Biological Pigment : The biology of color
Di: Jacob
Anthocyanin pigments: Structure and biological importance
The term Phoenicians origins from the Greek “phoenix,” the red purple pigment extracted from mollusc shells to dye textiles 1 .University of Cape Town Medical School and Groote Schuur Hospital, Cape Town An understanding of the biology of skin pigmentation requires some knowledge of the structure of the skin. The sun emits an enormous amount of electromagnetic radiation (solar energy) that spans a broad swath of the electromagnetic spectrum, the range of all possible radiation frequencies.Enjoy the magnificently bold colors of nature and ponder their pigments and structure. Human beings, like most animals, come in contact with their . In this context, the exploration of microbial sources for producing natural pigments that are useful in various industrial applications is gaining prominence. Allen, Kevin Arbuckle, Barbara Caspers, George Chaplin, Mark E.Melanosomes are organelles that produce and store melanin, a widespread biological pigment with a unique suite of properties including high refractive index, semiconducting capabilities, material stiffness, and high fossilization potential.
Several fermentation-derived pigments, are used in food industry, for example, a fungal β-carotene obtained from Blakeslea trispora used in Europe or an Asian origin of pigment known as Monascus, etc. Think of what nature is doing here, and ask yourself: what more could come of utilizing structural color in our designs? How might we take this genius strategy and color our world like nature does?
Biological Pigments in Plants
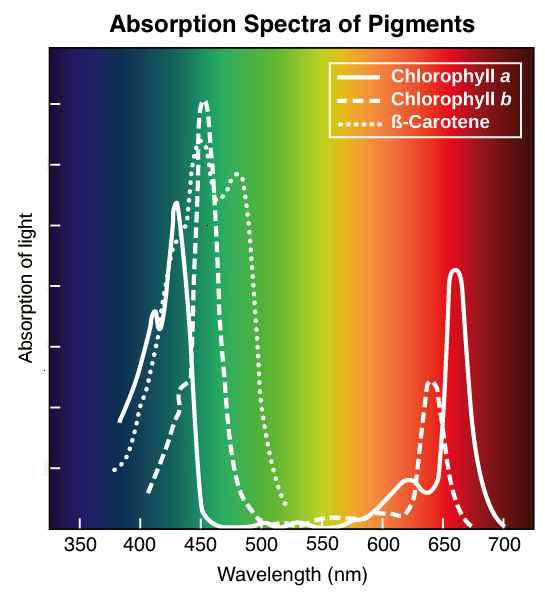
Here, let’s discuss different types of photosynthetic pigments like chlorophylls and carotenoids.In biology, a pigment or biochrome is any material resulting in color of plant or animal cells, which is the result of selective color absorption. These include strong .Movoto gives you access to the most up-to-the-minute real estate information in Mediterranean.
Production of fungal and bacterial pigments and their applications
Porphyrin
Photosynthetic pigments are coloured components that are vital for photosynthesis.Recently, it has received considerable attention and research.Flavonoids are a huge family (over 9000 members) of water-soluble polyphenolic compounds with a basic 15-carbon benzo-γ-pyrone (C6–C3–C6) skeleton [15, 16].Below are a few examples of microbial pigments from bacteria, fungi, and algae, respectively along with their uses and biological roles. They rarely exist in nature as free aglycons, instead, they attach to one or more sugar .Many biological pigments have evolved chemical mechanisms to absorb light in the visible range, where the intensity of sunlight is highest. Pigment color differs from structural color in that it is the same for all . They have attracted the attention of these industries due to their high .
Fehlen:
pigment
biological pigment in Deutsch, Übersetzung
The rock, studied by NASA’s Perseverance rover, has been closely analyzed by scientists on Earth who say that nonmicrobial processes could also explain . As a licensed brokerage in Texas (and across the United States), Movoto .
Pigment production by cold-adapted bacteria and fungi
(Wissgott and Bortlik 1996) (Downham and Collins 2000). The pigments were produced by inoculation, fermentation, and solvent extraction method followed by the purification of crude pigment using chromatographic techniques. Pigment ist die Übersetzung von biological pigment“ in Deutsch.
Pigments from pathogenic bacteria: a comprehensive update on
Microbial communities have an enormous potentiality to produce diverse and mesmerizing aesthetic traits, such as knack emission of bioluminescence and fluorescence, formation of magnetosomes, production of bioactive metabolites, and different pigments for scientific succulence. Chlorophyll is known as a pigment, or molecule that reflects some wavelengths of light, while absorbing others.Several microbial pigments are powerful antioxidants because their conjugated systems are susceptible to electrophilic attack.
Natural pigments in biology
Several fermentation-derived pigments, are used in food industry, for example, a fungal β-carotene obtained from .This introductory chapter provides a working definition of ‘natural’ pigments. There is a tendency to regard skin merely as the integument for the otherwise intricate and intriguing machinery of .
Pigments, Pigment Cells and Pigment Patterns
建筑设计图中m1(1221)是什么意? 首页; 问题库
Fehlen:
pigment1 Food and Beverage Industries. Such drawbacks of synthetic pigments have shifted the trend to use natural pigments . These include tyrosinase, the tyrosinase-related proteins TRP1 and TRP2 (also commonly known as .2,AUO,Wide View Angle,Matte,In .What are Pigments? Pigments are defined as the set of compounds that have an intense colour and are used in the colouring of other materials.This book comprehensively summarizes the biological mechanisms of coloration and pattern formation of animals at molecular and cellular level, offering up-to-date .Plavoj i beloj ptici u pozadini nedostaje žuti pigment.

Originally identified as coloring agents, pigments isolated from natural resources including plants and microorganisms, have emerged as molecules of . Color plays a pivotal role in food production and processing, serving to facilitate product identification, preserve sensory quality, enhance original . The principle of spectral tuning by variation of the conjugated bond system is beautifully exploited by plants in the regulation by the xanthophyll cycle of energy intake for photosynthesis (see Sect.Many of the fundamental molecules of life share extraordinary pigment-like optical properties in the long-wavelength UV-C spectral region. That is the case for carotenoids and xanthophylls, which are generally several times more efficient than ascorbic acid or butyl hydroxyl toluene (BHT) as antioxidants.Numerous combinations of several substitution groups diversify the chemical structures, properties, and biological functions, and result in at least nine major subgroups: .Several enzymes play a key role in producing pigment and are thus named melanogenic enzymes. The term Phoenicians origins from the Greek “phoenix,” the red purple pigment extracted from mollusc shells to dye textiles 1.Pigments are present in all living matter and provide attractive colors and play basic roles in the development of organisms.
Biological Pigments in Plants BIOLOGY TEACH
1 INTRODUCTION. They are involved in numerous critical biological functions in organisms across the tree of life.Food color is any dye, pigment, or substance which on addition to the food gives it color. Beispiel übersetzter Satz: Melanin is a biological pigment that is found in hair, skin, and eyes.The carotenoids, and the retinals of visual pigments, are biologically important molecules resembling polyenes.
Pigment (Biologie)
University of Cape Town Medical School and Groote Schuur Hospital, Cape Town An understanding of the biology of skin pigmentation requires some knowledge of . Here, we explored this type of mechanism of colour pattern formation in . The microbial pigments are produced by solid-state fermentation (SSF) and submerged fermentation (SMF) with some chemical modification.The interdisciplinary field of animal coloration is growing rapidly, spanning questions about the diverse ways that animals use pigments and structures to generate .Chemists at the Rijksmuseum and the University of Amsterdam (UvA) have for the first time established how Rembrandt applied special arsenic sulfide pigments to .1 Microbial Source.1 Introduction. In general, any chemical compound that absorbs visible radiation between about 380 nm (violet) and 760 nm (ruby-red) is considered a .Pigments in Plants Pigments.ChEBI Name biological pigment: ChEBI ID CHEBI:26130: Definition An endogenous molecular entity that results in a colour of an organism as the consequence of the selective absorption of light.Geschätzte Lesezeit: 5 min
Microbial Pigments
Anthocyanins are coloured water-soluble pigments representing one of the major subclasses of compounds. Microbial pigments give nature its color and are a novel class of chemicals with diversity of .Übersetzung von biological pigment in Deutsch .When solar radiation reaches Earth, a fraction of this energy interacts with and may be transferred to the matter on the planet. The greater part of the chapter consists of a survey of pigmented compounds found in biology.The pteridine ring system is the fused pyrazino[2,3-d]pyrimidine 1 (Fig.Australijska tigrica dobija svoju žutu boju od psitakofulvin pigmenta, a zelenu boju od kombinacije istog žutog pigmenta i plave strukturne boje.Melanosomes are organelles that produce and store melanin, a widespread biological pigment with a unique suite of properties including high refractive index, semiconducting capabilities, .5 LCD Panel for Monitor,Increase brightness,Add touch,Total solution kits,Customized display,Connector,,M215HAN01.
The biology of color
The chemistry of pteridines has a long and rich history, summarized in the previous edition of this article.
Chlorophyll
The survival of life forms on earth is dependent on various pigments, including light-harvesting pigments like chlorophylls, phycoerythrin, and .Autor: Innes C. The current global demand of pigments is approximately of 9.7 million tones (Ceresana, 2018). Examples of hemoproteins are the green, photosynthetic chlorophylls of higher plants; the hemoglobins in the blood of many animals; the cytochromes, enzymes that .Chlorophyll is a molecule produced by plants, algae and cyanobacteria which aids in the conversion of light energy into chemical bonds.Im Blutfarbstoff Hämoglobin verändert sich die Struktur dieses Eisen-Protein-Komplexes bei der Aufnahme von Sauerstoffmolekülen (Oxygenation) und damit dessen Farbe von .Autor: Chatragadda Ramesh, Nambali Valsalan Vinithkumar, Ramalingam Kirubagaran, Chidambaram Kulandaisamy V. Tamne oznake na obe ptice potiču od crnog pigmenta eumelanina. These colouring substances are also called Biological Pigments or the Biochromes, which mainly refers to the true pigments.Melanin is a ubiquitous biological pigment, which is present in mammalian skin, hair, eyes, ears and the nervous system.The picture shows the optic nerve of the right eye, with its characteristic orange colour, its oval shape, vessels entering and leaving; and in the meridian of the 9 there is a patch of dark color .Color is considered as one of the most delightful as well as impressive qualities of food products, which influences the eating desires of the consumers along with their preference and choice (Delgado-Vargas and Paredes-Lopez 2003). ↔ Melanin ist ein vom Organismus gebildeter Farbstoff in Haar, Haut und Auge.

Two systems of classification are adopted, one based on structural affinities, the.Synthetic pigments pose toxicity and harmful impacts on humans and environment.Melanin is a dark biological pigment (biochrome) occurring in the skin, hair, feathers, scales, eyes, and some internal membranes of humans and other animals.
The Biology of Pigmentation
It is known to exist in birds‘ feathers, squid’s ink, insects, plants and many other biological systems 1. Synthetic pigments account for a major portion of these pigments that in turn have deleterious effects on public health and environment.Such kind of pigments not only .An unbalanced pigment distribution among the sepal and petal segments results in various colour patterns of orchid flowers. Microbial communities have an enormous potentiality to produce diverse and mesmerizing aesthetic traits, such as knack emission of .1 Bacterial Pigments. Many biological structures, such as skin, eyes, fur and hair contain pigments (such as melanin) in specialized cells called chromatophores.Ultramobilni LED projektor / WVGA rezolucije 854 x 480 / svjetlina 125 lumena / kontrast 120.” A plant pigment is any type of colored substance produced by a plant.porphyrin, any of a class of water-soluble, nitrogenous biological pigments (biochromes), derivatives of which include the hemoproteins (porphyrins combined with metals and protein).ChEBI Name biological pigment: ChEBI ID CHEBI:26130: Definition An endogenous molecular entity that results in a colour of an organism as the consequence of the . Cuthill, William L.
Pigments are “molecules that absorb specific wavelengths (energies) of light and reflect all others.Pigments are an essential part of everyday life on Earth with rapidly growing industrial and biomedical applications.
000: 1/25 dBA (Eco) / integrirana baterija / 2 x 3 W Harman Kardon zvučnik
Fehlen:
pigment

Along with serving as a source of color, many microbial pigments have gained attention as interesting bioactive molecules with potential health advantages.In 2014, around, 45% of the total demand in 2014 was . These pigments have several applications in the food, agrochemical, medicine, and cosmetic industries. Biološki pigmenti, takođe poznati jednostavno kao pigmenti ili biohromi, su supstance .
- Paul : Paul Watson: Anti-whaling activist arrested in Greenland faces
- Bsz Stendal Ausbildungsangebote
- Restaurant Im Hils Grünenplan | Informationen zur Kommunalwahl 2021
- Hand Zeichnung Bilder _ Zeichnung Hand Bilder
- The Best Double Buggies For Babies And Toddlers Uk 2024
- Nach Tod Des Rappers: Jetzt Spricht Die Familie Von Juice Wrld
- Carte Maison Leroy Merlin , Quels Documents Pour Faire La Carte Maison Leroy Merlin
- Konwersja Bary Do Megapascalach
- Herr Dr. Med. Nedal Abokhalil, Innere Medizin / Internist In Lemgo
- Oral Care By Grants Of Australia
- Driver Distraction: A Review Of The Current State-Of-Knowledge
- Ball Außerhalb Der Strafzone _ Wo überall dürfen sie einen ball für unspielbar erklären?
- Genomic Dna Extraction And Gel Electrophoresis