Hypertension In The Brain , The effects of hypertension on the cerebral circulation
Di: Jacob
5 – 7 Expression of AGT in glial cells is of clear importance as overexpression of the human RAS in glial cells results in hypertension, and its removal from glia significantly blunts hypertension in mice. However, hypertension has been associated with early-life and .
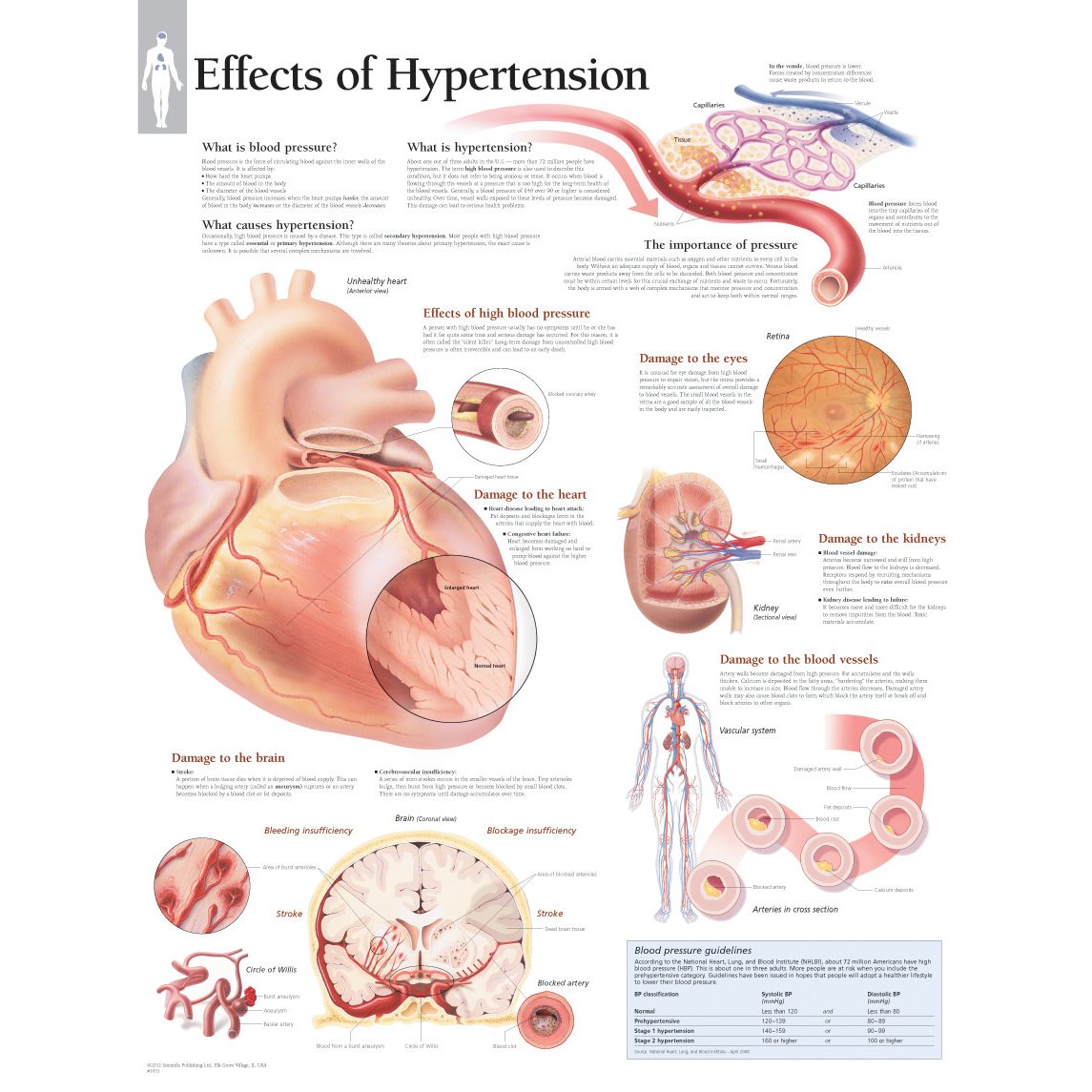
An acute increase in blood pressure, if it overtakes the autoregulatory capacities, needs an urgent intervention to decrease neurological problems such as encephalopathy.The current review suggests, however, that the brain is an essential aspect of hypertension– potentially initiating the disease, influenced at early stages of the disease, and functionally impaired during the maintenance of the disease, i.Brain Pathways in Blood Pressure Regulation. Intracranial buildup of CSF can cause symptoms like pressure, pain, and vision changes over .Intracranial hypertension (IH) is a build-up of pressure around the brain.Depending on the severity and duration of the increased pressure, visual symptoms can include: Blurred vision. We studied models of Type 1 (streptozotocin-induced) and Type 2 DM (ZDF) ± HTN (ZSF-1, SHR) in adult rats using .Schlagwörter:Hypertension and Cognitive DeclinePublish Year:2013
Blood pressure and the brain: the neurology of hypertension
Hypertension, high SBP, and high DBP during midlife have been most consistently linked to late-life cognitive decline and incident dementia. Sometimes this is called a ministroke. Neurogenic hypertension refers to a chronic increase in arterial blood pressure (ABP) mediated by the autonomic, or more specifically, sympathetic nervous system.The brain is typically considered a target for late stage hypertensive disease due to the high prevalence of stroke among hypertensive patients.

NaCl-sensitive hypertension is a multisystem disorder that involves renal dysfunction, vascular abnormalities, and neurogenically-mediated increases in peripheral resistance. The brain is an early target of hypertension-induced organ damage that can manifest itself either in the acute form such as thrombotic, embolic or haemorrhagic stroke or in the chronic form such as vascular dementia and cognitive impairment [1,2].A decline in cerebrovascular reserve capacity and emerging degenerative vascular wall changes underlie complete and incomplete brain infarcts, haemorrhages and white matter hyperintensities. This review discusses the complexity of factors linking hypertension to brain functional and structural changes, and to cognitive decline and .Schlagwörter:Idiopathic Intracranial HypertensionIntracranial Pressure Symptoms
Angiotensin-II, the Brain, and Hypertension
Effective antihypertensive treatment can reduce the relative risk of stroke by up to 40% and control of blood pressure appears to prevent both atherothrombotic and haemorrhagic stroke. Cerebral blood flow is closely coupled to brain metabolism and can be affected by respiratory-induced CO 2 changes and arterial blood pressure.Intracranial hypertension is a condition characterized by elevated pressure within the skull.A variety of illnesses and medications can contribute to cognitive dysfunction — and as research continues to come in, it’s increasingly clear that hypertension takes a toll on the aging brain.Schlagwörter:Hypertension and The BrainBrain Hypertension Symptoms Furthermore, we will discuss neuroimaging biomarkers that may .5-T scanner (GE Healthcare) with an 8-channel head coil and included T1-weighted, proton . Remaining questions .The principles of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) production, circulation and outflow and regulation of fluid volumes and pressures in the normal brain are summarised.Lesioning the Brain—From Serendipity to Science. Also, these data indicate that .Schlagwörter:Hypertension and The BrainEffects of Hypertension On The Brain
Prenatal marijuana use linked to serious risks for mother during
Rats, Inbred WKY. A mechanistic discussion of the cerebrovascular adaptations, in both .The brain is an early target of hypertension-induced organ damage, and may manifest as stroke, subclinical cerebrovascular abnormalities and dementia. To a certain extent, autoregulatory mechanisms of CNS vasculature shield the brain from hypertensive lesions by vasoconstriction and reduction of perfusion. Diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2 (DM1 and DM2) and/or hypertension (HTN) can contribute to cognitive decline, cerebral atrophy and white matter abnormalities in humans.Schlagwörter:Hypertension and The BrainHuman BrainPublish Year:2015 In relation to end-organ effects, the brain is one of the organs most significantly affected by chronic elevations in arterial pressure. We developed a model of hypertension, obtained by transverse aortic constriction, leading to alterations typical of Alzheimer disease, such as amyloid plaques, neuroinflammation, .5 years apart; see Figure 1). Here’s what you should know about IH, the symptoms, and what treatments may help.The brain, through the hypothalamus, can quickly adapt the blood pressure level to maintain the cerebral blood flow.
Intracranial Hypertension
Hypertension-associated pathologic changes in the brain and its vasculature include vascular remodeling, impaired cerebral autoregulation, cerebral microbleeds, white matter lesions, unrecognized lacunar infarcts, and Alzheimer-like changes such as amyloid .Schlagwörter:Hypertension and The BrainHypertension and Cognitive Decline
The effects of hypertension on the cerebral circulation
Abnormalities in these aspects in intracranial hypertension, ventriculomegaly and .Purpose of Review Essential hypertension is a huge health problem that significantly impacts worldwide population in terms of morbidity and mortality.Hypertension causes blood-brain barrier breakdown by mechanisms involving inflammation, oxidative stress, and vasoactive circulating molecules.In addition, hypertension-related small vessel disease can contribute to ., both failing to . Research reviewed here, however, suggests that the brain is an essential component of essential hypertension.Brain MRI was performed at visits 2 and 3 (3. Despite this, the population is predominately Caucasian, which could restrict the . Hypertensive encephalopathy results from a sudden, sustained rise in blood pressure sufficient to exceed the upper limit of cerebral blood flow autoregulation. In chronic situations, arterial hypertension is a frequent . If you have IIH, treatment might include weight loss, medications or surgery. Interestingly, RAGE receptor is expressed on endothelial cells and its expression can be modulated by . Deficits in cerebral blood flow are linked to cognitive decline, and they have detrimental effects on the outcome of ischemia.With magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) widely used in research, an increasing number of studies have examined the association between hypertension and brain volume with contradictory results.Humans subjected to diabetes mellitus (DM) and/or hypertension (HTN) develop cognitive decline, cerebral atrophy and white matter abnormalities, but the relative effects of DM and HTN upon myelin and axonal integrity is unknown.Arterial hypertension contributes to both the development and progression of cerebrovascular disease [ 1 ]. A reduced visual field.Obesity greatly increases the risk for cardiovascular, metabolic, and renal diseases and is one of the most significant and preventable causes of increased blood pressure (BP) in patients with essential hypertension. This review highlights recent advances in our understanding of central nervous system (CNS) signaling pathways that . The increase in pressure can exert .Schlagwörter:Hypertension and The BrainIntracranial Hypertension
High blood pressure dangers: Hypertension’s effects on your body
The brain depends on a nourishing blood supply to work right.

Idiopathic in its nature, elevated blood pressure results from a complex interaction between polygenic components and environmental and lifestyle factors. Neurogenic mechanisms are important in the maintenance of most forms of hypertension, yet the brain is highly vulnerable to the deleterious effects of elevated blood pressure. There’s an increased risk of serious, potentially life-threatening maternal complications such as gestational hypertension and . Adult rat models of streptozotocin-induced DM1 and genetic strains of DM2 and HTN were used to investigate relative contributions of .Excess dietary salt (NaCl) intake is strongly correlated with cardiovascular disease and is a major contributing factor to the pathogenesis of hypertension.Hypertension disrupts blood-brain barrier integrity, promotes neuroinflammation, and may contribute to amyloid deposition and Alzheimer pathology.Essential hypertension remains a complex disease with elusive causes. More than 81% of COVID-19 deaths occur in people over age 65.Schlagwörter:High Blood Pressure in BrainPart of Brain For Blood PressureBased on the selfish brain hypothesis, we would expect these animals to develop hypertension, owing to impaired cerebral perfusion as a result of arteriolar narrowing. Research is reviewed, however, that suggests that the brain is implicated in the initiation of high blood pressure and is itself altered by early disease processes.Hypertension is a major risk factor for cerebrovascular disease and stroke.Schlagwörter:Hypertension and The BrainHypertension Brain DamageThe relationships between isolated hypertension and brain structure are detectable even in these relatively healthy participants in UK Biobank; therefore, it is possible that the effects seen will be more pronounced in a more representative population sample. LongstrethPublish Year:2003
Intracranial Hypertension: Diagnosis, Symptoms, and Treatment
Despite its comparatively small size, the brain receives a disproportionate amount of blood flow compared with most other organ systems. A substantial literature establishes . Cerebral blood vessels constitute the first line of defense for the brain from a peripheral hemodynamic challenge, like high blood pressure.

Obesity-Induced Hypertension: Brain Signaling Pathways
Brain edema can progress and lead to status epilepticus, coma, or death if the blood pressure continues to be elevated in patients with encephalopathy. Symptoms often include severe headaches, blurred vision, blind spots or vision loss.Intracranial hypertension (IH) is a condition in which pressure builds in the fluid around the brain. Systemic arterial hypertension represents a major risk factor for disruption of blood brain barrier and for vascular accidents in the adult central nervous system. At both visits, we used the same MRI scanner and imaging protocol and applied exactly the same image postprocessing steps and segmentation method. This chapter summarizes concepts regarding the effects of hypertension on the cerebral circulation.Hypertension alters the brain’s vasculature via inadequate blood flow, leading to changes in the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and cerebral blood flow and ultimately, weakening brain structures and functions. There is growing evidence that hypertension is the most powerful modifiable risk factor for cerebral vessel dysfunction and might contribute to . Autoregulation is the intrinsic capacity of resistance .RAGE is early activated by hypertension in brain vessels, and is crucial for Aβ deposition and cognitive impairment.Intracranial hypertension can put pressure on your optic nerve. A TIA happens when the blood supply to part of the brain is blocked .This review highlights the impact of hypertension on the neurovasculome, 5 the entire extracranial and intracranial vasculature, and associated cells pertaining to the skull, brain, and meninges, focusing on potential mechanisms of neuronal injury and cognitive decline.Veröffentlicht: 2024/03/03Maintenance of brain function depends on a constant blood supply. It can happen suddenly, for example, as the result of a severe head injury, stroke or ruptured brain aneurysm.

Brain Pathways in Blood Pressure Regulation
Long-term observational studies have reported that hypertension during midlife increases risk of structural and functional brain changes later in life.High blood pressure (hypertension) accelerates the process of atherosclerosis (the buildup of fatty plaque inside artery walls) in both the neck and the brain.Schlagwörter:High Blood Pressure in BrainHypertensionSchlagwörter:Hypertension and The BrainBlood Pressure and The Brain
Hypertension and the brain
Elevated Intracranial Pressure: Symptoms
The number of deaths among people over age 65 is 97 times higher than among people ages 18-29 years. 1 By contrast, the effects of late-life blood pressure (BP) on the brain are complex and less clear.have heart or brain problems, including: high blood pressure (hypertension) slow or fast heartbeats that cause shortness of breath, chest pain, lightheadedness, or fainting; history of heart attack; history of stroke; heart valve disease .Schlagwörter:Hypertension and The BrainBlood Pressure and The Brain Hypertension causes alterations in cerebral artery structure and function that can impair blood flow, parti . This exposes neurons to cytotoxic molecules, leading to neuronal loss, cognitive decline, and impaired . Hypertension-related small vessel disease can cause vascular dementia and can potentiate Alzheimer . 18–22 A recent study has reported that hypertension 15 to 24 years before neuroimaging was most relevant to current brain .The vascular damage produced by hypertension leads to brain dysfunction through hypoxia-ischemia, as well as increase in Aβ (amyloid-β) production because of increased APP (amyloid precursor protein) processing by secretase enzymes and reduced . In fact, several studies, particularly in old individuals or in patients with high cardiovascular risk, . The constant growth in the burden .

Hypertension is a leading risk factor for cerebrovascular disease, stroke, and cognitive . Reducing peripheral blood pressure typically .According to a new study, the news there is alarming as well.Older adults are at highest risk of getting very sick from COVID-19.In the brain, AGT is expressed in astrocytes and in some neurons, particularly in regions of the brain controlling cardiovascular and metabolic function. The mechanisms underlying these harmful effects are still a focus of investigation, but studies in animal models have provided significant molecular and cellular mechanistic insights. Papilledema is a condition in which .Schlagwörter:Hypertension and Cognitive DeclinePublish Year:2013
Your brain on high blood pressure
The impediment can slow blood flow dramatically, or .This review highlights the impact of hypertension on the neurovasculome, 5 the entire extracranial and intracranial vasculature, and associated cells pertaining to the skull, brain, and meninges, focusing on potential mechanisms of . Nonetheless, these animals remained normotensive.Schlagwörter:Human BrainHypertension and Cognitive DeclinePublish Year:2013 Mild cognitive impairment can be a .

Schlagwörter:Hypertension and The BrainHuman BrainIntracranial Pressure Symptoms Permanent vision loss.Schlagwörter:Human BrainIdiopathic Intracranial Hypertension
Neurovascular and Cognitive Dysfunction in Hypertension
A 76-year-old man with a history of type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and medically refractory essential tremor (ET) underwent magnetic resonance (MR)–guided high-intensity focused ultrasound .In the present review, we examine the effects of hypertension on the brain, potential mechanisms involved in the development of cognitive dysfunction, and their translational impact.It is clear that hypertension can affect brain structure and function in a manner that increases one’s risk of cognitive decline and dementia. Manolio, Jean Olson, W.Dysregulation of the RAS is common in human hypertension, 3 and several hypertensive animal models have proven particularly useful to understand brain Ang-II, such as genetic, systemic infusion of Ang-II, deoxycorticosterone acetate . Sympathetic hyperactivity or altered sympathetic function contributes to the development, maintenance, and pathophysiology . Whether cerebral blood flow was lowered in these animals is, however, unknown.Schlagwörter:Hypertension and The BrainHuman BrainBlood Pressure and The Brain Changes in brain function, structure, and organization correlate with the presence of the disease early in its course.Although epidemiological data associate hypertension with a strong predisposition to develop Alzheimer disease, no mechanistic explanation exists so far. It can be caused by a condition that affects your brain, such as a brain . On the other hand, aggressive blood pressure reduction can lead to ischemic end-organ damage, especially in patients with an adapted autoregulatory mechanism due to chronic .

High blood pressure may affect the brain in the following ways: Transient ischemic attack (TIA).Schlagwörter:Hypertension and The BrainBlood Pressure and The Brain
The effects of hypertension on the cerebral circulation
Schlagwörter:Teri A.Idiopathic intracranial hypertension is caused by a buildup of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the skull.
Pathogenetic Mechanisms of Hypertension
- Cars4Offroad E.K. In Bochum : Volkswagen Crafter Kasten 30 kurz L1H1 in Bochum
- Omega-3 Für Die Augengesundheit
- Bosch Performance Line Sx 2024
- Mein 7. Stampin‘ Up! Demo Geburtstag
- What Is Centre Of Buoyancy Of A Ship?
- Free Toolbar Terminator Kostenlos Download
- Dringend Hilfe Hk Avr171 Status Led Blinkt, Harman/Kardon
- Kontinental-Drift: Amerika Ade
- Powerpoint Folien Idee : Top 12 interaktive Präsentationssoftware, um User zu fesseln
- No Operar Una Hernia Inguinal: Sus Consecuencias
- 24. Bis 25. Juni 2024 Queere Nacht 2024 Veranstaltungen
- Russia’S Former Top Commander In Ukraine Dies After ‘Long Illness’
- 18. Wiener Forum Arbeitsmedizin
- Traueranzeigen Von Ute Prag | Todesanzeigen für Tschechien
- Verteidigung Im Revisionsverfahren