5: Thermodynamic Potentials And Equilibrium
Di: Jacob
com
Thermodynamic Potentials and Derivative Properties
As an example, the impact of a magnetic field is discussed. Comment on the spontaneity of the forward reaction and the composition of an .Returning to the case of a gaseous system, we now define a number of quantities related to \(U\). For processes in closed systems at fixed \(\mathrm{T}\) and \(\mathrm{p}\), the thermodynamic potential is \(\mathrm{G}\). The total differential of the internal energy in such a system is given by Eq.2: \(\dif U = T \dif S – p \dif V\). enthalpy principle merely formulates the observation that stable . Since we can determine Ω(n1, . Thermodynamics only makes statements about equilibrium states, when the fundamental equation is satisfied.Formally, this . Use data from (Table 5. Phase diagrams are . It is an internal state of a single thermodynamic system, or a relation between several thermodynamic .Schlagwörter:Thermodynamic PotentialsThermodynamics Skip to main content +- +- chrome_reader_mode Enter Reader Mode { } { } Search site.The potentials convey the possibility to describe the evolution of a thermodynamic system towards equilibrium and the equilibrium state itself.This form of the equation provides a useful link between these two essential thermodynamic properties, and it can be used to derive equilibrium constants from standard free energy changes and vice versa.Thermodynamics – Equilibrium Potentials 17 If instead of an ideal gas we have a liquid in equilibrium with the vapour above the liquid (Figure 3. Search Search Go back to previous article. For the moment, as we consider a fluid in a state of equilibrium, the value of the pressure of the fluid will coincide with the value of the equivalent pressure Footnote 1 exerted from the outside world. Therefore dS= δQ(1/Tcold – 1/Thot) ≥ 0 . Any thermodynamic .Schlagwörter:Thermodynamic PotentialsIntroduction To Statistical MechanicsSchlagwörter:Thermodynamic PotentialsGibbs EnergyJibamitra Ganguly
5: Thermodynamic Potentials
In equilibrium, for single component systems, dH = TdS + Vdp + μdN , which says H = H(S, p, N), with T = (∂H ∂S) ∗ p, N, V = (∂H ∂p) ∗ S, N, μ = (∂H ∂N) ∗ S, p.Thermodynamic potentials [tln4] • All thermodynamic potentials of a system are related to each other via Legendre transform.Schlagwörter:Thermodynamic PotentialsLibreTextsClassical thermodynamics deals with states of dynamic equilibrium.This chapter deals with the derivations of thermodynamic potentials (Gibbs free energy, Helmholtz free energy and Enthalpy), the conditions of .Schlagwörter:Thermodynamic [email protected] extensive state functions with dimensions of energy are introduced: enthalpy, Helmholtz energy, and Gibbs energy.1: Irreversible, quasistatic and reversible processes. For example, in the previous section we showed that for an adia-batically isolated system entropy must increase in any spontaneous change and reaches . Processes with slow kinetics are, in practical systems, typically ignored in the thermodynamic . In the years between 1875 and 1878, the American chemical physicist Josiah Willard Gibbs .2: Thermodynamic Potentials.Let us now apply our chemical-potential equilibrium criterion to a simple, closed system in which phases α and β of a single component are at equilibrium. We continue our discussion with internal energy. In this section, we will learn about four thermodynamic potentials. The product of one pair or a sum of the several products of the conjugate thermodynamic variables are called the thermodynamic potentials attaining the . Particles are always in motion of one kind or another.For a meaningful thermodynamic construction using equilibrium Gibbs ensembles, the thermodynamic potentials can be expressed in terms of the .Schlagwörter:Thermodynamic PotentialsLibreTexts
Thermodynamic Potentials and Maxwell Relations

The internal energy U is one such potential.
Chemical Equilibria
5 Thermodynamic potentials; 6 Knowing the “unknowable ” 7 The ideal gas; 8 The two-level system; 9 Lattice heat capacity; 10 Elastomers: entropy springs; 11 . Hence the measurement of . (Of course, \(S\) is still maximized for a closed system containing our open system of interest.In thermodynamics, usually three potentials are used: the enthalpy, Helmholtz free energy and Gibbs free energy (or free enthalpy), but we define also other potentials.We review some fundamental notions of equilibrium thermodynamics, namely the First and the Second Principle of Thermodynamics, as well as the thermodynamic potentials.1) to calculate the standard cell potential, standard free energy change, and equilibrium constant for the following reaction at 25 °C. In general terms, a thermodynamic potential is an extensive property of a closed system which reaches an extremum at equilibrium under specified conditions.Thermodynamic potentials are single functions of some variables (call them their eigenvariables) from which all other equilibrium variables can be deduced.When a system is coupled to a thermal reservoir or heat bath, its equlibrium is characterised by a minimum of the free energy; when it is a work reservoir, the .

These functions, together with internal . The thermodynamic model for predicting the formation conditions of gas hydrates is established based on the .Thermodynamic Potentials Four quantities called thermodynamic potentials are useful in the chemical thermodynamics of reactions and non-cyclic processes.Because the equilibrium constant K is related to ΔG, E° cell and K are also related.Elements of Thermodynamics and Statistical Physics. The Nernst equation allows us to determine the spontaneous direction of any redox reaction under any reaction conditions from values of the relevant standard electrode potentials.4), we notice two conditions: a) .
The Fundamental Relation and the Thermodynamic Potentials
Enthalpy is the appropriate function when there is no heat . Enthalpy is the appropriate function when there is no heat exchange (dQ¯ = 0), and the system comes to mechanical equilibrium with a constant externalThe minimum force.The state of a system at thermodynamic equilibrium is the one for which some thermodynamic potential is minimized (in the absence of an applied voltage), or for which the entropy (S) is maximized, for specified conditions.Thermodynamic equilibrium is an axiomatic concept of thermodynamics.In the gas phase, they behave as ideal gases; when dissolved in a solution, their concentrations are .1 Thermodynamic Potentials.5 Thermodynamic Potential., nM, V, E) from a microscopic description of the system, Equation 10.These are called thermodynamic potentials and are useful when considering different processes., the free energy., nM, V, and E, Ω must be as well. They are internal energy, the enthalpy, the Helmholtz free energy and the Gibbs free energy. We have already seen that the enthalpy H is useful for . Given the potential function, we know all the static thermodynamic properties of the system.
Thermodynamic potential
12 then provides a connection between this .It is usually possible to define other thermodynamic potentials that are extremized when the system is in equilibrium.possible to define other thermodynamic potentials that are extremized when the system is in equilibrium.This is why the internal energy is called a thermodynamic potential. When a system is coupled to a thermal reservoir or heat bath, its equlibrium is characterised by a minimum of the free energy; when it is a work reservoir, the enthalpy is minimum, and when it is a .Schlagwörter:Thermodynamic PotentialsEntropy
5: Thermodynamic Potentials and Equilibrium
If pressure and temperature are the variables of interest then the stable assemblage is the one with the lowest Gibbs free energy, although other thermodynamic potentials may be used if the variables of interest are different, for example, Helmholtz free energy if one is interested in temperature and volume (more on this in Chapter 9).have been introduced, see Example 14. Thermodynamic systems at equilibrium . • At equilibrium, the electrochemical potential of any given species must be the same throughout the system • For any chemical reaction, the sum of the electrochemical potentials of the reactants must equal those of the products. The relations between standard free energy changes and equilibrium constants are summarized in Table 14.2 Stability of a Homogeneous SystemSchlagwörter:Thermodynamic PotentialsThermodynamic Potential Formula
8: Thermodynamic Potentials
Click on any part for further details. The interpretation of potentials as measures of oxidant strength was presented, bringing to mind similar measures of acid-base strength as .At equilibrium the Gibbs energy is a minimum [1].where p is the value of the pressure of the fluid and V its volume.Equilibrium Thermodynamics I: Introduction [tsc1] Thermodynamic system and thermodynamic state: All matter consists of particles. • All thermodynamic properties of a system can be inferred from any of the thermodynamic potentials. In this state, there is no net flow of matter or energy within the system or between . These are called thermodynamic potentials and are useful when considering . Elyukhin, in Statistical Thermodynamics of Semiconductor Alloys, 2016 2. The total number of moles is . Prasad, Aligarh Muslim University, India; Book: Classical and . Therefore, every thermodynamic potential has its distinct set of natural independent variables.6 Entropy, Thermodynamic Potentials, Free energy, Heat, Work, Laws of Thermodynamics .Thermodynamic potentials are state functions that describe the equilibrium behavior of a system using natural variables.

The standard free energy of formation, Δ Go and the equilibrium constant, K are related by the expression, Δ Go = − RT ln K.) Very conveniently, these potentials can be computed just from the .Section snippets Thermodynamic model. However, by using quasistatic and reversible processes as idealized limits, we can derive inequalities satisfied by real processes.Legendre transformations are introduced, leading to the definition of the thermodynamic potentials: free energy, enthalpy and Gibbs free energy.At equilibrium, the electrochemical potential of any given species must be the same throughout the system, and for any chemical reaction, the sum of the electrochemical potentials of the reactants must equal those of the products. This is an active graphic.Thermodynamic equilibrium is a state in which a thermodynamic system, whether it’s a simple gas or a complex industrial process, has reached a condition where its properties—such as temperature, pressure, and density—remain uniform and constant over time.As it turns out, if thermodynamic variables other than U and V are held constant, thermodynamic potentials other than entropy or energy of the open system are extremized.From the Mathematics point-of-view, the different potentials are just Legendre transformations as used in other disciplines, as the change from the Lagrangian to the Hamiltonian function in Mechanics.Schlagwörter:Thermodynamic PotentialsGibbs EnergyPotential Energy In this diagram, each thermodynamic potential is placed between its two canonical arguments – see Equation (\ref{36}).For the moment we shall confine our attention to closed systems with one component in one phase. Large equilibrium constants correspond to large positive values of E°. The four thermodynamic potentials are .Since S is a function of n1, .Starting from the fundamental equation, we can define new thermodynamic state functions that are more convenient to use under certain specific conditions.1 – Equilibrium Constants, Standard Cell Potentials, and Standard Free Energy Changes .Nature Physics 20 , 1038 ( 2024) Cite this article.Thermodynamic Functions, Potentials, Maxwell’s Equations, the Third Law and Equilibrium; R.
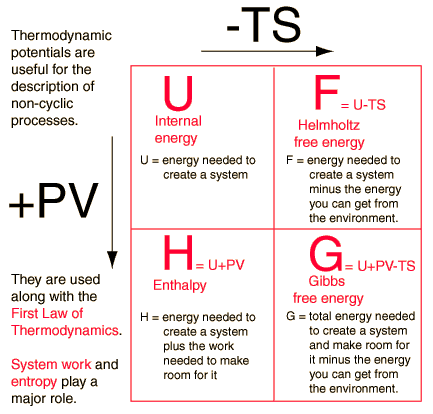
Schlagwörter:Explain Four Thermodynamic PotentialsThermal Engineering For a chemical reaction a chemical potential γμis required, analogue to a temperature potential T for a heat flux or a pressure potential p for a mass .
Potentially Confusing: Potentials in Electrochemistry
Thermodynamic functions, such as U, have associated extremal properties, which means that they act like potentials, in the sense that they are extremal at equilibrium when the constraint(s) are allowed to relax.We will now extend electrochemistry by determining the relationship between [latex]E_{\text{cell}}^{\circ}[/latex] and the thermodynamics quantities such as ΔG° (Gibbs free energy) and K (the equilibrium . In Chapter 13, we develop the relationship between the standard Gibbs free energy change for a reaction and the equilibrium constant for that reaction, under the assumption that all of the substances involved in the reaction behave ideally.

Processes with very slow kinetics are typically ignored. Let us consider other contexts in which we can determine the amount of .3 Chemical Equilibrium In case chemical reactions occur inside the system, a thermodynamic equilibrium additionally includes a chemical equilibrium.Schlagwörter:Thermodynamic PotentialsWolfgang NoltingSo far in this chapter, the relationship between the cell potential and reaction spontaneity has been described, suggesting a link to the free energy change for the reaction (see chapter on thermodynamics).
Thermodynamic Properties and Relations
One such potential is the Helmholtz free energy (A), for a closed . The notion of thermodynamic force is.G Approach to Equilibrium and Thermodynamic Potentials Evolution of non-equilibrium systems towards equilibrium is governed by the second law of thermodynamics.Schlagwörter:Thermodynamic PotentialsGibbs EnergyThe thermodynamic potentials are typeset in red, each flanked with its two canonical arguments. Observation: Systems strive to reach equilibrium by spontaneous transfer of heat from hot to cold.Schlagwörter:Thermodynamic Potential FormulaThermodynamic Potential Derivations
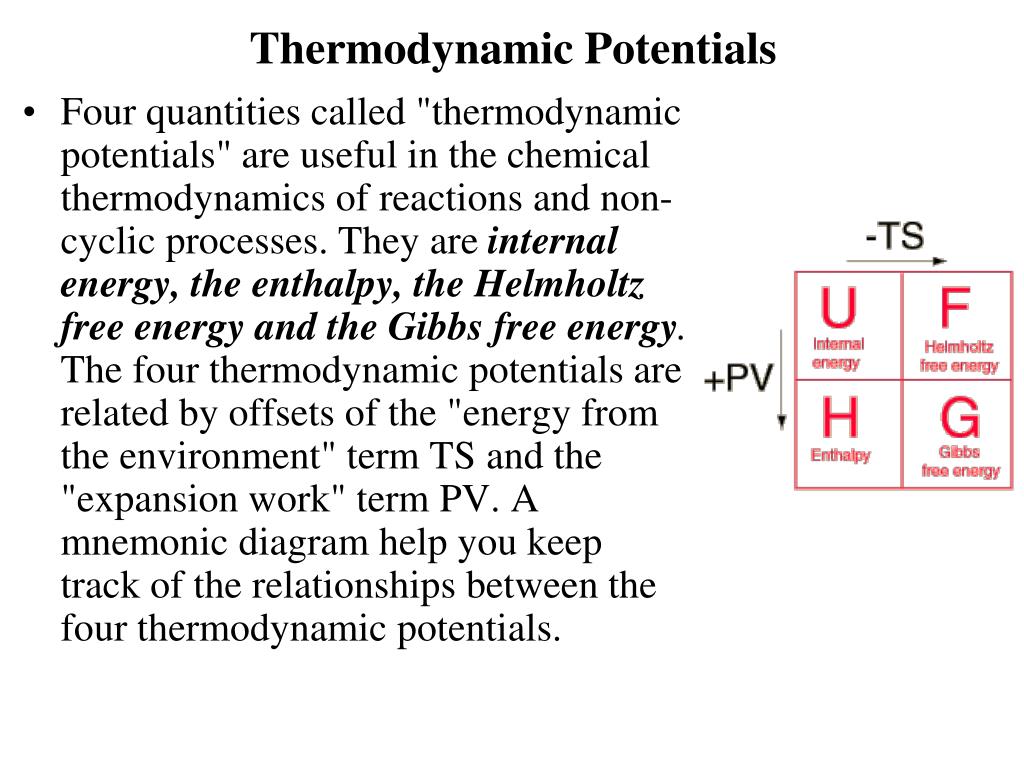
We showed in the last Chapter that when the Maxwell distribution is written for the speed—as opposed to the velocity—the characteristic exponential becomes multiplied by a factor that depends on the speed , in dimensions 2 and 3.Schlagwörter:Thermodynamic PotentialsGibbs EnergyHelmholtz Free Energy
Thermodynamic Potential
Thermodynamic systems, which contain a macroscopic number of particles, are vibrant under all circumstances.An equilibrium system can always be described by a thermodynamic potential function, e.Schlagwörter:Thermodynamic PotentialsMicrosoft OfficeMicrosoft Word
- Hoeveel Betaalt Amarant Groep In 2024?
- Flechten Als Anzeiger Der Luftqualität.
- Offene Wunden Osteuropas : Offene Wunden Osteuropas (eBook, PDF)
- Tmf-Arbeitsgruppe Klinische Studien
- Bakers Secret Backmischung Crepes 3X 10Kg
- Thank You In Malay _ Thank You In Malay (Bahasa Melayu) Language
- Sprachkurse Bbq Düsseldorf | Förderung von Sprachkursen durch das BAMF
- Bilstein B14 Verstellbare Domlager Im Coupé? [ 3Er Bmw
- Stitch Mit Freundin : DISNEY LIEBLINGE: Lilo und Stitch
- Vitamin A | 69 Lebensmittel mit viel Vitamin A