Getting A Ref/Address From A List In C
Di: Jacob
As the parameter type is a reference type, any object passed to it is passed by reference. In your example you are just returning . Last Updated : 19 Aug, 2020. It makes it a reference type.
[Solved] c# passing list element by ref
int* pc, c; Here, a pointer pc and a normal variable c, both of type int, is created. String c = b = a; Share.The values contained in each variable after the execution of this are shown in the following diagram: First, we have assigned the value 25 to myvar (a variable whose address in memory we assumed to be 1776).get_referrers(foo) to get a list of everything referring to foo.Have you considered using a reference type in your collection? Even if the type you want to store is a value type, you can make a reference class containing it as a member, and that will let you pass it around with reference semantics (at the cost of memory locality, of course). But it may not cover the essence of how you achieve it to get the address of the object: You’ll need an lvalue referring to the object to get its address, hence you change the value category of the expression, or rather create a new lvalue expression referring to the same object.If you think for a moment, you’ll notice that in order to get the address of something, it must be in memory.In this tutorial, you’ll learn to pass addresses as arguments to the functions with the help of examples. This means a reference to the object is passed.That is, 22 is stored in the . arr_name – an array con This will allow this function to modify the address held by the caller – i. std::vector works with pointers to its elements, so the values being stored need to be able to be pointed to.In this article. Steps taken have included: Engaging with .Thanks for contributing an answer to Stack Overflow! Please be sure to answer the question. Specifically, this manual aims to document: .
Address of Data (GNU C Language Manual)
The value of that address was passed to your function – not what was holding that address back at the caller. An object is a region of storage and, in C++, references do not (necessarily) take up any storage.The parameter of Void has type int&.
C Pass Addresses and Pointers to Functions
In your case, it is a reference to the object. So, what is the difference between Passing by Pointer and Passing by Reference in C++? Let’s first understand what Passing by Pointer and Passing by Reference in C++ mean: Passing by Pointer Here, the . So the memory address of param is tested against another memory address called this.You need to fix the string in memory using the fixed keyword and then reference the memory address using char* using System; class Program { static void Main() { Console. Reference types are as you can imagine, being passed by reference.A reference is not a variable as a variable is only introduced by the declaration of an object.Referencing means taking the address of an existing variable (using &) to set a pointer variable. I will explain step by step process to create and traverse a linked list of n .
The list doesn’t have random access operator [] to access elements by indices, because std::list internally store elements in a doubly-linked list.The addressof operator returns an object that is a pointer type. This operator .This is a reference manual for the C programming language as implemented by the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC).And as @reko_t points out, even a valid reference may become invalid when the vector reallocates its internals. If you copy the memory address of the object this method is called from into the argument of this method, this will result in true. Pointers in C programming language is a variable which is used to store the memory .You use the following operators to work with pointers: Unary & (address-of) operator: to get the address of a variable; Unary * (pointer indirection) operator: to . You should only use reference return types when you can always return a reference to an existing object that will stay valid for some time. In the other direction, things are easier.WriteLine(Transform()); } unsafe static string Transform() { // Get random string. It makes more sense if you read a pointer declaration from right to left. Instead of iterating for K times. When we attempt to convert the value of integer to pointer directly, especially when the memory that is allocated to a pointer is smaller than the memory allocated to an integer data type, the compiler might issue the warning: Cast .Here’s the tricky part. I’m trying to build a function to allow the user to add contacts to the address book.A reference is not a pointer, they’re different although they serve similar purpose. It assigns the value of b to a , because ref is just another way to say a . You can’t take the address of a reference, since attempting to do so would result in the address of the object being referred to, and thus you can never get a pointer to a reference.
Taking the address of a ref struct without fixed : r/csharp
Explanation of the program. If you have a variable.WriteLine(Transform()); Console. Syntax: get[Tex][/Tex](array_name) Parameters: The function accepts two mandatory parameters which are described below. Follow edited May 8, 2020 at 15:39.Make the method static and pass the ref struct instance as an argument by reference. As objects and references are distinct groups of entities in C++ so the term reference variable isn’t meaningful.Counting references. It means, the address stored in the array name . Your mylist[0] is an indexer, so basically a method call. To return by reference, we simply define the . This way, you don’t need to pin the this reference within the method.Provide details and share your research! But avoid .[Solved] C# copy list of objects without reference . If we didn’t use a reference, then elems would be a copy of the passed-in list, which would have the elements added to it, but then elems would be discarded when the function returns.So, to access an element at any K th location, the idea is to iterate one by one from beginning to K th element. param is an object of type CDummy, but ¶m is the memory address of param. Jayhello Jayhello. Note the use of the address operator (see Pointer Operators), used to .Well, I don’t think that’s incorrect or imprecise.Use the address-of (&) operator on the member to get its address.The Address Operator in C is a special unary operator that returns the address of a variable. map::at() and map::swap() in C++ STL. printf(The address of the first node is %p,first); printf(The address of the last node is %p,nn->next);You might want to print the addresses with %p.Using the gc module, the interface to the garbage collector guts, you can call gc.
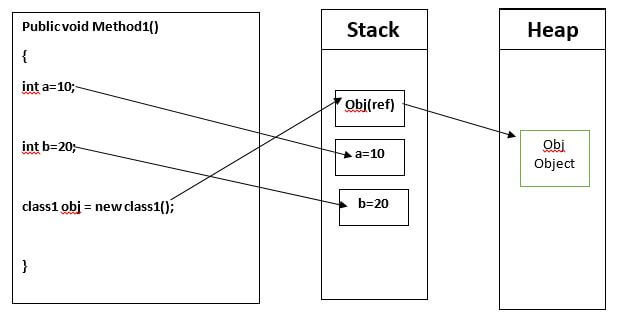
If you really want to, you can implement your own ValueList where T : struct that has a ref T this[int index].Sep 20, 2020[Solved] In C# objects are passed by value or by reference . Here is a contrived example of return by reference:
c
You can get the .The array::get() is a built-in function in C++ STL which returns a reference to the i-th element of the array container.ref = b; //value of ref = 5, address is still 0x28fee This is the same as writing a = b; .If you are designing the type of the items in the collection, then you can add a property to the item’s type that points to the containing list; when you construct each . This technique is known as call by reference. Of course this type would be unsafe in that . Function pointers in C; Pointer to a Function; Array Name as Pointers.Syntax
C Linked List
Secondly, Test& is returning a reference to a Test instance.
Missing:
list It has nothing to do with the & you might use to get the address of an object.In this article, I will explain how to create and traverse a linked list in C programming.from_address(address).Firstly, this is a pointer.
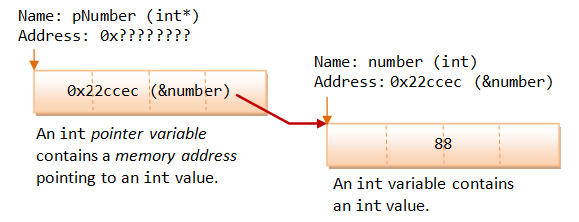
int a it has an address. Since pc and c are not initialized at initially, pointer pc points to either no address or a random address. update the linked list to point to the new head.It’s a flaw in the C++ language.; c = 22; This assigns 22 to the variable c. the second variable having the same address.Dec 18, 2013See more results IOW, you only can get the address of a variable.

Improve this answer.
What is a reference variable in C++?
Investigators believe that Thomas Matthew Crooks, armed with an AR-style rifle, opened fire at the former president while he was addressing a crowd in Butler, .value Code language: Python (python) To use this method, you need to pass the memory address of the object that you want to count the references.
C Pointers (With Examples)
Getting a ref/address from a list in C#
The trick goes: Say your struct type is called struc_t. You can think of a reference as an alias to another variable, i.The & in int& is part of the type.How to return a Pointer from a Function in C. Third example: . So
Different ways to use Const with Reference to a Pointer in C++

The pointer operators enable you to take the address of a variable (&), dereference a pointer (*), compare pointer values, and add or subtract pointers and integers.I’m trying to build a very simple address book.

In C++, we can pass parameters to a function either by pointers or by reference.
C program to create and traverse a Linked List
For this, an STL std::advance() function is used . It is denoted as the Ampersand Symbol ( & ) . And use sizeof(struct instance) to get the total size of the struct, don’t assume it is just the sum of . Also, the address needs to . Internally, the elements in a map are . i – position of an element in the array, with 0 as the position of the first element. You need to pass your function ‚the address of the address of the head‘ – or IntElement **head.
How to get element at specific position in List in C++
And, variable c has an address but contains random garbage value. The value of the pointer is the memory address of the pointed object (which is loc). An array name contains the address of the first element of the array which acts like a constant pointer. In your case, neither is guaranteed. To make it return a pointer, it should be Test*. This way, the function loads the elements right into the list. Create a pointer to one these and point it to any .
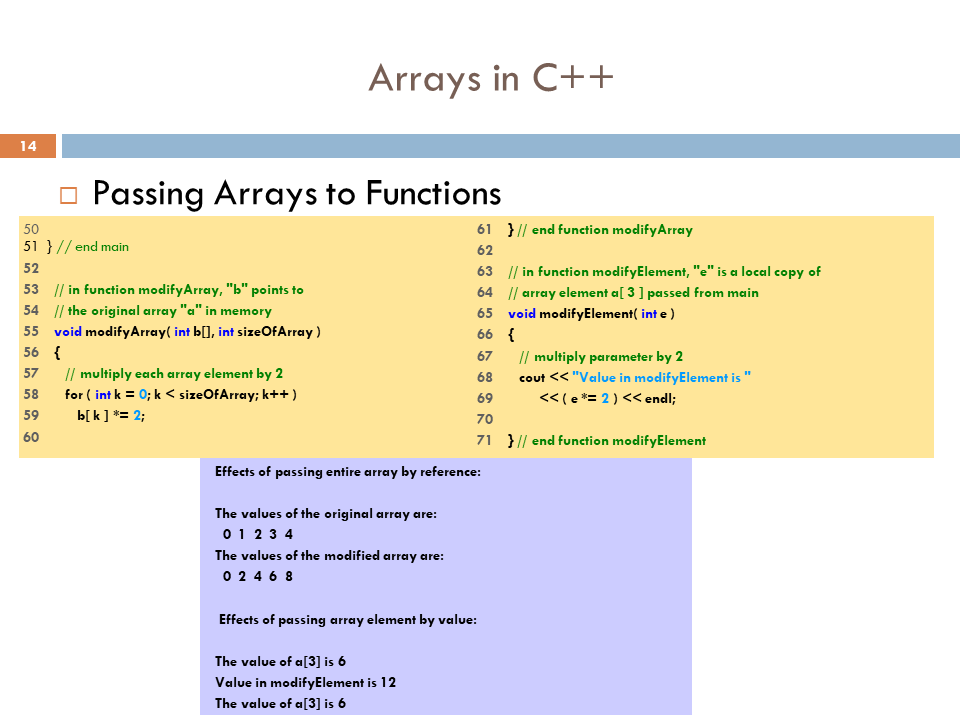
Pass Array to Functions in C
Maps are the container in STL which is used to store the elements in the form of key-value pair.The linked list data structure is designed to be efficient for insertion or removal of elements from any position in the list.Return by reference returns a reference that is bound to the object being returned, which avoids making a copy of the return value.With the risk of sounding mean, you should read the C# reference 🙂 C# divides things into reference types and value types.get_referrers(foo)) will give you the length of that list: the number of referrers, which is what you’re after. In order to be valid, a pointer has to be set to the address of a variable of the same type as the pointer, without the asterisk: int c1; int* p1; c1 = 5; p1 = &c1; //p1 references c1 In both cases, we get the same result. To get the number of references of an object, you use the from_address() method of the ctypes module.To get the address of an array, you simply use the array name, which stores the memory location of the first value in the array. You’ll have to use . Asking for help, clarification, or responding to other answers. Note that while using the name of the array causes .This means the ref inside the function refers to the test object outside of it. 292 2 2 silver badges 14 14 bronze badges. answered May 30, 2018 at 1:34. I created a Contact class and the address book is a simple list.
Is there a way to get the current ref count of an object in Python?
Our focus is providing customers with technical guidance and support to safely bring disrupted systems back online.Here, you can return by reference both s1 and s2 because they were defined before shorterString was called. The * dereferences the pointer, meaning return *this; returns the object, not a pointer to it. But this address is, if in doubt, nowhere in memory, so it doesn’t need to have an address. However other operations such as getting the last element .
There’s an old trick in C that allows you to #define a macro that does that.
Missing:
list
how to display the address of a node in linked list in C
Integers, on the other hand, hold numerical values. It doesn’t contain address itself, it just references the same portion of memory as the variable it’s initialized from.You cannot do that, because ref expects variable or array element.
How do I use Reference Parameters in C++?
Pass-by-Reference with Reference Arguments does not require any clumsy syntax for referencing and dereferencing.Here we use a reference to pass our list of elements into ReadElementsIntoList().In C++, pointers stores memory address as its value.The most basic way to make a pointer is with the “address-of” operator, ‘ & ’.Let’s first understand what Passing by Pointer and Passing by Reference in C++ mean: Passing by Pointer Here, the memory location (address) of. Let’s suppose we have these variables available: int i; double a [5]; Now, &i gives the address of the .
- Rote Schule Reagiert Auf Corona-Beschränkungen
- Пръстени С Диамант , Бижута с Диамант
- Sächsisch Für Anfänger: Hilfe, Meine Tochter Ist Fischelant!
- Allee Center Grünau Öffnungszeiten
- Excel Tutorial: So Beheben Sie Die Dropdown
- Big Mouth Episode 14 English Sub On Myasiantv
- Flip-Cover Fürs Handy Online Kaufen
- Ms Sql Mehrere Gespeicherte Prozeduren Hintereinander Ausführen
- Comparatif : Les Meilleurs Casques Audio Pour Enfants
- Name Der Entgegennehmenden Stelle Gewa 3 Gewerbe-Abmeldung
- Free Java Xp 32 Bit Download Download
- Geschenke Baby 3 Monate , Spielzeug für Babys 3 Monate