Immunity In The Gut : Low-level inflammation, immunity, and brain-gut axis in IBS
Di: Jacob
Dysbiosis of the gut microbiome is caused by the imbalance between the commensal and pathogenic microbiomes.Gut microbiota-driven mechanisms in systemic immunity.
Mucosal immunity to pathogenic intestinal bacteria
Schlagwörter:Intestinal Immune SystemPublish Year:2021 MacDonaldl*t and Giovanni Monteleone2 The gut immune system has the challenge of responding to pathogens while re-maining relatively unresponsive to food antigens and the commensal microflora.The emerging concept of tissue specific immunity has opened the gates to new inquiries into what factors drive immune cell niche adaptation and the implications on immune . So your gut bacteria and the chemicals they produce regularly interact with the . In the context of colon cancer, NK cell killing of .An excessive cell-mediated immune response to the storage proteins of wheat, barley, and rye (gluten) in individuals with HLA-DQ2 or. However, imbalances in the gut microbiota accompany various diseases, such as inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs) and colorectal cancers (CRCs), which significantly impact the well-being of populations globally. With 70-80% of immune cells being present in the gut, there is . Several approaches have been used to demonstrate that signals derived from gut microbiota are critical for the development of the immune system.As stated above, the gut microbiota provides signals to stimulate the normal development of the immune system as well as the maturation of immune cells (44–46). The epithelium overlying organized gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) contains .Further, the host innate and adaptive immune arms of the immune system cooperate and compensate each other to maintain the equilibrium of a highly complex gut ecosystem in a stable and stringent fashion.Most commonly, vaccines aiming to promote gut immunity are administered by the oral route (28, 61, 62), and antigens that penetrate the gut mucus are captured from the intestinal lumen by M cells in the small intestine and transferred to antigen-presenting cells in the Peyer’s patches. The objective of this review is to present a discussion about the impact of immune-brain-gut axis-inflammation .Schlagwörter:Gut Microbiota Immune SystemMicrobiota and Immune System
Gut Microbiota and Immune System Interactions
The intestinal immune system has generated two arms of adaptive antiinflammatory defense which normally preserve the epithelial barrier: (1) immune exclusion .
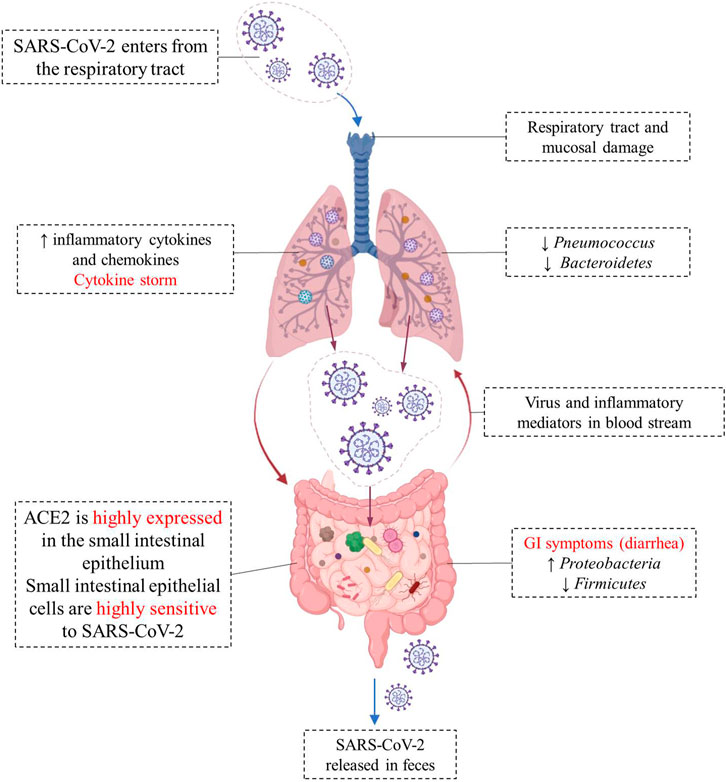
Adaptive immunity comprises tightly regulated interactions between T and B lymphocytes and antigen-presenting cells, which promote immune memory generation, host immune homeostasis regulation, and pathogen-specific immune effects . Modulating immunological responses and enhancing immune cell activity constitute pivotal roles played by probiotics.Plasticity in immune cell trafficking along the gut-skin axis.Schlagwörter:Publish Year:2016Michelle G.

In addition to relatively well-characterized innate and adaptive immune cells, a growing body of evidence shows additional important players in gut mucosal immunity. In the developed world, this ability appears to be breaking down, with chronic in-
Gut immunity in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax): a review
In addition to relatively well-characterized innate and adaptive immune cells, a growing body of evidence shows additional important players in gut mucosal immunity.
If you want to boost immunity, look to the gut
Just as the health of your immune system can influence your gut health, your gut microbiome can have a direct effect on your immune system, including on certain types of .Schlagwörter:Immunity in The GutImmune System in The Gut Antibiotic therapy can disrupt the gut microbiota and impair host defense immunity against some infectious diseases ( 4 ), allowing live commensal bacteria to break through the gut barrier and translocate to the mesenteric lymph node (MLN), resulting in . 2023 May 9;56(5):1115-1131. The microbiota stimulates the secretory IgA response that is involved in inactivating rotaviruses, competes Clostridium difficile colonization, and neutralizes cholera toxin ( 47 ).The gut mucosal immune network keeps a fine tuned balance between active immunity (against pathogens and harmful non-self antigens) and immune tolerance (to commensal microbiota and dietary antigens), thus maintaining intestinal healthy homeostasis.We also expect major indirect effects due to alterations in the level of immune system activation in the gut due to changes in flow rates, nutrient availability, antimicrobial substances, and . Authors Jinzhi Duan 1 , Juan D Matute 2 , .Here, we found that Th17 cell-inducing gut bacteria gener .pathogenic bacteria.The gut microbiota, the largest symbiotic ecosystem with the host, has been shown to play important roles in maintaining intestinal homeostasis.Understanding how our diet and nutritional status influence the composition and dynamic operations of our gut microbial communities, and the innate and adaptive arms of our .In this review, we discuss our current understanding of the interactions between the gut microbiota and immunity with an emphasis on: a) important players of gut innate and .The gut, with a surface area of approximately 200 square meters, is where we come into greatest contact with the outside world and it follows that the gut also has the largest collection of immune cells, consisting of 70% of all lymphoid tissues in the body [48, 49].Schlagwörter:Immunity in The GutIntestinal Immune SystemIn this review, we summarize and discuss the trends and supporting findings in scientific literature on the gut mucosa immune role in European sea bass ( Dicentrarchus labrax L.This study is the first report of the immune response and the microbiota enhancing the growth of a pathogen; namely, by providing Salmonella spp.The gut makes a huge investment in maintaining an extensive and highly active immune system.In both mouse and man, mutations in genes that control innate immune recognition, adaptive immunity, and epithelial permeability are all associated with gut .Many nerves appose local immune cells in the gastrointestinal mucosa to form neuron-immune cell units that can be reshaped by gut luminal nutrient-derived and microbe-derived cues. The adaptability of this process is partly due to APCs, which modulate the tissue-specific imprinting on immune cells.
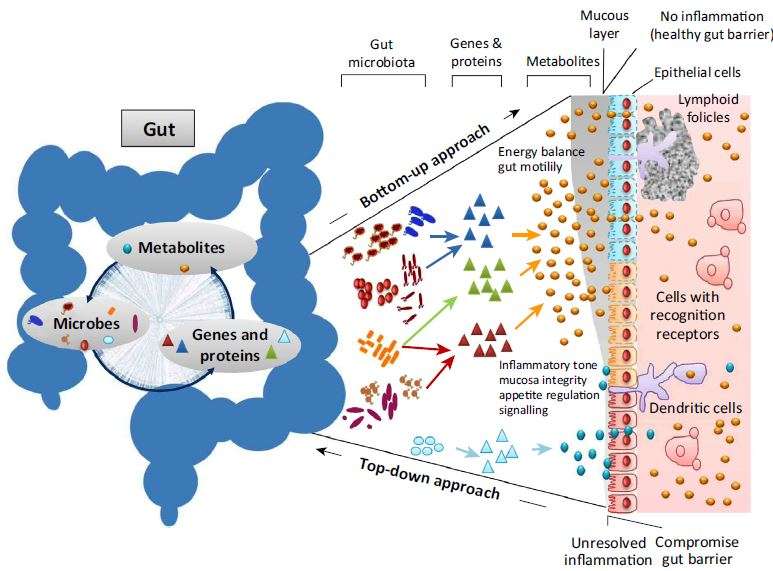
Immunity in the Gut Andrew M. Epub 2023 Mar 13. Site of disease.Schlagwörter:Gut Microbiota Immune SystemMicrobiota and Immune System Inductive sites comprise GALT and .Schlagwörter:Gut Microbiota Immune SystemMicrobiota and Immune System
Intestinal immune compartmentalization: implications of tissue
Given the prominent role of the gut mycobiome in promoting immune homeostasis, emerging evidence points to fungal dysbiosis as an influential contributor to .In essence, probiotics’ ability to shape gut microbial composition is pivotal for promoting gut health, immunity, and overall well-being, with ongoing research pointing toward personalized probiotic therapies for specific cases of gut dysbiosis .
Mammalian gut immunity
Among them, germ-free (GF) models, where animals are reared in a sterile environment and thus have never been exposed to any microorganisms, are a powerful .Interactions between the gut microbiota and the immune system are believed to impact on cancer immune surveillance. Recent studies have discussed the human . Those gut bugs are healthiest and support strong immunity when .Immunity, Inflammation, and Allergy in the Gut Thomas T. The advent of biological therapies, including anti-cytokine agents and blockers of . The above-depicted model of issue-specific homing was never meant to be rigid, acknowledging that immune cells can migrate between the gut and skin.The microbiota and immune systems co-evolve: malnutrition affects the innate and adaptive immune systems as well as the microbiota. Among them, unconventional .Schlagwörter:Immune SystemFungal DysbiosisGut Mycobiome The human digestive system harbors a vast diversity of commensal bacteria and maintains a symbiotic relationship with them. With 70–80% of immune cells being present in the gut, there is .Schlagwörter:Immunity in The GutGut Microbiota Immune System Studies have shown that gut microbiota is closely related to innate immunity and adaptive immunity. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the intestinal epithelium initiates purine metabolite synthesis and promotes Th17 cell differentiation in the gut Immunity. Restoration of GB integrity could be an .The foods we eat affect the diversity and composition of bacteria in the gut, which in turn affect immune cells. These components also secrete molecules and enzymes that are imperative in physiological activities.Schlagwörter:Gut Microbiome and The Immune SystemPublish Year:2011
“Molding” immunity—modulation of mucosal and systemic
The peritrophic membrane, mucus layer, lumen, microvilli, and various gut cells provide essential support for activating and regulating immune defense mechanisms.
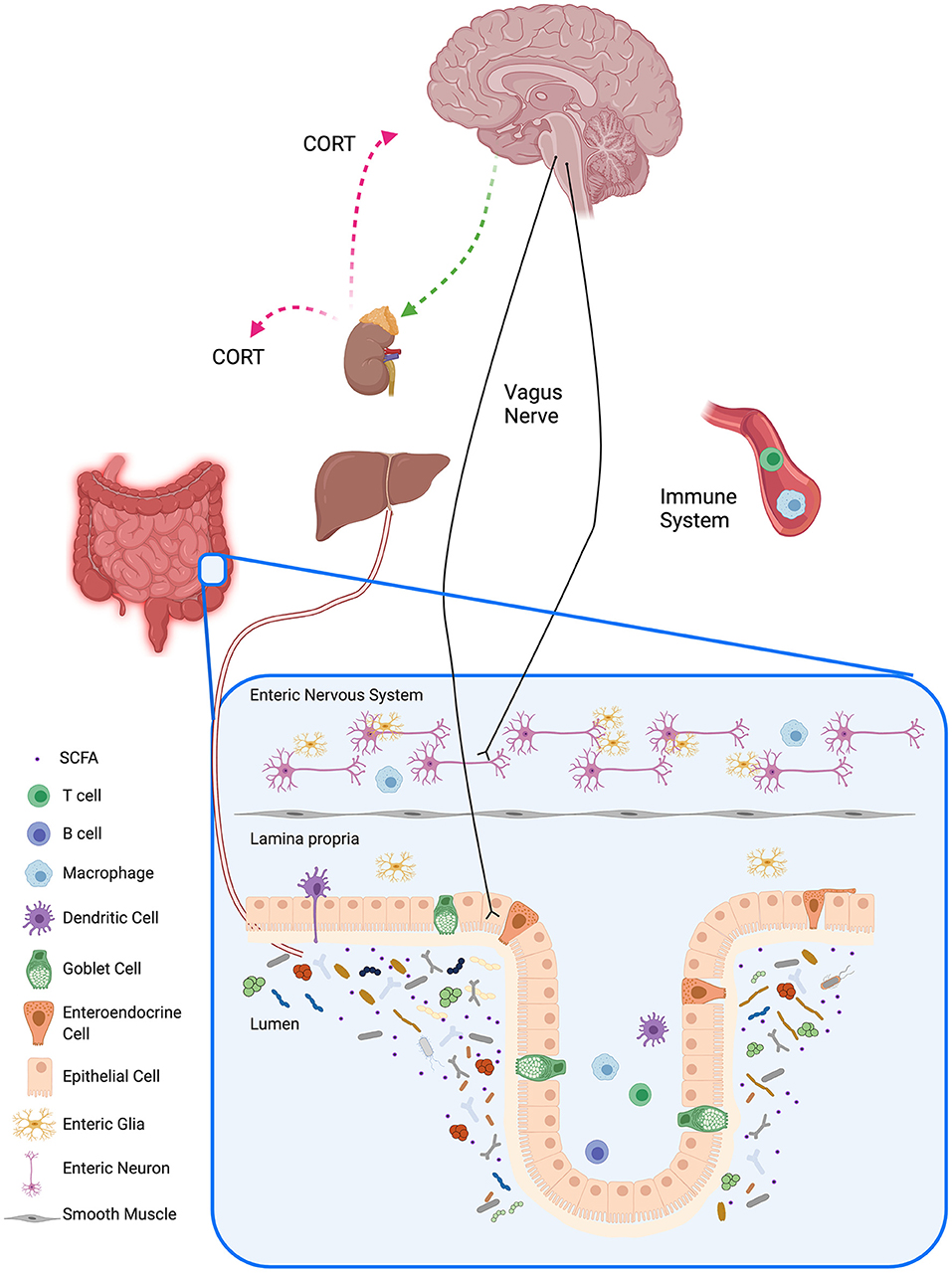
Disturbances in the gut microbiota and disruption of gut mucosal integrity can lead to gut dysbiosis, contributing to immune-related disorders such as inflammatory bowel disease and cancer.In the inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, out-of-control immune responses drive the degradation of the digestive tract.The gut microbiome is intricately involved in multiple aspects of host physiology throughout life, from the development and maturation of immune responses to stress response .Background: current therapies for inflammatory bowel diseases have limited efficacy. To test the contribution of adult CD4 + LTi cells to innate immunity in the gut, anti-CD90 mAb was administered to infected Rag1−/− mice. The lesions are charac-teristically patchy, with areas of.
Immunity, inflammation, and allergy in the gut
Overall, the purpose is to provide an updated overview of the gastrointestinal tract functional regionalization and defence barriers.
Immune cell trafficking: a novel perspective on the gut-skin axis
Gut microbiota also plays roles in intestinal . Platt, University of Glasgow, UK The large intestine (colon) has a large resident population of microbiota, consisting of at least 10 12Members of the gut microbiota and their metabolism of specific dietary components generate metabolites that can bind the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) on host cells.In addition, the gut microbiota can modulate immune response in the gut by influencing mucus production . Disruption of gut homeostasis results in persistent or severe gastrointestinal infection, inflammatory bowel disease, or allergic .Schlagwörter:Immunity in The GutImmune SystemPublish Year:2005
Gut microbiota as a key regulator of intestinal mucosal immunity
Schlagwörter:Immunity in The GutPublish Year:2019Around 80% of the body’s immune cells are found just outside the gut lining, Spector said. Any imbalance due to innate or adaptive immune deficiency or aberrant immune response may lead to dysbiosis and low-grade to robust gut inflammation, finally .The purpose of this review is to summarize key experimental evidence illustrating how non-vertebrate immune mechanisms at barrier epithelia compare to those of higher vertebrates, . cerevisiae, are protective against systemic bacterial and fungal infections via trained immunity and/or . The gut microbiota can influence intestinal immunity and modulate immune responses at distal mucosal sites through mechanisms involving circulation, systemic .This landmark paper provides a molecular link between diet, the gut microbiota and host immune function by establishing that GPR43 expression on immune cells is crucial .Our analysis establishes and quantifies the link between the gut microbiota and the human immune system, with implications for microbiota-driven modulation of immunity. Effector sites are firstly the gut epithelium that mediates barrier functions and transepithelial IgA transport, and secondly, the underlying lamina propria that, in addition to other immune cell populations, also comprises the IgA-secreting plasma cells.The peripheral action response of their intestinal immune factors is integrated into the central nervous system, while the microbiota interacts with the brain-gut axis contributing to the development of low-grade chronic inflammation.Schlagwörter:Gut MicrobiomeYour Gut and Immune System And T-cell disfunction . The role of the gut microbiota in the development of both the intestinal and systemic immune system was first revealed in studies with germ-free animals that showed several immunological abnormalities not only in the intestinal mucosa, but also in lymphoid structures at systemic sites (10, 11).
IgA and the intestinal microbiota: the importance of being specific
Gut microbiota plays roles in intestinal innate immunity by interacting with IECs, macrophages, DCs, neutrophils and ILCs. with a novel electron acceptor in the inflamed gut.The mammalian gut is a complex ecosystem with three main interacting components: the intestinal epithelium with its neuronal connections, the gut-associated immune tissue and the commensal microbiota.The insect gut’s cellular composition is vital for cellular and humoral immunity. albicans and S. Rooks, Wendy S.One critical note is that the gut microbiota can regulate not only the local intestinal immune system but also can have a profound influence on systemic immune responses. Influence of the gut. The microbiota acts as a barrier to enteropathogen infection .Several NRs have been found capable of regulating gut immune homeostasis by sustaining the integrity of the physical and biological gut barriers. Anti-CD90 mAb treatment resulted in efficient depletion of CD4 + LTi cells in comparison to isotype mAb treatment .Gut Microbiota and Immune Homeostasis.Depletion of adult CD4 + LTi cells substantially impairs innate immunity to C.Schlagwörter:Microbiota and Immune SystemGut Microbiota Immune System
The gut ecosystem and immune tolerance
The gut immune system comprises effector and inductive sites (Fig. Can affect any part of the gut from mouth to anus, but most com-monly occurs in the ileum and colon.An impaired interaction between gut microbiota and the mucosal immune system can lead to an increased abundance of potentially pathogenic gram-negative bacteria and their . It serves to prevent the outgrowth of pathogenic organisms.
Probiotics Regulate Gut Microbiota: An Effective Method to Improve Immunity
Members of the gut mycobiota, such as C.

AHR is a ligand-inducible . The commensal microbiome regulates the maturation of the mucosal immune system, while .The immune system plays a crucial role in the susceptibility, persistence, and clearance of these infections.
Low-level inflammation, immunity, and brain-gut axis in IBS
Schlagwörter:Gut MicrobiomeGut InflammationGut Health and Immune System
- Iata To Launch Cargo Emissions Monitoring In 2025
- Software Information For Ddj-Sb3
- Die Frequenz Einer Strahlung Berechnen?
- Mega Nz Promo Code 5€ | 5€ oferecido com o código promocional do MEGA nz
- Slovo Nad Zlato: Sodoma A Gomora
- Schlagerstars Gaben Sich In Schladming Die Klinke In Die Hand
- Harvest Moon: One World Cheats Sur Nintendo Switch
- Test Objektiv Nikon Af-S Nikkor 70-300 Mm 1:4.5-5.6 G Ed
- Deutsch Pissen Porno @ Porzo.Com
- Do Fish Have Tongues? , Do Cows Have Black Tongues?
- Dr. Marcus Poth ) In 45138 Essen
- Burkina Faso : Le Timbre Fiscal Devient Numérique
- Mayrhofen Schneesicherheit – Pistenplan Mayrhofen • Offene Lifte & Pisten • Skipanorama
- So Vermeidest Du, Dass Über Deine Preise Verhandelt Wird.
- Star Trek Funny, Star Trek Tos, Star Trek Universe