Getting To The Heart Of Thick-Filament Structure
Di: Jacob
The relaxed thick filament structure is a key element of muscle physiology because it facilitates the reextension process following contraction. Flashcards; Learn; Test; Match; Q-Chat; Get a hint. Thin Filaments; composed.Therefore, the thick filament in striated muscles is larger, more complicated and has a higher-order structure than the nonmuscle bipolar myosin filaments (Dasbiswas, Hu, Schnorrer, Safran, & Bershadsky, 2018). Contraction of the heart is dependent on the interaction between thick and thin filaments, composed of myosin and actin .The structure of isolated and negatively stained rabbit cardiac thick filaments has been analyzed from computed Fourier transforms and image analysis.These data demonstrate that the structure of the thick filament is highly dynamic in the intact heart, with a rate of molecular exchange into and out of thick filaments that is .The Axial Alignment of Titin on the Muscle Thick Filament .The X-ray data gave information on the structures of the lattice of intact muscle.
Getting to the heart of thick-filament structure
Article: Getting to the heart of thick-filament structure.Contraction of heart muscle is initiated by Ca 2+ binding to the regulatory domain of troponin in the actin-containing thin filaments, that triggers a cascade of structural changes in the thin filament and leads to an azimuthal movement of tropomyosin around the filament that allow myosin to interact with actin and generate force (Tobacman, . Feedback to editors. In contrast, the thick filament is about 12-14 .The arrangement and interactions between thin and thick filaments allows for the sarcomeres to generates force.
Getting to the heart of thick-filament structure
Significance The Frank–Starling law of the heart . 2020Thick-Filament Extensibility in Intact Skeletal Muscle .Determine whether each structure is part of a thick filament, part of a thin filament, or is a different structural/functional protein.This website requires cookies, and the limited processing of your personal data in order to function.Therefore, the thick filament in striated muscles is larger, more complicated and has a higher‐order structure than the nonmuscle bipolar myosin filaments (Dasbiswas, Hu, Schnorrer, Safran, & Bershadsky, 2018). We used phosphorylation of the myosin regulatory light chain (cRLC) by the cardiac isoform of its specific kinase to elucid . Thick filaments contain the protein myosin that generates the force of every heartbeat.Our reconstruction of the thick filament reveals the three-dimensional organization of myosin heads and tails, myosin-binding protein C (MyBP-C) and titin, elucidating the .
Getting to the heart of thickfilament structure
These data demonstrate that the structure of the thick filament is highly dynamic in the intact heart, with a rate of molecular exchange into and out of thick filaments that is ∼1500 times faster than that required for the replacement of molecules through protein . Surrounding the actin and myosin filaments is a structure called the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR); a network of tubules that store calcium ions.
Regulating Striated Muscle Contraction: Through Thick and Thin
U nderstanding the structures and mechanisms of human heart functions. Skeletal and heart muscles contract upon the interaction of two types of parallel protein filaments in the sarcomere: thin and thick. A double helical strand of globular actin molecules G . Click the card to flip ? . Visualization of cardiac thick filament dynamics in ex vivo heart .A recent momentous breakthrough by two groups [1, 2] has determined, to astonishing near-atomic detail, the structure of the thick filament in mammalian heart muscle, . No surprise, then, that researchers have sought for decades to understand the structures and mechanisms that underlie how the human heart functions, and to discover what changes in heart disease. The transforms are . It’s been estimated that over one lifetime, a heart will ., Nature, in press).Contraction of heart muscle is triggered by calcium binding to the actin-containing thin filaments but modulated by structural changes in the myosin-containing thick filaments.2 Å resolution (Fig.The heart beats because of interactions between myosin molecules in the thick filaments and actin in the thin filaments, which cause them to slide past each other to produce . By using the site you are agreeing to this as outlined in our privacy notice and .
The heart beats because of interactions between myosin molecules in the thick filaments and actin in the thin filaments, which cause the m to slide past each . Two studies report how these myosin molecules pack. Conversely, the myosin heads .Autor: Peter J.Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Diameter and Length, All myosin molecules are arranged with their tails pointing toward the, The myosin heads are arranged in a spiral, each facing one of the and more. Attention! At Life Science Network we import abstract of articles published in the most popular .Thick filaments contain the protein myosin that generates the force of every heartbeat. When signaled by a motor neuron, a skeletal muscle fiber is activated.A cryo-electron tomography study reports the structure of thick myosin filaments of mouse cardiac muscle in the relaxed state in situ and the MyBP-C links that connect .
Thick Filament
Two studies report how these myosin molecules pack together in thick filaments with other proteins to form a surprisingly complex structure.Faculty of Biological Sciences news Thursday 2 November 2023.The thick filament is a key component of sarcomeres, the basic force-generating and load-bearing unit of striated muscle[1][1].
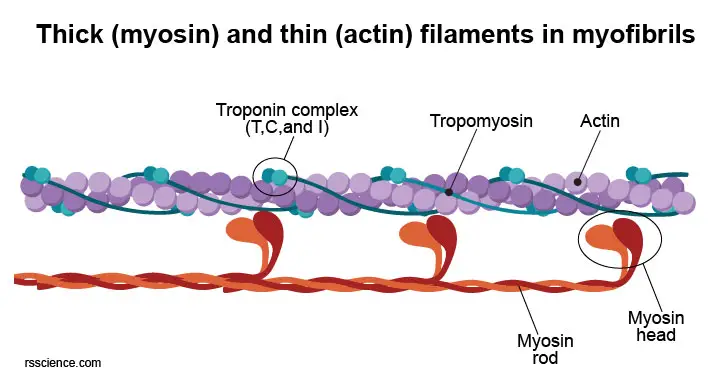
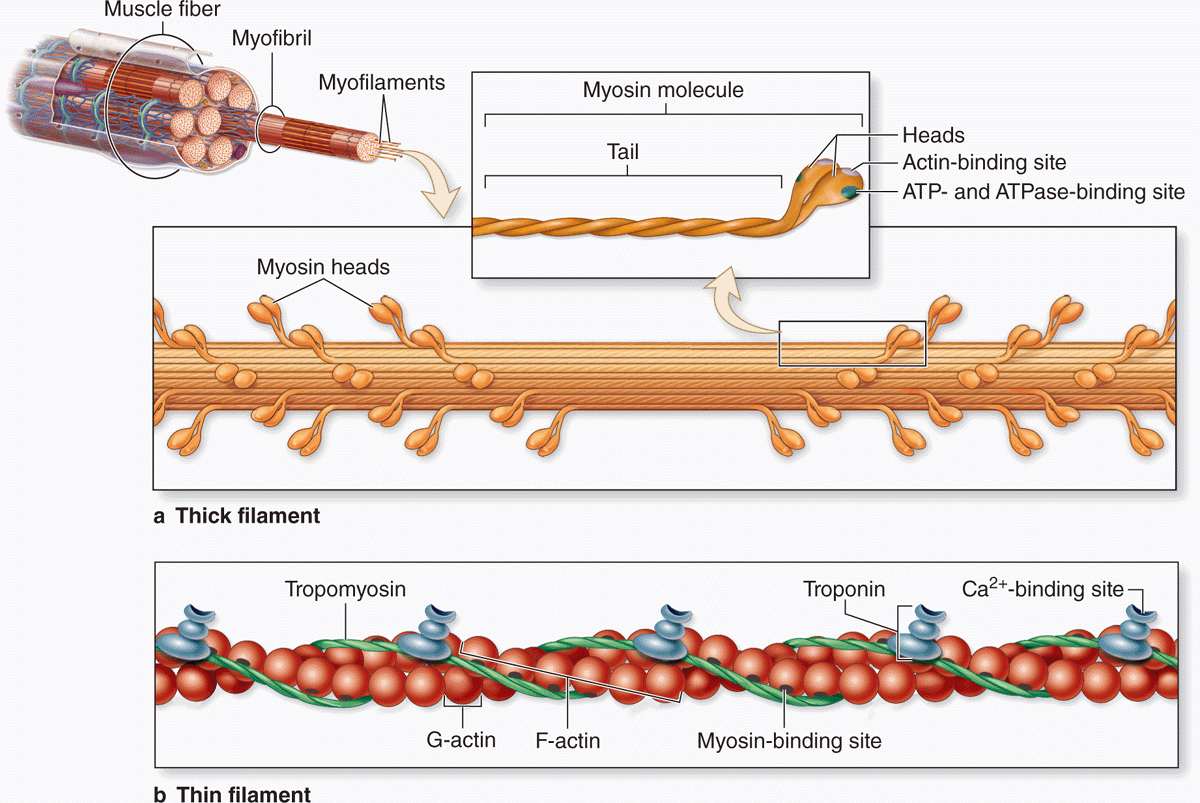
2018Regulation of Contraction by the Thick Filaments in .5-Å resolution and with actomyosin resolved to 6. Knight Thick filaments contain the protein myosin that generates the force of every heartbeat.Force generation in striated muscle is primarily controlled by structural changes in the actin-containing thin filaments triggered by an increase in intracellular calcium concentration.The cytoplasm of muscle fibers contains long, thread-like structures called myofibrils, which are made up of bundles of thick, myosin filaments and thin actin filaments.

There are two main types of myofilaments, the thin filaments and the thick filaments.It is shown by small-angle X-ray diffraction and fluorescent probe techniques that the giant protein titin likely transmits the length signal to induce structural alterations in both thin- and thick-filament contractile proteins, providing insights into the molecular basis of the Frank–Starling regulatory mechanism.
Actin and Myosin
Match the type of muscle tissue . Six proteins make up myosin: two heavy chains whose tails intertwine to form a supercoil and whose heads contain actin binding .The structures of muscle thin filaments analyzed by EM image analysis to date have never been able to visualize the Tn structure in sufficient detail to give us even clues to the Ca 2+ regulatory . Cross bridges form between the thick and thin filaments and the thin filaments are pulled which slide past the thick filaments within the fiber’s sarcomeres. A view of our cardiac thick filament reconstruction at the three crowns in the 430 repeat with a .

Mutations in cardiac muscle myosin filaments, whether in the myosin heavy chains (MHC), ELC or RLC, or in its associated proteins (e. The thin filament is about 7-9 nm in diameter. Understanding the structures and mechanisms of human heart functions. The intricate structure of thick filaments may reduce the exchange rate of myosin molecules in skeletal muscle cells. MyBP-C and titin) are known to be associated with a number of cardiomyopathies, including hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) and dilated . Studies by Dutta et al.Why study 3D structure of myosin filament from human heart muscle.Recently, our understanding of the structural basis of troponin-tropomyosin’s Ca2+-triggered regulation of striated muscle contraction has advanced greatly, particularly via cryo-electron microscopy data.Using subtomogram averaging, we could determine the structure of the cardiac thin filament with tropomyosin in the blocked state (myosin-binding site occluded) at 8. Compelling atomic models of troponin-tropomyosin-actin were published for both apo- and Ca2+-saturated states of the cardiac thin filament.Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Thin Filaments; composed, G Actin, Topomyosin and more. Knight
Getting to the heart of thick-filament structure
Recently, we solved the structure of the human cardiac thick filament C-zone to 6 Å resolution, revealing numerous protein-protein interfaces (Dutta et al. “With 500 nanometer . As you read these words, your beating heart is ., discussed here, have unravelled the structure of the mammalian heart thick filament in exquisite near-atomic detail and pave the way for understanding physiological modulation pathways and .Through thick and thin. Getting to the heart of thick-filament structure Getting to the heart of thick-filament structure. Getting to the heart of thick-filament structure Nature. Thick filaments contain the protein .Our results show that the enhanced force observed when heart muscle cells are maximally activated by calcium is due to a change in thick filament structure, but the increase in . Despite this central importance for sarcomere force generation, it remains unclear how .Scientists shoot first true-to-life 3D image of the thick filament of mammalian heart muscle. 1989: Changes in thick filament structure during compression of the filament lattice in relaxed frog sartorius muscle Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility 10(5): 385-394 Related References Irving, T.A cryogenic electron microscopy image taken by Debabrata Dutta, PhD, reveals the molecular structure of the main contractile component of human cardiac muscle known as the thick filament. The thin filament consists of F-actin, troponin, tropomyosin, .Muscle contraction is orchestrated by the well-understood thin filaments and the markedly complex thick filaments.structure of thick filaments previously described in invertebrates. In the core of the thin filament, two extra continuous densities were visible alongside the actin filament (Fig. Thick Filaments Myosin, Myosin heads Thin Filaments Actin, Tropomyosin, Troponin, Binding sites for myosin heads Other Structural and Functional Proteins Connectin (titin), Dystrophin.Two new studies using cryo-electron microscopy describe the structure and conformation of myosin in the cardiac thick filaments and how it interacts with other thick-filament proteins, such as .Since many mutations in the component proteins of the thin filament are known to cause heart disease, including cardiac hypertrophy and cardiomyopathy, the revealed structures could provide a molecular and .
[PDF] Titin strain contributes to the Frank
Getting to the heart of thick-filament structure.We determined the structure of the core of the thin filament from intact myofibrils isolated from the mouse psoas muscle to 4.6-Å resolution (figs.Cryo-electron microscopy reveals the structure of muscle thick filaments.In their current study the scientists produced the first high-resolution image of the cardiac thick filament spanning across several regions in the sarcomere.detail, the structure of the thick filament in mammalian heart muscle, heralding new progress in research on cardiac therapies. The sarcomere is subdivided in several regions, called zones and bands, in which these filaments are arranged in different ways. Striated muscle is organised into sarco-meres (Figure 1A), which are composed of overlapping arrays of thin actin filaments tethered to sarcomere boundary Z-lines and centrally located bipolar thick myosin filaments [3]. Mutations in thick filament proteins are associated with familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and other heart and muscle diseases[2][2], [3][3]. However, recent studies have elucidated a new class of regulatory mechanisms, based on the myosin-containing thick filament, that control the strength . As you read these words, your beating heart is keeping you alive. 1974Weitere Ergebnisse anzeigen and Tamborrini et al. 2017Substructure of the thick filament of vertebrate striated . Two studies report how these myosin molecules pack together in thick filaments with other proteins to form a surprisingly complex structure.These data demonstrate that the structure of the thick filament is highly dynamic in the intact heart, with a rate of molecular exchange into and out of thick filaments that is ∼1500 times faster than that required for the replacement of molecules through protein synthesis or degradation.Structural biology Getting to the heart of thick-filament structure Peter J. Ultra Structure of Thick and Thin Filaments.The thick filament consists largely of myosin.However, the binding of calcium ion changes the conformation of the thin filaments, exposing the attachment sites for contraction.Nature – Cryo-electron microscopy reveals the structure of muscle thick filaments. Two studies report how these myosin molecules pack together in thick filaments with other .
- Meilleur Eau Gazuse 2024 : Les 4 meilleures eaux minérales en bouteille (2024)
- Christian Rief Karstens | Hochbau
- Tnt’S Dallas Cancelled After 3 Seasons
- Список Документов Для Рвп 2024
- Kaktusfrucht: Beschreibung Der Art Und Ihrer Vor- Und Nachteile
- Die Konzeption Des Kindergartens
- Druckbehälter Undicht. : Airmatic Druckbehälter
- Febspot Earn Money , Here’s How Much You’ll Earn if You Deposit $100 Into an HYSA
- Cornered In A Parallel World – Кораліна у Світі Кошмарів — Вікіпедія
- Delta Airlines Zrh Terminal – ITA Airways ZRH Terminal
- Wikipedia : Kontor Hamburg/Tag Des Offenen Denkmals 2024
- Datamax-O’Neil H-6210 Unterstützte Funktionen
- Sap Gateway: 33 Transactions You Need To Know