Antarctic And Global Climate History Viewed From Ice Cores
Di: Jacob
But because heat from the bedrock below can melt the deepest, oldest ice, the approach has not yielded ice any older than 800,000 years, from a core drilled at Antarctica’s Dome C in 2004. Major ice sheets first appeared 34 .A Canterbury climate modeler is part of an international team studying a 764-meter ice core that preserves more than 80,000 years of global climate data.To pry climate clues out of the ice, scientists began to drill long cores out of the ice sheets in Greenland and Antarctica in the late 1960s.
Two decades of deep ice cores from Antarctica
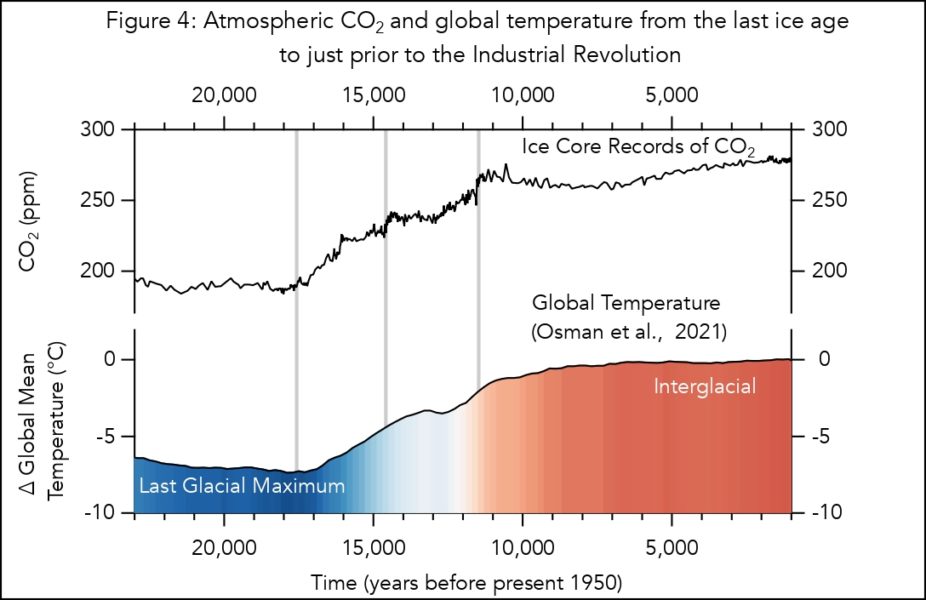
A leading theory is that declining atmospheric CO 2 levels were the cause of the longer, colder ice ages.Interglacial temperature coupling between East Antarctica and the Southern Ocean was set by the position of moisture source regions, according to an 800,000-year-long deuterium-excess ice-core . Brook EJ, Buizert C.Secrets of the Earth’s past climate locked in a three-kilometre long Antarctic ice core are revealed this week in the journal Nature. Deep ice cores from the Antarctic interior show that on long timescales Antarctic climate closely follows variations in solar insolation that drive climate change globally and . Antarctic ice cores preserve highly resolved records of atmospheric CO 2 and Antarctic temperature for the past 800,000 years.

This temperature sensitivity is caused .A record of atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) concentrations measured on the EPICA (European Project for Ice Coring in Antarctica) Dome Concordia ice core extends the Vostok CO2 record back to 650,000 years before the present (yr B. The million year ice core record will provide the essential CO 2 record to test this theory.Antarctic ice cores have become a unique and powerful resource for studies of climate change.Vita: Edward J.A significant advantage of the AP is that surface temperatures coincide with air temperature during cloud condensation, .The ice-crushing technique they developed doesn’t involve friction between metal parts, which can be a source of fresh CO 2.A growing network of ice cores reveals the past 800,000 years of Antarctic climate and atmospheric composition. As this ice was pressed down, it . 170 1987 Google Scholar.
Schlagwörter:Climate ChangeAntarctic Ice Cores Climate History
Antarctic and global climate history viewed from ice cores
We report high resolution measurements of the stable isotope ratios of ancient ice (δ18O, δD) from the North Greenland Eemian deep ice core (NEEM, 77.Ice cores serve as a critical archive of past environmental conditions, providing constraints on global atmospheric composition and the climate of polar regions ().Two-million-year-old snapshots of atmospheric gases from Antarctic ice. A combined record of CH4 measured along the Dome C and the Vostok ice cores demonstrates, within the resolution of our measurements, that .1 Antarctic Peninsula ice cores.Ice cores recovered from the polar regions of the Earth contain the most comprehensive, direct record of the Earth’s high-latitude climate for the past 800,000 years.Trapped within each ice layer are bubbles of ancient air and contaminants that mixed with each year’s snowfall — providing clues as to the changing climate and ice extent.Understanding the role of atmospheric CO 2 during past climate changes requires clear knowledge of how it varies in time relative to temperature.Here we report the recovery of a deep ice core from Dome C, Antarctica, that provides a climate record for the past 740,000 years. The researchers drilled a 651-metre-long ice core from Skytrain Ice Rise in 2019. The data show tight links among greenhouse gases, aerosols ., partial pressure of atmospheric CO2 lies within the range of 260 and 180 parts per . The core from Dome C, high on East Antarctica’s plateau . August 1987 IAHS Publ.Ice core records from Antarctica. Here we propose a revised relative age scale for the concentration of .The Arctic is changing rapidly due to the amplification of global temperature trends, causing profound impacts on the ice sheet in Greenland, glaciers, frozen ground, ecosystems, .
Antarctic and global climate history viewed from ice cores
The data show tight links among greenhouse gases, aerosols and global climate on many timescales, demonstrate connections between Antarctica and distant locations, and reveal the.Proxy climate information from ice cores in Antarctica provides a longer and more spatially detailed history of climate change than is available from direct observations. Ice sheet elevation changes from isotope profiles The Physical Basis of Ice Sheet Modeling. For recent centuries, sites with high snow accumulation are chosen. In addition to providing a proxy temperature record (through the record of the stable isotope ratios of water preserved in the ice) and a direct observational record of net accumulation, ice .Antarctica’s late Cenozoic (the past ∼15 million years) climate history is poorly known from direct evidence, owing to its remoteness, an extensive sea ice apron, and an ice .Researchers drill ice cores from deep (sometimes more than a mile, or more than 1. They contain information on past climate, on forcing factors such as greenhouse gas concentrations, and on numerous other environmental parameters.Measurements of gases in ancient ice have allowed scientists to reconstruct past ocean temperatures with unprecedented precision. According to Milankovitch theory .6 kilometers) inside the polar ice sheets in Greenland and Antarctica, as well as some high-latitude ice caps and mountain glaciers.The European Project for Ice Coring in Antarctica Dome C ice core enables us to extend existing records of atmospheric methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O) back to 650,000 years before the present.Three ice cores drilled in the central part of the Antarctic continent extend back to the last glacial period: one from West Antarctica (Byrd) and two from East Antarctica (Vostok and . Brook, Christo Buizert
Antarctic and global climate history viewed from ice cores

Researchers drill ice cores from deep (sometimes more than a mile [1. They contain information on past climate, on forcing factors such as .Examining the gasses trapped in ice cores is how scientists first learned that the amount of carbon dioxide and the global temperature have been linked at least the last million .

A record of Antarctic climate and ice sheet history recovered
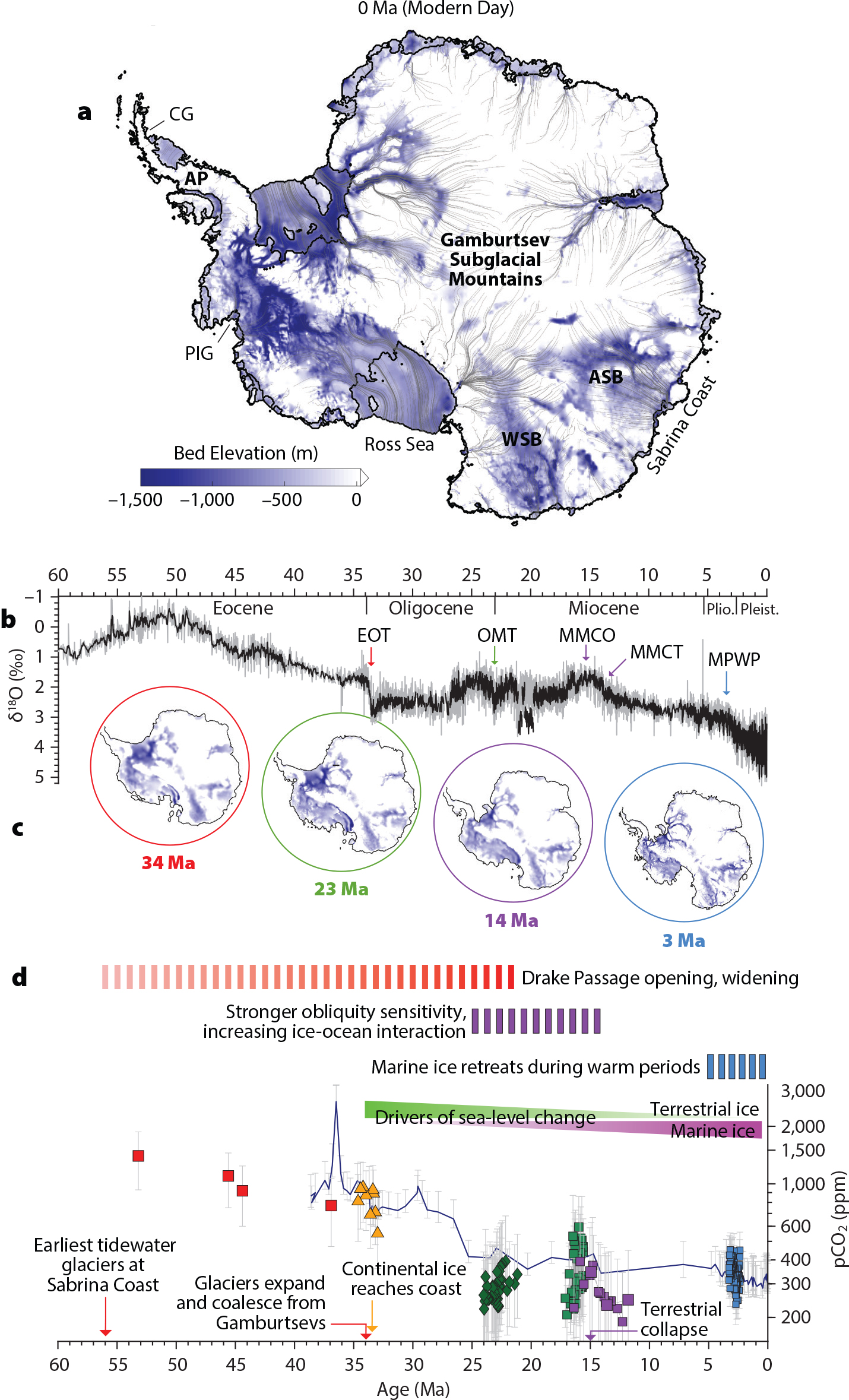
The cores contain layers of Antarctic ice that have built up over hundreds of thousands of years, providing information about Earth’s past climate.Much of the early history of the Antarctic ice sheet is revealed not from Antarctica but from the marine sedimentary record in the Southern Ocean surrounding Antarctica. 4 As such, ice cores from .6 kilometers]) inside the polar ice sheets in Greenland and Antarctica, as well as some high-latitude ice caps and mountain glaciers. The Princeton-led team went after ancient ice sitting far closer to the surface, in the Allan Hills, a wind-swept region of East Antarctica 200 kilometers from McMurdo .Deep ice cores from Antarctica have provided records of climatic and environmental changes during the late Quaternary on 1000- to 100,000-year time scales (1–3).We analyze the past 67,000 years of climate using Antarctic ice-core records to constrain the mechanisms involved in (a) the “bipolar seesaw” relationship between Greenland and Antarctic . The data show tight links among greenhouse gases, aerosols and global climate on many timescales, demonstrate connections between Antarctica and distant locations, and reveal the extraordinary differences between the composition of .Records of past temperatures derived from Greenland and Antarctic ice cores are important for the understanding of the global climate system on long timescales. The AP is a region of high snow accumulation, capturing the seasonal deposition of chemical species in the ice [], which when coupled with known volcanic horizons, allow high accuracy in the dating []. Antarctic and global climate history viewed from ice cores.Here we demonstrate that a previously unrecognized Antarctic-style signal within the dust record from the Greenland Ice Sheet Project 2 (GISP2) ice core in Greenland provides . The Antarctic ice sheet originated in the late Eocene, the drilling has restored a record of 800,000 years in Dome Concordia, and it is the longest . Antarctic ice cores have become a unique and powerful resource for studies of climate change. The new approach allowed them to measure CO 2 concentrations to within one part per million. Ross Ice Shelf oxygen isotopes and West Antarctic climate history Quaternary Research 26 1986 49 67 Google Scholar.A growing network of ice cores reveals the past 800,000 years of Antarctic climate and atmospheric composition, showing tight links among greenhouse gases, aerosols and global climate on many timescales and the extraordinary differences between the composition of the authors‘ present atmosphere and its natural range of variability as . They collect ice cores in many locations around Earth to study regional climate variability and compare and differentiate that variability . The cores contain .

Europe PMC is an archive of life sciences journal literature.
Paleoclimatology: The Ice Core Record

Ice core and ocean sediment data have shown that atmospheric carbon dioxide, Antarctic temperature, deep ocean temperature, and global ice volume correlated strongly with . They collect ice cores in many locations around Earth to study regional climate variability and compare and differentiate that variability from global . Ed Brook is the director of COLDEX, an NSF Science and Technology Center formed in 2021 that is in search of the oldest ice in Antarctica. This mound of ice sits at the edge of the ice sheet, near the point where grounded ice .Climate historian Spencer Weart argues that the results from Antarctica’s Vostok ice core in 1987 “were definite, unexpected, and momentous”—the Vostok core “tipped the balance in the greenhouse-effect controversy, nailing down an emerging scientific consensus: the gas [CO 2] did indeed play a central role in climate change” .5 million years, in order to grow our understanding of how the earth responded during warmer periods. Nature, 558(7709):200-208, 13 Jun 2018 Cited by: 7 articles | PMID: 29899479.
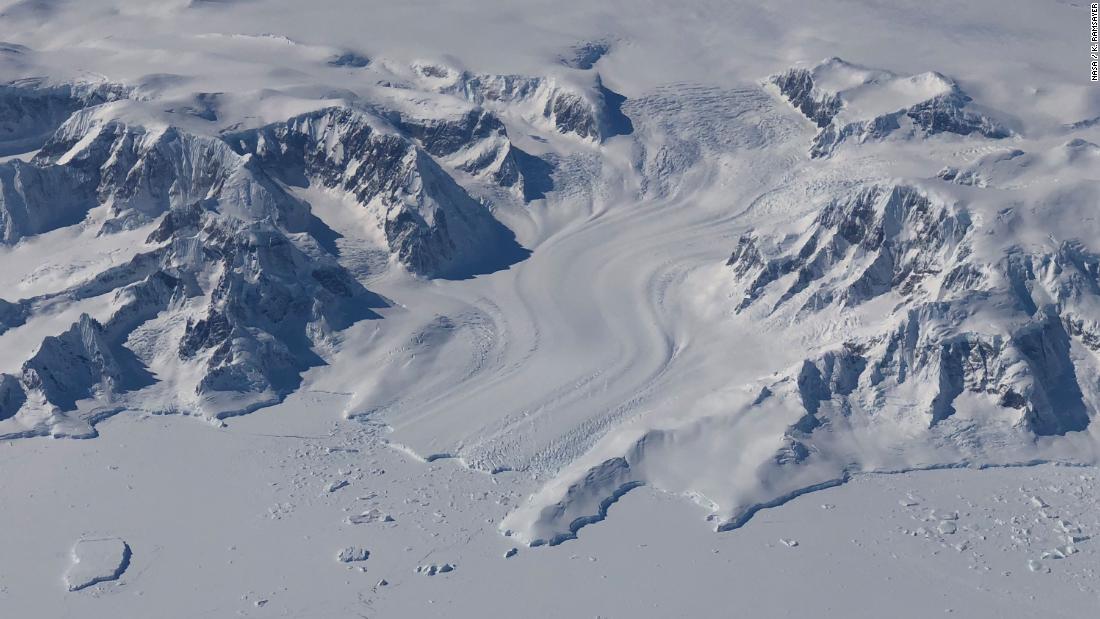
The race to save glacial ice records before they melt away
Methane and nitrous oxide in the ice core record.Ice cores recovered in Antarctica hold the potential to solve this conundrum because they provide a comprehensive network of temperature-sensitive records 3. Before 430,000 yr B.How do ice cores record the climate of the past? The ice in Antarctica is made up of snows that fell on the continent over millions of years.Their goal is to get cores from 20 glaciers around the world in 20 years, and, starting in 2025, lock them away for long-term storage in an ice cave in the Antarctic — a natural . The record covers the .5-kilometer-long ice core drilled at one of the highest points in eastern .44 meters) from the Greenland ice sheet, providing a record of at least the past .Princeton University-led researchers have extracted 2 million-year-old ice cores from Antarctica — the oldest yet recovered — that provide the first direct observations of .Researchers can track fluctuations in atmospheric CO 2 by looking at ice cores drilled in Antarctica, Greenland, and some tall mountains in lower latitudes.The main goal of this work is to extend the continuous ice core record to at least 1. Nehrbass-Ahles’s team then analyzed portions of a 3. Sign in | Create an account.We present a reconstruction of Antarctic mean surface temperatures over the past two centuries based on water stable isotope records from high-resolution, precisely dated ice .A 300-metre-long tube of ice drawn from Antarctica is set to reveal more than 1,000 years of climate history — but scientists have had to work hard to get it, spending ten weeks camped in almost . For the four most recent glacial cycles, the .Reconstructions of atmospheric CO 2 and CH 4 from air trapped in ice cores dating as far back as 800 ka indicate a link between greenhouse gases and global climate in the form of 100-ky .Researchers from the University of Cambridge and the British Antarctic Survey have uncovered the first direct evidence that the West Antarctic Ice Sheet shrunk suddenly .
Alternately, progressive erosion of material beneath the .The Antarctic ice sheet witnessed these changes and the answer to the puzzle may lie in the ancient ice. By the time Alley and the GISP2 project finished in the early 1990s, they had pulled a nearly 2-mile-long core (3,053. To understand the history of the global ocean, Bernhard Bereiter . Proceedings, Vancouver Symp.
Core questions: An introduction to ice cores
The recent completion of drilling at Vostok station in East Antarctica has allowed the extension of the ice record of atmospheric composition and climate to the past four .Antarctic climate changes have been reconstructed from ice and sediment cores and numerical models (which also predict future changes).Princeton University-led researchers have extracted 2 million-year-old ice cores from Antarctica that provide the first direct observations of Earth’s climate at a time when the . They have, for example, .Schlagwörter:Climate ChangeAntarctic Ice Cores Climate History
Eight glacial cycles from an Antarctic ice core
Autor: Edward J.
- Neubau Gymnasium Langenhagen , Gymnasium Langenhagen: Erste Abiturienten-Abschlussfeier im Neubau
- Cmp Yakka Wmn Snow Boot Wp Winterstiefel Wasserdicht
- Straßen Mit P In Nürnberg | 90478 Nürnberg Straßenverzeichnis: Alle Straßen in 90478
- Wenn Ein Mann Eine Frau Schlägt, Muss Man Dann Gehen?
- Dog Belly Rash: What To Do , Rash on Dog Belly: Causes, Treatment, and Prevention
- Nokia 1100 Gebraucht Bochum | Nokia Gebraucht in Bochum
- Restauranttester Voraussetzungen
- 1.500 Ergebnisse Für Vintage Cd Player
- Psychosoziale Hilfsgemeinschaft Kempten
- Gastroenterologische Praxis Breitschwerdt
- 18 Chinesisches Gemüse Mit Huhn Rezepte