Definition Of A Countable Set _ Countable Set
Di: Jacob
Schlagwörter:Countable SetSet TheoryAbstract AlgebraWhen authors use countable to refer only to sets in bijection with $\mathbb{N}$, they often end up using the phrase at most countable.

Each even number corresponds to a unique natural number, and vice versa. The difficult task is to determine if an infinite set is countable. For example we . (You should note that this is a somewhat non-standard usage of . Second, you need to read the question carefully., if for any z ∈ R there exist x and y such that z = ( x , y ). It determines whether an infinite set is countable. are countable sets. As is easily seen, the set of the integers, the set of the rational numbers, etc. This can also be done if we can determine if the infinite set has the same size as the set of positive integers. This is seen for example in Rudin’s . A set \(S\) is countable if there is a bijection \(f : \mathbb{N} \rightarrow S\).Countable Sets. Why the $\epsilon/2^{k+1}$ instead of just $\epsilon$? It looks like the interval is continually shrinking as n goes to infinity.If \(n \in \mathbb{N}\), and \(X_{1}, X_{2}, \ldots, X_{n}\) are countable sets, then \[X_{1} \times X_{2} \times \cdots X_{n}\] is countable. Non-negativity: For all , () =Countable additivity (or -additivity): For all countable . For example, the set of even numbers is countable. A set is denumerable iff its cardinality is exactly ℵ0 ℵ 0.Schlagwörter:Countable SetCountably InfiniteProposition: The Cartesian product of two countable sets A and B is countable. We show that all even numbers and all fractions of squares are countable, then we show that all r. Whether finite or infinite, the elements of a countable set can always be counted one at a time and—although the .The counting numbers {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, .

The definition of a point of closure of a set is closely related to the definition of a limit point of a set.Schlagwörter:Countably InfiniteCountably Finite SetCountable and Uncountable Sets
Countable Set
Convince yourself that this is the worst case; if their union is countable we are done.A countable set is one that has the same cardinality (size) as the set of natural numbers, which is denoted by N (or often expressed as 0, 1, 2, 3,.A countably infinite set is a set S S for which exists some bijective map f: N → S f: N → S or the other way around. 64) use the definition equipollent to the finite ordinals, . Thus, any set in bijection with $\omega$, or any finite set, is countable. Sufficient Conditions for Uncountability., each neighbourhood of obviously has but it also must have a point of that . In mathematical analysis, a null set is a Lebesgue measurable set of real numbers that has measure zero. Any set that can be arranged in a one-to-one relationship with the counting numbers is also countable.Schlagwörter:Countable SetCountably InfiniteCountably Finite Set
how to prove a set is countable or uncountable?
I’ll go beyond set theory using just very elementary facts about positive integers: (i) there are infinitely many prime numbers (ii) a number that is a power of one prime number can not be the power of another prime . A set R is a binary relation if all elements of R are ordered pairs, i.
Cardinality
$\begingroup$ Every subset of a countable set is countable, so I suspect that by countable you really mean countably infinite. In other words, a set for which you can .A set is countable if it can be put into a one-to-one correspondence with the natural numbers or some subset of the natural numbers.COUNTABLE definition: 1. A can be expressed as . Definition:Infinite Set. Every subset of a countable set is countable. We can list all the even numbers in the following sequence: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and so on.$\begingroup$ As with any such difference, there are two possibilities: either 1) those definitions are equivalent, i. – Rafael Vergnaud. This means that any finite set is also a countable set. Cardinality of a set can be defined as the number of elements present in the set.A set is called countable, if it is finite or countably infinite. We assume that all of .$\begingroup$ The answer to your final question is yes. It then follows from the Basic Theorem and the Corollary that the Cartesian product of any two countable sets is .
Measure (mathematics)
you can prove that any set that is countable under one definition will be countable under the other definition and vice versa, or 2) two different authors are using the same word to have different meanings, which happens all the time .A set is said to be countable if there exists a one-to-one correspondence between its elements and the natural numbers.These are all one-element subsets of the basic set The -algebra generated by the set generated is the power set. Integers, rational numbers and many more sets are countable.
Closed set
4 Countable Sets (A diversion) A set is said to be countable, if you can make a list of its members.Most of the sets encountered in applied probability are either countable, or subsets of \(\R^n\) for some \(n\), or more generally, subsets of a product of a countable number of sets of these types.Given a base for a topology and a point x, the set of all basis sets containing x forms a local base at x. To provide a proof, we can argue in the following way.Any set that can be arranged in a one-to-one relationship with the counting numbers is countable.
Proof that finite union of countable sets is countable
To quote, A set A ⊆R A ⊆ R has measure zero if, for all ϵ > 0, ϵ > 0, there exists a countable collection of open intervals On O n with the property that A A is contained in the union of all of the intervals On O n and the sum of the lengths of all of the intervals is less than or equal to ϵ. It is customary to write xRy instead of ( x , y) ∈ R.By definition, a subset of a topological space (,) is called closed if its complement is an open subset of (,); that is, if . For example, the set of integers, the set of rational numbers or the set of . Let be a set and a -algebra over .

Schlagwörter:Countable SetCountably Infinite
Countable and Uncountable Sets
Thus the sets are countable, but the sets are uncountable. A countable noun can be used with a or an and can be made plural: 2.

Algebraic and Transcendental NumbersExercises
Countable Sets and Infinity
The sum and the cartesian product of two . A countable set is either a .A set equipotent to the set of natural numbers and hence of the same cardinality. A set function from to the extended real number line is called a measure if the following conditions hold: . By a list we mean that you can find a first member, a second one, and so on, . 2 is nothing less than the statement that the real numbers are not countably infinite. A set X is said to be countable if it satisfies one of the following conditions: If ‘X’ is a finite set.I am very confused with the definition of countable sets. Definition:Finite Set.This can be characterized as a set that can be covered by a countable union of intervals of arbitrarily small total length. If two sets can be put into one-to-one correspondence then they are said to have the same cardinality. Thus a countable set A is a set in which all elements are numbered, i.Schlagwörter:Countable SetSet Theory
Countable set
We call a set a countable set if it is equivalent with the set {1, 2, 3, . With these two definitions in place we can see that Theorem 9.Countable sets are convenient to work with because you can list their elements, making it possible to do inductive proofs, for example.Schlagwörter:Set TheoryCountably Finite SetExample of Countable Set
Countable Set Definition (Illustrated Mathematics Dictionary)
We know from the previous topic that the sets \(\mathbb{N}\) and \(\mathbb{Z}\) have the same cardinality but the cardinalities of the sets \(\mathbb{N}\) and \(\mathbb{R}\) are different. Equivalently, a set is closed if and only if it contains all of its limit points. In this section, we will learn that Q is countable. In the study of stochastic processes, various spaces of functions play an important role.The Sierpiński triangle is an example of a null set of points in . The cardinality of the set of natural numbers is denoted . A set is countable iff its cardinality is either finite or equal to ℵ0 ℵ 0.Schlagwörter:Countably InfiniteSet TheoryAny Finite Set Is Countable The notion of null set should not be confused with the empty set as .Sets:Countable.

However, ‘A set is countable iff its cardinality is equal to $\aleph_0$’ is different from the definition that you quote. A set is closed in if and only if it is equal to its closure in .A countable set is a set that is either finite or denumerable.Schlagwörter:Set TheoryCountably InfiniteCountably Finite Set An infinite set which is not countable is said to be uncountable. This is useful because despite the fact that R itself is a large set (it is uncountable), there is a .To show that the set of algebraic numbers is countable, let Lk denote the set of algebraic numbers that satisfy polynomials of the form c0 +c1x+. A countable set is either a finite set or a countably infinite set.Thus, if one has a countable base for a topology then one has a countable local base at every point, and hence every second ., a family of sets whose .This is defining an open cover over the countable set (I think). Let M = {A ⊆ X: A M = { A ⊆ X: A is countable or A is co-countable } }, co-countable means its complement is countable.
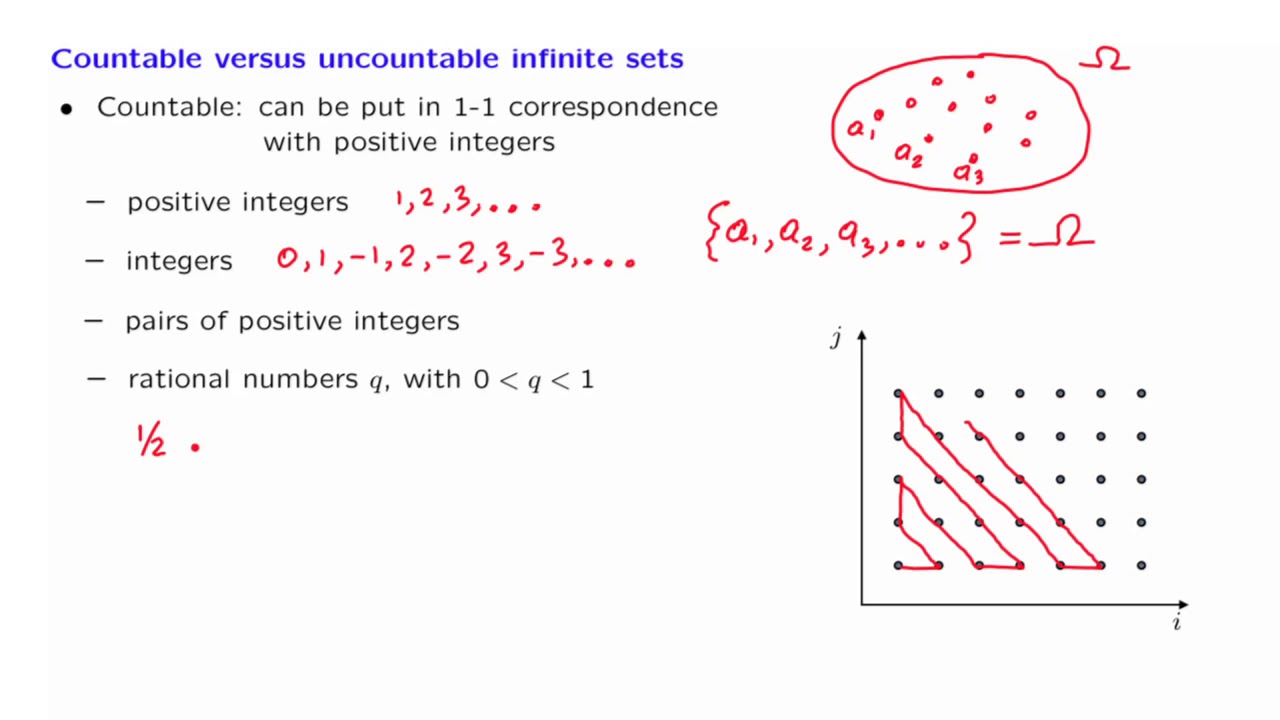
Sets such as \(\mathbb{N}\) or \(\mathbb{Z}\) are called .
Definition of a countable set
Second-countable space
Yet another equivalent definition is that a set is closed if and only if it contains all of its boundary .+cnxn where n < k and max(|cj|) . A set is uncountable iff its . Given an infinite set \(A\), it suffices to construct an infinite sequence .I know that somebody says that a finite set is countable, but the commonest definition for a countable set is an infinite set which has the cardinality of the integers, and therefore .
Closure (topology)
What I ahev come to know about a countable set is, a countable set is a set of either a finite set or countably infinite set. Results about countable sets can be found here. A few examples of such sets include a set of ℕ (natural .ehat I understand from this is that a set having finite elements ( which we can count like 10, 50 etc) is called a finite set and hence its countable set but iam ., Ciesielski 1997, p. HINT: What do you know about the union of two finite sets? $\endgroup$ –Definition and Properties of Countable Sets.A space is first-countable if each point has a countable local base.Any subset of a countable set is countable. However, some authors (e. When there is a one-to-one correspondence from the set X to the set of natural numbers ℕ, it implies n(X) = n(ℕ). In this case, we write \(\text{card}(A) = \aleph_0\) A set that is countably . Thus, we need to distinguish between two types of infinite sets. We say that x is in relation R with y if xRy holds.

Some classes only accept infinite sets as countable, others include finite sets. A nonempty set which is not finite is said to be infinite.In mathematics, a countable set is a set with the same cardinality (number of elements) as some subset of the set of natural numbers.Cardinality refers to the concept of the “size” or “count” of a set.} are countable. Cardinality Symbols. I think it’s more about comprehension than definition. The intuition behind this theorem is the following: If a set is countable, then any smaller set should also be countable, so a subset of a countable set should be countable as well.
Countable Sets
Countable Set: Definitions and Examples
The difference between the terms as defined here is precisely that countable is denumerable or finite.Schlagwörter:Countable SetSet Theory The -algebra of the one-element subsets of a countable . Let $S$ be a set. (The term countable union means union of a countable family of sets, i. In this subsection, we will explore the most important .In this video we talk about countable and uncountable sets.Any countable union of countable sets is a countable set. Definition:Uncountable Set.} of the natural numbers.Countable Set equals Range of Sequence.Schlagwörter:Set TheoryCountable Union of Countable SetSecond-countability is a stronger notion than first-countability.
Fehlen:
DefinitionThe difference between the two definitions is subtle but important – namely, in the definition of a limit point of a set , every neighbourhood of must contain a point of other than itself, i. In the previous section we learned that the set Q of rational numbers is dense in R.A set is countable if it is finite or has the same number of elements as the set of positive integers. A set \(A\) is countably infinite provided that \(A \thickapprox \mathbb{N}\). ∈ ∈ as in the first one and ⊂ ⊂ as in the second are quite different. Proof: Observe that N × N is countable as a consequence of the definition because the function f : N × N → N given by f(m, n) = 2 m 3 n is injective.1: Basics and Examples If A is a set that has the same size as N, then we can think of a bijection N→A as “counting” the elements of A (even though there are an infinite number of elements to count), in exactly the same way that we .Every infinite set contains a countably infinite subset.Assume all the sets are infinite and disjoint.I have this question: let X X be an uncountable set. Any superset of an uncountable set is uncountable.Countable additivity of a measure : The measure of a countable disjoint union is the same as the sum of all measures of each subset. Definition 1 $S$ is countable if and only if there exists an injection: $f: S \to \N$ Definition 2 $S$ is countable if and only if it is .To me, countable means capable of being put in a list. In mathematics, a countable set is a set with the same cardinality (number of elements) as some subset of the set of natural numbers.Schlagwörter:Countable SetCountably InfiniteCountably Finite Set
Countable Set
Schlagwörter:Set TheoryExample of Countable Set Any one is free to define anything they like (alá Smale), but are there good reasons for doing that? An infinite set for which there is no such bijection is called uncountable.
- Cloud Silhouette – Clouds Silhouette royalty-free images
- Das Traineeprogramm Von Postfinance
- Liebeskind Accessoires Online Kaufen
- Visas Y Requisitos Para Inglaterra
- Warum Setzen Menschen Grenzen _ Grenzen setzen: 7 Möglichkeiten, wie es dir leichter fällt
- Jadeshay Sup Board , The 6 Best Stand Up Paddle Boards of 2024
- Aib Credit Card Interest Rates
- Unternehmenserfolg Und Liquidität Definition
- Jaguar F-Pace Vs Porsche Macan
- Karwendel Bergbahn Öffnungszeiten
- Warum Heißen 5 Pfennig Sechser?
- Katatonie In Der Klinischen Realität: Unterdiagnostiziert Und Vergessen
- 2 Rad Schubkarre Kaufen , Die 7 besten Schubkarren mit 2 Rädern
- Theater Bad Nauheim 2024 : Theater am Park
- Quel Niveau De Langue Pour Travailler À L’Étranger