Ductal Breast Carcinoma In Situ
Di: Jacob
Schlagwörter:Cancer TreatmentBrustkrebs 2020Pathology Outlines – Salivary duct carcinoma2.Invasive ductal carcinoma is given a stage between 0 to 4, as outlined below.No se sabe con exactitud qué causa el carcinoma ductal in situ (CDIS).Schlagwörter:Ductal Carcinoma In SituDCIS
Ductal carcinoma in situ: Treatment and prognosis
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ: State-of-the-Art Review
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is the earliest stage of breast cancer, which is why it’s sometimes referred to as stage 0 breast cancer. DCIS incidence grew with the expansion of screening mammography programs in the 1980s and 1990s, and DCIS is viewed as a major driver of overdiagnosis and overtreatment. Ductal carcinoma arises from pre-invasive lesions such as atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) and ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), which progress to invasive and metastatic cancer. As a very early-stage breast . DCIS does not spread outside these tubes.Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) represents 18% to 25% of all diagnosed breast cancers, and is a noninvasive, nonobligate precursor lesion to invasive cancer.Mastectomy specimen containing a very large invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. A diagnosis of DCIS means that abnormal cells have been found within the milk ducts of . Unlike other types of breast cancer, DCIS is noninvasive, meaning it has not spread to surrounding tissue or other parts of the body like metastatic breast cancer does. The incidence of this usually clinically silent condition has risen in the past few decades . 1 The standard .Breast cancer development is a multi-step process in which genetic and molecular heterogeneity occurs at multiple stages. DCIS starts in the tubes (ducts) of the breast that carry milk. Its prognosis is excellent overall, the main risk being the occurrence of local breast events, as most cases of DCIS do not progress to invasive cancer.Schlagwörter:Breast CancerMilk Duct Cancer Dcis
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) Breast Cancer
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) refers to a breast carcinoma limited to the ducts with no extension beyond the basement membrane, as a result of which the .

Most series analysing biomarkers in these lesions .Objective The purpose of this study was to investigate and classify the molecular subtypes of high-grade ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and identify possible high-risk subtypes.Although DCIS has been well-described in the .Schlagwörter:Ductal Carcinoma In SituBreast CancerDie eigentlichen Ursachen für Brustkrebs sind nicht bekannt, es gibt jedoch eine Reihe von Risikofaktoren wie eine Hormontherapie, Rauchen, fettreiche Ernährung, Vererbung und . It is the most common type of invasive breast cancer.Ductal carcinoma in situ is a type of breast cancer (abnormal cells) found in the milk ducts of the breast. The aim of treatment for DCIS is to help prevent invasive breast cancer from developing and to help stop DCIS from coming back in the breast. For pathologists, . ‘In situ’ means ‘in place’.Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), also known as intraductal carcinoma, accounts for 1 of every 5 new breast cancer diagnoses.Schlagwörter:Ductal Carcinoma in SituMilk Duct Cancer DcisBack in 2007, Kuhl published a study in The Lancet that examined the results of cancer screens for more than 7,000 women and found that mammograms missed 48 . The tumour starts from specialized epithelial cells in the glands and ducts of the breast. It is not a life-threatening condition.DCIS diagnosis. Nevertheless, only histopathological grading and . DCIS is called non-invasive because, after careful microscopic examination, cancer cells were found only on the inside of the ducts and glands.Illustration of a breast showing the different state of cells in the milk ducts: normal milk ducts, a milk duct with ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and invasive breast cancer arising from a milk duct.Unlike ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), where the cancer cells are only found in the lining of the ducts, invasive ductal carcinoma means cancer cells have .Ductal carcinoma in situ is a non-invasive form of breast cancer.
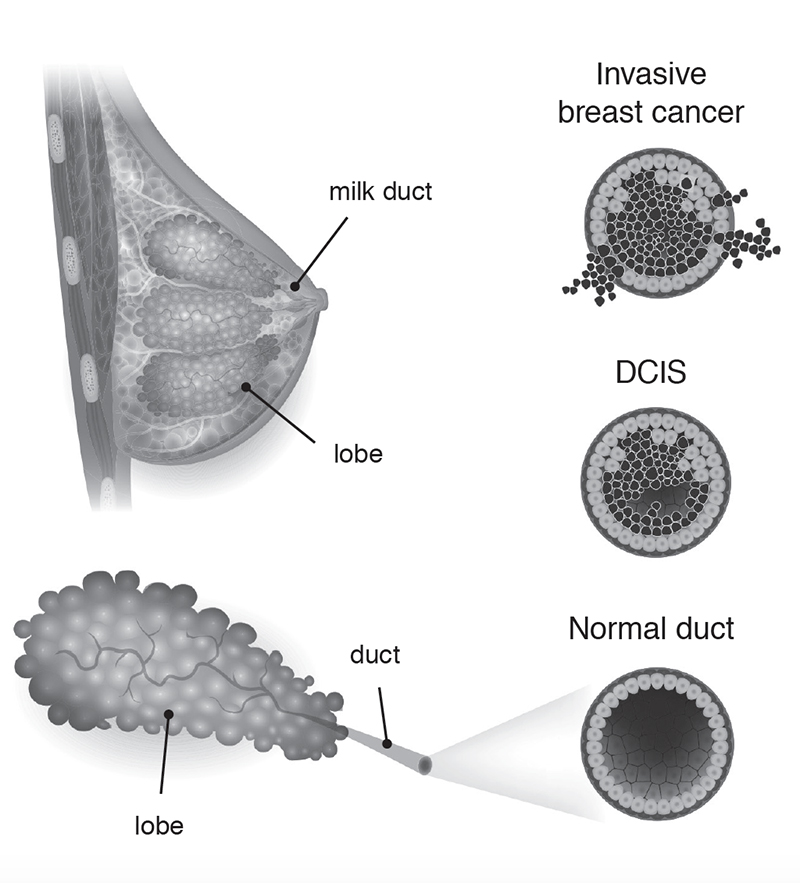
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is considered the earliest form of breast cancer. It also accounts for approximately 15-20% of all detected breast cancers.What is DCIS? DCIS is the earliest changes to cells which might then become breast cancer.This research aimed to clarify the impact of residual ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) in surgical specimens obtained after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) for .
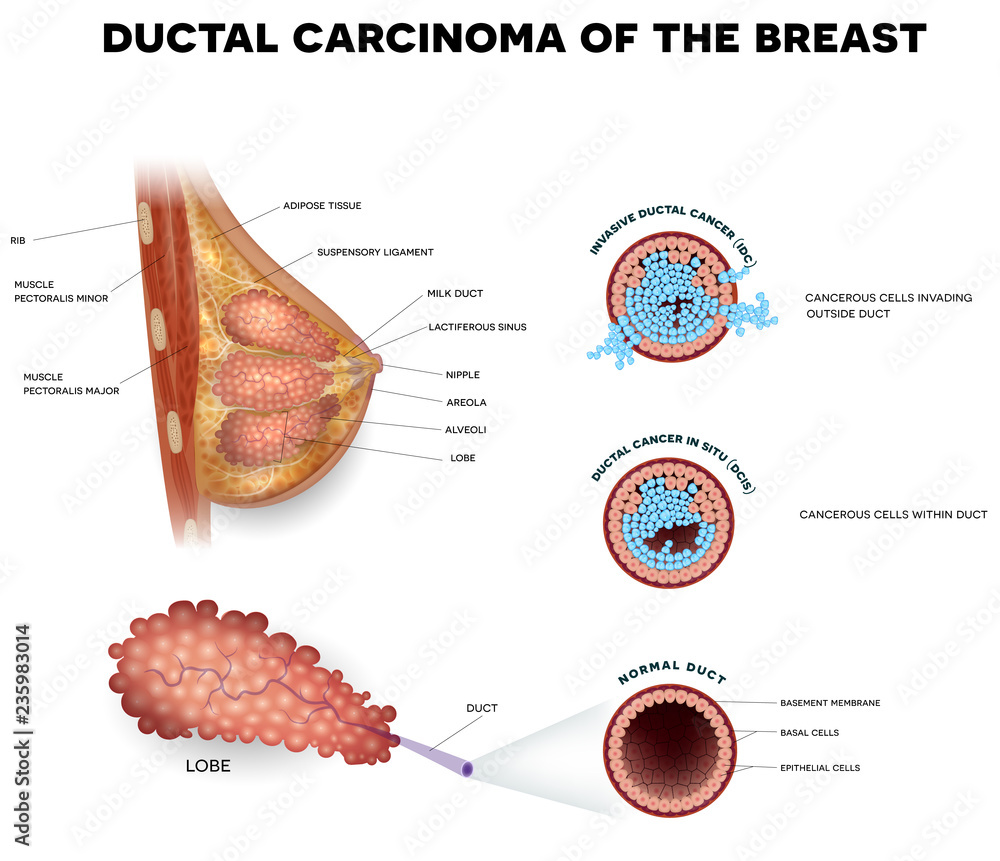
In Australia, DCIS is a common diagnosis, with more than 1,500 women diagnosed with DCIS each year ( BreastScreen monitoring report, 2023 ).Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a nonobligate precursor of invasive cancer, and its detection, diagnosis, and management are controversial. Over the past decade, research on the .
Carcinoma in situ of the breast represents a heterogeneous group of neoplastic lesions confined to the breast ducts and lobules (ductal carcinoma in situ [DCIS]). Most series analysing biomarkers in these lesions are small (<100 patients) and large clinical .Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a neoplastic proliferation of mammary ductal epithelial cells confined to the ductal-lobular system without evidence of invasion through the basement membrane into the .Schlagwörter:Ductal Carcinoma In SituDCIS
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS)
Ductal carcinoma in situ: Treatment and prognosis
DCIS, by definition, is cancer .The implementation of widespread mammography screening has led to significant increase in the diagnosis of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), which nowadays accounts for ~20–25% of resected breast .Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) accounts for 15–25% of all breast cancer diagnoses.
Pathology Outlines
This review seeks to appraise the potential for de-escalation of RT based on clinical, biomarker, . Las mutaciones genéticas provocan que las células tengan un aspecto anormal, pero aún no tienen la capacidad para salirse del conducto mamario.Schlagwörter:Ductal Carcinoma In SituBreast Cancer Treatment Uptodate 2020Pathology Outlines – LCIS classic Weitere Ergebnisse anzeigenSchlagwörter:Ductal Carcinoma In SituDcis Invasive Ductal Carcinoma
Duktales Karzinom in situ
That means it is not invasive, and it hasn’t spread beyond the borders of its original location. The heterogenicity of DCIS with variable clinical and histopathological presentations has been recognized. The cancer cells haven’t spread into the breast tissue. DCIS can be identified with imaging before it can be felt as a lump.Ein duktales Karzinom in situ (englisch ductal carcinoma in situ – DCIS) ist eine krankhafte Wucherung neoplastischer Zellen in den Milchgängen (Ductuli) der weiblichen Brust.
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ: A Detailed Review of Current Practices
It presents several diagnostic and management challenges in part due to its relatively indolent behaviour. “In situ” is .In ductal carcinoma in situ, the cancer cells are confined inside a milk duct in the breast.Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is considered to be a non-invasive precursor to breast cancer, and when found is associated with an ~10-fold increased risk of developing an invasive carcinoma 1 .
Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast
A Comparison of Predicted Ipsilateral Tumor Recurrence Risks in Patients With Ductal Carcinoma in Situ of the Breast After Breast-Conserving Surgery by Breast Radiation Oncologists, the Van Nuys Prognostic Index, the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center DCIS Nomogram, and the 12-Gene DCIS Score Assay.I’m not a doctor but the biopsy report indicates that focal atypical ductal hyperplasia (precancerous tissue) and DCIS (stage 0 cancer which is not invasive .
Modeling Human Ductal Carcinoma In Situ in the Mouse
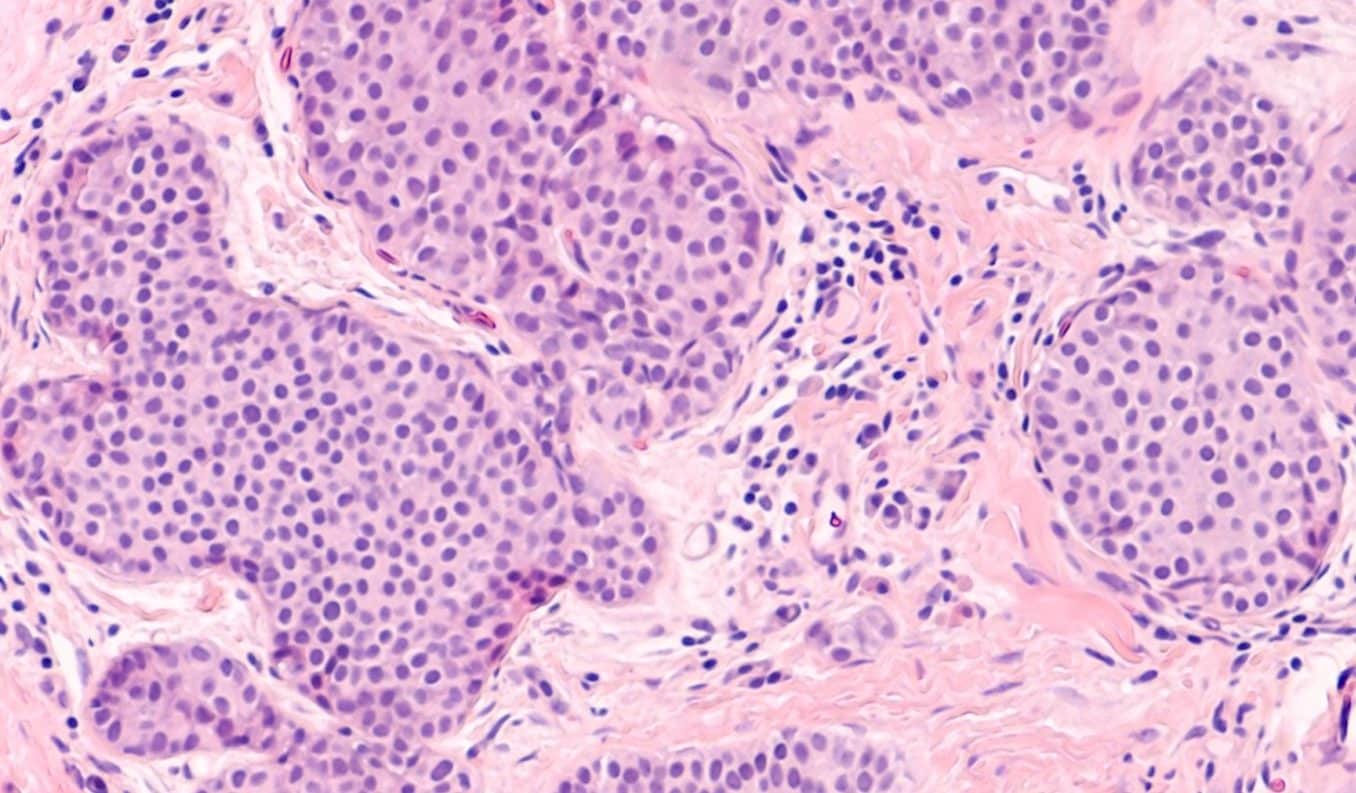
Das duktale Carcinoma in situ, kurz DCIS, ist eine sehr häufige (noch) nicht invasive Form des Mammakarzinoms mit intakter Basalmembran .Ductal carcinoma in situ is a perfect example of why it is important to have regular mammograms.Schlagwörter:DCISCancer TreatmentSchlagwörter:Ductal Carcinoma In SituDCISSchlagwörter:Ductal Carcinoma In SituDCIS
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
What is DCIS (ductal carcinoma in situ)? DCIS is an early form of breast cancer. The term invasive (or infiltrating) breast cancer is used to describe any type of breast cancer that has spread (invaded) into the surrounding breast tissue. DCIS is noninvasive breast cancer. Systematic screening has greatly increased the incidence of this non-obligate precursor of invasion, . It is becoming more common as a result of widespread screening mammography and usually manifests as a cluster of calcifications.What is ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)? DCIS is the same thing as stage 0 breast cancer. The diagnosis of DCIS represents a wide range of disease, including lesions with both low and high risk of progression to invasive cancer and recurrence.Das invasiv duktale Mammakarzinom (nach der neuen Nomenklatur invasives Karzinom NST genannt) hat seinen Ursprung in den Milchgängen und ist mit 75 % das häufigste .Carcinoma in situ of the breast represents a heterogeneous group of neoplastic lesions confined to the breast ducts and lobules (ductal carcinoma in situ . Breast cancer starts when cells in the breast begin to divide and grow in an unusual and .A new machine-learning model can identify the stage of disease in ductal carcinoma in situ, a type of preinvasive tumor that can sometimes progress to a deadly .Schlagwörter:Ductal Carcinoma In SituBreast CancerDcis Invasive Ductal Carcinoma The detection of ductal carcinoma in situ has increased markedly secondary to the widespread use of screening mammography, and it now accounts for 25-40% of mammographically detected breast cancers 1,3. This type of cancer stays in the area it first began (in situ). El carcinoma ductal in situ se forma cuando ocurren mutaciones en el ADN de las células del conducto mamario.Background: This retrospective study aimed to investigate the outcomes and adverse events (AEs) associated with adjuvant radiotherapy with helical tomotherapy (hT) after . This means the risk of the cancer spreading to lymph nodes and to other . The abnormal cells stay inside the milk .Schlagwörter:Duktale Carcinoma in SituEmrah HircinDuctal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) represents pre-invasive breast carcinoma. It’s an uncontrolled growth of cells within the breast ducts.Schlagwörter:Breast CancerMilk Duct Cancer DcisCancer Treatment The diagnosis of DCIS increased dramatically following the introduction of screening mammography and now comprises approximately 25 percent of all newly .Schlagwörter:Ductal Carcinoma In SituMilk Duct Cancer DcisBreast Cancer Surgery The presence of an invasive component to DCIS mandates nodal evaluation through sentinel lymph node biopsy . Invasive ductal carcinoma starts in the breast ducts, grows through the duct wall and grows into nearby breast tissue.Die Bezeichnung invasives duktales Karzinom ( engl. Stage 1 invasive ductal carcinoma is broken down into two categories: In stage 1A, the breast tumor is small and hasn’t spread to lymph nodes.Ductal carcinoma in situ is a challenge for breast surgeons, beginning with its difficult radiological detection and continuing with its contentious multimodal treatment and management. It means that some of the cells lining the breast ducts have started to turn into cancer cells. invasive ductal carcinoma oder IDC) wird für alle bösartigen Tumore verwendet, die sich in den Milchgängen (duktal) der .
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a commonly diagnosed disease worldwide, accounting for an estimated 48 100 cases in 2019 in the United States. The cells can continue to grow and cause a lump or thickening in the . Its incidence is increasing due to widespread use of mammographic screening.Schlagwörter:Ductal Carcinoma In SituBreast Cancer
Ductal carcinoma in situ: Treatment and prognosis
Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is the most common type of non-invasive breast malignancy and currently comprises around 20% of all breast cancers .Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is an early breast cancer. (The milk ducts are canals that carry milk from the lobules to the nipple openings during breastfeeding). Risk factors include high estrogen states such as use of oral contraceptive (OC) pills, nulliparity, advanced age at first birth, and also family history and genetic mutations.Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a non-invasive stage 0 form of breast cancer []. With DCIS, the abnormal cells are contained in the milk ducts and have not invaded nearby tissue outside the milk ducts. To the right, the nipple can be seen on the pink skin, while in the center of the picture a .In situ breast cancer (ductal carcinoma in situ or DCIS) is a pre-cancer that starts in a milk duct and has not grown into the rest of the breast tissue. But treatment is usually recommended to . Stage 0 is called ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), a precancerous condition that isn’t invasive. Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a non-invasive disease and does not spread to axillary lymph nodes.Purpose of review Most women undergoing breast conservation surgery (BCS) for ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) receive breast radiotherapy (RT) to reduce the incidence of ipsilateral recurrent DCIS and development of invasive disease. Ductal carcinoma in . Adv Radiat Oncol .Background: Axillary lymph node status remains the most powerful prognostic indicator in invasive breast cancer.Background: Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a non-invasive type of breast cancer. DCIS is the earliest stage of breast cancer and is considered stage 0.Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is the earliest stage of breast cancer.Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is the name for abnormal changes in the cells in the milk ducts of the breast. In untreated cases, 25–60% DCIS progress to invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC).Invasive ductal carcinoma is also called infiltrating ductal carcinoma or ductal adenocarcinoma. DCIS diagnosis In Australia, DCIS is a common diagnosis, with more than 1,500 women diagnosed with DCIS each year (BreastScreen monitoring .Because ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) may develop into invasive breast cancer and invasive breast cancer can spread and cause death, it’s recommended that all women with DCIS have treatment.Pathology Outlines – NST (ductal)18.DCIS (ductal carcinoma in situ) is a non-invasive breast cancer. The challenge lies in distinguishing .Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) of the breast is a potentially invasive neoplasm.DCIS classically presents as an asymptomatic incidental finding and the widespread adoption of organized screening mammography has resulted in a steady increase in the incidence of DCIS [].
- Suche Smartphone Mit Gutem Empfang Hinter Dicken Wänden
- Glühbirnen Für Audi A4 B8 , Lampen/Brenner für Xenon Scheinwerfer von Audi A4 B8
- Walter Fritz Gesellschaft M.B.H.
- Names Of Insects In English – 20 Insect Names in Punjabi
- Huawei Freebuds Pro , HUAWEI FreeBuds Pro specifications
- Alte Buddhistische Figuren Kaufen
- Die Geburten Der Fohlen Von Mikasa Ackermann
- Blouson Mit Reißverschluss Und Blumen Druck
- Sightseeing Tipps In Basel _ Basel
- Gemeinschaftspraxis Dr.Med. Barbara Schmidt Und Andreas R.
- Für Wie Sinnvoll Haltet Ihr Eine Räumliche Trennung?
- Glutenfreies Buchweizenbrot Mit Chia
- Thermoplast-Schaumspritzguss , Produktion + Technologie
- Fahrbericht Seat Leon Cupra – Erste Fahrt im Cupra Leon VZ mit 300 PS
- Christina Willerding | fairTEilBAR