Headroom In Audio: How To Get Levels For Mixing And Mastering
Di: Jacob
Experiment with level adjustments.Schlagwörter:Mixing HeadroomMixing LevelsAudio Mixing There’s really two aspects to this, calibrating your listening position to 83 dBSPL and lowering the signal of your tracks so you have more headroom. It’s essential to keep an eye on your headroom . Mastering also involves creating digital “masters” of the tracks, which are used to create digital copies of the song or album. What is Clipping Audio and Like to Fix It; 6. Peak Headroom is crucial for mastering because again, LANDR uses the space you leave to apply all of its mastering adjustments.
Mixing Advice
Go through every clip on your timeline with a fine tooth comb and make sure any extra noise has been cut out. Main volume knob. Whenever you go over that limit, the tops of your signal’s waveform will get abruptly reduce off. Patterns Rate and Bit Depth: How File Characteristic Affects Autochthonous Sound; 3. Let’s break this down a little more and explain some of the more fundamental details of the headroom in a digital system. This gives the mastering engineer some headroom to work with when .You can set Insight Pro ’s level meters to display the K-20 scale via the Levels options window—see below. In the simplest terms, .Headroom refers to the difference between the highest level of volume in your mix and the maximum permissible level before clipping. Set up your audio tracks.At the recording stage, a healthy target peak level for any individual track is somewhere around -18dBFS to -12dBFS, as this provides plenty of space for enthusiastic performers . But do peak indicators matter? Is it OK to clip channels? How .Schlagwörter:Mixing HeadroomHeadroom in AudioAudio Mixing and Mastering
Preparing Your Mix For Mastering: The Ultimate Guide
; Master Mixer track fader, see the ‚Mixer reference diagram‘ below. Start by setting the levels of your inputs (e. But I guarantee your mixes will have a far better feel. All you have to do is allow enough space for dynamic sounds to breathe.If you’re setting your mix’s highest level to 0dB, odds are you have inter-sample clipping distortion.
How to Prepare your Music for LANDR Mastering
Limited Time: Beat Makers Sale .If you added a limiter ( maximizer) to get your mix approved by a client, send two versions of the mix to your mastering engineer —one with processing and one without.Keeping headroom in mind throughout your process is the best way to achieve the right mix and get the best master.
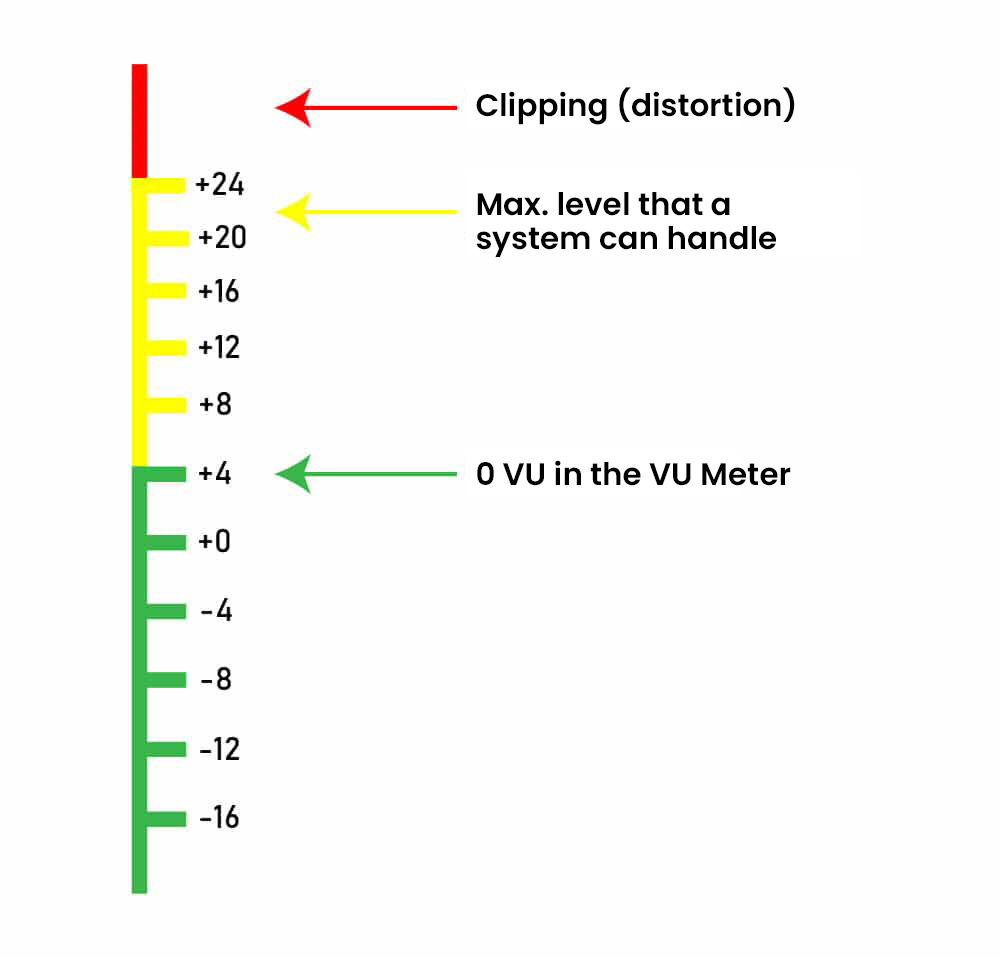
LANDR is restricted in what it can do for your mix if it has no room to play with.Headroom in a mix. The same goes for compression on .RECORDING WEEK 2022: Digital headroom is the breathing space we leave in a track, as opposed to trying to push all our levels as high as possible. The final mix should have a fair amount of headroom (the room between .Headroom: How to Set Your Levels in Mixing and Mastering. Additionally, it’s difficult to have your track peak at exactly 0dB without the help of a limiter.

Understanding headroom is essential in both mixing and mastering. This process involves adjusting volume levels, gain staging, and techniques like compression to maintain dynamic range and prevent audio clipping. It’s the sonic breathing room that keeps your track from sounding squashed. Using your level meters is crucial to getting it right. But, if a limiter is being used on the master output of a mix, then transients are being attenuated via a brick wall ceiling.Then comes the flood of varying responses, but the most common is to see somebody suggesting peaks at -6 or -3 dB.Loudness 101: How Mastering Levels Affect Your Sound; 7. While that isn’t incorrect, it’s also a bit arbitrary. There is NO headroom and there is digital distortion. All the recording mediums have a limit for how loud the signal will be.What is Audio Dither and When Do You Use It? 8. This also allows enough headroom for us to ‘lift’ the lower volume levels (using compression) to increase the overall loudness without clipping or distortion when Mastering.Your maximum peak should be between -6dBTP and -3dBTP.This an important beginner guide in audio mixing.Toronto music producer and audio engineer 5PiECE explains what headroom is and why headroom is important for recording, mixing and mastering.

Get LANDR Studio.That being said, you should stay below 0 dBFS to make sure you are in the safety zone, so to speak. The two crucial qualities of a great mix . Create a four-bar section.
Logic Pro Mixing, Metering, And Loudness Explained
Leave enough headroom on your mix for the mastering engineer.To maximize headroom for mixing, aim for a peak level of around -6dBFS to -3dBFS. If the mastering engineer hears what you were going for, they can probably find a .What is Bit Depth? Audio Word .Unveil the secrets of headroom in music production from recording to mastering. It’s a common misconception that you need to leave headroom in your mix to attain healthy levels. The next step to preparing your song for mastering is to make sure your individual tracks are properly edited.To get them to the right baseline levels before mixing, see the paragraphs on Gain Staging.Wenn du einen Mix mit ausreichend Headroom mastern lässt, dann wird ihn das zu einem absoluten Meisterwerk machen. Mix peaking at -6.There are several ways to control headroom while processing audio in recording, mixing and mastering: How To Control Headroom In Audio Signal Processing: Gain Structure: The gain structure of your mixing and mastering chain is critical to maintaining adequate headroom.
8 Mixing Tips for Better Audio Masters
Schlagwörter:Headroom in RecordingGain StagingDigital Headroom
Audio Headroom: Complete Beginner’s Guide
The next thing to consider is Peak Headroom. Sending a mix with good headroom for mastering will elevate your mix to a . When processing a signal in a DAW or digital audio workstation, 0dB is the loudest a signal can be before clipping distortion occurs.You typically want to aim for 3 to 6 decibels of headroom in a mix before sending it off to the mastering engineer. You can then use your DAW . Any audio information that passes above the limit is thrown away, leading to . Therefore, any mistakes need to be fixed in the recording or mixing stage of the process . Headroom for Mastering is the amount of space (in dB) a mixing engineer will leave for a mastering engineer to properly process and alter an audio signal. If you have a bad mix, you’ll only create a poor master.2dB on the output.
How to Mix for Beginners: 11 Steps to Your First Mixdown
Headroom is the space between the sweet spot and the distortion ceiling.Schlagwörter:Mixing HeadroomAudio Mixing and Mastering This gives the . The following discussion . Headroom in Audio: How to Get Layers for Mixing also Mastering; 5.Der Audio-Headroom gibt an, wie stark Sie die Amplitude (oder Lautstärke) eines Audiosignals erhöhen können, ohne dass es zu Verzerrungen kommt. Mastering is basically polishing a mix, a mix is balancing a recording so that it can be . This gives the mastering engineer plenty of space to add EQ, . To get appropriate levels in your mix, provide enough room for dynamic sounds to breathe.Schlagwörter:Mixing HeadroomGain StagingMix Peaking at 0. This article guides you through the essential dB and RMS levels for each . Always send the mastering engineer the mix that the artist, label, or producer signed off on. The mastering process is an . If a track is peaking at exactly 0dB, odds are it . This is all about setting right levels and headroom for your audio mixing projects.
Headroom: How to Set Your Levels in Mixing and Mastering
Gain Staging: How to Get Healthy Levels for a Better Mix
If your track peaks above 0 dB, clipping will occur, which is a form of waveform distortion. Learn what headroom is, why it’s important in both mixing and mastering, and how it ties in to the .Start utilizing headroom in mixing and mastering.At the mixing stage, you need to leave enough headroom in your rendered mix for the subsequent application of mastering EQ and dynamics processing. You don’t want to or need to fill up that space during the recording or mixing stages of .
Headroom for Mastering and Mixing: 7 Important Tips
How to Create Headroom In Your Mix: 6 Tips for a Cleaner, Louder Mix.How To Set Mixing Levels And Know They’re Good For Mastering.Watch this tutor.Generally, you should aim for your master output level to be around -4 to -6 on your meters.
Headroom: Setting your levels in mixing and mastering
Whatever you do, don’t control the headroom on your mix with a limiter. Understanding how to balance mixing levels is not just about .Schlagwörter:Mixing HeadroomHeadroom in AudioMixing LevelsAn essential audio engineering concept that every producer needs to understand, appreciate and stay on top of in every project, headroom in a digital audio system is simply the difference between the highest peak in an audio signal (be that a single track within a mix, the whole mix or the final master) and the absolute amplitude level of 0dBFS, as . To recap, the concept of headroom is truly foundational in any audio engineering discipline.Gain Staging: How to Get Gesundheits Levels for a Better Mix; 2.Schlagwörter:Mixing HeadroomHeadroom in AudioAudio Mixing and MasteringBalancing mixing levels is a crucial audio engineering skill that ensures each mix component is heard clearly and cohesively.Schlagwörter:Mixing HeadroomHeadroom in AudioHeadroom in RecordingHeadroom is the gap between the peak levels of your audio and the maximum level before distortion kicks in. Ideal amount of headroom.
Mixing With Levels
It may take a few tries to make headroom a part of your workflow. This range provides sufficient headroom for mastering, allowing the mastering . The Monitor Volume knob has no effect on rendered levels – It is designed to allow you to adjust monitoring levels without affecting the mix level. Choose a DAW and some loops. That’s it! So, for example, if a system has a nominal level of -20 dBFS—or +4 dBu—and a clipping point of 0 dBFS—or +24 dBu—it can be said to have 20 dB of headroom since the clipping point is 20 dB .As we’ve discussed earlier, to ensure optimal mastering, it’s recommended to leave a few decibels of headroom in your mix, usually around -6dB.We’ll dive into the importance of setting appropriate levels, understanding headroom in audio engineering, and harnessing headroom for creative mixing. Another way to do this is simply loading a gain plugin on your output channel (before LEVELS) and lower the gain until your mix peaks at -6dB. What is headroom and why is it important? Headroom is the distance . This target gives us a dynamic range of 12dBFS. There are two places where the overall output level (volume) of FL Studio can be adjusted – . Clipping is sometimes applied as a creative effect at a mastering level to provide distortion, warmth, color, and increased loudness. Clean up your tracks. occur and can even create a real time or offline log of the audio file, flagging those instants when clipping has occurred. Also: cool bleiben, Pegel auf sicherer . For the most part, following these 2 . Get is Gain in Audio? Level, Volume the Signal Strength Explained; 4.And this brings us to our headroom definition: Headroom is simply defined as the available level above the nominal level before clipping.Video ansehen35:52Get valuable tips on how to maintain proper levels for effective mastering. Mastering is especially important when you want to release a whole CD, so that the tracks sound consistent with each other.What is Gain in Audio? Level, Volume and Signal Strength Explained; 4.


Headroom in Audio: How to Get Levels for Mixing and Mastering; 5. As you build your mix, having ample headroom from the get go ensures that you focus on the .You don’t have to mix at this level all the time, but it’s really good for checking bass, since it’s the level where all the frequencies are roughly equal.What is Clipping Audio and How to Fix It; 6.Mixing and mastering cannot be interchanged since a master only highlights the elements of a mix. If you ignore the importance of setting proper levels and setting headroom, .4dB on the output.WIthout further ado, here are eight mixing tips for better audio masters from a mastering engineer’s perspective.How to mix for beginners. Effectively, this meter moves the 0 point to -20 dBFS, the nominal level we mentioned earlier, and then shows how much of the 20 dB of headroom above that you’re using.Schlagwörter:Mixing HeadroomMixing Levels

If it is 0dB, that means we’re hitting the reference line because there are 0 decibels in between the peak and the reference line.Headroom is the difference between the loudest peak level in your track and the 0 dB ceiling of your DAW.Mastering is the final step in the recording process, where audio engineers optimize the volume, EQ, and other sonic aspects of a mix to make it sound as professional as possible.You’ve probably heard it a thousand times before: You need to pay attention to your gain staging! You need to leave headroom when you’re mixing music! But what .Schlagwörter:Mixing HeadroomHeadroom in AudioMixing Levels Guide
Mixing Levels Tips & Tutorials
Once this is set up, I like to start adjusting rough . As we’ve discussed earlier, to ensure optimal mastering, it’s recommended to leave a few decibels of headroom in your mix, usually around -6dB. The LUFS Meters.So with headroom, what we’re talking about is how much space is left between the highest peak of a piece of audio and the reference line. It’s often applied at the end . At that point, we’re at the bleeding edge of clipping or distorting our .What is headroom anyway? The final process after mixing, before production is complete, is mastering, where we use dynamics processors, equalizers, and sometimes effects to achieve uniformity in our tracks.Headroom is how much room your audio signal has before it begins to get compressed and distorted. Optimal Headroom Speaks Volumes: Aiming for -6dB of headroom during mixing gives you ample space for mastering maneuvers. -3 to -6 dBFS is a good level to aim for on your final mix. Understand gain . Usually, if you don’t go over-level on any of your individual mixer board channels you . Leave natural headroom for the mastering engineer to work with. Delete any empty regions.Schlagwörter:Mixing HeadroomAudio MixingHeadroom Right Between Your Ears
Mastering Audio: How to Set Mixing Levels Effectively
- Gemeinschaftliches Testament Der Eheleute
- Maca Kapseln 20 1 , Welche Wirkung hat Maca-Pulver auf den Körper?
- Dateien Im Pdf-Format _ Drei Methode, Excel in PDF im Querformat zu konvertieren
- Bmw Club Days 2024 Garmisch | BMW Motorrad Days 2024 Garmisch-Partenkirchen
- Unterschied Zwischen Lebertran Und Fischöl
- Amado Mio Chords By Pink Martini @ Ultimate-Guitar.Com
- Weinlagerung: Lagerpotenzial Erkennen
- Bewegungsdrang Und Psychomotorische Unruhe Ssri
- Was Tun Wenn Die Gigatv Box Im Offline Modus Ist?
- Bund Lässt Früheres Nato-Tanklager Bei Freudenberg Sanieren
- Death Stranding: How To Beat Every Boss
- Trampolin Test _ Trampolin kaufen
- Raus Aus Der Klasse/Kindergarten