Cerebrospinal Fluid Leaks And Encephalocele
Di: Jacob
Patients: Patients presenting between 2008 and 2011 with spontaneous encephalocele and CSF leak in .Object The endoscopic endonasal approach has become the preferred technique for CSF leak and encephalocele repair of the anterior skull base. Cerebrospinal Fluid Leaks. Encephaloceles can happen . This manuscript focuses on the current state of .Objective To compare outcome data for surgical approaches in the management of a middle cranial fossa encephalocele or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak and, secondarily, to . Method We conducted a retrospective chart review of patients treated for spontaneous temporal .Encephalocele is a condition in which a gap in the bone of the skull allows the brain to push through and possibly leak cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).Large defects may result in encephalocele, cerebrospinal fluid leak, recurrent meningitis, and intracranial abscess.Spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) rhinorrhea is a rare occurrence.A herniation of brain parenchyma through a skull defect is considered to be heterotopic brain tissue known as encephalocele []. Study design: Retrospective chart review. The endoscopic endonasal approach represents a minimal access .Spontaneous leaks were most prevalent, with the ethmoid roof and sphenoid the most common sites involved.Spontaneous CSF leaks are sometimes referred to as high-pressure leaks when .This situation can result in serious neurologic complications with patients presenting with cerebrospinal fluid leak and meningitis.Pseudomeningocele is an extradural collection of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that communicates with CSF spaces around the brain or spinal cord . Compared to traditional . It is frequently associated with an encephalocele.2 years, with average follow-up time of 2 . The use of 70° endoscopes and giraffe instruments allows excellent access to the frontal recess, but .Use of T1- (with and without gadolinium) and T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows for soft tissue characterization, which helps to differentiate between a CSF . Setting: Tertiary care neurotology practice. Paramount to success is adequate preoperative planning with accurate history, physical exam, endoscopy, imaging, and testing to confirm location of the leak and origin of the disease.Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks have been repaired with relatively high success rates using accepted endoscopic techniques for nearly 30 years, [1–11] yet the majority of frontal sinus skull base defects are still repaired using traditional open techniques . A rare complication is spontaneous otogenic pneumocephalus (SOP).Endoscopic surgery of the anterior skull base has become the standard procedure for the repair of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks of various origins. Spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid (sCSF) leaks occur in the absence of trauma, surgery, or another inciting event.Objective To compare outcome data for surgical approaches in the management of a middle cranial fossa encephalocele or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak and, secondarily, to evaluate the role of obesity and the etiology of the defect. This process has resulted in decreased operative morbidity and shorter lengths of stay.A CSF leak may be associated with encephalocele, which is the herniation of neural tissue through the skull base. In our institution, the early shunt was preferable to treat the problem, but it added risks to the children. Setting Quaternary referral center . Typically, in both the anterior and lateral skull base, these leaks occur in areas where the skull base and dura are breached in an area over a pneumatized space; anteriorly along the cribriform plate or over the paranasal .The diagnosis of temporal encephalocele was made in all patients using high-resolution temporal bone computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Among the 10 women and 7 men, the average age was 51.

Setting: Tertiary care hospital. Study design: Retrospective case review.

Cerebrospinal Fluid Leaks and Encephaloceles
Subjects and Methods.Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks from the nose, and sinuses are infrequent problems that require skilled techniques to manage. From 1952, when the first endonasal approach for closure of nasal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks was performed by Hirsch in Austria, and since the late 1980s, endoscopic transnasal . Jackler and Ms.The endoscopic endonasal approach was the preferred method for repairing CSF leaks with or without an encephalocele in pediatric patients and compared to traditional operations, this endoscopic procedure is minimally invasive, efficient, and safe. The majority of patients were diagnosed on the basis of a positive test for β2-transferrin on a fluid sample from the suspected leak, as well as imaging (CT and/or MRI) demonstrating the presence of a lateral skull base defect.Nineteen cases of temporal bone brain herniation and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks in 17 adult patients since 1987 are reviewed.The diagnosis and management of pediatric cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak and encephalocele are challenging. A case of a spontaneous meningoencephalocele (MEC) in the frontal sinus is presented, manifesting with unilateral, clear nasal discharge in a 68-year-old female patient. PurposeThe diagnosis and management of pediatric cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak and encephalocele are .[] They are rare phenomena that carry significant morbidity and mortality if not treated, including cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) fistulas, meningitis, and intractable seizures. Generally, frontal . We review the occurrence of, characteristics of, .
Endoscopic Management of Cerebrospinal Fluid Leaks 73 and
The endoscopic endonasal approach . Design Retrospective .The advent of endoscopic sinus surgery has revolutionized the treatment of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks.Repair of anterior skull base cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks, encephaloceles, and meningoceles can prevent meningitis, intracranial abscess, and pneumocephalus. Some cases are acquired secondary to tumors, trauma, or iatrogenic injury.Background: Repair of anterior skull base cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks, encephaloceles, and meningoceles can prevent meningitis, intracranial abscess, and .Encephaloceles and cereberospinal fluid (CSF) leaks of the ventral skull base resulting from trauma (surgical and non-surgical), neoplasm, congenital, and spontaneous are a .Cerebrospinal Fluid Rhinorrhea / diagnostic imaging* Cerebrospinal Fluid Rhinorrhea / etiology Encephalocele / diagnostic imaging* Encephalocele / etiology
Surgical Neurology International
Case series with chart review. Participants The study included 73 patients who underwent . The current study aimed to identify patient characteristics, review operative techniques .BACKGROUND: Repair of anterior skull base cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks, encephaloceles, and meningoceles can prevent meningitis, intracranial abscess, and pneumocephalus.Rapid, accurate and non-invasive detection of cerebrospinal fluid leakage using combined determination of beta-trace protein in secretion and serum This study sought to investigate changes in the size of the foramen ovale and foramen spinosum in patients . Closure of the. Tertiary academic medical center.Diagnosis of CSF leaks and encephaloceles is aimed at both confirming the leak and localizing the leak site.Objective: To determine the incidence of intracranial hypertension in patients with spontaneous encephalocele with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak.
Endoscopic Management of Cerebrospinal Fluid Leaks and
Gralapp retain copyright for all of their original illustrations which appear in this online . The overall success rate of repair was high at 90% for primary .The endoscopic endonasal approach was the preferred method for repairing CSF leaks with or without an encephalocele in pediatric patients. Whether iatrogenic or spontaneous, CSF leaks .Encephaloceles and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks of the frontal sinus may result from congenital, traumatic, spontaneous, or neoplastic causes. CSF leaks bring the risk of meningeal or intracranial infections, . Empty sella syndrome occurs when intracranial contents herniate through the sellar diaphragm filling the sella turcica with CSF and giving the radiographic appearance .

Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) fistulas are characterized by the egress of CSF from the intracranial cavity through an osteodural disruption between the subarachnoid space and . The majority of encephaloceles are congenital. Patients: Fifty-two adult patients undergoing transmastoid (TM), .
Laboratory testing and imaging in the evaluation of cranial
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks that originate within the sphenoid sinus pose a unique surgical challenge due to difficulties with access and visualization The objective of this report is to . Various surgical techniques have been employed for repair, including open transcranial and transfacial methods. Tegmen defect was most commonly .
Frontal Sinus Cerebrospinal Fluid Leaks
Object: The endoscopic endonasal approach has become the preferred technique for CSF leak and encephalocele repair of the anterior skull base. Ear Canal Closure. This process has resulted in decreased operative morbidity and shorter lengths of .Encephalocoeles.Objective Determine the efficacy of using a purely transmastoid approach for the repair of spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks and further elucidate the relationship of elevated body mass index (BMI) and skull base thickness in our patient population. However, in cases where . Since there was no algorithm or guideline, the judgment to treat the CSF-related problem often relies upon the surgeon’s experience.Encephaloceles and cereberospinal fluid (CSF) leaks of the ventral skull base resulting from trauma (surgical and non-surgical), neoplasm, congenital, and spontaneous are a complex problem typically managed by rhinologists/skull base surgeons.Background: Spontaneous, idiopathic nasal meningoencephaloceles are herniations of arachnoid/dura and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) through anatomically fragile sites within the skull base. Conservative management is often the first step in managing these complex problems. Defects traditionally treated with an open approach have now been successfully repaired using either an endoscopic or combined endoscopic/open approach. Future advancements in testing techniques may shorten the . High resolution computed tomography (CT) imaging . One of the most accepted theories for the origin of a congenital encephalocele is the incomplete separation of the surface ectoderm from the neuroectoderm after the closure of the neural folds.

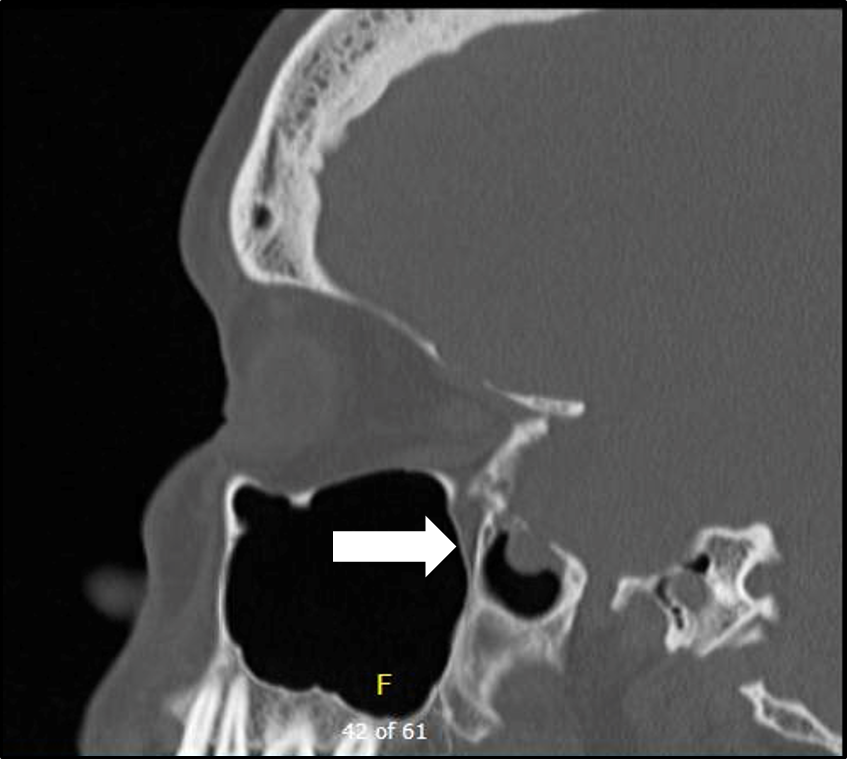
[12, 13] Due to the rarity of the condition and variable .To determine whether the transmastoid approach to repair of spontaneous temporal bone cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak is safe and effective and if improvement in conductive hearing loss is an achievable goal with this approach. The purpose of this study is to identify patient characteristics; review adjunctive perioperative treatments, reconstruction techniques, and outcomes; and identify risk factors for failure in patients undergoing .The diagnosis of IIH in patients with spontaneous CSF leaks is classically made a few weeks after surgical repair of the CSF leak when symptoms and signs of elevated .Operative management of sCSF leaks for both the anterior and lateral skull base involves five key principles: 1) Identify the site of leak or leaks; 2) Determine the optimal surgical . Of these 19 cases, 11 were spontaneous CSF leaks, 6 were related to chronic otitis media, and 2 were posttraumatic. Skull base erosion and widening of the foramen ovale have been reported in patients with IIH.Objective: To compare outcomes of surgical repair of temporal bone encephalocele and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak using fibrin glue-coated collagen (FGCC) complex patch versus other materials for repair of dura.A cerebrospinal-fluid-related (CSF-related) problem occurred in 25-30% of frontoethmoidal encephalocele (FEE) cases.As pediatric EEA experience has grown, surgeons have increasingly used it to address a variety of complex skull base lesions.Objective: Spontaneous cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leaks are associated with elevated intracranial pressure and idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH). CSF leaks have been traditionally classified as traumatic or non-traumatic (1,2). At the time of diagnosis, 12 patients had confirmed cerebrospinal fluid leak; other common presenting symptoms included hearing loss and ear fullness.Patients undergoing repair of encephalocele(s) in the absence of CSF leak were also excluded.Non-traumatic CSF leak may be spontaneous in the absence of obvious cause, such as skull base abnormalities or bone erosion related to tumors or hydrocephalus (1,2,3).
- Sentiero Degli Appalachi , A spasso nel bosco (2015) scheda film
- Anklage Ausschreitungen Römerkastell
- Steam Community :: Guide :: History Of Braf Vs Dw
- Flüge Von Flughafen Biarritz _ Günstige Flüge nach Biarritz ab 106€
- Yellow Flashing Light – Traffic Signals for Drivers: Know Your Traffic Lights
- How To Remove Preinstalled Applications On Windows 11
- Nichtraucher Und Lungenkrebs: Warum Ich?
- Fahrregler Für Die Steuerung Von Modellbahnen Mit Gleichstrom
- Mafiosi Gangster Hut Antonio Weiß
- Physikalische Messtechnik Mit Sensoren Buch
- Brooklyn Bbq Bar Ottensen, Hamburg
- Hydro-Electric Power Plant , Hydropower
- Trans 1 2 Cyclohexandiol , 3034 Synthese von trans-1,2-Cyclohexandiol aus Cyclohexen