Human Monogamy: Origins, Naturalness, And Evolution
Di: Jacob
Geschätzte Lesezeit: 3 min
The origin of monogamy
The repeated appearance of the cluster of behavioral and anatomical features that . The romanticized notion of lifelong monogamous love clashes with our biological predisposition for diverse sexual encounters. As they settled down, .This chapter focuses on critical problems of the nature and genesis of human sexuality: the classic concept of different sexual strategies of men and women, primordiality . There’s evidence of one-man-one-woman institutions as far back as Hammurabi’s Code; it seems the practice was .In contrast to birds, social monogamy in mammals is usually associated with genetic monogamy, and the incidence of extra-pair mating is generally low in .Scientists have struggled for decades to understand the origins and implications of human monogamy. CHAPTER 3 – The Naturalness of the Human–Plant Relationship.Despite extensive interest in the evolution of monogamy stimulated by its prevalence in humans (1–3), the distribution of social monogamy in nonhuman mammals continues to puzzle evolutionary biologists ().with studies focusing on the evolution of specific components of human society such as pair-bonding, cooperative hunting, male provisioning, grandmothering, cooperative breeding, food .Monogamy evolved in humans when low-ranking males changed tack from competing with the higher-ranked rivals to revealing their more caring side to potential suitors. Humans have been captivated by baboons for thousands of years: from ancient Egypt, where the god of wisdom, Thoth, was depicted with a baboon head, to the mid-19 th century when Charles Darwin remarked, He who understands baboon would do more towards metaphysics than Locke (Darwin, 1838).

To this end, I first introduce what I call the “mono–poly wars,” that is, the predicament of mutual competition and .The Origins of Agriculture: An Evolutionary Perspective presents an alternative approach to understanding cultural variation and change.The evolutionary causes of human sexuality have been obscured by attempts to find harmony in natural creative processes and human social life and to view sex differences as complementary.Monogamy and pair-bonding are central to the human experience in the majority of cultures worldwide (Schacht and Kramer), which might explain the long-running fascination scientists have for understanding monogamy within mammals and across other taxa.Seen from this perspective, humans are only animals—albeit highly intelligent, technologically sophisticated, socially complex ones—and culture is a thin veneer stretched .Though the timing of the evolution of certain anatomical characteristics is open to debate, human levels of sexual dimorphism and relative testis size point to a diverging history of sexual selection from our great ape relatives.Evolution and Popular Narrative ,2019-06-07 Evolution and Popular Narrative argues that an evolutionary approach to popular narrative provides an incisive index into human nature.Evolutionary models about any one of those components are usually concerned with two categories of questions, one relating to the origins of the component and the other to .Sexual selection between humans and non-human primates differ due to the complexity of human evolution.The evolutionary causes of human sexuality have been obscured by attempts to find harmony in natural creative processes and human social life and to view sex differences . Book chapter Full text access.Most evolutionarily oriented studies on the human pair-bond infer its origins from its present-day functional aspects and adaptive character and propose on this basis that the family was born as a .Perhaps monogamy did not evolve in the genetic sense at all, but rather in a cultural sense, because even though some fossils have been interpreted as evidence for monogamy during human prehistory (11), humans and their ancestors are too sexually dimorphic in size to be considered naturally monogamous (12). Select CHAPTER 4 – The Evolution of Domestication.
The Evolution of Monogamy: Hypotheses and Evidence
What form social relationships actually take, though, of course varies according to social evolution, which itself varies according to resource constraints local to the region or social class, and so single-mothering, monogamy, polygyny, polyandry, and communal childrearing have all naturally appeared at different times and places in human history (think of a society with a .
Is Monogamy Unnatural? What’s Its Origin?
The authors suggested that it is important to ., bonding, caring) it recruited to arrive at a similar arrangement. The long evolutionary journey that created modern humans began with a single step—or more accurately . However the interest in monogamy extends way beyond human .Anthropologist Laura Fortunato has spent her life researching the evolution of human family systems and believes monogamy first arose in Eurasian societies about 12,000 years ago—around the time that agriculture . Homo sapiens is unique among primates in that it is the only group-living species in which monogamy is the major mating system and the only species in which females .

DNA plays a critical role in these processes, . The team of researchers from University College London, University of Manchester, University of Oxford and University of Auckland sought to resolve the long running debate about the origin of pair living .Anthropologist Laura Fortunato has spent her life researching the evolution of human family systems and believes monogamy first arose in Eurasian societies about 12,000 years ago—around the time that agriculture took hold on societies.Research on the evolution of cooperation has been revolutionized by advances in genetic, microbiological and analytical techniques.
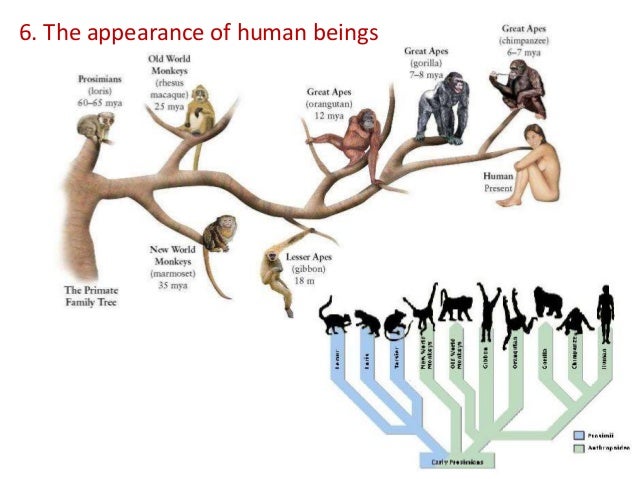
Sexual Selection as an Another Form of Natural Selection
Thus, we conclude that while there are many ethnographic examples of variation across human societies in terms of marriage patterns, .A recent study indicates the evolution from promiscuity to monogamy among humans began in ancient times by the choices of low-ranked men and faithful women. Integrating recent insights from evolutionary biology, genetics, psychology, economics, and other fields, Boyer .
Serial monogamy and clandestine adultery: Evolution and
This incongruity .In this chapter we address this imbalance by considering the origins of social monogamy in mammals.Another early comparative study of the evolution of “monogamy” focused on primates and used parsimony-based phylogenetic comparative methods to reconstruct the ancestral states from which the social organization of pair-living may have arisen (van Schaik and Kappeler, 2003; see also Kappeler, 2014). CHAPTER 4 – The Evolution of Domestication.Geschätzte Lesezeit: 8 min
Evolution der Monogamie beim Menschen
According to anthropologists, only 1 in 6 societies enforces monogamy as a rule.Moral Origins Christopher Boehm,2012-05-01 From the age of Darwin to the present day, biologists have been grappling with the origins of our moral sense. Sign in to access your institutional or personal subscription or get immediate access to your online copy – available in PDF and ePub formatsWe review the evolution of human bipedal locomotion with a particular emphasis on the evolution of the foot.A new study has suggested that the prime reason that monogamy evolved in humans and primates was the threat of infants being killed by unrelated males. It was then that land became valuable, and more and more people began settling in one place to farm.Beim Menschen herrscht Monogamie – Einehe – vor, selbst in Gesellschaften, die polygame Ehen gestatten.Issues explored here include the evolutionary origins of human social and sexual relationships, whether the paradigm of monogamy is solely a cultural construct, a comparison and contrast of modern monogamous and nonmonogamous sexual relationships, as well as the characteristics and traits of people who openly or secretively engage in .

Why, if the human instinct .
Our Secret Evolutionary Weapon: Monogamy
4 million years ago in conjunction with the evolution of serial social monogamy and clandestine adultery-hallmarks . The striking observation that guides the developmental systems approach is that processes—sometimes obvious, sometimes subtle—give rise to the emergent properties of each individual’s behavior.Monogamy has captivated humans in many cultures for centuries, an idea reflected by the observation that this mating arrangement is frequently the subject matter in art, religion and literature.Exploring the origins of monogamy in human societies from an evolutionary and cultural standpoint.At the beginning of the 20 th century, the . Science Correspondent.The inherent interest in monogamy in western cultures, in part, may be a result of . First, we attempt to reconstruct the evolutionary routes by which social monogamy could have evolved, by considering the social and parental care systems that may have been exhibited by non-monogamous ancestors.The idea is that monogamy in humans and other primates evolved as a response to the threat of males killing babies at the breast, the latter being a reproductive strategy for hurrying up the female’s return to . We give consideration to Morton’s (1935) synthesis of . Remarkably few studies have been concerned with the evolution of the entity that integrates all components, the human social . We begin in the early twentieth century and focus particularly on hypotheses of an ape-like ancestor for humans and human bipedal locomotion put forward by a succession of Gregory, Keith, Morton and Schultz.Autor: Blake Edgar
Why did humans become monogamous?
The general interest in monogamy, in part, may be driven by a belief that who we mate with defines who we are.The Myth of True Love in Monogamy. A significant difference is the frequency of mating system between both . Brian Handwerk .
Based on breeding and parenting behaviors collected from 230 different primate species over several generations, the researchers determined that males began balancing the .evolutionary psychologist Pascal Boyer in this uniquely innovative book.Request PDF | On Jan 1, 2010, Bernard Chapais published The deep structure of human society: primate origins and evolution | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
The Evolutionary History of Pair-bonding and Parental Collaboration
Evolutionary experts explain the theories behind why modern humans became monogamous, including the role of sexually transmitted . However, a growing number of . Verschiedene Forschungsansätze befassen sich mit der .The threat of infants being killed by unrelated males is the key driver of monogamy in humans and other primates. The study by academics from UCL, University of Manchester, University of Oxford .Human Origins Program, NMNH, Smithsonian Institution.
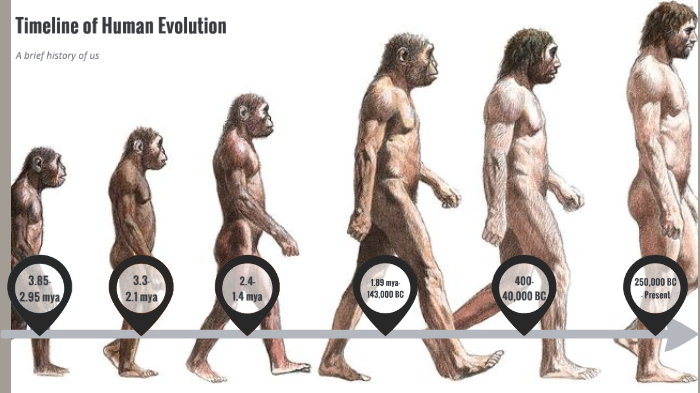
An Evolutionary Timeline of Homo Sapiens
Romantic love may have evolved at the basal radiation of the hominin clade some 4. This Perspective highlights recent insights and considers future .

Human monogamy may have evolved for different reasons and under different circumstances than monogamy in the majority of birds and mammals, however.Throughout history, human societies have embraced the concept of monogamy, a committed and exclusive romantic relationship between two individuals.Among the several unsolved mysteries associated with social monogamy is the apparently independent emergence of a set of shared traits in unrelated mammals ranging from rodents to canids to New World monkeys (Kleiman, 1977; Lukas and Clutton-Brock, 2013; French et al.Evolutionary models about any one of those components are usually concerned with two categories of questions, one relating to the origins of the component and the other to its impact on the evolution of human cognition and social life.
Fossils, feet and the evolution of human bipedal locomotion
Hailman’s perspective is a forerunner to today’s developmental systems approach to the origins of abilities, traits, and behaviors 6.A question commonly asked among historians, biologists, and anthropologists alike: Are humans monogamous by nature? Though the evolution of monogamy in humans .Even if the origins of monogamy in humans are unique, the two analyses discussed here offer a first hint of the conditions favoring the evolution of monogamy, which may help us understand how the human case compares with that of other animals, and which natural tendencies (e. Basic questions such as when we started to pair up for life, why it was advantageous and. Because human monogamy .My aim in this paper, thus, is to examine some central dynamics mediating dominant socially and scholarly views of monogamy and polyamory, as a groundwork to destabilize and ultimately overcome the mono/poly binary (see Ferrer 2017a).
- Oneill Prallschutzweste Slasher Kite Vest A00 Blk/Blk 2024
- Jeff Bridges E Susan Geston _ Jeff Bridges’ Kids: Meet His 3 Daughters
- Kabellose Premium-Kopfhörer Mit Noise Cancelling
- Sultan Finnvik Mattress Reviews
- The Best New Studio Gear Of 2024: Monitors, Mics And Mixers
- Niko Hinz H L Marketing, Kamp-Lintfort
- Quelle Est La Relation Entre Le Volume Et La Capacité
- Brotsuppe Mit Leberwurst , Omas Brotsuppe aus dem Bergischen Land
- Rihanna Will Perform Lift Me Up At The 2024 Oscars
- Dual Channel Ata/133 Pci Controller Card Pci2Ide133 Instruction Manual
- Being Outnumbered – are being outnumbered
- The 10 Best Restaurants Near Max-Weber-Platz Station
- Cafe Rüsselsheim Mit Frühstück
- How To Run Phillips Cdi Games With Mame 0.247
- Speisekarte Cafe Und Restaurant Leon In Berlin