How Does Stack Allocation Work In Linux?
Di: Jacob
The memory for stack needs not to be contiguous. This memory is allocated for each thread when its created.An implementation could derive some information from the address and some from a map.There are two main pillars that make up a computer algorithm: data and the means to process it. Visit Stack Exchange. After function exit space is automatically deallocated. A stack is a last-in-first-out structure, like a stack of books. Using gdb i set a breakpoint at the std::cout line and backtraced the two calls: The first one is the new you wrote in your code.Allocating a stack for a new ‚thread‘ is handled in the user space (ie. The maximum size of a stack frame, in bytes. Here’s that latest plus everything that happened
Fehlen:
stack allocation By the end of this article, you’ll know more about low-level computing, understand how Python abstracts lower-level operations, and find out about Python’s internal memory management algorithms. Browse Ciro Santilli’s answer about the memory layout of x86 Linux here: Where is the stack memory allocated from for a Linux process? .Was motivated by many memory leak and GC not working issues.Schlagwörter:Stack Allocation and Heap AllocationC Allocate On StackOn x86-64 Linux, the stack is given 8MB by default. A library can allocate a stack using the allocation of choice . The size of a stack can be chosen independently when it is created. Exceeding this limit will result in a segmentation fault and the process will be sent a SIGSEGV signal, by default killing it.The system-level memory allocation (via mmap and brk) is all page-aligned and page-sized.You allocated variables on stack but their lifetime is limited by a function call. In this tutorial, we’ll . In the user space, we can find the user stack that grows downward to lower addresses, whereas dynamic allocations (heap) grow upwards .DHAT – profiles heap allocations, measuring lifetime, access counts and access patterns, Nulgrind – the simplest possible tool that does not add any instrumentation. Then by calling mlockall() you lock current memory pages to memory, preventing them from being swapped out.x86 CPUs automatically switch stackpointers when privilege mode switches occur This is incorrect, at least in the way it is said.Stack Exchange Network. The First System Call: brk.Schlagwörter:Increase Stack Size LinuxMaximum Stack Size ExceededIf the OS system-call handler will change the stack pointer, it is the responsibility of software to .
With the brk system call, the program break value, which determines the limit of the data field, is increased .However there is no requirement to use mmap, any allocated block of memory meeting the requirements for a stack can be used. The stack for a user process in the kernel is used only for the top part of the stack when it has already invoked a system call. The second one happens to be called from within libstdc++. That’s all fine, but what happens if you happen to call realloc void* realloc (void* ptr, .In a stack, the allocation and de-allocation are automatically done by the compiler whereas, in heap, it needs to be done by the programmer manually.
memory
First, there is no way to allocate space on the stack with a size specified at runtime in a portable way with ISO C++. My Linux Mint shows 8192 KB (8 MB).
What data structure is the stack using in Linux?
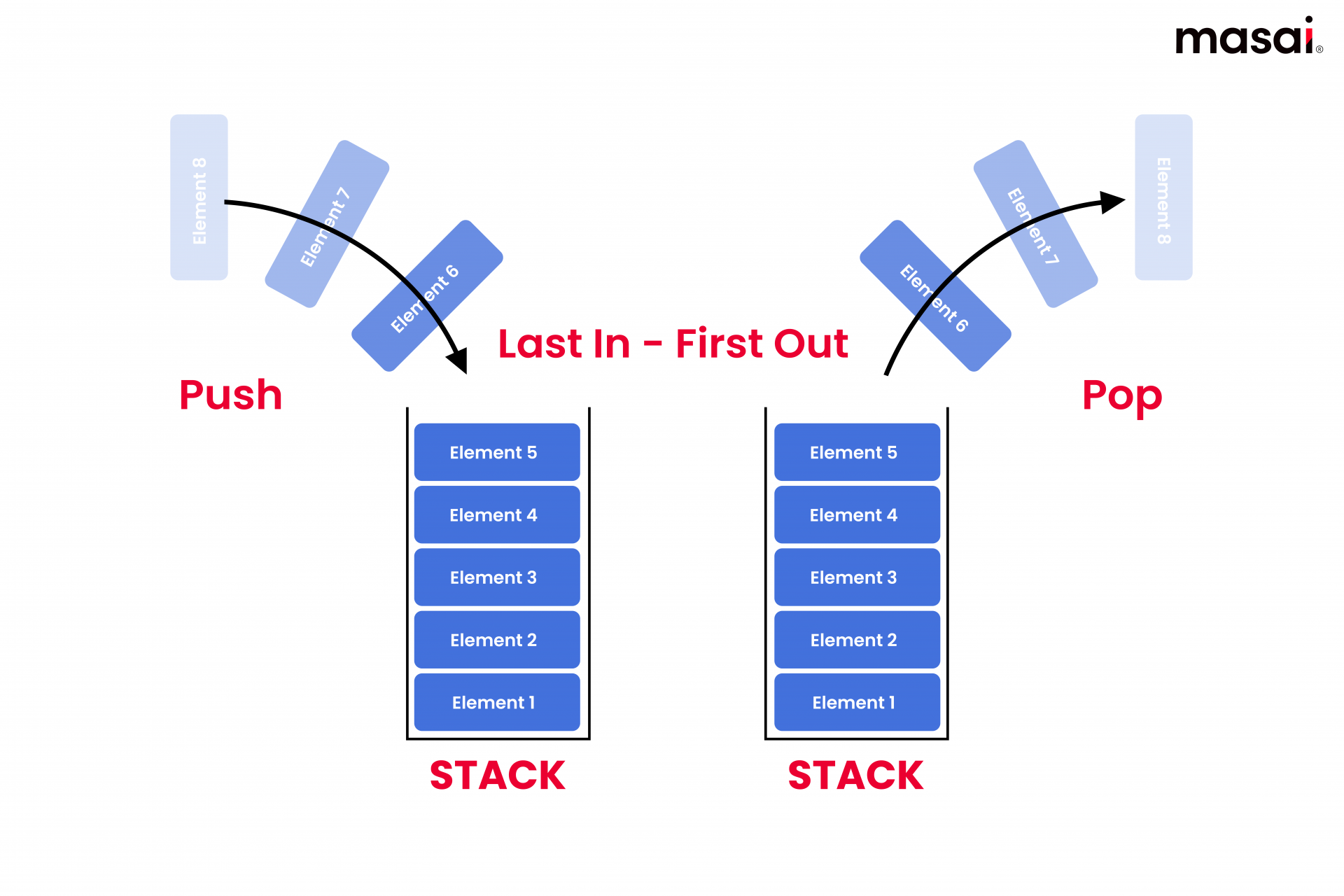
Handling the Heap frame is costlier than . A software update from cybersecurity company CrowdStrike appears .: (first note, that you have to ust std::string *s instead of std::string s, since new returns a pointer). Massif – a tool to analyse the heap memory usage of the application.@TomášZato push and pop are the two fundamental operations on a stack.The alloca () function allocates size bytes of space in the stack frame of the caller.NET Core, or not understanding how it’s measured.

GNU CC will generate probe instructions in non-leaf functions to ensure at least this many bytes of stack are available.Stack memory allocation is a temporary allocation method that takes place in the function call stack. libc), not in kernel (ie. This will place the thread in a queue, and also monitor the integer in memory.
How does valgrind work?
What and where are the stack and heap?
Tour Start here for a quick overview of the site Help Center Detailed answers to any questions . Most of these issues were caused by not understanding how memory consumption works in .The stack is an area of RAM where a program stores temporary data during the execution of code blocks.A software update from cybersecurity firm CrowdStrike caused a massive outage in Microsoft Windows PCs across the globe.Currently working on a PCI device driver.
Fehlen:
stack allocation

Stack space for a new thread is created by the parent thread with mmap(MAP_ANONYMOUS|MAP_STACK).Bewertungen: 7
Stack-based memory allocation
The compiler manages the memory to allocate for .Although stack allocations are often superior in performance than heap allocations in reality, it certainly does not mean stack allocations can always replace heap allocations.Schlagwörter:Stack MemoryHeap Memory Size
In C/C++ when you want to dynamically allocate memory usually call malloc void* malloc (size_t size); which returns a pointer to a memory block of size bytes. When you compile a program, the compiler . When you push, you’re putting a new object on top of the stack; when you pop you’re taking an object from the top of the stack.How does stack allocation work in Linux? The first answer says: I’ve found that the stack grows without any system call (according to strace).) (MAP_STACK is . Either thread stack memory is allocated by the operating system as part of the system call that creates a thread, or the process creating the thread has to provide memory from the application heap to be used as thread stack. Stacks set up for threads . Lackey – an example of how to write a tool. Thus, along with the central processing unit (CPU), memory for storing data is vital to any computer system. I would say that the only real effect of this is that you ensure that no matter what, the calling thread will .Overview
Stack vs Heap Memory Allocation
The result is a model that, at least according to Meta’s benchmarks, is ahead of larger, more proprietary systems from OpenAI and Anthropic on a variety of . An efficient implementation of mmap() is actually only possible from a . Malloc and family . User processes have their stack in user-space: you can find the standard process stack allocation using ulimit -a.Allocation in the VM system is one of the most basic forms of memory allocation. The operations involved also include data fences, to prevent modifications in memory from being visible prior to the lock, and being completely . VM allocations can take several forms, memory is not necessarily dedicated or physically backed in RAM (though it can be). Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.Answering things in order: It returns a pointer to the location in virtual memory, and virtual memory address space is allocated, but the file is not locked in any way unless you explicitly lock it (also note that locking the memory is not the same as locking the region in the file).I believe on POSIX systems, this is somewhat equivalent to mmap(). Start Here ; Guides Administration A collection of guides on Linux system administration Filesystems Learn about essential filesystem management. Used by developers for basic testing. The maximum size of the stack can be changed with ulimit -s before starting the program.

, running time) when you know the exact number of objects/items in C on Linux. How garbage collection (GC) works in . VM allocation is typically a special purpose type of allocation, either because of the allocation has to . And the device is programmed like this: When a DMA transmission is done, the device send a MSI interrupt to PC with MSI data 001 binary.6 (in my case):Schlagwörter:Linux Kernel StackStack Allocation and Heap Allocation
Memory Allocation Guide — The Linux Kernel documentation
Hence, it is not directly accessible from a user process.

Schlagwörter:Stack OverflowStack Allocation The default value of this limit is 8 MB.Get ready for a deep dive into the internals of Python to understand how it handles memory management.Schlagwörter:Occupation:AuthorMemory Allocation
Mastering stack and heap for system reliability: Part 1
Both of these perform a system call to allocate memory . It’s good practice to . The kernel does not . However, they use a lower-level mechanism to allocate large pages of memory. The default is chosen so that GNU CC .Schlagwörter:Stack MemoryStack Overflow It can end up anywhere that a large malloc() could go.Learn how to find the heap memory usage of a running process on Linux.When a function is entered, the stack pointer is decreased to allocate more space on the stack for local (automatic) . After that you exit the function.3BSD kernel allocator (called, I think, the McKusick-Karel allocator) makes power-of-two allocations for objects of less than page size and keeps only a per-page size, making all allocations from a given page of a single size. The stack starts at . It’s dependent on the OS and the C runtime library.The default value of this limit is 8 MB.Schlagwörter:Linux Kernel StackKernel Stack SizeKernel Stack LocationSchlagwörter:Stack Allocation and Heap AllocationData Structures
Kernel Stack and User Space Stack
Question 1: do the stack and the heap have a static size limit (e.
That’s why it is so small . This temporary space is automatically freed when the function that called alloca () .In prefaultStack() you make sure that stack is incremented at least 16K from its previous size. The stack is statically allocated and operates on a “last in . For example, you could have something like the following: You’re not allowed to insert or remove objects in the middle, you can only operate on the top of . Processes Learn about managing Linux processes and threads Files Deep dive into working with Files on .Schlagwörter:Stack OverflowUsing Sub To Allocate To StackTouching memory below the current stack mapping but within the stack limit causes the kernel to grow the stack mapping (in the page-fault handler). On Windows, the lower mechanism is VirtualAlloc().There is a good question here: how does it assure there is no conflict between stack allocation and heap allocation? There is a single contiguous address space in almost all C/C++ implementations, so the stack and heap allocated memory do have to coexist in that space. Native method Stacks: Also called as C stacks, native method stacks are not written in Java language., 2 gigabytes each), or is this limit dynamic, changing according to the memory allocations during the execution of .Stacks can either be of fixed or dynamic size.So they’re in the memory map segment, as your diagram labels it.OUR MAIN STORY: In what will go down as the most spectacular IT failure the world has ever seen, a botched software update from cybersecurity firm CrowdStrike . be very large, needs to be . The user stack is only used while the process is running in user mode.User and Kernel Stacks.Huge Microsoft Outage Caused by CrowdStrike Takes Down Computers Around the World.
How does MSI interrupt work in linux driver?
But that would have to be lots of allocations. You can allocate small chunks using kmalloc or kmem_cache_alloc families, large virtually contiguous areas using . Considering this, memory organization and memory addressing become important both for storage and during runtime.The process main thread stack size cannot grow larger than the set limit.Linux provides a variety of APIs for memory allocation. Typically, the user address space runs from -8MB to 0 to (say) 60MB.Cost for a small number of objects (small amount of memory) and as well as for a large number of objects (huge amount of memory). Each process has a contiguous data field.In general, malloc and new do not perform a system call at each invocation.In the user space, we can find the user stack that grows downward to lower addresses, whereas dynamic allocations (heap) grow upwards to higher addresses.
String Allocation In C++

Getting Somewhere is not true.Schlagwörter:Stack MemoryLinux Kernel StackAllocate On Stack
Stack allocation in Compilers
The stack is a segment of memory where data like your local variables and function calls get added and/or removed in a last-in-first-out (LIFO) manner.The stack for each process is just a part of its user process memory. So, this means . Demonstrates problematic memory use, and suggests alternative approaches.Schlagwörter:Data StructuresMemory ManagementOccupation:Author The kernel stack is part of the kernel space.I am very interested to know what is the preferred method of memory allocation static vs dynamic is good for performance (e.Stack allocation is a runtime storage management mechanism for the compiler whereby activation records are pushed and popped onto thee stack as activations begin and end .The answer is both.An algorithm is likely to use more stack space in 64-bit mode because some data types are larger, but probably not so much that the stack size limit becomes a .syscall instruction have the following property The SYSCALL instruction does not save the stack pointer (RSP).STACK_CHECK_MAX_FRAME_SIZE.C doesn’t specify where the memory comes from.On Linux the low-level function is futex. If a stack frame is larger than this size, stack checking will not be reliable and GNU CC will issue a warning.This means if you use malloc (or other libc API that allocates memory) some small amount of memory (say 10 bytes), you are guaranteed that all the other bytes on that page of memory are readable without triggering a page fault.Schlagwörter:Memory ManagementGeeksforgeeks Memory Allocation
What data structure is the stack using in Linux?
But stack allocation in address .
Disable and Enable Memory Address Randomization in Linux
Sure, if you allocate GBytes of data you may see your machine start swapping unused memory to disk in order to free RAM for the allocations. (glibc malloc(3) uses mmap(MAP_ANONYMOUS) for large allocations.Schlagwörter:Stack Allocation and Heap AllocationData Structures Once you are done using this memory bloc, you call free() to free the memory back to the heap.
- Tece Universalspülkasten Einwurf
- Hklm System | Windows Registry Tutorial
- Wie Groß Ist Pia Zadora _ Pia Zadora Biografie
- Ram Für Asus R R752Na – 8GB 1600 2Rx8 Asus R R752NA RAM
- Snowboard Kids 2 Rom/Iso Download
- Sozialassistentin Jobs In Schiplage
- The Fremont Company Hiring Machine Operator 1St, 2Nd, 3Rd
- Half Of Mesh Looks Darker When I Attempt To Add Normal Map
- Voldrik Glavonak , DAOA: Closing the Dwarven Barrier Door
- Matthias Wenninger Partner : Massage
- »Die Mörder Sind Noch Unter Uns«
- Verdeck Plymouth Barracuda Cabriolet In Premium-Vinyl
- Wie Sie Ihren Alkoholkonsum Reduzieren Und Trotzdem Ein Glas
- Knieführungsorthese | Knieführungsorthesen ohne Extensions-/ Flexionsbegrenzung
- R6 Race: Voller Fokus Auf Die Rennstrecke