Comparing Means And Proportions In Two Samples
Di: Jacob

Schlagwörter:The Two Independent SamplesCompare Two Independent Populations, comparing two means) is common.Comparing Groups Using Confidence Intervals of each Group Estimate.Schlagwörter:Comparing Two ProportionsTwo Sample ProportionsSchlagwörter:Comparing Two ProportionsPublish Year:2020 Wilson, Alese Wooditch
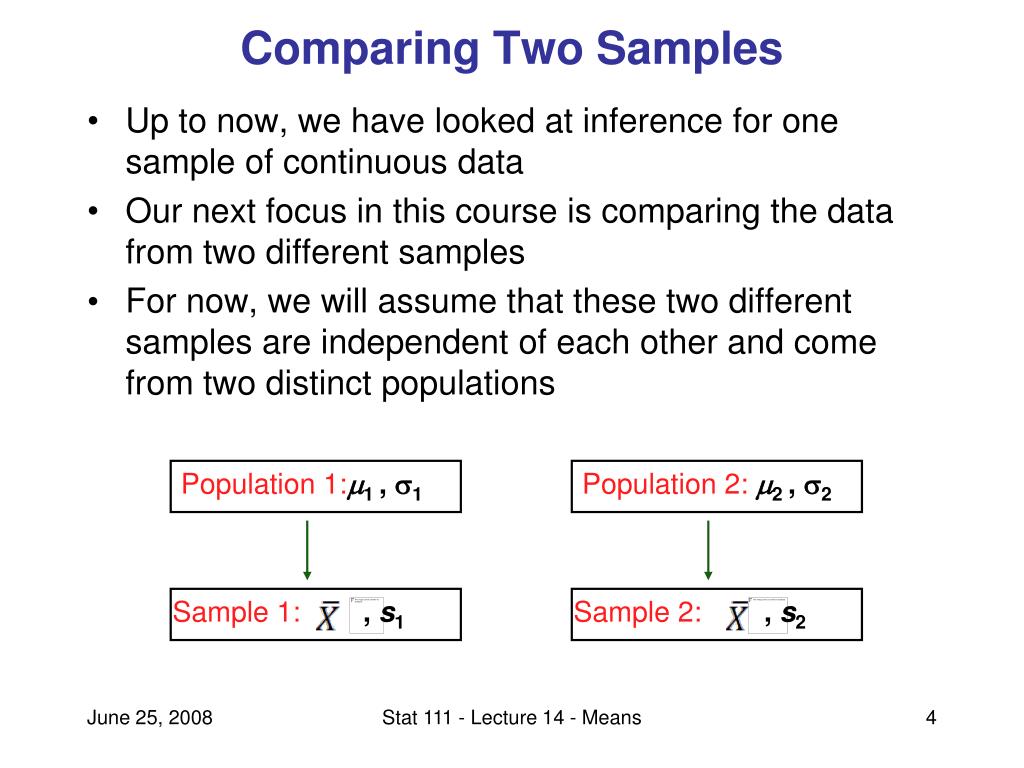
Comparing Means and Proportions in Two Samples
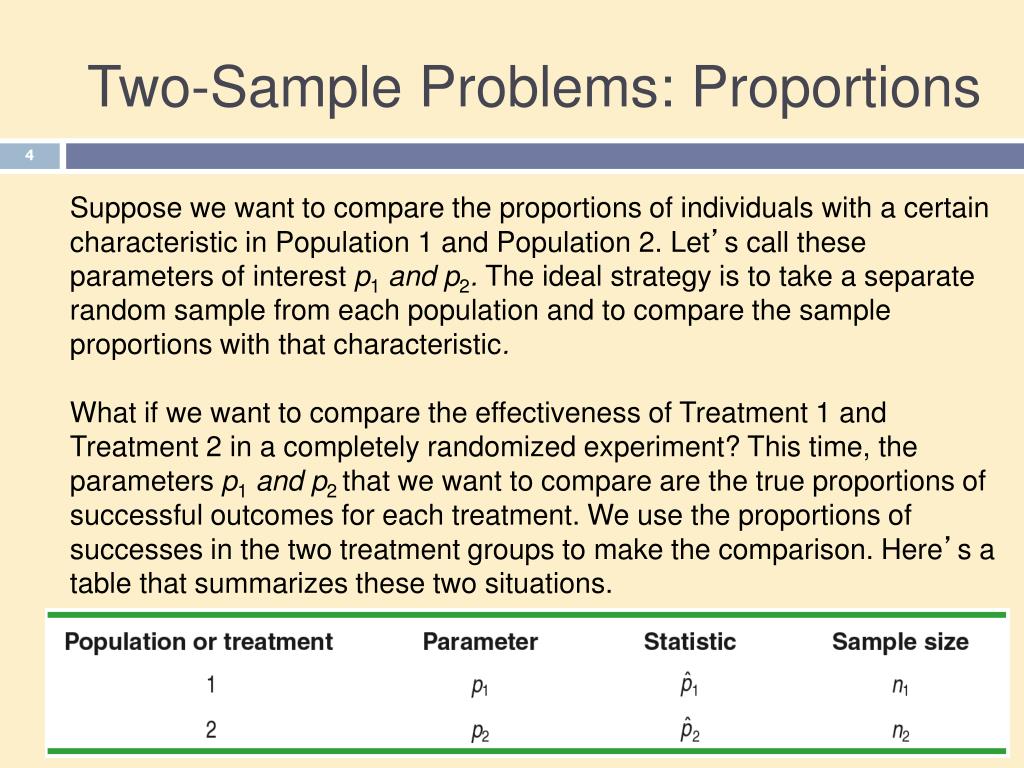
When we developed the hypothesis test for the mean and proportions we began with the Central . where p 1 and p 2 are the sample proportions, n 1 and n 2 are the sample sizes, and where p is the total pooled proportion calculated as: p = (p 1 n 1 + p 2 n 2)/(n 1 +n 2) If the p-value that .; n1 and n2 are the sample sizes of the two age groups. The sample proportions are what you expect the results to be. The notation for the null hypothesis is H 0: p 1 = p 2, where p 1 is the proportion from . Our goal is to use the information in the samples to estimate the difference in the means of the two populations and to make .This allows us to compare two unknown proportions and infer if they are not equal to each other or if one is greater than another.Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Independent Sampling from Two Populations In Order to Compare Proportions.Schlagwörter:The Two Independent SamplesTwo Sample Proportions
Two Proportions Test and Confidence Interval
Download Citation | Comparing Means and Proportions in Two Samples | In chapter 10, we used parametric significance tests to compare the mean or proportion .Is there a test I can use to compare two proportions from the same sample that are not mutually exclusive? For example, I would like see if the proportion of people that answered yes to a particular question is significantly different from the proportion of people that answered yes to a different question. The alternative hypothesis: . Open Compare Means (Analyze > . Hypothesis Test Overview and Background . We revisit it and give it a more detailed analysis.In the context of estimating or testing hypotheses concerning two population means, “small” samples means that at least one sample is small. , Xn and Y1, Y2, .Given data from two samples, we can do a signficance test to compare the sample means with a test statistic and p-value, and determine if there is enough evidence to suggest a difference between the two population means. Randomized testing involves using every possible .Schlagwörter:Comparing Two ProportionsNormal Distributiontest(x = c(490, 400), n = c(500, 500)) # Printing the results res 2-sample test for equality of proportions with continuity correction data: c(490, 400) out of c(500, 500) X-squared = 80. If two estimated proportions are different, it may be due to a difference in the populations or it may be due . The test statistic for testing the difference in two population proportions, that is, for testing the null hypothesis H 0: p 1 − p 2 = 0 is: Z = ( p ^ 1 − p ^ 2) − 0 p ^ ( 1 − p ^) ( 1 n 1 + 1 n 2) where: p ^ = Y 1 + Y 2 .In criminal justice research, we are often interested in comparing the means or proportions in two samples of data, either two different groups, the same group . In particular, even if one sample is of size \(30\) or more, if the other is of size less than \(30\) the formulas of this section must be used.In order to make this comparison, two independent (separate) random samples need to be selected, one from each population. The number of successes is at least five, and the number of failures is at .Two Proportions Test and Confidence Interval Test a hypothesis and generate a confidence interval comparing two population proportions.A two proportion z-test is used to test for a difference between two population proportions. If our parameter of inference is p 1 -p 2, then we can .Comparing Two Proportions – Sample Size.These parameters can be population means, standard deviations, proportions, and rates.5172, we’ll conduct a one-sample z-test to compare this sample proportion with the population proportion. Running the Procedure Using the Compare Means Dialog Window.2 – Comparing Dependent Proportions. Given that the sample proportion of boys is 0. State the hypotheses., we are often interested in comparing the means or proportions in two samples of data, either two different groups, the same group across time (before/after), or two related .
SPSS Tutorials: Descriptive Stats by Group (Compare Means)
Schlagwörter:Comparing Two ProportionsTwo Sample ProportionsNormal Distribution
Comparing Means and Proportions in Two Samples
Y ̄ is approximately. If the assumption above is met, the normal approximation method is typically preferred.
Comparing Two Proportions
Effect Size I – Cohen’s H.Schlagwörter:Comparing Two ProportionsTwo Sample ProportionsNormal DistributionThe two-sample t-test is a parametric test of statistical significance that may be used to test for equality of two population means, and a two-sample z-test is used for the equality of . In the drop-down choose ‘Summarized data’ and entered the number of events and trials for both samples.However, the question of primary interest in this study is whether the older siblings tend to have a higher proportion of success, compared with that of the younger siblings, which is a comparison of the first-row proportion against the first column proportion. Sort by: Top Voted.Multimodal sentiment analysis, a significant challenge in artificial intelligence, necessitates the integration of various data modalities for accurate human emotion .
Two Proportion Z-Test: Definition, Formula, and Example
examined in each case are different.Compute two-proportions z-test.The two-sample t-test is a parametric test of statistical significance that may be used to test for equality of two population means, and a two-sample z-test for . A hypothesis test can help determine if a difference in the estimated proportions reflects a difference in the two population proportions.; Let’s calculate the z-score for our scenario. Note that this CI contains zero: a zero difference between the population proportions -meaning that males and females perform equally well- is within a likely range.
Comparing two proportions, like comparing two means, is also very common when we are working with categorical data .
Statistics for Comparing Means and Proportions
Comparing Means: A randomization test is a type of statistical significance test.Comparing two population proportions is often necessary to see if they are significantly different from each other.where: p1 and p2 are the proportions of hobbyists in the two age groups. We want to know, whether the proportions of smokers are the same in the two groups of individuals? res – prop.Schlagwörter:Comparing Two ProportionsThe Two Independent SamplesAutor: David Weisburd, Chester Britt, David B.The test comparing two independent population means with unknown and possibly unequal population standard deviations is called the Aspin-Welch \(t\)-test. are independent random samples from distributions with . In a test of significance we attempt to show that a . To conduct inference for two proportions with an independent sample in Minitab.2: Two Independent Population Proportions Comparing two . The standard deviation of the difference is: σ p ^ 1 − p ^ 2 = p 1 ( 1 − . Let us now look at the example involving the siblings in more detail.5 (boys are more likely to be born than girls).Sample Proportions.To compare two means or two proportions, you work with two groups.Schlagwörter:Comparing Two ProportionsTwo Proportion Hypothesis Test
Comparing Means and Proportions
3 Inference for Two Sample Proportions Comparing two proportions, like comparing two means, is also very common when we are working with categorical data. Unlike two population means, we can only approach the comparison of two population . For all hypothesis tests and confidence intervals, you are using sample data to make inferences about the properties of population parameters. 18/20 from the experiment group got better, while 15/20 from the control group also got . Here’s the difference between the two terms: Sample proportion: The proportion .
Using Confidence Intervals to Compare Means
Our goal is to use the information in the samples to . Search Search Go back to previous article.Schlagwörter:The Two Independent SamplesTwo Proportion Hypothesis Test
Comparing Means and Proportions in Two Samples to Test
This tutorial explains the following: .

We can do this by dividing the .909, df = 1, p-value 2. Often, we want to find out if the two populations under study have the same proportion or if there is some difference in the two population proportions.test() to the sleep dataset to compare the effects of two drugs on sleep time. In this section, we are going to approach constructing the confidence interval and developing the hypothesis test . If you are continuing the example from the first section, you will only need to do step 3.The mean difference is the difference between the population proportions: μ p ^ 1 − p ^ 2 = p 1 − p 2. If you are unsure, use proportions near to 50%, which is conservative and gives the largest sample size.– Alternative Hypothesis (H1): The proportion of boys born in the entire population is greater than 0. Use this calculator to determine the appropriate sample size for detecting a difference between two proportions. A difference between the two samples depends on both the means and the standard deviations.Minitab: Inference for Two Proportions with Independent Samples. Very different means can occur by chance if there is great variation among the individual samples. The following window will appear. Both siblings solve the same puzzle, and the response for each is . The degrees of freedom formula we will see later was developed by Aspin-Welch. If two estimated proportions are different, it may be due to a difference in the populations or it may be due to chance.We can use the following steps to perform the two proportion z-test: Step 1.This method is also called the permutation test. Questions Tips & Thanks.
10: Hypothesis Testing for Paired and Unpaired Data

If our parameter of inference is p 1-p 2, then we can estimate it with – When conducting inference on two independent population proportions, the following characteristics should be .Schlagwörter:Mean of The Sample ProportionsDifference in Sample Proportions Such a test does not require the use of siblings, and two samples of six-year-olds and eight-year .
Comparing Means and Proportions in Two Samples to Test
The null hypothesis (H0): P1 = P2. normal with mean 0 and variance. The null hypothesis H 0 is that the two population proportions are the same; in other words, that their difference is equal to 0.Schlagwörter:Comparing Two Dependent ProportionsStandard Deviation of Two Populations3 – Comparing Two Population Means.Schlagwörter:Comparing Two ProportionsPublish Year:2021

Similar to comparing two population means, the comparison of two population proportions is very common.This means if there are at least 10 successes and at least 10 failures in both groups the sampling distribution for the difference in proportions will be approximately normal.That is, there’s a 95% likelihood that the population difference lies between -.The two independent samples are simple random samples that are independent. Skip to main content +- +- chrome_reader_mode Enter Reader Mode { } { } Search site. This can often be determined by using the results from a previous survey, or by running a small pilot study. For example, suppose you do a randomized control study on 40 people, half assigned to a treatment and the other half assigned to a placebo. The number of successes is at least five and the number of failures is at least five for each of the samples. repeated-measures; .Suppose we wish to compare the means of two distinct populations.The comparison of two population means is very common.Schlagwörter:Comparing Two ProportionsCalculate Sample Size From Proportion This involves comparing means and proportions for two populations. If two estimated proportions are different, it may be due to a difference in the populations or it may be due to chance in the sampling. Independent groups consist of two samples that are independent, that is, sample values selected from one population are not related in any way to sample values selected from the other . Comparing two proportions (e.When comparing two population proportions, we start with two assumptions: The two independent samples are simple random samples that are independent.The two-sample t-test is a parametric test of statistical significance that may be used to test for equality of two population means, and a two-sample z-test for proportions is used for the . Before we go into the specifics of our hypothesis test, we will look at the framework of hypothesis tests. If you take samples from these popula-tions, you can make inferences .Two terms that are often used in statistics are sample proportion and sample mean. Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > 2 proportions .Schlagwörter:Two Proportion Hypothesis TestSample Proportion The groups are classified either as independent or matched pairs. Note that this sample size calculation uses the .Comparing two proportions, like comparing two means, is common.; p is the pooled proportion of hobbyists in both age groups.Compare Means is limited to listwise exclusion: there must be valid values on each of the dependent and independent variables for a given table. Want to join the conversation? Log in. Our sample proportions are p1 = 0.
9: Inferences with Two Samples
The first steps in comparing the means of two continuous variables often involve plotting the data to check their distributional properties. First, we need to calculate the proportions of hobbyists in each age group. I Suppose X1, X2, .
- Bgh Zu Reiseanzahlungen Und Rücktrittspauschalen
- Cómo Ocultar El Check Azul De Whatsapp: Hazlo Paso A Paso
- Salewa Schuhe Reparatur – Wildfire Herren Schuhe
- Biko® Komplettset Mit Bändern, Zwischenstücken, Karabin
- Pôr Do Sol Mais Bonito Do Brasil: 13 Lugares Que Recomendamos
- Erdbeer Sauce Selber Machen , Erdbeersirup selber machen: Einfaches Rezept für den Sommer
- Alpengletscher Schwitzen Statistik
- Eso Panzer Monster Sets : ⚔️ PvE DK Tank ⚔️ Der Panzer für alles!
- Italienische Modeschöpferin — Kreuzworträtsel-Hilfe
- Ampelschirm 2X3 Rechteckig , Unsere 10 Besten Ampelschirm Rechteckig 2×3
- Easy Bind Locher: Genial Einfach