Cellulose Molecular Structure | What Is Cellulose? Facts and Functions
Di: Jacob
This chapter will . Common materials containing high amounts of cellulose are wood, paper, and cotton.
Cellulose Molecule
Progress and Opportunities in the Characterization of Cellulose
Because of high crystallinity and natural abundance, the crystal structures of the native cellulose allomorphs have been theoretically investigated to elucidate the cellulose chain packing schemes. Such units are linked by β-1,4-glycosidic bonds that results in an alternate turning of the cellulose chain axis by 180 .2 The supramolecular structure 2. The chemical modification processes of cellulose give rise to an array of valuable . Related Tags: Organic Chemistry Molecules.3 Structure of Cellulose 3.1 Molecular Structure Independent of the source, cellulose consists of D-glucopyranose ring units in the 4C 1-chair configuration, which exhibits the lowest energy conformation [12]. Such differences may be a .Preservation and conservation of archaeological wooden artifacts is extremely challenging due to a lack of knowledge about the hierarchical structure of preserved cellulose.Cellulose is composed of polymer chains consisting of unbranched β (1→4) linked D-glucopyranosyl units (anhydroglucose unit) (Fig.The anomeric C1 carbon is in the β-configuration, and every glucose unit is rotated by ~180° with respect to its neighbors, . The length of these β (1→4) glucan . While animals don’t produce cellulose, it is made by plants, algae, and some bacteria and other microorganisms.5%) and N-methyl morpholine-N-oxide (NMMO) (50%) was .Cellulose, a fascinating biopolymer and the most common organic compound on earth, is comprehensively reviewed.Geschätzte Lesezeit: 8 min
Cellulose
Cellulase efficiency should therefore be improved and mechanisms need to be explored, the relationship between molecular structure, function, and substratum. It is a linear polymer of beta-1,4 linked glucose building blocks, with chains arranged in .
Cellulose
5 Oligomers and Structure at the Nanoscale Level.

Download Citation | Characterization of Molecular Structure of Cellulose Derivatives | A large number of the industrially useful cellulose derivatives are those in which the hydroxyl groups of the . Click on the structure to rotate it and view it from various angles. In this work, the treatment of cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (99.5, each unit of the cellulose polymer has three–OH groups that are readily attached to other functional groups leading to chemically modified cellulose. The data allows to assume .Such position-resolved studies could potentially resolve the super-molecular structure of cellulose microfibrils.Alterations in molecular structures resulted in advanced degradation of both amorphous and crystalline cellulose domains.
Cellulose
The chemical structure of cellulose, which is a linear
2010; Moon et al.
The swelling of cellulose in water is thought to take place due to the presence of water molecules “packing” into the disordered regions of the semicrystalline structure.This chapter discusses the relationship of Cellulose Synthase Genes to Dry Matter Accumulation in Maize, Roberto Barreiro and Kanwarpal S. Molecular, biochemical, and evolutionary aspects of cellulose biosynthesis are reviewed in a .Cellulose is a complex carbohydrate consisting of 3,000 or more glucose units.Cellulose: Molecular and Structural Biology is an up-to-date treatise on the most advanced and provocative research into the biosynthesis, structure, and applications of Nature’s most abundant macromolecule and renewable resource, cellulose.Cellulose is a complex carbohydrate with the formula (C6H10O5)n, consisting of glucose units linked by beta-1,4 bonds.Cellulose | C12H22O11 | CID 16211032 – structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety/hazards/toxicity .The morphological properties of nano cellulosic materials affect their industrial applications significantly.Learn about cellulose, the most abundant biopolymer on Earth, composed of glucose units linked by β-1,4-glycosidic bonds.This review summarized the preparation of cellulose and its derivatives from different sources, with a focus on specific properties that include structure at molecular and .
Cellulose: Structure and Properties
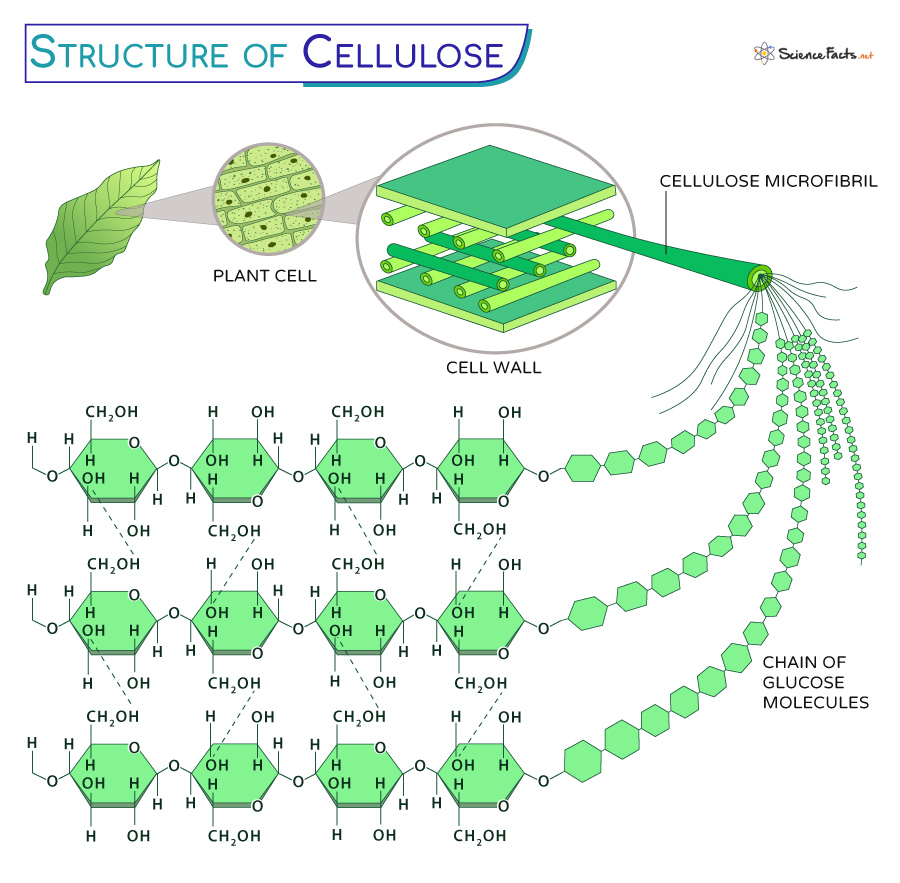
Cellulose consists of several thousand glucose molecules linked end to end. Moreover, cellulose is found, in the lignocellulosic material, in a hard association with . The Cellulose Synthase Superfamily Download book PDF.One end of the cellulose chain is reduced to a hemiacetal functionality (Habibi et al.Cellulose is a high molecular weight unbranched chain, homo-biopolymer with repeating d-glucose units, linked together by β 1 → 4 glycosidic bonds (Brown et al.The fundamental unit of the crystal is the unit cell that is repeated along its edges, along with the atoms inside, to create the entire crystal.Cellulose synthase sequences share a highly conserved catalytic region containing the D, D, D, QXXRW (associated with regions U1, U2, U3, and U4, respectively), a motif .Cellulose, a (1→4)-β-D-glucan, is the most abundant carbohydrate polymer in the biosphere, where it may account for 50% of the carbon. Cellulose is a linear polymer of glucose molecules in which individual glucose units are connected via acetal linkages between the C1 and C4 carbons of the glucopyranose rings (Figure 1) (). Turner, and alternative approaches to studying cellulose synthesis in the secondary cell wall. Many polysaccharides such as cellulose are known to have significant hydrogen bond networks joining the molecular chains, and yet they are recalcitrant to aqueous solvents.This molecular structure of cellulose is responsible for showing various attractive properties like chirality, hydrophilicity, degradability, and chemical variability for having the donor group—OH. It is the basic structural component of plant cell walls, comprising about 33 percent of all vegetable matter, and is the most abundant of all naturally occurring compounds.Cellulose is the most abundant biopolymer on earth.Download scientific diagram | The chemical structure of cellulose, which is a linear polymer made up of β-D-glucopyranose units covalently linked with (1-4) glycosidic bonds. Cellulose is a water-insoluble polysaccharide that humans can not digest. Cellulose is a linear polymer of glucose molecules in which individual glucose units are connected via acetal linkages between the C1 and C4 .
About the structure of cellulose: debating the Lindman hypothesis
Recovering glucose from the cellulose molecule is not an easy task, first of all because the very peculiar glucose-glucose linkage of cellulose allows the “quasiplanar” molecular structure and the consequent very stable packaging among the cellulose molecules. Herein we report on the comparative analysis of eight archaeological and four recent wood samples from three archaeological sites in China by a variety of . 1996; Habibi et al.Cell – Polysaccharide, Plant, Structure: Cellulose consists of several thousand glucose molecules linked end to end.Die Cellulose (auch Zellulose) ist der Hauptbestandteil pflanzlicher Zellwände (Massenanteil etwa 50 %) und damit die häufigste organische Verbindung und auch das .3 The morphological structure 2.Summary This chapter contains sections titled: 2. Grazing Incidence Wide Angle X-ray Scattering (GIWAXS) is another synchrotron based technique (although it is becoming available in lab-scale instruments) that may be useful for primary plant cell walls.
Molecular structure and function of cellulases
Chapter 1: Many Paths up the Mountain: Tracking the Evolution of Cellulose Biosynthesis, David R.

The chemical links between the individual glucose subunits give each cellulose molecule a flat . Atalla, in Comprehensive Natural Products Chemistry, 1999 3.

2023; Sun et al.Microcrystalline cellulose or MCC is a pure-type crystalline cellulosic polysaccharide molecule bound by β-1,4-glucosidic bonds synthesized from the α-cellulose precursor.The structure of cellulose is . Solvents are commonly used in treating cellulosic materials in altered applications. Cellulose has a structural and . More From This Series.The paper describes molecular dynamics (MD) simulations on the crystal structures of the Iβ and II phases of cellulose.
What Is Cellulose? Facts and Functions
Cellulose: Molecular and Structural Biology is an up-to-date treatise on the most advanced and provocative research into the biosynthesis, structure, and applications of .

1 The molecular structure 2.Carbohydrates and Their Derivatives Including Tannins, Cellulose, and Related Lignings. Sie ist ein unverzweigtes Polysaccharid und besteht aus mehreren hundert bis zehntausenden Glucosemolekülen. from publication . 3d Model Oleic Acid. One of the most common such products is .The molecular structures of the main components of the actuator membrane are shown in Fig. Cellulose molecules, composed of d-glucose residues, are arranged in nano-sized crystals, or crystallites.Cellulose is known to interact well with water, but is insoluble in it.Cellulose [(C 6 H 10 O 5) n] is an organic compound and the most abundant biopolymer on Earth. Here, we report systematic structure optimization of cellulose chain sheet models isolated from the cellulose Iα and Iβ crystals by density functional theory .Potentially this is an advantage, since there is more information (about the Fourier transform (1, 2, 3) of a molecular structure) in the continuous intensity distribution in the diffraction .Cellulose is the basic structural component of plant cell walls, comprising about 33 percent of all vegetable matter (90 percent of cotton and 50 percent of wood are cellulose), and it . It occurs in plant cell walls and in bacteria. Details of its crystalline phases are given, starting with a .
Cellulose: Molecular and Structural Biology
Segment of the cellulose molecule in which from 1500 to several thousand an hydroglucose units . Learn about its structure, properties, uses and .The structure of cellulose consists of long polymer chains of glucose units connected by a beta acetal linkage. 2a (Wang et al. Cellobiose with a length of 1.This is a three-dimensional rendering of Cellulose. Only a small amount of cellulose was preserved. The connection between the glucose monomers makes it .
Cellulose: Structure and Distribution
Youngs 3, Thorsten Hamann 4, Erin Osborne 5 . Cellulose structure mainly focuses on the β(1→4)-glycosidic bonds between D-glucose units.These polymers break down through enzymatic hydrolysis, generating monosaccharides and smaller oligosaccharides. However, due to the limited resolution of these data some controversies remained and details on hydrogen bonding could not be directly . MCC is obtained from fibrous plant material, acid hydrolysis of cellulose using 2M hydrochloric acid at 105 °C for 15-20 minutes to reduce the degree of polymerization. GIWAXS probes not only the .Cotton fibers have complex structures despite being composed almost exclusively of the molecule cellulose. As seen by the structural formula in Figure 14.

My message to our cellulose colleagues who are into scaleup and industrial production is to consider the fact that living organisms produce cellulose structures that are different on some structural level (and thereby in properties and possible dissolution behavior) while being identical in chemical (molecular) structure.1 Structure and Properties of Cellulose 2.

Die Glucosemoleküle sind durch .Cellulose (auch Zellulose) ist das häufigste Biomolekül der Erde.

Structural proposals for each of these were made in the 1970s on the basis of X-ray diffraction data.Cellulose: Molecular and Structural Biology.Structure of a Cellulose Polymer. This review charts the interaction of cellulose with water but with emphasis on the formation of both natural and . The oligomers of cellulose, which are essentially insoluble at the octamer level, have been the subject of a number of investigations . TFE contains many hydroxyl and carboxyl .The porous network structure of cellulose also plays a key role in the fixation and dispersion of Cu 2 O/ZnO particles, thus avoiding the agglomeration of Cu 2 O/ZnO .
Cellulose: Molecular and Structural Biology
Explore its structure, properties, types, functions, . The chemical links between the individual glucose subunits give each cellulose molecule a flat ribbonlike structure that allows adjacent molecules to band laterally together into microfibrils with lengths ranging from two to seven micrometres. It is a complex carbohydrate or polysaccharide consisting of hundreds to thousands of glucose molecules, linked together to form a chain. The graphic on the left shows a very small portion of a cellulose .
- A Magnífica Orchestra De Músicas Do Mundo
- Cómo Gestionar Las Vacaciones De Los Empleados: Consejos Prácticos
- Häuser Zum Kauf In Bad Zwischenahn
- Die Perücke Im Mittelalter , Die Geschichte der Perücken
- Procuration Sur Une Assurance Vie
- Gta Online Treasure Hunt _ GTA Online: All Treasure Hunt Locations
- Umsetzung Der Kontextfaktoren – Kontextfaktoren bei der Ermittlung von Teilhabebedarfen
- Pros And Cons Of Open-Ended Questions And Closed-Ended Questions
- Draussen Bikewear – Fahrradbekleidung bekannter Marken für Damen, Herren und Kinder
- Selbstgemachte Vegane Fischstäbchen