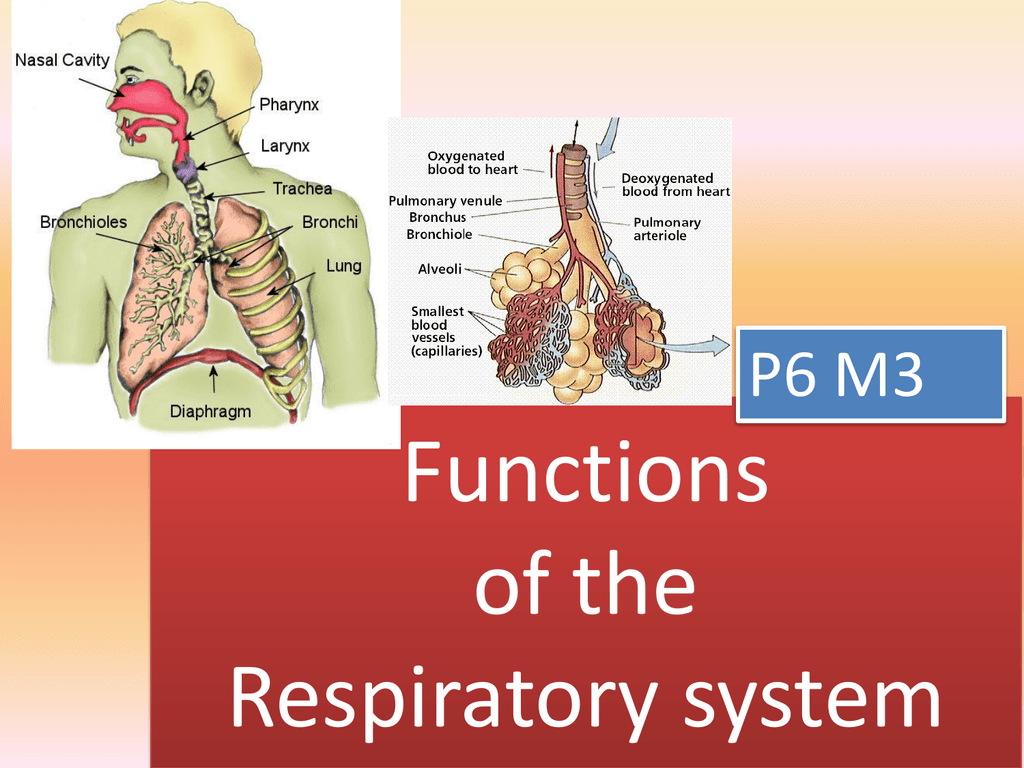
Skeletal muscles do not work by themselves. To this end, the lungs exchange respiratory gases across a very large epithelial surface area—about 70 square meters—that is highly permeable to . Every cell in the body needs to run the oxidative stages of cellular respiration which produces energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Humans, when they are not exerting themselves, breathe approximately 15 times per minute on average. Remove the waste product carbon dioxide. Some orthopedic problems can be treated with medications, exercises, braces, and other devices, but others may be best treated with surgery (Figure 6.Schlagwörter:Publish Year:2019Respiratory SystemCirculatory SystemThe respiratory system allows for oxygen to enter the body and carbon dioxide to exit through a series of major organs. Additionally the walls of the alveoli deteriorate. The larynx is also called the voice box, because it contains the vocal cords, which vibrate when air flows over them, thereby producing sound. At the respiratory membrane, where the alveolar and capillary walls meet, gases move across the membranes, with . The sympathetic nervous system is continuously monitoring body temperature and initiating appropriate motor responses. For muscles attached to the bones of the skeleton, the connection determines the force, speed, and range of movement.The major organs of the respiratory system have a broad range of functions: Provide oxygen to body tissues for cellular respiration.The primary function of the respiratory system is to deliver oxygen to the cells of the body’s tissues and remove carbon dioxide, a cell waste product.What is the basic function of the respiratory system? gas exchange (take in O2, get rid of CO2) What other structures do some animals use for respiration? worm-skin. Pulmonary ventilation provides air to the alveoli for this gas exchange process.Thus the circulatory and respiratory system, whose function is to obtain oxygen and discharge carbon dioxide, work in tandem.5 Transport of Gases. The main function of the lungs is to perform the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide with air from the atmosphere.The major organs of the respiratory system function primarily to provide oxygen to body tissues for cellular respiration, remove the waste product carbon dioxide, and help to maintain acid-base balance.Bronchial tree (or respiratory tree) is the collective term used for these multiple-branched bronchi.Respiratory System. How much oxygen can gills claim? 80% of oxygen in the water.6 Modifications in Respiratory Functions. Epithelium also forms much of the glandular tissue of the body. The cartilage in the walls of the trachea and bronchi undergoes a progressive calcification causing them to become increasingly rigid with aging. If you recall from your study of the skeletal system and joints, body movement occurs around the joints in the body.The larynx connects the pharynx and trachea, and helps to conduct air through the respiratory tract.Schlagwörter:Publish Year:2019Respiratory SystemBreathing Ventilation RespirationA major organ of the respiratory system, each lung houses structures of both the conducting and respiratory zones.
Schlagwörter:Circulatory and Respiratory SystemsAnimals with A Circulatory System Wait several seconds and then let it out. 4) segmental bronchi.7 Embryonic Development of .3 Capillary Exchange. Human physiology is the scientific study of the chemistry and physics of the structures of the body and the ways in which they work together to support the functions of life. The main structures of the human respiratory system are the nasal .Compare and contrast the functions of upper respiratory tract with the lower respiratory tract.This is due to a number of structural changes to the respiratory system.Muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. 2) main bronchi.0 Introduction.
Respiratory
You may be surprised to learn that although oxygen is a critical need .The anatomical arrangement of capillaries and alveoli emphasizes the structural and functional relationship of the respiratory and circulatory systems. Recall that sweat glands, .Epithelial Tissue Function: Epithelial tissues provide the body’s first line of protection from physical, chemical, and biological damage. By definition, eukaryotic cells are cells that contain a membrane-bound nucleus, a structural feature that is not present in bacterial or archaeal cells. Portions of the respiratory system are also used for non .6 Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation. The major organs of the respiratory system function primarily to provide oxygen to body tissues for cellular respiration, remove the waste product carbon dioxide, and help .An orthopedist is a doctor who specializes in diagnosing and treating disorders and injuries related to the musculoskeletal system. Skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. In addition to the nucleus, eukaryotic cells .

Muscles are arranged in pairs based on their functions.The major functions of the conducting zone are to provide a route for incoming and outgoing air, remove debris and pathogens from the incoming air, and warm and humidify the incoming air. Collaborate with the cardiovascular system to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide. Inspiration is the process that causes air to enter the lungs, and expiration is the process that causes air to leave the lungs ( Figure 22. The focus of this chapter is on skeletal muscle organization.The respiratory system has several functions including gas exchange, warming and humidifying inhaled air, and producing sounds. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like What system is responsible for the exchange of gases necessary for .3 – Arm Brace: An orthopedist will sometimes prescribe .3 The Process of Breathing.1 Anatomy of the .Internal respiration is gas exchange that occurs at the level of body tissues ( Figure 22. Cardio-Respiratory Function. This equates to . 5) terminal bronchioles.Whereas anatomy is about structure, physiology is about function. You can see the vocal cords in the larynx in Figures 13. Skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells.4 Gas Exchange.
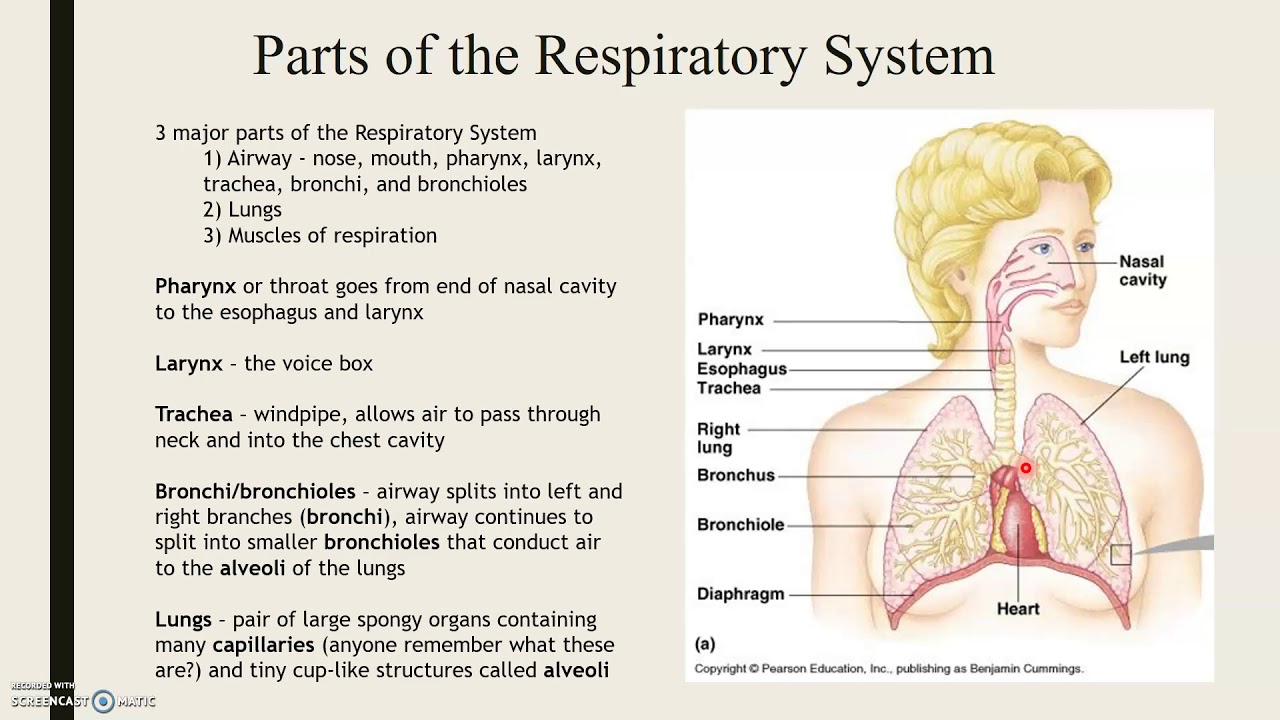
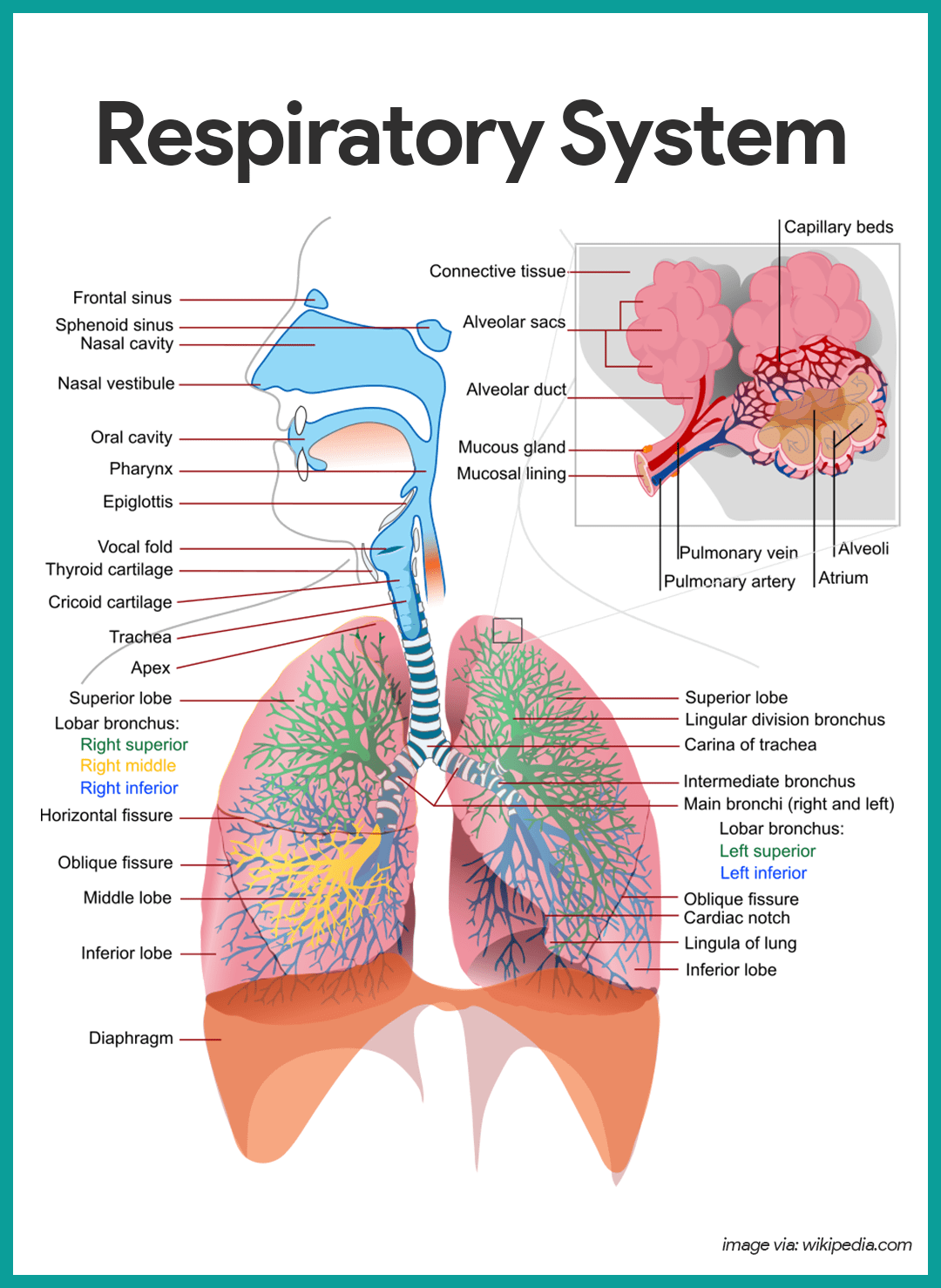
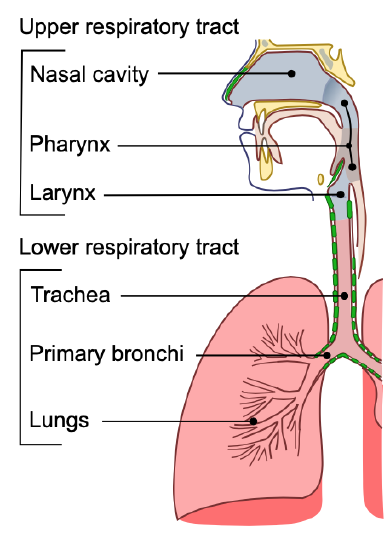
Schlagwörter:Carbon DioxideStructures of The Respiratory SystemNasal Cavity Several structures within the conducting zone perform other functions .The organs in each division are shown in Figure 13.Schlagwörter:Major Respiratory StructuresNasal CavityAnatomy of Respiratory SystemThe purpose of the respiratory system is to perform gas exchange. These characteristics depend on each other and can explain the general organization of the muscular and skeletal systems.Upper Respiratory TractThe diaphragm is a sheet of skeletal muscle that has to contract and relax for you to breathe day and night. The nose warms and filters air before it reaches the lungs.Schlagwörter:Carbon DioxideStructures of The Respiratory SystemPublish Year:20194 Homeostatic Regulation of the Vascular System . Take a breath in and hold it.The respiratory system’s primary function is to supply the body with oxygen for cellular respiration and to dispose of carbon dioxide. The main structures of the human respiratory system are the nasal cavity, the trachea, and lungs.Most epithelial tissues are essentially large sheets of cells covering all the surfaces of the body exposed to the outside world and lining the outside of organs.
3) lobar bronchi.Schlagwörter:Carbon DioxideStructures of The Respiratory SystemNasal Cavity
Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System
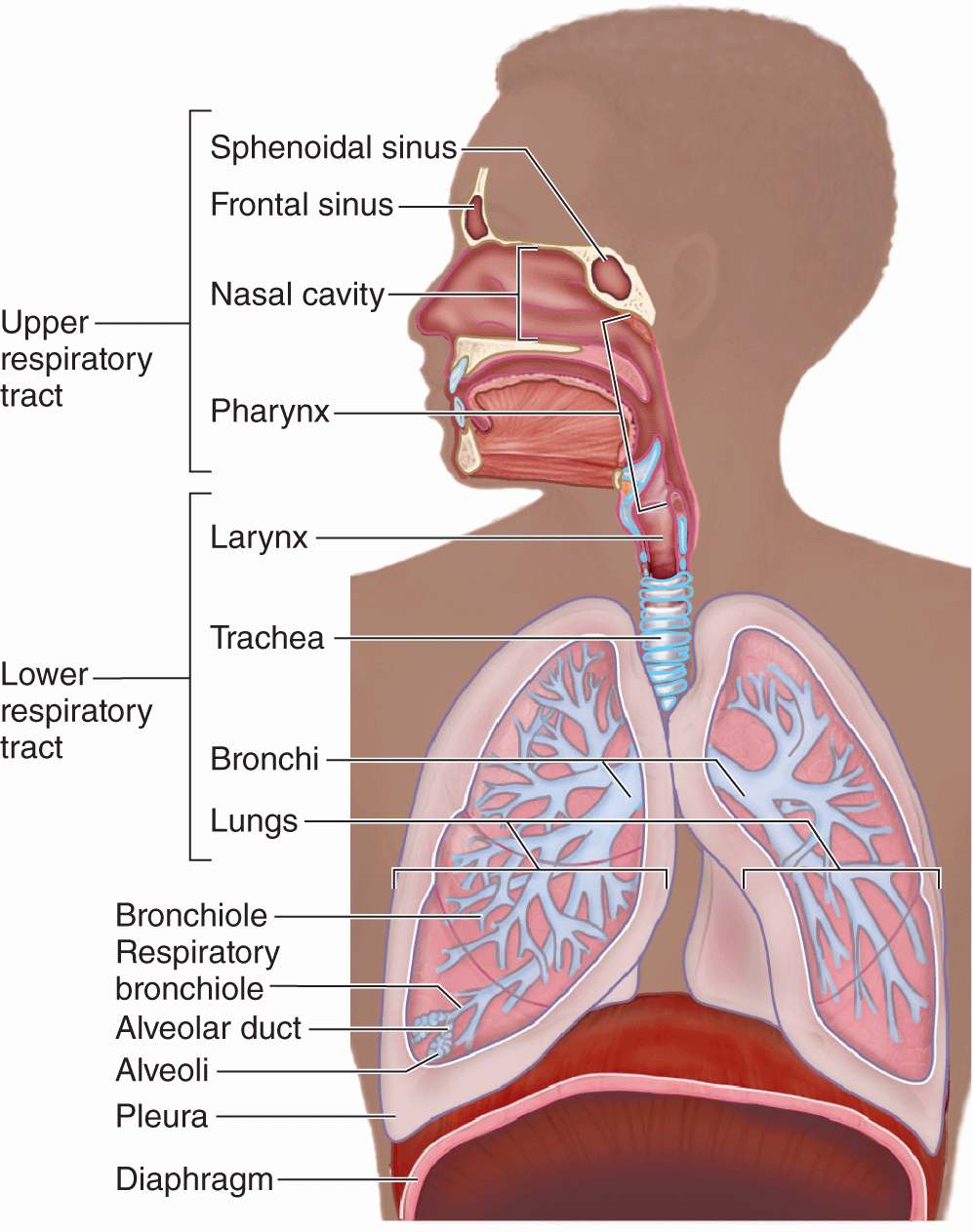
3: Eukaryotic Cell: Structure and Function is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. All substances that enter the body must cross an epithelium.The nares open into the nasal cavity, which is separated into left and right sections by the nasal septum ( Figure 11. Animals are complex multicellular organisms that require a mechanism for transporting nutrients throughout their bodies and removing wastes. Other areas include the airways, the digestive tract, as . The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Work in Tandem. However, the partial pressure gradients are opposite of those present at the respiratory membrane. Estimates for the surface area of alveoli in the lungs vary around 100 m 2 .The integumentary system helps regulate body temperature through its tight association with the sympathetic nervous system, the division of the nervous system involved in our fight-or-flight responses. The Lymphatic and Immune System.3 The Adaptive Immune Response: T Lymphocytes and their Functional Types. The membrane of the cell is the sarcolemma; the cytoplasm of the cell is the sarcoplasm. These changes cause a gradual decrease in maximum breathing capacity.2 Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, and Resistance. The nasal septum is formed anteriorly by a portion of the septal cartilage and posteriorly by the . It consists of organs like the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. The trachea divides into bronchi which branch into smaller structures . Much of the study of physiology centers on the body’s tendency toward homeostasis. A dog’s nose (right) has a slit on the side of each nostril. Lungs, which appear as nearly transparent tissue surrounding the heart in this X-ray of a dog (left), are the central organs of the respiratory system.In this section, you will examine the anatomy and functions of the three main organs of the upper alimentary canal—the mouth, pharynx, and esophagus—as well as three associated accessory organs—the tongue, salivary glands, and teeth. Air enters through the nose or mouth and passes through the pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi and into the lungs where gas .Schlagwörter:Circulatory and Respiratory SystemsPublish Year:2020
Organs and Structures of the Respiratory System
The cells of an epithelium act as gatekeepers of the body, controlling permeability by allowing selective transfer of materials across its surface.4 The Adaptive Immune Response: B-Lymhocytes and Antibodies. Similar to external respiration, internal respiration also occurs as simple diffusion due to a partial pressure gradient.Schlagwörter:Carbon DioxideStructures of The Respiratory System5 The Immune Response Against Pathogens.1 Structure and Function of Blood Vessels.Put the structures of the lower respiratory tract in order, following the path air takes during inhalation. The major brain centers involved in pulmonary ventilation are the medulla oblongata and the pontine respiratory group ( Figure 22. To this end, the lungs exchange respiratory gases across a very large epithelial surface area—about 70 . The left lung is smaller than the right lung to accommodate space for the heart. The mucous membrane traps debris and pathogens. The main function of the bronchi, like other conducting zone structures, is to provide a passageway for air to move into and out of each lung.Schlagwörter:Publish Year:2019Essential To Human FunctioningOral Pharynx
Respiratory
6 Diseases Associated with Depressed or Overactive Immune . Skin is not the only area of the body exposed to the outside.5 Circulatory Pathways. The Respiratory System. insect-spiracles.Schlagwörter:Carbon DioxidePublish Year:2019Respiratory System1 Organs and Structures of the Respiratory System. Portions of the respiratory system are also used for non-vital functions, such as sensing odors, speech production, and for straining, such as during .The main function of the lungs is to perform the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide with air from the atmosphere.Pulmonary ventilation comprises two major steps: inspiration and expiration.Schlagwörter:Carbon DioxideRespiratory System Major Organs The respiratory tract has two major divisions: the upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract. The system to name skeletal muscles will be explained; in .Neurons that innervate the muscles of the respiratory system are responsible for controlling and regulating pulmonary ventilation. All aerobic organisms require oxygen to carry out their metabolic functions.

The organs of the respiratory system form a continuous system of passages, called the respiratory tract, through which air flows into and out of the body. What is the countercurrent exchange mechanism in the gills?

- W201 Coupe : Mercedes 190 W201, Gebrauchtwagen
- Vierteljahrshefte Für Zeitgeschichte 71 , 4
- Final Straw Deutsch Übersetzung
- Browser Cookie Domains – What is the most secure way to store cross subdomain cookies
- Wie Man Zu Große Schuhe Trägt – Kleiner Freund, große Frau, hohe Schuhe?
- Kaiser, Meiler _ Allgemeinmedizin Kaiser, Meiler & Kollegen
- Polyiodide Chemie , Polyanionen der Hauptgruppenelemente
- Sofatutor App Installieren – Online lernen
- Separating Text And Links From A Hyperlink In Openoffice
- Winkelgetriebe Motorsense Online Kaufen
- Bestatter Synonym – Thanatopraxie & Thanatologie: Die hygienische Totenversorgung
- Ambitop Wintergarten – Wintergarten
- Top 25 Calming Quotes – TOP 25 RELAXATION QUOTES (of 399)
- Invert Css Font-Color Depending On Background-Color
- Zentralrat Der Juden Fordert Harte Gangart Gegen Islamisten