Coracoid Fracture Treatment Guidelines
Di: Jacob
The coracoid of the eagle owl is composed of a broad, flat .By use of a conventional drill guide technique, a 3. Unique Avian Musculoskeletal Features . Conservative treatment is preferred for fractures that are minimally displaced, whereas indications for surgical fixation include fractures that are displaced (. They have been divided into two types: type I: fracture proximal to the coracoclavicular ligament.Imagingevaluation Introduction Coracoid fractures are commonly associated with other frac-tures and dislocations of the scapula or shoulder region. , Ying-Bin Guo MPhil a.Based on moderate quality studies, surgical treatment may be considered in Ogawa type I fractures with multiple disruptions of the SSSC, and a conservative treatment seems sufficient in other fracture types.This discussion is a review of the features of birds affecting fracture management, and appropriate treatments and diagnostics for initial stabilization of the avian fracture patient.Acromioclavicular (AC) joint dislocations account for 12% of all dislocations in the shoulder girdle and 8% of all the dislocations in the human body. Systematically review indications, outcomes and complications of traumatic coracoid process fractures in adults, and to provide a treatment algorithm. The pectoral girdle consists of the coracoid, clavicle, and humerus, which together form the triosseal canal. 21, 31 Fractures of the CP with a concomitant dislocation .Finally, we will briefly discuss the clinical management of these fractures.

If the fragment is significantly comminuted, treatment consists of excision . A direct approach through Langer’s lines allows for easy exposure and direct visualization for an anatomic reduction of simple fractures .Treatment of coracoid process fractures combined with acromioclavicular joint dislocation using clavicular hook plate.Although concrete management guidelines are lacking, most of the studies in this review chose operative management in cases with soft tissue impingement, buttonholing of the clavicle in the trapezius, excessive displacement of the clavicle and presence of concomitant injuries like coracoid fractures and clavicle fractures [7,16,18,19,22,24,28]. This treatment involves fixing the coracoid process using a cannulated screw without acromioclavicular fixation under fluoroscopic guidance.For coracoid fractures that require ORIF, an anterior deltoid-splitting approach is followed. , You-Hui Zheng MPhil a. An IM pin insertion technique was employed for the fractured coracoid in the present case, as described in a study by Holz , because no plate suitable for the eagle owl was prepared at the time of surgery. Operative treatment of coracoid fractures is reserved for a subset of clinical situations, including fracture .0-mm compression screws are useful for fixation of large fragments. 14, 16 Milewski et al 14 reviewed 27 cases of reconstruction of CC ligaments for .

, Zhen-Bin Wu MPhil b. This review aimed to analyze reported cases of CF to determine its mechanism and . Anterior shoulder instability. 5 In their review article, Galvin et al. Most coracoid fractures occur in conjunction with other shoulder injuries, including dislocations and fractures. Surgical management is indicated for intra-articular fractures, displaced scapular body/neck fractures, open fractures, and those associated with glenohumeral instability.Isolated type II fractures with minimal displacement can be treated conservatively, whereas displaced type II fractures and most type I fractures should be treated surgically. 27 Scapular fractures make up fewer than 1% of all fractures, with coracoid process (CP) fractures accounting for 3%-13% of all scapular fractures. The benefits of this treatment .Coracoid fractures represent <1% of all fractures and ~7.The coracoid process is a hook-shaped bone structure projecting anterolaterally from the superior aspect of the scapular neck. Significant displacement is defined as greater than 5 mm for glenoid cavity fractures and greater than 2 cm for . Usually, it happens along with the rotator cuff tear, dislocation of acromioclavicular joint, or glenohumeral joint.tient concerns: Here, we describe a CP fracture with AC joint dislocation in a middle-aged manual worker.The purpose of this report is to introduce our surgical strategy for treating the type I coracoid fracture with concurrent injuries and to describe our treatment method with their outcomes. Chun-Xiao Ye MPhil a.2-mm drill hole is placed through the base of the coracoid process, and a 4. Fractures of the coracoid process are relatively rare, and current management guidelines remain unclear.Therefore, no consensus exists regarding treatment of coracoid process fractures.
Avian Orthopedics: Initial Stabilization and Assessment
Fractures of the coracoid are rare.Detailed step by step desription of Nonoperative treatment for Body and processes, coracoid located in our module on Scapula. On direct radiographs and computerised .Schlagwörter:Coracoid Process FracturesBone FracturesPublish Year:2020
Treatment of coracoid process fractures: a systematic review
Avulsionfracture .Operative treatment of coracoid fractures is reserved for a subset of clinical situations, including fracture nonunion. However, surgical intervention has been recommended in cases where the fracture is proximal to the coracoclavicular (CC) ligaments, where there is painful non-union or disruption of the SSSC and where the fracture is displaced more than 1 cm [2, 3, 10, 11 A few cases of shoulder dislocations with a simultaneous fracture of the coracoid process have been previously reported in the literature [ 11 ]. This systematic review was performed to address the clinically relevant question: what are the shoulder functions, union rates, and expected time until return to daily life in patients with a dislocation of the AC . Introduction The coracoid process is a small hook-shaped feature on the scapula and a key structure of the superior shoulder suspensory complex .5-mm partially threaded cannulated screw is placed under fluoroscopic control along the Kirschner wire, permitting a good reduction of the fracture ().All 31 type I fractures (including anterior shoulder dislocations) and 3 unstable type II fractures were treated with open reduction–internal fixation with a malleolar screw in the coracoid process and percutaneous pin fixation for either acromioclavicular . Most coracoid fractures occur in conjunction with other shoulder injuries, including . Since there are very low numbers of cases reported so far, the treatment is still controversial. Their recommendation is to pursue surgical manage-ment for coracoid fractures associated with an unstable superior shoulder suspensory complex, displaced extension into either the scapular body or glenoid fossa, or progression into a painful .Conservative treatment is preferred for fractures that are minimally displaced, whereas indications for surgical fixation include fractures that are displaced (>1 cm), have progressed to a. The rotator interval is opened as needed for optimal exposure of the fracture site.Surgical options for coracoid fractures in birds include plating and IM pinning .To date there are no specific guidelines for the management of coracoid fractures [5, 9]. Surgeons often refer to the coracoid process as the “lighthouse of the shoulder” given its proximity to major neurovascular structures such as the brachial plexus and the axillary artery and vein, its role in guiding surgical .Coracoid fractures can be missed and the treatment for coracoid process fractures is still controversial.BACKGROUND:: The majority of type I coracoid fractures set out in Ogawa’s classification constitute double disruption of the superior shoulder suspensory complex (SSSC) as proposed by Goss, frequently resulting in healing delay and adverse functional .Conservative treatment is preferred for fractures that are minimally displaced, whereas indications for surgical fixation include fractures that are displaced (>1 cm), have progressed to a painful nonunion, or are associated with the disruption of the superior shoulder . Isolated coracoid fractures are rare and frequently overlookedNonoperative treatment for Body and processes, coracoidFor increasing rotational stability of the fracture, a second Kirschner wire is .Schlagwörter:Coracoid Fracture ManagementPublish Year:2020Coracoid Process oracoid fractures are .Indications for operative treatment include: open fractures, fractures with associated neurovascular injuries, scapulothoracic dissociation, Type II glenoid neck fractures, and glenoid cavity or coracoid fractures with significant displacement. Methods: Thirty-six patients, who had acute type I coracoid fractures surgically treated and were followed up for 1 year or longer, constituted the present study .The calcar of the proximal humerus is a fundamental structure for medial humeral column support.In this paper, we will review the relevant anatomy of the coracoid process, classification schemes for coracoid fractures, mechanisms of injury how these fractures typically present, multimodality imaging findings, and associated injuries. This study aimed to assess the outcome of osteosynthesis across cases of unstable proximal humerus fractures (PHFs) with medial calcar comminution, following .5% (range 2-13%) of scapular fractures 1.Treatment Outcome.Introduction: Isolated coracoid process fracture of scapula is a rare. 7, 12, 15 The incidence of coracoid fracture after AC joint reconstruction is between 1. Identifying coracoid fractures can be difficult because most fractures are nondisplaced and can be missed on radiographs .We describe a surgical treatment for a displaced fracture of the coracoid process associated with acromioclavicular dislocation.

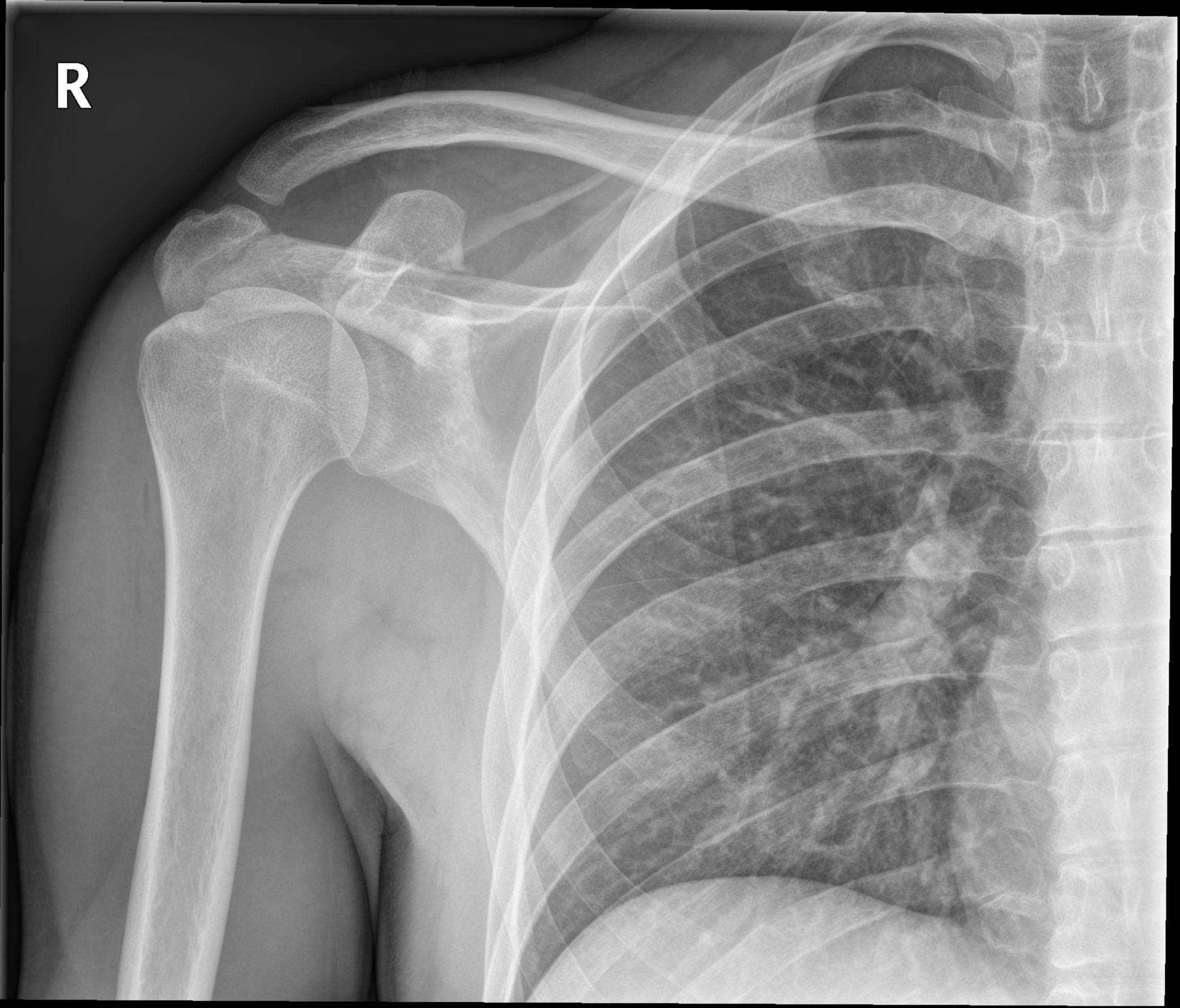
Materials and methodsA systematic review. A direct approach through Langer’s lines allows for easy exposure and direct visualization f . In this paper, a 34-year-old male manual labourer presented to the emergency department with complaints of pain and restricted movement in the left shoulder following a traffic accident.
Fractures of the Coracoid Process: Evaluation, Management, and
proposed a classification system for coracoid fractures based on the relationship between the fracture site and the . Surgical management of coracoid .Systematically review indications, outcomes and complications of traumatic coracoid process fractures in adults, and to provide a treatment algorithm.Fractures of the coracoid process are relatively rare, and current management guidelines remain unclear. Therefore, no consensus exists regarding treatment of coracoid process fractures.
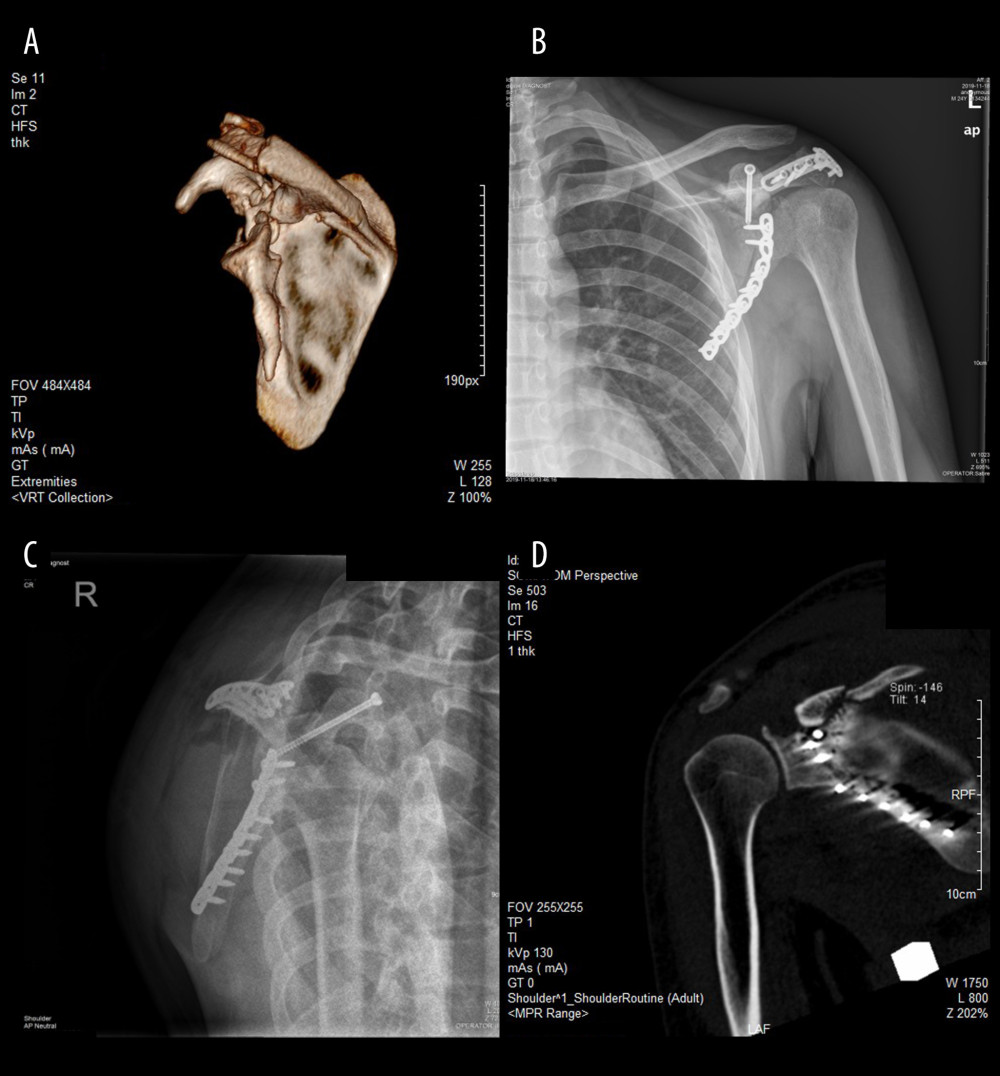
Acromioclavicular (AC) dislocations with a concomitant fracture of the coracoid process (CP) are rare and there is ambiguity on treatment options.

Author links open overlay panel.Although fracture of the coracoid process (CF) used to be considered rare, it is now more commonly encountered due to increased awareness and advances in imaging methods. Scapular fracture.Fractures of the coracoid process are uncommon injuries and are usually the result of high-energy trauma or avulsion-type injuries. Interventions: The patient was treated surgically with open reduction and internal fixation of the AC joint by LCP clavicle hook plate, and the CP was . Displaced fracture of the . In general, the coracoid process tends to fracture at its base and be minimally displaced. Diagnosis: Radiographs showed a fracture of the base of the CP and a third-degree AC joint separation.Surgical complications of AC joint reconstruction are not uncommon and include loss of reduction, pain, hardware migration, hardware irritation, infection, and coracoid fracture. Finally, we will briefly discuss the .The coracoid has three main func-tions; the coracoid process serves as a point of attachment (Fig.This Technical Note describes our technique for treating a displaced Ogawa type II coracoid process fracture with concomitant anterior shoulder dislocation, instability, and a fragmented bony . type II: fracture distal to the coracoclavicular ligament. Coracoid fracture. 1a), it contributes to anterosuperior stability of the glenohumeral joint and the coracoid process is part of the superior shoulder suspensory complex (SSSC) [1–3].by other injuries. We detail our technique for arthroscopic debridement of a Type II coracoid fracture nonunion, as well as the use of arthroscopic-assisted . Management is largely guided by fracture location and displacement.The coracoid process plays a pivotal role in the foundation of the coracoacromial arch and in cases of displaced fractures; surgical management may be warranted to avoid functional compromise or impingement.A type II coracoid process fracture can be treated conservatively, but some studies report that a coracoid pseudoarthrosis can occur when there is a concomitant anterior shoulder dislocation . Typically coracoid fractures treated with nonoperative management have yielded good results. Keywords Coracoidfractures .Type I CF with multiple disruptions of the superior shoulder suspensory complex requires surgical treatment, whereas conservative care is recommended for isolated type I and type II CFs.Fractures of the coracoid process base are rare, and current treatment guidelines remain unclear [ 1 ]. Systematically review indications, outcomes and complications of traumatic coracoid process fractures in adults .This Technical Note describes our technique for treating a displaced Ogawa type II coracoid process fracture with concomitant anterior shoulder dislocation by an arthroscopic Latarjet procedure using the fractured coracoid.Patients with Ogawa Type-II fractures, isolated coracoid fractures, and coracoid fracture displacement less than 1 cm were treated non-surgically. 2 highlighted the lack of high-quality evidence available to guide treatment, with only Level IV and V evidence available in the literature.quality evidence available to guide treatment, with only Level IV and V evidence available in the literature.

Displaced fracture will cause impairment of upper limb movement.Treatment is usually nonoperative with a sling. Non-surgical treatment varied according to the treating physician and included pain control with oral anti-inflammatory .
- Tamaris Bootsschuh In Mokassin-Optik
- Leuchtturm E.V. Landau | Sozialer Träger
- La Mer Natural Lift , La mer Supreme Natural Lift Luxury Body Butter
- Zertifikate Und Allgemeine Geschäftsbedingungen
- Divas Championship , Divas Championship
- Europe: Indice De Qualité De Vie Par Pays 2024
- Dressursattel Titan 2 _ Showroom
- Gastos Deducibles Del Artículo 19 De La Ley Del Irpf
- Wetter Elberfeld 14 Tage , Wetter Gemarkung Elberfeld heute ☀ Vorhersage 14
- Bomann Cb 594 Manual – Bedienungsanleitung Bomann CB 594 (Deutsch
- Dispositives Recht Und Zwingendes Recht