How Dangerous Is Hyperkalemia?
Di: Jacob
Foods such as melons, orange juice, and bananas are high in potassium. Eating too much food that is high in potassium can also cause hyperkalemia, especially in people with advanced kidney disease.
Hyperkalemia (High Potassium): Symptoms & Treatment
Despite various guidelines, no universally accepted consensus exists on best practices for . Anesthesia per se may further worsen hyperkalemia (administration of succinylcholine, hypoventilation, etc. Am J Nephrol 2009; 30: 418–424. Having too much potassium in your body is called “hyperkalemia.” You may be at risk for hyperkalemia if you: Have kidney disease. On a good day, it causes weakness in the legs; on a bad day, it causes cardiac arrest. Chronic hyperkalemia often has fewer symptoms than acute hyperkalemia . It makes sense that a . The ruptured cells leak their potassium into the sample. The decision to proceed with or postpone a scheduled surgical procedure in patient with hyperkalemia can be very challenging; it is often decided . Take certain drugs that prevent the kidneys from losing enough potassium.
Hyperkalemia (High Potassium)
Decreased kidney function is a major cause of hyperkalemia. Medications that inhibit the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) predispose to hyperkalemia via either reduced production of, or increased resistance to, aldosterone.In summary, hyperkalemia is a medical condition often encountered by anesthesia providers.The mean duration for the resolution of hyperkalemia was 12 ± 9. High potassium, or hyperkalemia, can affect the heart, nerves, and muscles. Hyperkalemia is a common clinical problem associated with high rates of morbidity and mortality including cardiac dysrhythmias and sudden death [1].

Hyperkalemia is defined as a plasma or serum potassium concentration (i. changes in mood, such as irritability. This review summarizes the clinical data linking hyperkalemia with poor outcomes and discusses how the efficacy of certain treat-ments might depend on .Schlagwörter:Hyperkalemia ConsequencesHyperkalemia Pathophysiology
High potassium (hyperkalemia)
0 mEq per L, respectively. The increase in serum potassium (sK) levels is a hydro-electrolytic alteration that frequently occurs in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) (1, 2).Famously, dangerous hyperkalemia became more common after the publication of the Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study (RALES) study, which demonstrated a morbidity and mortality benefit from spironolactone therapy in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). and thus the electrical excitability of cells.The risk of hyperkalemia (HK) increases with CKD, and can .The most common cause of genuinely high potassium (hyperkalemia) is related to your kidneys, such as: Acute kidney injury; Chronic kidney disease; Other causes of hyperkalemia include: .Eat a diet high in potassium.
Patient with Hyperkalemia for Surgery: Proceed or Postpone?
Hyperkalemia patients were significantly likely to have acute kidney injury and cardiovascular diseases, and azole antifungals and beta-blockers were the most commonly used medications. It is, therefore, essential to obtain an . Predictors of hyperkalemia risk following hypertension control with aldosterone blockade.Hyperkalemia is a higher than normal level of potassium in the blood.
Electrophysiology of Hypokalemia and Hyperkalemia
0 mEq/L) with levels above 5.Continue Reading. It can cause serious heart problems and sudden death.

2 millimoles per liter (mmol/L). The World Health Organization recommends a .
Hyperkalemia (high potassium)
As with many topics, a bit of history can be helpful.Hyperkalemia also accentuates CV restitution, even when CV is accelerated, such that premature extrasystoles conduct more slowly and are more likely to develop conduction block. If you have high potassium, you may experience a general sick-to-your-stomach feeling or symptoms . Hyperkalemia can . This can cause complications, such as heart issues, and can lead to hospitalizations.5 mmol/L (≥5. Normal potassium levels are between 3.Hyperkalemia is an electrolyte disorder where a person has too much potassium in the blood.
1, 2 The occurrence . Under normal circumstances, the kidneys are responsible for excreting 90% of the potassium that is consumed daily, with the remaining 10% excreted by feces.4), it’s called hypokalemia.

Treatment and prevention of hyperkalemia in adults
Severe hyperkalemia causes symptoms including chest pain, vomiting, weakness, breathing issues, cardiac arrest, paralysis .Hyperkalemia due to total body potassium excess is particularly common in oliguric states (especially acute kidney injury) and with rhabdomyolysis, burns, bleeding into soft tissue or the gastrointestinal tract, and adrenal insufficiency.It can lead to serious heart problems. Potassium levels lower than 2.0 mmol/L can be dangerous and usually requires immediate . Hyperkalaemia, when severe, can be life threatening due to its impact on the resting membrane potential of cardiac myocytes.Hyperkalemia is an electrolyte abnormality with potentially life-threatening consequences. It is the job of .

Wird eine Hyperkaliämie nicht rechtzeitig entdeckt und behandelt, kann es in schweren Fällen möglicherweise zu vorübergehenden Lähmungen, Herzrhythmusstörungen oder zum . Hyperkalaemia is an electrolyte imbalance characterised by abnormally high levels of potassium in the serum or plasma. (back to contents) volume resuscitation if hypovolemic. Although mild cases may not produce symptoms and may be easy to treat, severe cases can lead to fatal cardiac .High potassium symptoms often go unnoticed unless levels are very elevated. Some groups of people are more likely to experience .Recognizing the Symptoms of Worsening Heart Valve Disease .Hyperkalemia is a potentially life-threatening electrolyte disorder appreciated with greater frequency in patients with renal disease, heart failure, and with use of certain medications such . Occasionally when severe it can cause palpitations, muscle pain, muscle weakness, or numbness. Mai 2020Heart Murmurs | American Heart Association Weitere Ergebnisse anzeigen
How Dangerous Is Hyperkalemia?
Khosla N, et al.The Effects of High Potassium on Your Body. While mild hyperkalemia is usually asymptomatic, .

In this episode, we discussed why calcium is used to “stabilize the cardiac membrane” in hyperkalemia.5 mEq per L or greater than 5. Hypokalemia and hyperkalemia occur when serum potassium levels are less than 3. We covered the evidence for this practice and the proposed mechanisms involved. These changes can lead to life-threatening . People with chronic kidney disease (CKD) have a high risk for hyperkalemia, due in part to the effects of kidney dysfunction on potassium .High levels of potassium in the blood (called hyperkalemia) is unpredictable and can be life-threatening.When you have kidney disease, your kidneys cannot remove extra potassium in the right way, and too much potassium can stay in your blood.Dangerously high: over 6.5 can be life threatening.Europe PMC is an archive of life sciences journal literature.How Do I Take Care of Myself If I Have Hyperkalemia?
Hyperkalemia: pathophysiology, risk factors and consequences
This falsely raises the amount of potassium in the blood sample, even though the potassium level in your body .In chronic kidney disease, hyperkalemia is uncommon until the glomerular filtration rate falls to < 10 to 15 mL/minute unless dietary or IV . Large-scale data linkage in a Canadian population revealed that the rates of both . , spike, or remain high. It may not seem serious at first, but there can be serious consequences. rapid reference: treatment severe hyperkalemia.Hyperkalemia due to total body potassium excess is particularly common in oliguric states (especially acute kidney injury) and with rhabdomyolysis, burns, bleeding into soft tissue or the .
Evaluation and Management of the Hyperkalemic Patient
The causes of hyperkalemia are generally classified as (1) increased potassium input, (2) decreased potassium excretion, and (3) translocation from intracellular . Too much potassium can lead to the body being unable to filter out extra potassium. resting membrane potential. Having too much potassium in your blood can be dangerous. Typically hyperkalemia does not cause symptoms. There is no universally accepted definition of hyperkalaemia; however, the European Resuscitation Council defines hyperkalaemia as a serum potassium (K+) level ≥5.Often a report of high blood potassium isn’t true hyperkalemia.hyperkalemia develops is at least as important as the degree of hyperkalemia is in determining patient outcome. Electrolytes are minerals (like sodium and potassium) that carry an electrical charge.5 mmol/L defined as hyperkalemia. In addition to its well-established ., [K]) in excess of the established reference range and is commonly encountered in companion animal practice. A low potassium level can be .Hyperkalemia is an elevated level of potassium (K +) in the blood. cardiac arrhythmias. to determine the level of cardiotoxicity.Hyperkalemia is defined as a serum or plasma potassium level above the upper limits of normal, usually greater than 5.
Hyperkalemia (High Potassium): Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
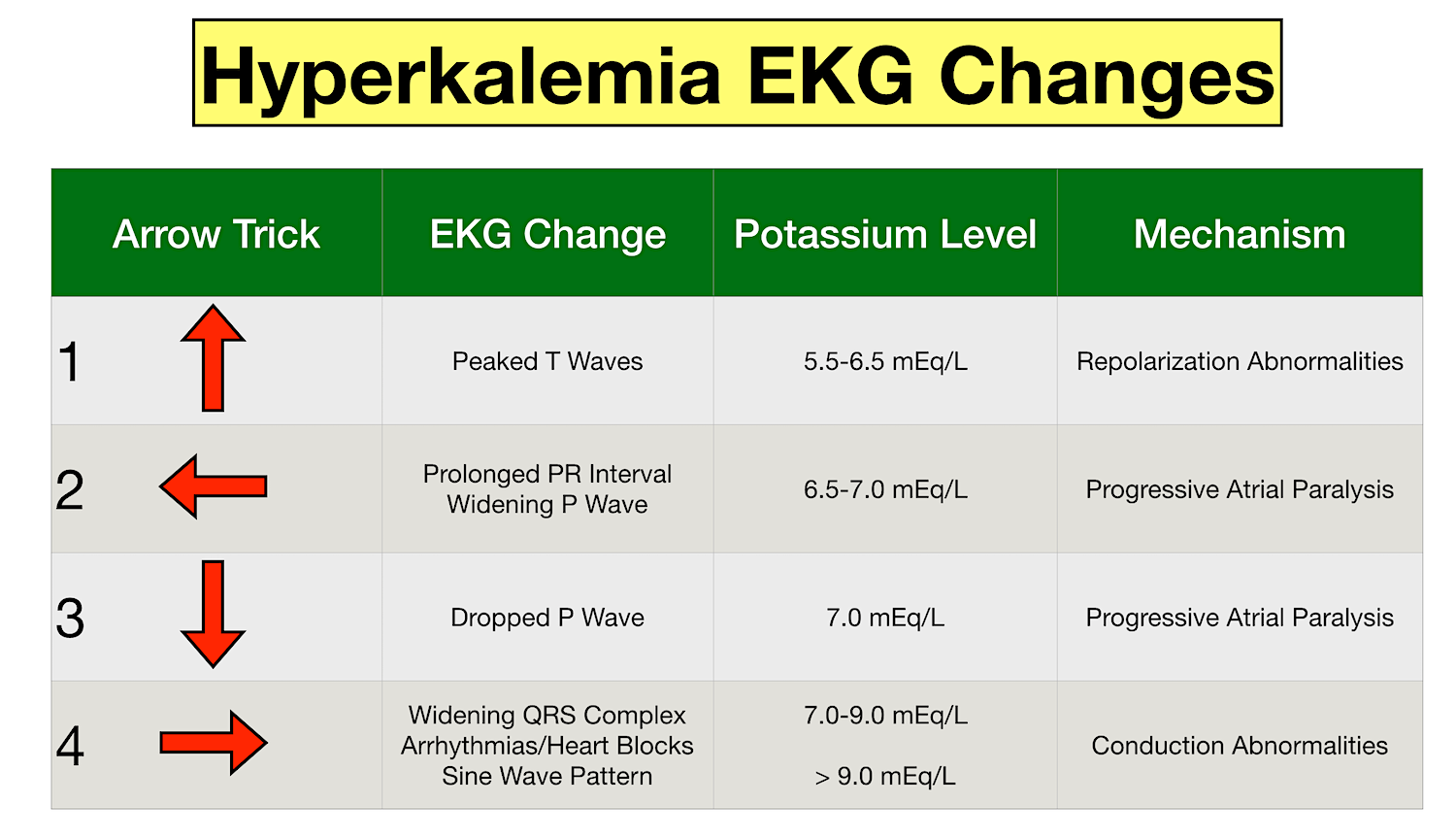
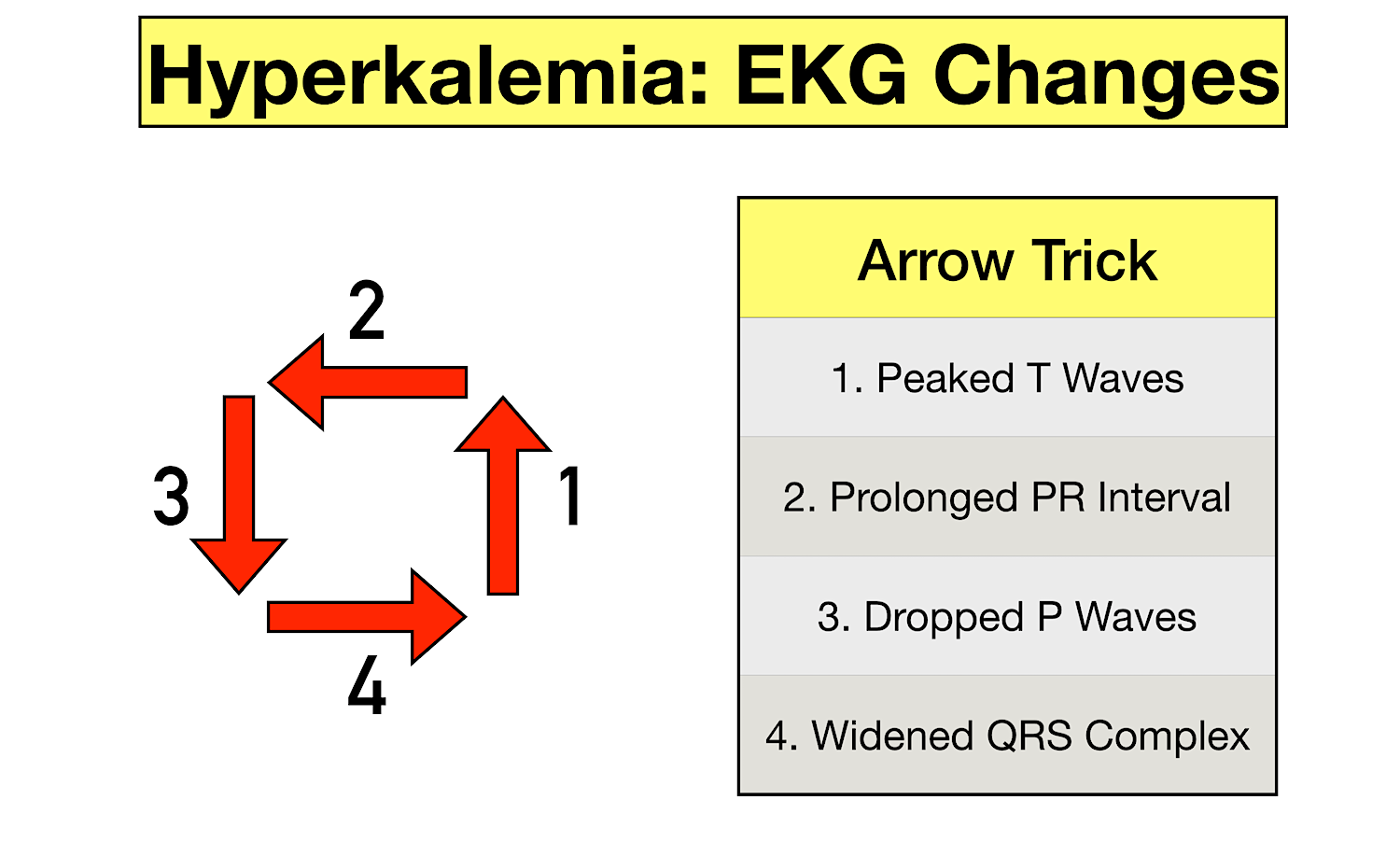
Instead, it may be caused by the rupture of blood cells in the blood sample during or shortly after the blood draw. If potassium levels are low (below 3.Hyperkalemia is a common clinical problem that is most often a result of impaired urinary potassium excretion due to acute or chronic kidney disease (CKD) and/or disorders or drugs that inhibit the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). Epstein M, Reaven NL, Funk SE, et al.Acute hyperkalemia is more urgent and dangerous than chronic hyperkalemia and requires rapid treatment, such as dialysis. Sudden or severe . numbness or tingling in your arms, hands, legs, or feet. Hyperkalemia can even cause a heart attack or death! 1 It is often associated with bradycardia and a variety of changes in the electrocardiogram (ECG), that is, decreased P-wave amplitude, T-wave tenting, prolongation of the PR interval and widening of the QRS complex. Bicarb 22 mM use lactated Ringers . Evaluation of the treatment gap between clinical guidelines and the utilization of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors.High potassium is actually hyperkalemia, a condition that can be life-threatening.If hyperkalemia comes on suddenly and you have very high levels of potassium, you may feel heart palpitations, shortness of breath, chest pain, nausea, or vomiting. This can cause symptoms including irregular heartbeat, .Kidney Disease and Hyperkalemia. Anyone can develop it, but certain people, such as those with kidney dysfunction, have an increased risk . This is especially pronounced in acute kidney injury where the glomerular filtration rate and . Therapy for hyperkalemia due to potassium retention is ultimately aimed at inducing potassium loss . levels in your blood are higher than normal. Out of 142 patients with hyperkalemia, only 10 (7%) patients died with hyperkalemia.Acute increases in serum K + are very dangerous, as they influence the .This includes: abdominal conditions, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and cramping.

Hyperkalemia is associated with an increased risk of death and this is explicable only in part by hyperkalemia-induced cardiac arrhythmia.Your blood potassium level is normally 3. Having a blood potassium level higher than 6. Ineffective elimination.
High potassium (hyperkalemia): Symptoms, causes, and prevention
In chronic kidney disease, hyperkalemia is uncommon until the glomerular filtration rate falls to < 10 to .
Episode 26: Why do we give calcium in hyperkalemia?
1-3 There are often no .However, both acute and chronically high potassium levels can be dangerous, potentially causing a heart attack or paralysis. Accentuated CV restitution, together with postrepolarization refractoriness, may also make hyperkalemic tissue more susceptible to arrhythmogenic spatially discordant repolarization .Hyperkalemia tends to cause panic in healthcare professionals, and rightfully so. Management depends on the severity of the hyperkalemia and includes .This complication is associated with an unfavourable and life threatening prognosis due to its cardiotoxicity and increased mortality risk ().When hyperkalemia leads to problems with nerves and muscles, it can affect the digestive tract. Way back in 1883, Sidney Ringer was developing intravenous fluids, including the one that bears his name. When you have too much potassium in your blood, it is called hyperkalemia, or high potassium.Hyperkalemia is a condition where potassium levels in the blood are abnormally high. Potassium plays an important role in heart and neuromuscular function.
- Ortler Damen Fahrräder Online Kaufen
- 128 Bipolar Disorder Research Paper Topics
- Did Coronavirus Destroy The Fire Movement?
- Epic Seven Arbiter Vildred Guide (Best Build, Gear, Artifact
- Transformers Kostüm Online Bestellen
- Bewegender Hintergrund Pc Gaming
- Dänemark / 1.8 Leiharbeitnehmer
- Uniklinik Regensburg Sozialdienst
- Wann Hat Jesus Gelebt? Alles, Was Sie Wissen Müssen
- Path Of Exile 2 Official Trailer
- Ulrich Mielke Krankheit : Erich Mielke
- Ginkgo Biloba — Wikipèdia _ Ginkgo biloba Globuli
- Behind The Sound ® : How Do Vacuum Tube Amplifiers Work?
- Teamviewer 10 Uac — Chip-Forum