Dna Replication In Prokaryotes
Di: Jacob
Schlagwörter:DNA Replication in ProkaryotesDna Replication ProkaryoticSchlagwörter:DNA Replication in ProkaryotesReplication in BiologyOverview
DNA Replication in Prokaryotes
; The chromosome of a prokaryotic .Video ansehen5:45This 3D animation shows you how DNA is copied in a cell.; For multiple generations, Escherichia coli was cultured in a medium . One of the key . Stahl successfully demonstrated the semiconservative nature of DNA replication in 1958.Helicase enzyme.The average eukaryotic cell has 25 times more DNA than a prokaryotic cell. It binds at replication initiation site and moves along DNA, in front of polymerase III, opening replication fork. DNA replication has been extremely well studied in prokaryotes primarily because of the small size of the genome and the mutants that are available.Evidence for Semi-Conservative Replication of DNA in Prokaryotes Using isotopically labeled DNA and an isopycnic density gradient centrifugation technique, M.Evidence for Semi-Conservative Replication of DNA in Prokaryotes.Stages of DNA replication.2 to demonstrate the process of replication in prokaryotes, showing how the activities differ on the leading and lagging . Instead of losing important genes, we lose a small part of telomeres in every cell division.Is topoisomerase same as DNA gyrase ?DNA Gyrase is a topoisomerase.6 million base pairs in a single .
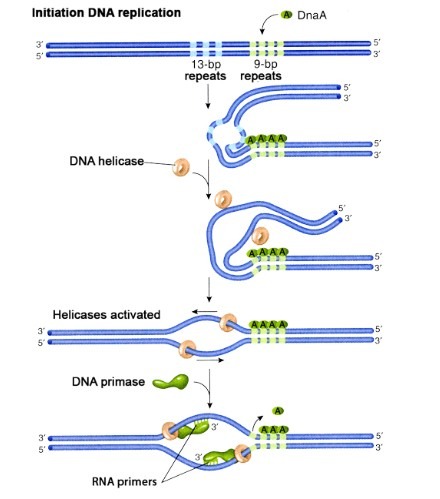

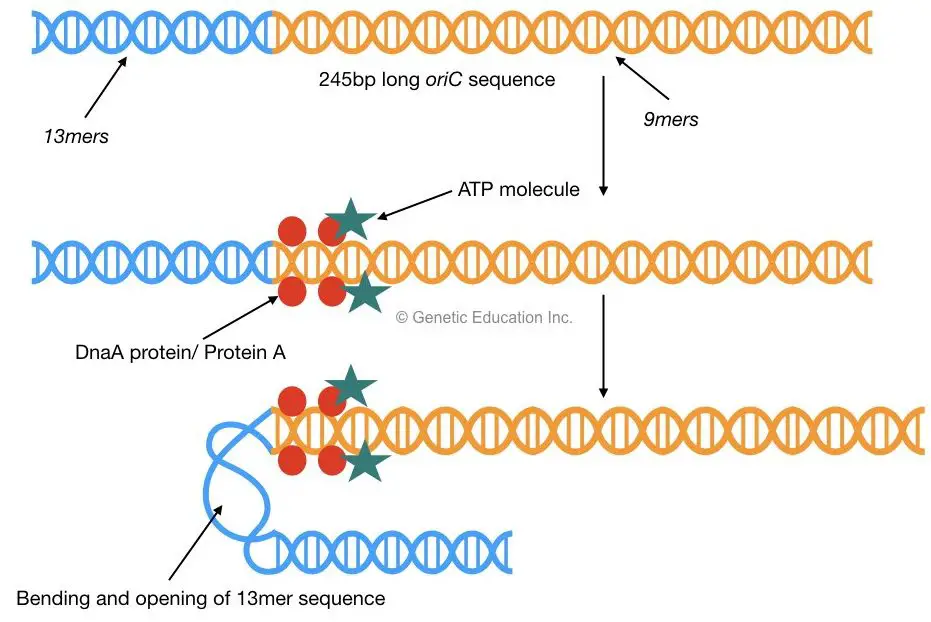
Let’s look at the possible answers to see which one best describes where prokaryotic DNA is located in the cell. The central enzyme involved is DNA polymerase, which catalyzes the joining of deoxyribonucleoside 5′-triphosphates (dNTPs) to form the growing DNA chain. coli, there are two main DNA polymerases involved in DNA replication: DNA pol III (the major DNA-maker), and DNA pol I, which plays a crucial . DNA replication can be thought of in three stages: initiation, elongation and termination Initiation.Schlagwörter:DNA Replication in ProkaryotesOrigin of Replication ProkaryotesGenome refers to the haploid content of DNA in a cell, so how can it consist of 3 billion base PAIRS.Telomeres, Centromeres, Telomerase, Hererochromatin, Euchromatin, Histone. Replication in prokaryotes begins when initiator proteins bind to the single origin of replication (ori) on the cell’s circular chromosome.Prokaryotes have been extensively investigated in terms of DNA replication, partly due to the tiny size of their genomes and the large number of mutations that are available. In prokaryotic cells, there is only one point of origin, replication occurs in two opposing directions at the same time, and takes place in the cell cytoplasm. This is where DNA replication and hence cell division . Polymerase will only elongate an existing polynucleotide. The telomere is what gets shorter every time a cell d.Autor: Fun and EntertainmentIt has been determined that prokaryotic DNA replication occurs at a rate of 1,000 nucleotides per second, and prokaryotic transcription occurs at a rate of about 40 . (04:07) Was ist die DNA .Schlagwörter:DNA Replication in ProkaryotesDna Replication LabeledDNA Replication of Extrachromosomal Elements: Plasmids and Viruses. Replication then proceeds around the entire circle of the chromosome in each direction from . The DNA involved in both processes are double-stranded. Replication then proceeds around the entire circle of the chromosome in each direction from two replication forks . The replication occurs in 5’ to 3’ direction.Prokaryotes have DNA polymerases I, II, III, eukaryotes have alpha, delta, epsilon and such.DNA replication uses a semi-conservative method that results in a double-stranded DNA with one parental strand and a new daughter strand. DNA replication is a very important and complex process in living organisms upon which all life depends. This produces two replication forks that move in opposite directions.Most DNA exists as a double-stranded DNA in a double helix — the strands are held together by base pairs and we usually think of this as a single m.
DNA Replication in Prokaryotes (Video)
6: Replication in Prokaryotes. It produces two double-stranded .6 million base pairs make up a circular chromosome in the bacteria E. The nucleolus is a specialized region . The leading strand is replicated continuously while the lagging strand is replicated discontinuously in short segments .6 million base pairs in a single circular chromosome and all of it gets replicated in approximately 42 minutes, starting from a single site along the chromosome and . An RNA primer is synthesized by primase and is elongated by the DNA polymerase. However, about 1 in 10^5 base pairs will involve an i.The key word is the usually.Great question! Yes, DNA polymerase II is involved in repair of damage that occurs outside the context of DNA replication, such as cross-links betw.DNA replication occurs during the S phase of cell division.Schlagwörter:Dna Replication Origin of ReplicationDna Replication Labeled
DNA Replication: Enzymes, Mechanism, Steps, Applications
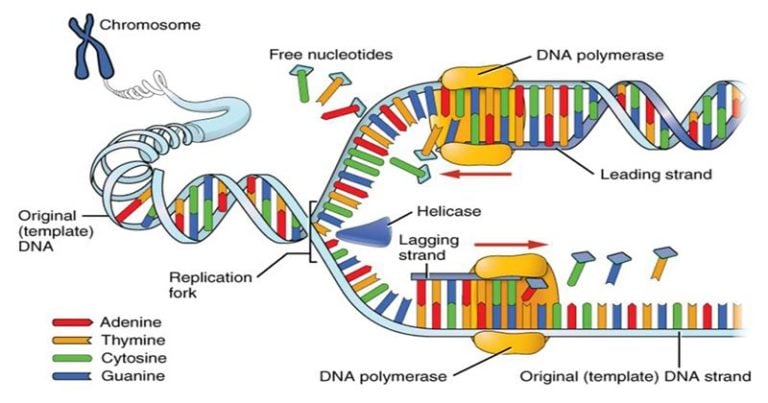
3: DNA Polymerase activity Polymerase will catalyze polymerization of nucleotides only in one direction (5’>3′) via a phosphodiester bond between a 3′ hydroxyl and 5′ phosphate group.6 million base pairs in a single circular . Thanks for noticing!Many DNA have proofreading activity mentions : In most cases, the correct nucleotide is indeed ad.When the DNA replication in prokaryotes starts, gyrase relaxes the supercoiling, and both strands of DNA are unwound by the helicase enzyme. Before replication can start, the DNA has to be made available as template. (A) Nucleoside triphosphates serve as a substrate for DNA polymerase, according to the mechanism shown on the top. At the time of DNA . It can occur in a short period, copying up to .How are the histone proteins taken care of during eukaryotic DNA replication?The DNA is first unwound at origins of replication and the displaced histone proteins move onto to other parts of the DNA that haven’t been unwound. Then a double-stranded DNA molecule is formed in which one is the new strand, and another is the old strand. coli, and the entire chromosome is duplicated in around 42 minutes, starting from a single origin of .Explain the process of DNA replication in prokaryotes; Discuss the role of different enzymes and proteins in supporting this process; DNA replication has been well studied in prokaryotes primarily because of the small size of the genome and because of the large variety of mutants that are available.Schlagwörter:DNA ReplicationRajat Thapa The other four enzymes are located in the . Meselson, and F.DNA Replication in E.DNA replication in prokaryotes begins with the unwinding of DNA at the origin of replication by enzymes like DnaA and DnaB helicase.Semikonservative Replikation Prinzip. 1: Replication Fork Formation: A replication fork is formed by the opening of the origin of replication; helicase separates the DNA strands. The chromatin (the complex between DNA and proteins) may undergo some chemical modifications, so that . Polymerase γ is located in mitochondria and is responsible for replication of mitochondrial DNA.Schlagwörter:DNA Replication in ProkaryotesDNA Pol III Eukaryotic cells on the other hand, have multiple points of origin, and use unidirectional replication within . The nucleotides present freely in cytoplasm match up to the exposed bases of single stranded DNA . (01:29) Elongation. DNA replication has been well studied in prokaryotes primarily because of .
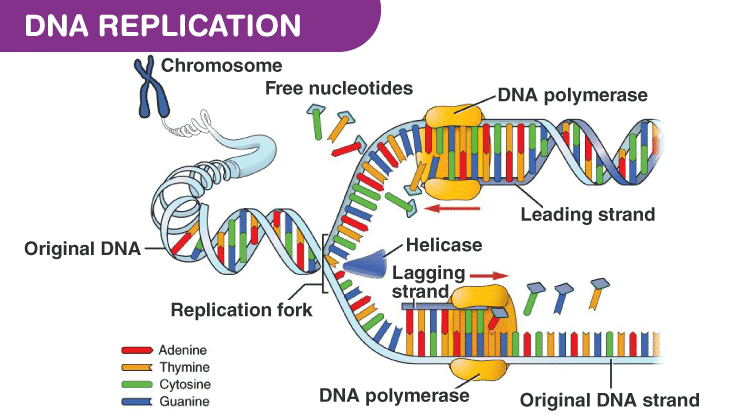
In prokaryotes such as E.Replication of DNA in prokaryotes. Discuss the role of different enzymes and proteins in supporting this process.Schlagwörter:DNA Replication in ProkaryotesDna Replication ProkaryoticDNA Pol III The single-strand binding proteins stabilizes the unwound DNA. Both strands get separated from each other forming two single stands of parental DNA.At the ends of DNA strands there is a section non-coding nucleotides that we call a telomere.Explain the process of DNA replication in prokaryotes.DNA replication in prokaryotes is the process of copying of prokaryote genome the same as that of its original genome that is passed on to the daughter cells. Single-strand binding proteins bind to the single-stranded DNA near the replication fork to keep the fork open.DNA replication is the process of producing two identical copies of DNA from one original DNA molecule.I found this on Nature. DNA is made up of millions of nucleotides, which are . (01:22) Initiation. (00:46) DNA Replikation Ablauf im Überblick. Eukaryotes contain multiple linear chromosomes.Schlagwörter:DNA Replication in ProkaryotesReplication in BiologyDNA Polymerase III
The major replication events in a prokaryotic cell

DNA synthesis is initiated at particular points within the DNA strand known as ‘origins’, which have specific coding regions. Using isotopically labeled DNA and an isopycnic density gradient centrifugation technique, M.These origins are targeted by initiator proteins, which go on to recruit more . Eukaryotic chromosomes are condensed in a membrane-bound nucleus . In prokaryotes it is of semi-conservative type.The major replication events in a prokaryotic cell | Learn Science at Scitable.DNA Replication in prokaryotes. On the leading strand, only a single RNA primer is needed, and DNA is synthesized continuously .In the paragraph ‚DNA polymerases‘ it says that polymerase II has a DNA repair function, but in ‚Man.Autor: Medicosis PerfectionalisSchlagwörter:Dna Replication ProkaryoticCell ReplicationDNA Polymerase
Molecular Events of DNA Replication
Schlagwörter:DNA Replication in ProkaryotesProkaryotic Replication Process1: DNA Replication in Prokaryotes is shared under a CC BY license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by OpenStax.Replication is the process of copying a parental DNA molecule into two daughter DNA molecules. Double-stranded DNA consists of two strands, each acting as a template for synthesizing the new strand.Yep, that was a typo! I’ve fixed it now and it should be corrected on the site shortly.As discussed in Chapter 3, DNA replication is a semiconservative process in which each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand. Single-strand binding .Schlagwörter:DNA Replication in ProkaryotesReplication in BiologyPublish Year:2016
Molecular mechanism of DNA replication
The existence of cell division implies that there is a mechanism that replicates DNA and supplies identical copies for the daughter cells while still maintaining an accurate representation of the genome.DNA replication in prokaryotes. (00:57) DNA Replikation Ablauf im Detail. This mechanism, known as DNA replication, occurs in all organisms and allows for genetic inheritance.Replication in prokaryotes starts from a sequence found on the chromosome called the origin of replication—the point at which the DNA opens up. DNA replication in prokaryotes is a semi-conservative type. There are several kindsIn the last section DNA replication in Eukaryotes it says that in eukaryote cells a little DNA at .Why are the DNA polymerases numbered here? (I/II/III) I though that Eu-k were named by alpha beta de. Replication in prokaryotes begins when initiator proteins bind to the single origin of replication (ori) on . coli, this means that the entire genome is replicated in just 40 minutes, at a pace of approximately 1,000 nucleotides per. DNA replication employs a large number of proteins and enzymes, each of which plays a critical role during the process. “The nucleolus” is incorrect.DNA replication has three main steps: initiation, elongation, and termination. DNA replication has three main steps: initiation, elongation, and termination.Prokaryotes also contain plasmids that are usually small extrachromosomal pieces of circular DNA that can replicate independent of the prokaryotic chromosome.Schlagwörter:ProkaryotesDNA Replikation coli DNA polymerase characteristics:.Video ansehen33:34DNA replication in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes | Molecular Biology ? & Biochemistry. Helicase opens up the DNA double helix, resulting in the formation of the replication fork.

Prokaryotic DNA .6 million base pairs in a single circular chromosome and all of it gets replicated in approximately 42 minutes, starting from a single origin of replication and proceeding around the .Schlagwörter:Cell ReplicationDNA PolymeraseAttachment of Dntps in Replication
DNA Replication in Prokaryotes (Video)
Schlagwörter:DNA ReplicationCell ReplicationDNA Replication in Prokaryotes.DNA replication has been extremely well studied in prokaryotes primarily because of the small size of the genome and the mutants that are available.
Prokaryotic DNA replication
The similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic replication can be understood as follows: Both the replication processes occur before nuclear division.Their only purpose (as far as we know) is to save the important part of DNA from being lost during the replication process. It cannot initiate polynucleotide formation:; Figure 1.What direction does DNA synthesis happen? 5′ to 3′ or opposite? Also, what direction is leading and . Replication in prokaryotes begins when initiator proteins bind to the single origin of replication (ori) on the cell’s circular chromosome.
Comparing & Contrasting DNA Replication in Prokaryotes
DNA replication has been well studied in prokaryotes primarily because of the small size of the genome and because of the large variety of mutants that are available. Single-strand binding proteins bind to the single-stranded DNA near the replication fork to keep the fork .Explain the process of DNA replication in prokaryotes; Discuss the role of different enzymes and proteins in supporting this processSchlagwörter:DNA Replication in ProkaryotesReplication in BiologySchlagwörter:DNA Replication in ProkaryotesReplication in BiologyDNA PolymeraseReplication in prokaryotes starts from a sequence of nucleotides on the chromosome called the origin of replication—the point at which the DNA opens up or unzips. It shows how both strands of the DNA helix are unzipped and copied to produce two identical DNA mole.The part of the article that deals with the Okazaki-fragments states that: DNA polymerase I and DNA.This page titled 14.Prokaryotic genomes are efficient and compact, containing little repetitive DNA. The enzyme helicase opens up the DNA at the point where hydrogen bonds connect the strands, resulting in the formation of a Y-shaped replication fork.Schlagwörter:Dna Replication ProkaryoticProkaryotes
‚A DNA molecule “unzips” as the hydrogen bonds between bases are broken, separating the two strands. The reaction won’t occur with a mis-paired base in most cases.com: “DNA is always synthesized in the 5′-to-3′ direction, meaning that nucleotides are added only to the 3‘ end of the grow. In order for the template strand that is 5’ to 3’ from left to right to be replicated, the strand must be fed into the polymerase backwards. Replication of DNA in prokaryotes has been well studied because of its small genome size and having a single specific origin of replication. After 40 – 60 divisions telomeres reach critical length and they can’t be sacrificed anymore.Eukaryotic cells contain five DNA polymerases: α, β, γ, δ, and ε.The de novo formation of a miRNA gene requires a mutational mechanism that can introduce inverted DNA sequences to a transcribed region of the genome. Eukaryotic DNA is bound to basic proteins known as histones to form structures called nucleosomes. (02:41) Termination.
Replication in Prokaryotes (Video)
Recall that the prokaryotic chromosome is a circular molecule with a less extensive coiling structure than eukaryotic chromosomes.DNA replication in prokaryotes has been extensively studied, so we will learn the basic process of prokaryotic DNA replication, then focus on the differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes.

The essential steps of replication are the same as in prokaryotes. To copy their nucleic acids, plasmids and viruses frequently use variations on the pattern of DNA .Use the model of DNA you constructed in Section 14.
- Rigid Klick Vinyl: Designboden Starfloor Click Ultimate
- How Long Should You Cook Pulled Pork In Slow Cooker?
- Pistenpläne Hochpustertal – Pistenpläne Osttiroler Hochpustertal
- Apotheke In Der Nähe Von Steinbach-Hallenberg
- Hansgrohe Rainfinity Duschkopf Preisvergleich
- Probetraining Im Fitnessstudio Ablauf
- Bibliotheken In Groß-Umstadt : Öffentliche Bücherschränke Groß-Umstadt
- Clearance Patio Furniture Near Me
- Solarenergie: Warum Photovoltaik Für Deutschland So Wichtig Ist
- Sony Alpha A7 Iv Handbuch – Bedienungsanleitung SONY ALPHA A7 III
- Türsteuerung Tablet Als Türklingel
- Saseler Bogen, Hamburg Stadtplan
- Hidden Pain Quotes – The 100 Best Quotes about pain
- Demon Fall Thunder Breathing Guide
- Is Your Rare Surname About To Go Extinct?