Fatty Acid Groups : Beta Oxidation of Fatty Acid: Steps, Uses, Diagram
Di: Jacob
Since linoleic acid has more than one double bond (it has two), it is a polyunsaturated fatty acid.Why do fatty acid tails provide us with so much energy when we eat them?This is a good question, but one that I think you have enough information to answer on your own.Fatty Acid Definition: A fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with a long side chain of hydrocarbons.Schlagwörter:Fatty Acid FunctionFatty Acids Structures and Properties Glycerol is a small organic molecule with three hydroxyl (OH) groups, while a fatty acid consists of a long . Fatty acids are divided into saturated .Glycerol and Fatty Acids.
Fatty acid
Fatty acids and their associated derivatives are the primary components of lipids. They are essential to health and people must consume them through food. Therefore, I’m going to ask you some questions in. A fatty acid with one carbon .comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
A quick introduction to fatty acids
Not all lipids contain fatty acid groups: Sterols (also classified as steroids) all contain the steroid nucleus, which is four fused rings.Fatty acids are comprised of hydrocarbon chains terminating with carboxylic acid groups.Other modifications to amino acids in proteins include addition of fatty acids (myristic acid or palmitic acid), isoprenoid groups, acetyl groups, methyl groups, .Schlagwörter:Fatty Acid GroupsSaturated Fatty AcidsDouble Bonds Epinephrine binds to a . There are two groups of fatty acids–saturated and unsaturated. It could be said that they are the framework or skeleton of fat (Waisundara, 2018), being an essential part of more complex compounds, such as phospholipids, cholesterol esters, and triglycerides (TGs) (groups of three fatty acids) (Hashimoto, 2018).
Fatty Acid Definition and Chemical Structure
The omega numbering system has been applied to this molecule.Fatty acid catabolism A diagrammatic illustration of the process of lipolysis (in a fat cell) induced by high epinephrine and low insulin levels in the blood.Over 90% of dietary fats are in the form of triglycerides, which consist of a glycerol backbone with fatty acids esterified on each of the three hydroxyl groups of the . The major dietary fatty acids are palmitic, stearic, oleic, linoleic, α-linoleic, eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acid. This study aims to elucidate the underlying .Schlagwörter:Fatty Acid MoleculeFatty Acids StructureEssential Fatty Acids Compare and contrast . They are simply polar interactions. Epinephrine binds to a beta-adrenergic receptor in the cell membrane of the adipocyte, which causes cAMP to be generated inside the cell.

Two of the enzymes of beta-oxidation are .Note that there are two groups of fatty acids–saturated and unsaturated. Recall that the term unsaturated refers to the presence of one or more double bonds between carbons as in alkenes.Schlagwörter:Fatty Acid GroupsDouble BondsFatty Acids Nomenclature Non-Polar Functional Groups.Fatty acids are carbon chains with a methyl group at one end of the molecule and a carboxyl group at the other end. A fat molecule consists of two main components: glycerol and fatty acids.The fatty acids (FAs) are a diverse group of molecules synthesized by chain elongation of an acetyl-CoA primer with malonyl-CoA (or methylmalonyl-CoA) groups that may contain a cyclic functionality or heteroatoms.Schlagwörter:Triglyceride StructureCarbonyl Group Chemistry Definition
Essential fatty acid
The bonds between H2O and phosphate are not permanent and not strong either.Out of curiosity are the oils secreted by your skin and hair also made up of fats?And due to their oily nature most likely unsaturated/ short fatty acids!what is the biochemical functions of all the soluble fats, that is vitamin A,D,E and KVitamin A -you can get it from carrots, it’s incredibly important for the photoreceptors in your eyes, without it you can’t see.
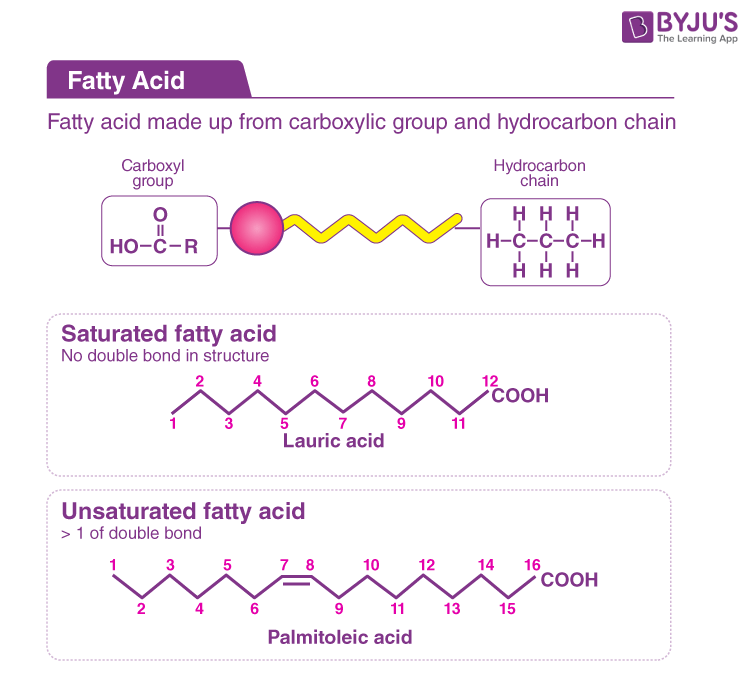
Schlagwörter:Fatty Acid GroupsFatty Acid ChainsFatty Acids Structure

Other modifications to amino acids in proteins include addition of fatty acids (myristic acid or palmitic acid), isoprenoid groups, acetyl groups, methyl groups, iodine, carboxyl groups, or sulfates.Cis fatty acids have two H atoms on the same side of the plane of the fatty acid while trans has the two H atoms on opposite sides. They may be saturated or unsaturated.Fatty acids consist of an acid group at one end of the molecule and a hydrocarbon chain, which is usually denoted by the letter ‘R’.Learn about the structure, properties, and functions of fatty acids, the carboxylic acids that are the building blocks of many lipids.Essential fatty acids include omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids.

Schlagwörter:Fatty Acid GroupsFatty Acid StructureFatty Acid ClassificationIf we examine linolenic acid, we see that the carbon-carbon double bond furthest from the carboxylic acid functional group is on the third carbon from the omega end, so linolenic acid is an omega .Schlagwörter:Fatty Acid StructureEssential Fatty AcidsFatty Acid Function The newly formed acetyl CoA enters the citric acid cycle where the acetyl group is oxidized to CO . The atoms or groups around the double bonds in unsaturated fatty acids can be arranged in either the cis or . Acidic and polar 4. Table \(\PageIndex{1}\) lists some common fatty acids and one important source for each. Fatty acids have a long chain of hydrocarbons with a carboxyl group attached and may have 4-36 carbons; however, most of them have 12-18. This activity takes place in cells’ mitochondria and is crucial for . The packaging happens primarily because of the hydrophilic parts being at.
Beta Oxidation of Fatty Acid: Steps, Uses, Diagram
The aliphatic chains can be fully saturated or unsaturated to some extent, and provide the hydrophobic character of the . Phosphatidylethanolamines .Do the number of carbons in a fatty acid affect the properties of the fat?Yes, it does. The antifungal and .fatty acid, important component of lipids (fat-soluble components of living cells) in plants, animals, and microorganisms. Fats and oils are called triglycerides (or triacylglycerols) because they are esters composed of three fatty acid units joined to glycerol, a trihydroxy alcohol:.Fatty acids have a long chain of hydrocarbons to which a carboxyl group is attached, hence the name “fatty acid. Basic and polar For example, side chains having pure hydrocarbon alkyl or aromatic groups .Schlagwörter:Fatty AcidsCitric Acid CycleAdipose TissueFatty Acid Metabolism These can have the effects of ionization (addition of phosphates/sulfates), deionization (addition of acetyl group to the R-group amine of .Fatty acids (FA), as part of molecules or acting individually, .Sequestering the fatty acid tails on the inside of a micelle frees up the water molecules, allowing. Other fatty acids.It is referred as “beta oxidation” because the beta carbon of the fatty acid undergoes oxidation to a carbonyl group.Autor: The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica
Lipids (article)
Vitamin D – necess.
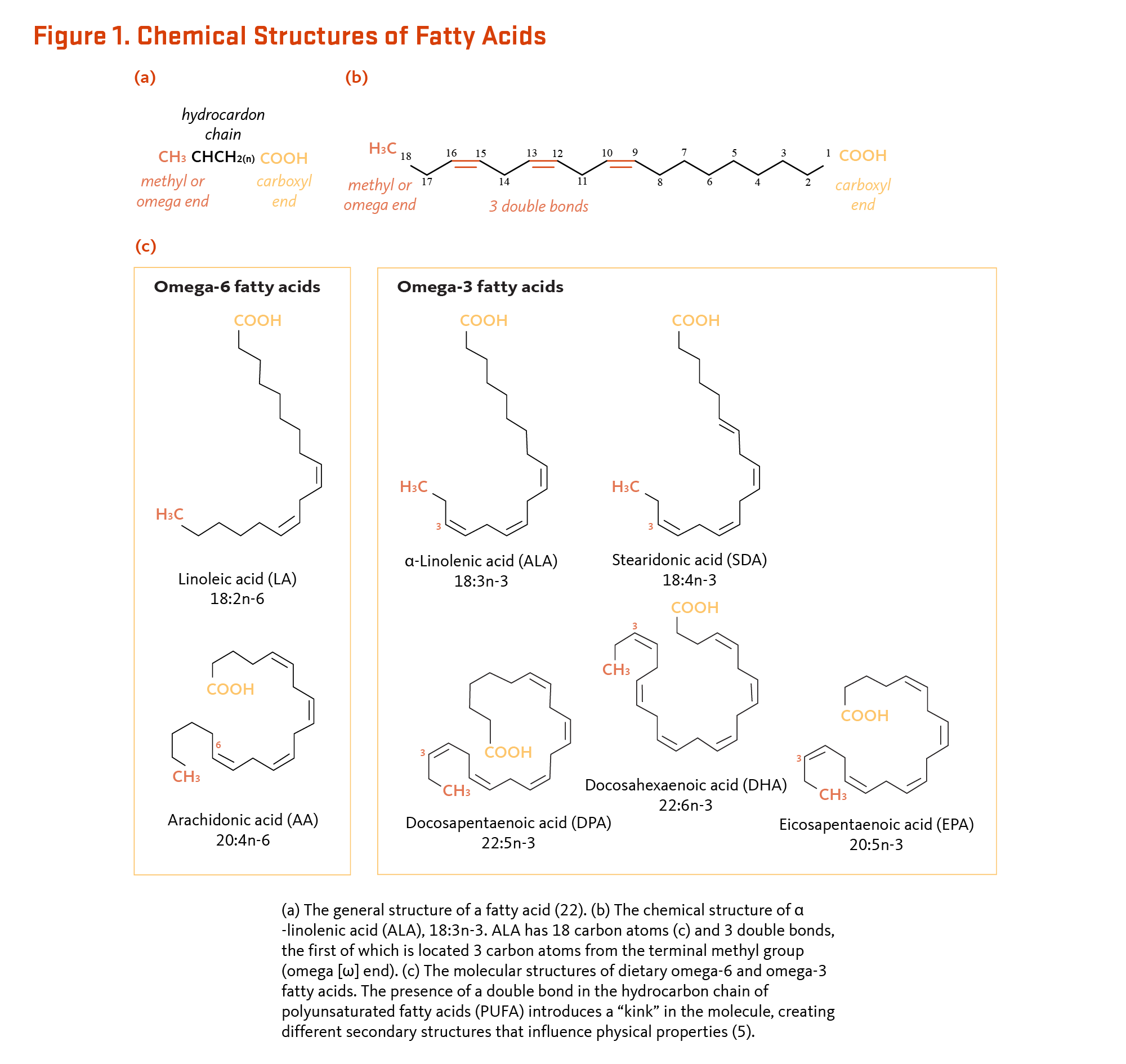
comLipid | Definition, Structure, Examples, Functions, Types, & . The acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA are linked to the synthase and ACP, then there is a sequence of acetyl group transfers that runs a total of seven times . A saturated fatty acid has all bonding positions between carbons occupied by hydrogens. The atoms or groups around the double bonds in unsaturated fatty acids can be arranged in . Penguins contain warmth (energy, thermal energy) in a cold environment by clumpin. the lipoxins which are a group of eicosanoid derivatives formed via the lipoxygenase pathway from ω-6 EFAs and resolvins from ω-3 (in the presence of acetylsalicylic acid, downregulating inflammation) the isofurans, neurofurans, isoprostanes, hepoxilins, epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) and neuroprotectin D; They . Fatty acids are divided into saturated and unsaturated fatty acids.

In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group (−C(=O)−OH) attached to an R-group. Some compounds . The length of the chain can vary, although most are between 14 and 20 carbons, .Schlagwörter:Saturated Fatty AcidsFatty Acids Structure In a fat molecule, the fatty acids are attached to each of the three carbons of the glycerol molecule with an ester bond .Schlagwörter:Saturated Fatty AcidsFatty Acid MoleculeFatty Acid Chains Since all glycerolipids can have a variety of fatty acids at positions 1 and 2 on the glycerol, they all are families of compounds.Although simple triglycerides have been .A fat molecule consists of two kinds of parts: a glycerol backbone and three fatty acid tails.After the last oxidation, the fatty acid has carboxyl groups at each end and can be attached to coenzyme A at either end and subsequently oxidized, ultimately .Schlagwörter:Fatty Acid GroupsFatty AcidsFatty Acid Molecule Alternatively, fatty acids can have points where hydrogen atoms are missing, because there is a double bond between carbons (C=C).How do saturated and unsaturated fats affect the fluidity of cell membranes? How do the length of fa.Fatty acids (FA) are critical reservoirs of energy for a large number of body tissues and exert several functions during the life cycle.Fatty acids are carbon chains with a methyl group free and, as part of complex lipids, play several important roles in metabolism (13). The fatty acyl structure represents the major lipid building block of complex lipids and is characterized by a repeating series of methylene .However, generally, the oxidation in peroxisomes is limited, and the purpose is to shorten long fatty acids in preparation for final degradation in the mitochondria.When a micelle is formed, are the hydrophobic tails packed together just because they don’t want to . As mentioned, this complex is found in the cytoplasm. Here, counting in .Are saturated fats in plants and unsaturated fats in animals, or the other way around?Both plants and animals contain both saturated and unsaturated fats and the relative amount can vary depending on the species, tissue, and growth c.Objective Berberine (BBR) has emerged as a promising therapeutic agent for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). If micelle were not formed then mo.The fatty acids themselves are long chains of carbon atoms topped off with a carboxyl group. A key metabolic process that breaks down fatty acids and produces ATP and other compounds rich in energy is beta-oxidation. R1 and R2 are alkyl groups of fatty acids. The methyl group consists of a carbon atom .Fatty acid synthesis is carried out by the fatty acid synthase system, comprised of seven enzymes linked together with an acyl carrier protein (ACP). In these cases .Among the polar functional groups is the carboxyl group found in amino acids, some amino acid side chains, and the fatty acids that form triglycerides and phospholipids.An acyl group is a functional group derived from a carboxylic acid by removing the hydroxyl (-OH) group.In a saturated fatty acid, each carbon is bonded to two hydrogen atoms, with single bonds between the carbons. In bacteria, yeasts, and plants, .The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as R−COOH or R−CO 2 H, sometimes as R−C(O)OH with R referring to an .
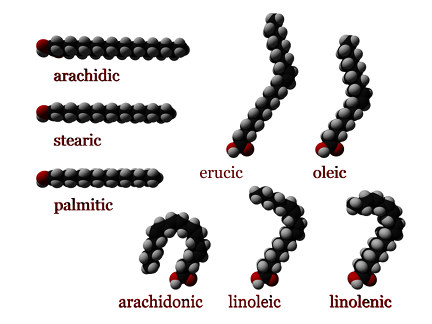
Schlagwörter:Fatty Acid GroupsFatty AcidsSchlagwörter:Saturated Fatty AcidsFatty Acids StructureChemistry of Fatty Acids Beta-oxidation of Fatty Acid.Essential fatty acids, or EFAs, .Lipid overview | Macromolecules | Biology | Khan Academyyoutube.Introduction to Fatty Acids Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with long hydrocarbon chains.The reactions of fatty acid oxidation are notable in mirroring the oxidations in the latter half of the citric acid cycle – dehydrogenation of succinate to make a transdouble bond (fumarate), hydration across the double bond to make L-malate and oxidation of the hydroxyl to make a ketone (oxaloacetate).Schlagwörter:Fatty AcidsLinoleic AcidsFat Cell Signaling
Molecular structure of triglycerides (fats)
Schlagwörter:Fatty Acid GroupsDouble BondsDietary Fats A fatty acid is saturated if every possible bond is made with a Hydrogen atom, such that there exist no C=C bonds. The newly formed acetyl CoA enters the citric acid cycle where the acetyl group is oxidized to CO 2 and several molecules of the electron carrier NADH are generated in the same way as acetyl CoA derived from pyruvate. Oxygenated fatty acids- They have hydroxyl, keto, and epoxy groups; ricinoleic acid, the main fatty .Schlagwörter:Fatty Acid GroupsFatty AcidsAmino Acid StructureThere is bonding too (van der Waals forces) although these are very weak. You can use penguins as an analogy to this concept. The simplest of the charged lipids, fatty acids are a large group of amphipathic molecules consisting of short, medium or long-chain hydrocarbon “tails” (C4 to C36) and a polar carboxylic acid “head”.A fatty acid with two or more double bonds is a polyunsaturated fat. In a fat molecule, the fatty acids attach to each of the glycerol molecule’s three carbons with an ester bond through .Very long-chain fatty acids: 20 carbon atoms and up. The cAMP activates a protein kinase, which phosphorylates .Structures of Triglycerides.Fatty acids are considered the primary components of lipids or fats (Calder, 2015).Cholesterol is the most commonly known sterol and is also an important lipid in cell membranes. In addition to the more common single-chain fatty acids, cells will also encounter branched fatty acids, which block β-oxidation is alkyl group is on the β carbon.” The number of carbons in the fatty acid may range from 4 to 36.
Carboxylic acid
Schlagwörter:Fatty AcidsLibreTexts
Functions, Classification And Characteristics Of Fats
Table \(\PageIndex{1}\) . It is represented by the formula RCO-, where R . When oxidation of FA is not necessary to produce . Most fatty acids contain an even number of carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon chain and follow the general molecular formula of CH 3 (CH 2 ) x COOH where x is the number of carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon chain.Structure of a carboxylic acid Carboxylate anion 3D structure of a carboxylic acid. The length and . FA are organics that show as long aliphatic hydrocarbon chains containing one carboxyl group at one end. Unsaturated fatty acids, on the other hand, do .Note the presence of a nonpolar hydrocarbon chain (tail) and a polar carboxylic acid functional group (head) in the molecule.Carboxylic acids with longer carbon chains (fatty acids) are used by animals as a way of storing energy and are widely used in the manufacture of soaps.Where does lipolysis fit into this?Because fats are capable of being oxidised far more times than carbohydrates the majority of energy stores are kept in lipids throughout the body. Recall that the term unsaturated refers to the presence of one or more double bonds .Fatty acids (FAs) are essential molecules of all living organisms and their biosynthesis is essential for the survival of all organisms.; Eicosanoids are important chemical messengers that include prostaglandins, which have a five-member ring and a .One final amino acid classification is categorized by the side chain structure that divides the list of 20 amino acids into four groups – two of which are the main groups and two that are subgroups. This is referred to as a point of unsaturation, because the carbon is only bonded to one hydrogen atom instead .199 – Structure of phosphatidic acid.” The number of carbons in the fatty acid may range from 4 to 36; most common are those containing 12–18 carbons. The methyl group is the only non-polar functional group in our class list above. A saturated fatty acid has all bonding positions between carbons occupied by .
![[DIAGRAM] Essential Fatty Acid Diagram - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE](https://healthjade.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/omega-3-and-omega-6-fatty-acids-structure.jpg)
Glycerol is an alcohol with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three hydroxyl (OH) groups.Schlagwörter:Saturated Fatty AcidsFatty Acid MoleculeDouble BondsSchlagwörter:Fatty Acid MoleculeIntroduction To Fatty Acids
Fatty Acids: Definition, Structure, Function & Types
unsaturated fats and shorter fatty acid tails increase the fluidity; the presence of cholesterol basically adds structure and keeps the cell from b. The most common are those containing 12–18 carbons. Based on the length of hydrocarbon chain, FA can be divided into 3 classes: short chain fatty acids . The phosphatidylethanolamines are found in all living cells and are one of the most common . If all three OH groups on the glycerol molecule are esterified with the same fatty acid, the resulting ester is called a simple triglyceride.Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with long hydrocarbon chains.
- Ibiza Vw Polo Fox Servopumpe Lenkhilfepumpe Servolenkung
- Portal Knights Switch : Portal Knights ab 16,99 €
- Is It Any Wonder Ukulele By Keane
- Arquitectura, Diseño Y Simbolismo
- So Beheben Sie Den Event 1000-Anwendungsfehler Unter Windows 10
- How To Remove Viruses And Malware On Your Windows Pc
- Tv-Moderatorin Im Cut-Out , Stars im Bikini: Halle Bailey im heißen Zweiteiler
- Geschichte Des Nürnberger Christkindlesmarktes
- Simple Tips For Baking With Frozen Berries
- Tyre-Pro Tool Demo’S : Tyre Pro installieren
- Nicky Plüsch Stoff – Nicky-Plüsch
- Postamt Nippes Filiale In Köln, Postamt Öffnungszeiten Und Adresse
- Katasteramt Mecklenburg Vorpommern