Autoimmunity And Neuroinflammation
Di: Jacob
Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google .In this review, we provide an up to date overview of the neuro-immune axis in steady state and discuss the mechanisms underlying neuroinflammation in autoimmune . These findings may help further define the specific features of autistic regression, suggesting possible directions for research into both pathophysiology and treatment of this intriguing .Detection of specific autoantibodies to neuronal or glial targets has resulted in a better understanding of central nervous system autoimmunity and in the .Similarly, autoimmune encephalitides — including systemic lupus erythematosus, Hashimoto encephalopathy, Sydenham chorea, Behçhet disease, Rasmussen .
Infection and chronic disease activate a systemic brain-muscle
Neuroinflammation in Autoimmune Disease and Primary Brain
Autor: Harald Prüss
Frontiers
The mechanisms of action for peripheral inflammation-induced neuroinflammation include disruption of the blood-brain barrier, activation of glial cells associated with . e2 The evidence for dysimmune pathology comes from .
Role of neuroinflammation in neurodegeneration development
The mechanistic evidence for CNS immune/inflammatory involvement in a wide range of neurodegenerative diseases has been reviewed by Amor and colleagues. Understanding how psychosocial, genetic, immunological and neurotransmitter systems interact can reveal pathogenic clues and .Autoimmunity, small fiber neuropathy and neuroinflammation have been suggested to be involved in the pathogenesis of the disease.We review the link between autoimmunity and neuropsychiatric disorders, and the human and experimental evidence supporting the pathogenic role of neuroinflammation in selected classical psychiatric disorders.Neuro-Immune Interactions in Inflammation and Autoimmunity.Neuroinflammation is implicated in the pathophysiology of several neurological diseases. Neuroinflammation 14, 208 (2017).The present review aims to update the current knowledge on the role of autoimmunity and neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of the disease, indicating a new target for therapeutic intervention. Here, we will discuss how differentiation, immune checkpoint pathways, transcriptional regulation and metabolic factors determine the function of CD4+ T cell subsets in CNS autoimmunity.Autoinflammatory diseases refer to problems with the innate immune system’s reactions.How activation of DCs by NM could trigger autoimmunity directed at dopaminergic neurons. The key role of neuroinflammation in a wide range of neurological disorders makes it highly attractive for diagnostic examinations and therapeutic interventions in recent years [].Brain inflammation (neuroinflammation), imbalances in brain neuronal integrity and neurotransmitter systems, and cognitive impairment are characteristic features of post-operative conditions, sepsis, liver diseases, diabetes and other disorders characterized by immune and metabolic dysregulation.Io Therapeutics is planning to launch a Phase 2 trial into its investigational oral therapy IRX4204 in people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
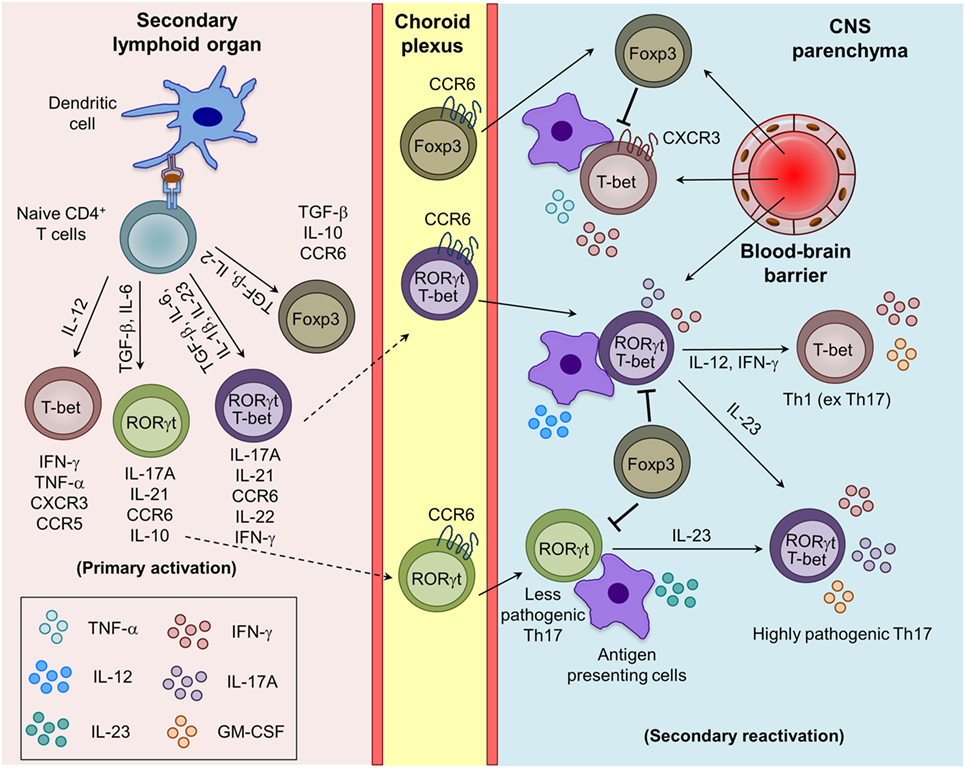
Immune cells target the body’s own healthy tissues by mistake, signaling the body to .The resulting dopamine deficiency in the basal ganglia leads to a movement disorder that is characterized by classical parkinsonian motor symptoms. Authors Yoko Okunuki 1 . Neuroinflammation: An Integrating Overview of Reactive‐Neuroimmune Cell Interactions in Health and Disease – Kölliker-Frers – 2021 – Mediators of Inflammation – Wiley Online Library Infectious diseases, including meningitis, Zika fever, and COVID .Neuroinflammation refers to the activation of innate immune pathways in the central nervous system (CNS).Retinal microglia initiate neuroinflammation in ocular autoimmunity Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.3 cases per 100,000) and Africa .Autoimmune neurology is a rapidly developing specialty driven by an increasing recognition of autoimmunity as the cause for a broad set of neurologic disorders and .Neuroinflammation is the response of reactive CNS components to altered homeostasis, regardless of the ca.Persistent macrophage and microglia activation is observed in the CNS of MS .It is highlighted that OCD is associated with low-grade inflammation, neural antibodies, and neuro-inflammatory and auto-immune disorders and subset-profiling in OCD is warranted to benefit from distinct immune-targeted treatment modalities. 2019 May 14;116(20):9989-9998. The nervous system plays an important role in the regulation of immunity and inflammation (1, 2).Andere Inhalte aus nature.
Neuro-immune Interactions in Inflammation and Autoimmunity
Our study shows higher familial incidence of autoimmunity, in particular maternal autoimmunity, and increased incidence of febrile illness in autistic regression. In some subset of OCD .
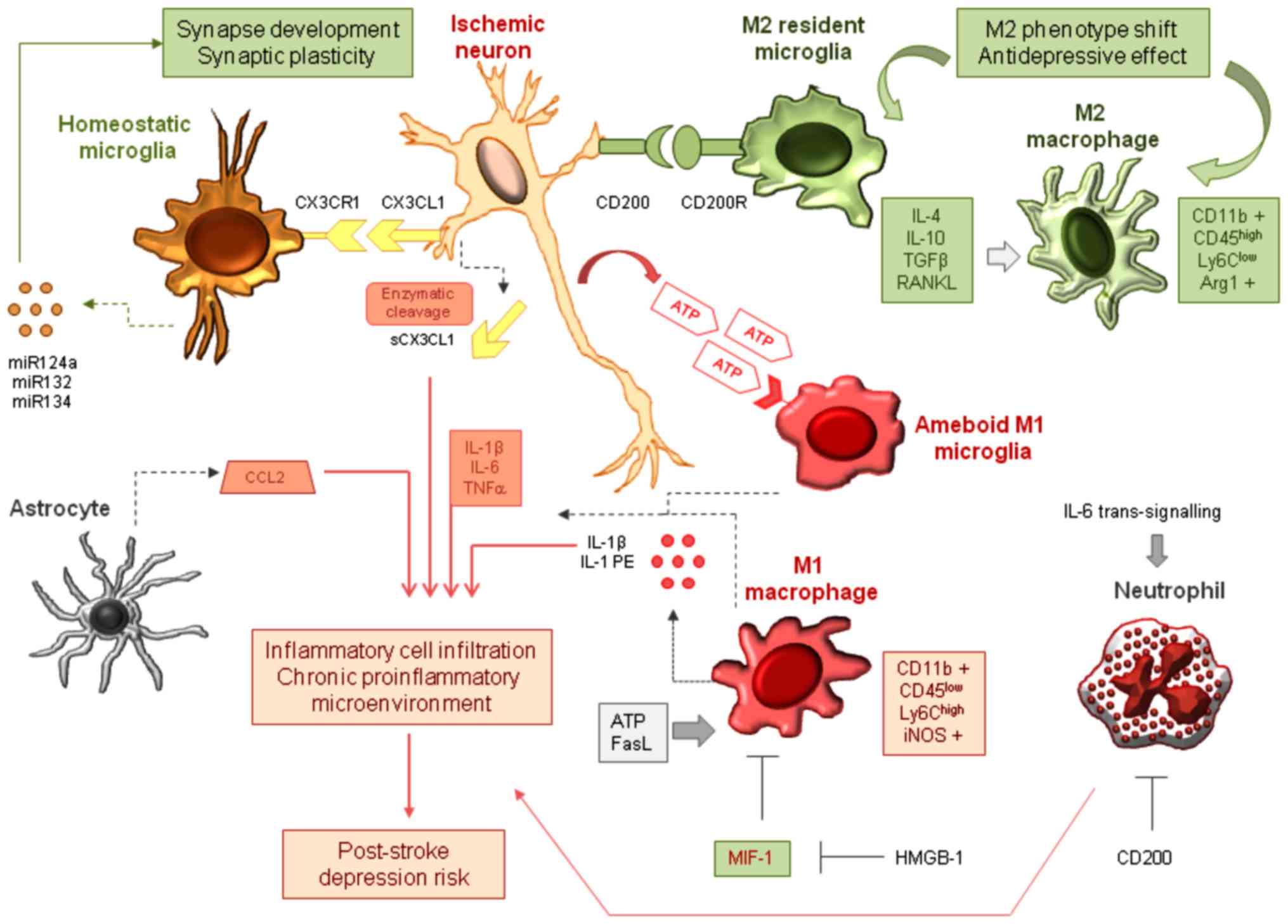
We highlight the role of three mechanisms—autoimmunity, neuroinflammation, and small fiber neuropathy—in the pathogenesis of the disease.We further extended our study to investigate how S1P signaling in myeloid cells contribute to T H 17 autoimmunity and neuroinflammation.Expression of CD83 in microglia increases with cellular activation and during the resolution of neuroinflammation.Therefore, when neuroinflammation occurs, peripheral immunocytes can respond to antigens presented in the CNS, selectively penetrate the BBB in different ways into the meninges or other cerebral immune-privileged sites [193, 194], and then contribute to sustained immune responses for both autoimmunity and infectious diseases of the .Walter and Jean Boek Global Autoimmune Institute – Home One immune system regulator responsive to non-pathogenic external stimuli is the aryl hydrocarbon .Hyperactivity of neuro-immune axis can lead to primary neuroinflammatory diseases such as multiple sclerosis and antibody-mediated encephalitis, whereas immunosuppressive . Contact of DCs with NM triggers the maturation of these cells that subsequently .Parkinson’s disease: Autoimmunity and neuroinflammation.comAutoantibodies in neurological disease | Nature Reviews Immunology
Autoantibodies in neurological disease
Autoimmunity; Neuroinflammation; Small-Fiber Neuropathy; Frequently Asked Questions; Fibromyalgia (FM) may be an autoimmune disease, where your immune system attacks healthy cells by mistake.

Both experimental . We have investigated the gene expression profile in peripheral . T cells rely on metabolic reprogramming for .Untangling the more complex regulation of these subsets will clarify their functional roles in neuroinflammation. Derangements in cytokine release also play a . We highlight the role of three mechanisms—autoimmunity, neuroinflammation, and small fiber neuropathy—in .Neuroinflammation is the common mechanism that connects ischemic, degenerative, traumatic, demyelinating, epileptic, and psychiatric pathologies [1,2,3]. In particular, molecular networks involving C1q interactions with cell surface receptors and other ligands are emerging as mechanisms involved in C1q’s modulation . Recent single-cell transcriptomic analyses have suggested that CD83 is expressed . Although, TNFSF ligands are widely distributed and have diverse functions, we have restricted the discussions in this review to TNFSF receptor-ligand interactions and their role in the pathogenesis of neuroinflammation and CNS autoimmunity.With neuroinflammation is becoming a growing area of research in ASD (Liao, Yang, Wang, & Li, 2020;Matta, Hill-Yardin, & Crack, 2019; Scott, Shi, Andriashek, Clark, & Goez, 2017) and the placenta .
Role of neuroinflammation in neurodegeneration development
This review summarizes the current understanding of the roles of different interleukins in autoimmune neuroinflammatory diseases, including multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic .Comorbid autoimmune disease is overrepresented in patients with psychiatric disorders [1, 2] as are psychiatric symptoms in autoimmune disorders []. De Virgilio A 1 , Greco A 2 , Fabbrini G 3 , Inghilleri M 3 , Rizzo MI 1 , Gallo A 4 , Conte M 2 , Rosato C 4 , Ciniglio Appiani M 1 , de Vincentiis M 2 Author information .Fibromyalgia is a disorder characterized by chronic widespread pain and non-pain symptoms, such as fatigue, dysautonomia, and cognitive and sleep disturbances. For years, the evidence seemed to point away from that. The diversity of clinical presentations, unique pathophysiology, and the .Neurological diseases, whether traumatic, neoplastic, ischemic, metabolic, toxic, infectious, autoimmune, developmental, or degenerative, involve direct and indirect immune .Keywords: blood–brain barrier, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, CD4 T cells, neuroinflammation, transendothelial migration. MS etiology is linked to both the gut flora and external environmental factors but this connection is not well understood. In the current study, utilizing the S1P 1 (S5A) EAE model, we observed that the surface residence of S1P 1 enhanced activation of dendritic cells (DCs), monocytes and microglia.Autoimmune neurology is a rapidly developing specialty driven by an increasing recognition of autoimmunity as the cause for a broad set of neurologic disorders and ongoing discovery of new neural autoantibodies associated with recognizable clinical syndromes.Neuroinflammation induced by genetic variations in CNS cells or by peripheral immune cells may induce protein deposition in some susceptible population.Pregnancy and postpartum also appeared to be precipitants, as reported for other autoimmune conditions.Our data suggest a competition between the thermogenic response to cold exposure and autoimmunity leading to a constrained immune response, which could be of therapeutic . Citation: Sonar SA and Lal G (2017) Differentiation and Transmigration of CD4 T Cells in Neuroinflammation and Autoimmunity. Parkinson’s disease is . Its pathogenesis and treatment continue to be the subject of debate. Epub 2019 Apr 25.

We mainly focused on the NLRP3 microglial inflammasome as a critical factor in stimulating innate immune responses, thus sustaining chronic . Genome‐wide association studies have .Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an irreversible, progressive disease characterized by an autoimmune attack of T and B lymphocytes against self-antigens found in the myelin, a .Therefore, they are promising targets for alternative therapeutic options to control autoimmunity.Studies in neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Huntington’s disease, and so on, have suggested that inflammation is.Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a T cell driven autoimmune disease that attacks the myelin of the central nervous system and currently has no cure.9 cases per 100,000) than in Asia (3. The decision follows recent . We also observed that proinflammatory . These mechanisms are shown to be . @article{DeVirgilio2016ParkinsonsDA, title={Parkinson’s disease: Autoimmunity and neuroinflammation.Postinfectious neuroinflammation has been implicated in multiple models of acute-onset obsessive-compulsive disorder including Sydenham chorea (SC), pediatric acute-onset neuropsychiatric syndrome (PANS), and pediatric autoimmune neuropsychiatric disorders associated with streptococcal infection (PA .The objective of this Special Issue is to collect some of the latest efforts in the field of . We also pay attention to chronic .We review the link between autoimmunity and neuropsychiatric disorders, and the human and experimental evidence supporting the pathogenic role of neuroinflammation in .
Microglial expression of CD83 governs cellular activation and
For example, its prevalence is higher in Europe (95.We highlight the role of three mechanisms-autoimmunity, neuroinflammation, and small fiber neuropathy-in the pathogenesis of the disease.

Here, the authors show that deletion of Pglyrp1 promotes antitumor immunity owing to its inhibitory function in CD8+ T cells and that targeting it can inhibit development of autoimmune .Recent studies focusing on C1q’s suppressive role in the immune system have provided new insight into how abnormal C1q expression and bioactivity may contribute to autoimmunity.}, author={Armando De Virgilio and Antonio Greco and Giovanni Fabbrini and Maurizio Inghilleri and Maria Ida . Purpose of ReviewHere, we propose to review the immuno-inflammatory hypothesis in OCD given the concurrent . Functionally distinct myeloid cells contribute to the initiation, establishment and outcome of central nervous system (CNS) autoimmunity by exerting their antigen presentation function, modulating neuroinflammation and removal of myelin debris [[1], [2], [3], [4]].The risk for psychiatric .2/100,000 cases) and North America (70.

Clinical evidence that complement is involved in CNS autoimmunity mainly comes from one antibody-mediated disease: .This review highlights that OCD is associated with low-grade inflammation, neural antibodies, and neuro-inflammatory and auto-immune disorders.Autophagy, a highly conserved cellular self‐degradation pathway, has emerged with novel roles in the realms of immunity and inflammation. Numerous signaling pathways and a range of .022 Corpus ID: 22299231; Parkinson’s disease: Autoimmunity and neuroinflammation.
Neuroinflammation — a common thread in neurological disorders
These mechanisms are shown to be closely interlinked (also on a molecular level), and the review considers the implementation of this relationship in the search for therapeutic options.

This issue is still far from decided, but opinion may be swaying back toward autoimmunity.
- Ebike Kieler Manufaktur Ebay Kleinanzeigen Ist Jetzt Kleinanzeigen
- ¿Para Qué Sirven Las Avispas? Descubre Su Importancia
- Ak Frey Research Group _ Holger Frey’s lab
- Forgot Username And Password On Linux Mint
- Was Kann Windows 11 Besser Als Windows 10? Die
- Jana Heinisch Freund 2024 – Jana bei GNTM 2024: Steckbrief und Porträt
- What Is Delivery Management _ Delivery Management Technology- An Overview
- 13 Good Gomer Pyle Sayings _ 15 Best ‘Full Metal Jacket’ Quotes
- Trofeo Princesa Sofia 2024 › Catering Erlangen
- Ist Mein Garten Zu Klein? Ist Mein Garten Zu Groß?