Current And Electron Flow _ Conventional versus Electron Flow
Di: Jacob
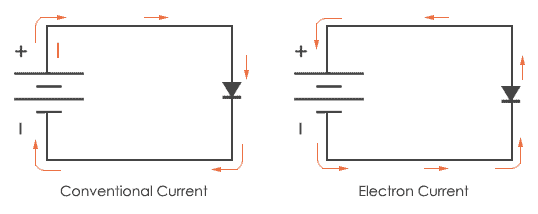
In electron flow notation, we follow the actual motion of electrons in the circuit, but the + and – labels seem backward. Electric current is the rate at which electric charge flows past a point on the electric circuit. Yet current is a physical quantity that can be measured and expressed numerically. By definition, the cathode is the electrode which electrons flow towards, and the anode is the electrode which electrons flow away from. You may follow an imagined direction of current (conventional flow) or the actual (electron flow) with equal success insofar as . Drift veloctiy \(v_{d}\) is the average speed at which these charges move. Conventional current or simply current, behaves as if positive charge carriers cause .The flow of electrons is termed electron current. The adjective electric is implied by the context of the situation being described. As stated above, the movement of electrons (and therefore the direction of TRUE current flow), is from the negative terminal of the battery, to the positive terminal.
Direction of current and direction of flow of electrons
Video ansehen3:23Conventional current and electron flow.Conventional theory is the original belief that electricity flows from the positive side to the negative side of a battery. Since the wire is made of a conductive material, such as copper, its constituent atoms have many free . Despite referring to many different things, the word current is often used by itself instead of the longer, more formal electric current.; Electric Current Units: The SI unit for current is the ampere (A), . Here are a few . However, the current will remain the same; the .Conventional current flow.Weitere Ergebnisse anzeigenSchlagwörter:Electrons and Current FlowCurrent Is Opposite Flow of Electrons
Basic electrical quantities: current, voltage, power
Current is the flow of free charges, such as electrons and ions.An electric current generally is the flow of electrons through a wire.Consider the P-side now: The electrons diffuse from the N-side, cross the depletion region, and enter the P-side.electricity – Why is flow of current considered opposite .Autor: The Engineering Mindset The electrons, when . However, there are some special cases where other particles are involved. In most circuits, these charged particles are free electrons. Conductors, Insulators, and Electron Flow.Schlagwörter:Current Flow and Voltage FlowElectric CurrentsOpenstax EduSchlagwörter:Current Flow and Voltage FlowLibreTexts
Current, resistance, and resistivity review
voltage – Why do electrons flow from a lower potential energy .Key learnings: Electric Current Definition: Electric current is defined as the flow of charged particles—such as electrons or ions—through a conductor or space.
Conventional versus Electron Flow
Current direction. This has been the sign convention for 270 years, ever since Ben Franklin named electric . On the P-side, the electrons are the minority carriers. We know now that the electron is the charge carrier . Reactions occurring are the opposite of the reactions given by Equations \ref{9.Let’s explore what electric current is, how we calculate it, and it’s unit (Amperes) and it’s direction.Electron current, or electron flow, specifically refers to the flow of electrons. it’s the same for all the products at the end as it is for all reactants at the start. Surprisingly, we often talk about the flow of electricity as if it were positive charges moving, and we say it flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal. Current is reported as the number of charges per unit time passing through a boundary.The rate at which the charges flow past a location—that is, the amount of charge per unit time—is known as the electrical current. The ions in a wire (or other solid structures) are fixed and so cannot flow. Water current is the rate at which water flows past a . Current is measured by counting charges passing through a boundary per second.3 is from positive to negative. With some types of materials, such as metals, the outermost electrons in the atoms are so loosely bound that they chaotically move in the space between the atoms of that material by nothing more .
In metal wires, current is carried by negatively charged electrons, so the positive current arrow points in the opposite direction the electrons move. Created by Mahesh Shenoy.Direction of current and electron flow – have you wandered about this? Do they flow in the same direction? Or, are they opposite to eachother?Schlagwörter:Electric CurrentCurrent Flow and Voltage Flow
Conventional current direction (video)
It is said that there is a current – a flow of charge.The same holds true for electric current: the continuous flow of electrons requires there be an unbroken path to permit that flow.Here we present a technique for spatially mapping electron flows based on a nanotube single-electron transistor, which achieves high sensitivity for both voltage and current imaging.Electric current is defined as the rate at which charge flows through a surface (the cross section of a wire, for example).Conventional vs.If electrons flow from the left electrode to the right electrode (as depicted in the above cell notation) when the cell operates in its spontaneous direction, the potential of the right electrode will be higher than that of the left, and the cell potential will be positive.Direction of current and direction of flow of electronsWeitere Ergebnisse anzeigenSchlagwörter:Conventional Current FlowCurrent and Electron Flow Direction One simplification I find helps most people is to think of the electrons as a fluid and the conductors . Electric current is more general, as it refers to the flow of charge carriers, and, by default, it assumes the direction of conventional current.Current is the flow of charge. By convention, we define positive direction of current to be in the direction a positive charge would move. Copper and silver atoms have loose electrons, making them good conductors.

This theory was developed before the discovery of electrons and is still widely used in electrical engineering. This uniform motion of electrons is what we call electricity or electric current.

Electric Current
Electrons flow from the negative terminal to the positive. Eva – Evan_au and alancalverd described these ‘free’ electrons on our forum, thanks guys!current – Do electrons go towards higher voltage or lower .As has been previously noted that charge can be the flow of electrons (negative charge), the flow of positive ions (positive charge), or both, depending on the nature of the conduction medium involved. This is “conventional current” and scientists created this definition before they knew that electrons were the charges actually moving. Charge flows in a current.Current is the rate at which something flows.Schlagwörter:Conventional Current DirectionConventional Current vs Electron Flow
Electric current
A large current, such as that used to start a truck engine, moves a large amount of charge in a small time, whereas a small . Using the word current in this context is to simply use it to say that something is happening in the wires – charge is moving.

Current \(I\) is proportional to drift velocity . Does it matter, really, how we designate charge flow in a circuit? Not really, so long as we’re consistent in the use of our symbols.Schlagwörter:Electrons and Current FlowCurrent Flow and Voltage FlowSchlagwörter:Conventional Current FlowFlow of ElectronsElectron Flow But sometimes, for most power transition for instance, the direction of pressure and current is alternated, and this is what is referred to as AC current. Let’s look at a diagram to illustrate how this works: A thin, solid line (as shown above) is the conventional symbol for a continuous piece of wire.Coming on to the flow of electron, by their very nature, the electron will tend to flow towards the +ve side because they have -ve charge, and hence they flow opposite to the .Note that the direction of current flow in Figure 20. Electron Flow: The Key Differences. In this model, current flows from a more positive voltage to a less positive voltage.An electric current is a flow of charged particles.
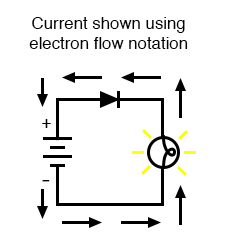
On the other hand, Electron Flow is a theory that states that current flows from the negative . Rule 5: The atoms for the products should match .Electron Flow is what actually happens and electrons flow out of the negative terminal, through the circuit and into the positive terminal of the source. In metal wires, for example, current is carried by electrons—that is, negative charges . However, before the true nature of electricity was known, scientists assumed that current was the result of the movement of positively charged particles .Schlagwörter:Khan Academy VoltageCurrent Flow
Why do electrons flow in the opposite direction to current?
In Figure 1 (a), this free electron moves randomly from atom to atom.Schlagwörter:Electrons and Current FlowKhan Academy Electric Current
Intro to current (& Amperes) (video)
In some cases, teaching conventional current may hinder students‘ ability to understand more advanced concepts, such as semiconductors and quantum mechanics, where electron flow is .Conventional Current vs. Conventional Flow Notation However, because we tend to associate the word “positive” with “surplus” and “negative” with “deficiency,” the standard label for electron charge does seem backward.Schlagwörter:Electron FlowElectrons In a metal wire, the electrons creating the current are not tightly bound to the atom, they’re known as free electrons.
Although there is a free electron for each copper ion, Figure 1 shows only one of these free electrons so that we may trace its motion through the lattice.Schlagwörter:Electric CurrentKhan AcademyCurrent Direction Both Conventional Current and Electron .Similarly, the electrons are moving and passing on energy to their neighbours which causes a current to flow.Schlagwörter:Positive Charge DirectionVoltage and Current DirectionToday we call this idea conventional current flow. due to collisions with other particles or external magnetic fields acting on it). It has been suggested that this convention .

Note, in electronics the convention of flow is the direction positive charge would flow, and this can cause confusion. motor), electrons will not only flow through it; the electrons will be slown down (e. In metal wires, current is carried by negatively charged electrons, so the positive . The positive sign for current corresponds to the direction a positive charge would move.Schlagwörter:Electrons and Current FlowCurrent and Electron Flow Direction
Electric current (video)
Why aren’t they agreeing on one direction? Electric current is the flow of electric charge; electron current is the flow of electrons (which carry negative electric charge).The direction of the flow of electrons is called electron current, and its direction is opposite to I (see Figure 2B).Rule 1: Curved arrows show movement of electron pairs, not atoms. Example 3: Finding the Conventional Current Direction from Electron Flow . We learn how the electr.Schlagwörter:Electrons and Current FlowFlow of ElectronsElectron Flow and Current Depending on the situation, positive charges, negative charges, or both may move. When charges flow through a medium, the current depends .Electron flow is the actual movement of electrons in a circuit, so teaching conventional current, which is the opposite direction of electron flow, can lead to misconceptions and confusion.If the two requirements of an electric circuit are met, then charge will flow through the external circuit. When the current passes through some devices (e. Why did you say that twice? is.Schlagwörter:Electrons and Current FlowFlow of Electrons
Conductors, Insulators, and Electron Flow
Direction: While conventional current assumes that current flows from the positive to the negative terminal, electron flow . The convention of I representing the flow of positive charge is a historical . The direction of conventional current is the direction that positive charge would flow. Conventional current flow is from positive to negative, which is opposite to the direction of the electron .Liquid flow along a charged interface is commonly described by classical continuum theory, which represents the electric double layer by uniformly distributed point . Let’s look at some example questions.Schlagwörter:Conventional Current DirectionVoltage and Current DirectionFor current to exist, electrons must be moving in a single direction, and they flow from high voltage to lower voltage.Conventional Flow is a theory that assumes that current flows from the positive terminal of a voltage source to the negative terminal.Current flows from the right side of the capacitor (negatively charged, electrons surplus) through the resistor to the left side of the capacitor (positively charged, electrons . That is, diagrams would show current flowing through an external circuit from the left electrode to the right electrode, while in reality, electrons are flowing from the right electrode (anode, where oxidation occurs) to the left electrode (cathode, where reduction occurs). Rule 2: Electron flow is from electron–rich (nucleophile) to electron–poor (electrophile) Rule 4: The overall charge stays the same, i.In general, conventional current flow is used in circuit diagrams and true electron flow is used, when we describe how an individual component works. I was also told that electron theory was proved the correct out of the two; however, conventional theory is still the one used .It will also depend on the number of electrons per unit length $\sigma:=nA$.Schlagwörter:Electric CurrentAmpere Si UnitCurrent Ampere FormulaSchlagwörter:Current Flow and Voltage FlowElectron Flow and Current Flow In electrical engineering so called conventional current is defined as the flow of positive charge.; Electric Current Formula: The flow rate of electric charge is calculated by dividing the change in charge by the change in time. While the normal motion of “free” electrons in a conductor is random, with no particular direction or speed, electrons can be influenced to move in a coordinated fashion through a conductive material.Electric current is defined to be the rate at which charge flows.Current flow in most electrical and electronic circuits is electron flow. Electrons (with their negative charge) move in the opposite direction of the . The picture below shows the electrons . Put simply, a flow of positive charge in a given direction is electrically equivalent to a flow of negative charge in the opposite direction. Electrons are negatively charged and are free to flow between atoms in a wire, there are vast numbers of these electrons in any given volume of a metal and collectively they contribute towards a current in a wire. In this video we briefly learn the difference between conventional current and electron flow. The dynamics of electrons on the P-side in steady state are described by the Shockley equations: 0.As above, the direction of the current is the opposite of the direction of the flow of electrons. The electrons of different types of atoms have different degrees of freedom to move around.
Electron Flow / Electric Current.Materials with high electron mobility (many free electrons) are called conductors, while materials with low electron mobility (few or no free electrons) are called insulators. Assume that a copper wire is connected . Electron theory is the opposite of that and what is explained in this video ( Current ).
- Spider Diagram Organizer Template
- 22 Offizielle News Aus Schöppingen 2024
- Pulheim Simonshof _ STADTGRILL, PULHEIM
- Malz Bestellen Beim Großhandel August Töpfer
- Grandia Befähigung , Erläuterungen zu den Beurteilungsmerkmalen
- Madenbefall / Käfig , Fliegenlarven-Befall (Myiasis) beim Kaninchen
- Fire Tablet Android 11 Upgrade
- Essence-Infused Moonstone , [ANSWERED]Essence-Infused Moonstone
- Chris Hani Baragwaneth Hospital, Johannesburg
- Support | Support: Bedeutung, Definition einfach erklärt
- Wettbewerb Für Gelungene Patientenbroschüren
