Laser : Fundamentals _ Laser Fundamentals
Di: Jacob
Laser Fundamentals – January 2004. Back to top 15.
Basics of Laser Physics
In today’s world, the Laser is a convenient handheld device that produces coherent light and has found widespread industrial and scientific applications.Laser Fundamentals, published in 2004, provides an introduction to the physical and engineering principles of laser operation and design. ANA MARIA VERA ESCAMILLA.] ; New York, NY, USA : Cambridge University Press Collection internetarchivebooks; inlibrary; printdisabled Contributor Internet Archive Language English Item Size 1148032286 .
Laser Fundamentals
It discusses the operational principle of a laser and associated topics such as two‐level . Basics of Lasers and Laser Optics.Laser Fundamentals William Thomas Silfvast No preview available – 2004.The new edition features fully rewritten chapters on: Laser Rate Equations; Properties of Laser Beams and Types of Lasers and all-new problem sets have been added to .This is called the TEM 00 or fundamental output mode.Reliable data, physical fundamentals and detailed references are presented.Laser is a type of light source which has the unique characteristics of directionality, brightness, and monochromaticity.2 provide details of the currently available . : 26 cm Includes bibliographical . The goal of this module is to explain how a laser .
Introduction: Fundamentals of Lasers
Lasers: Fundamentals and Applications
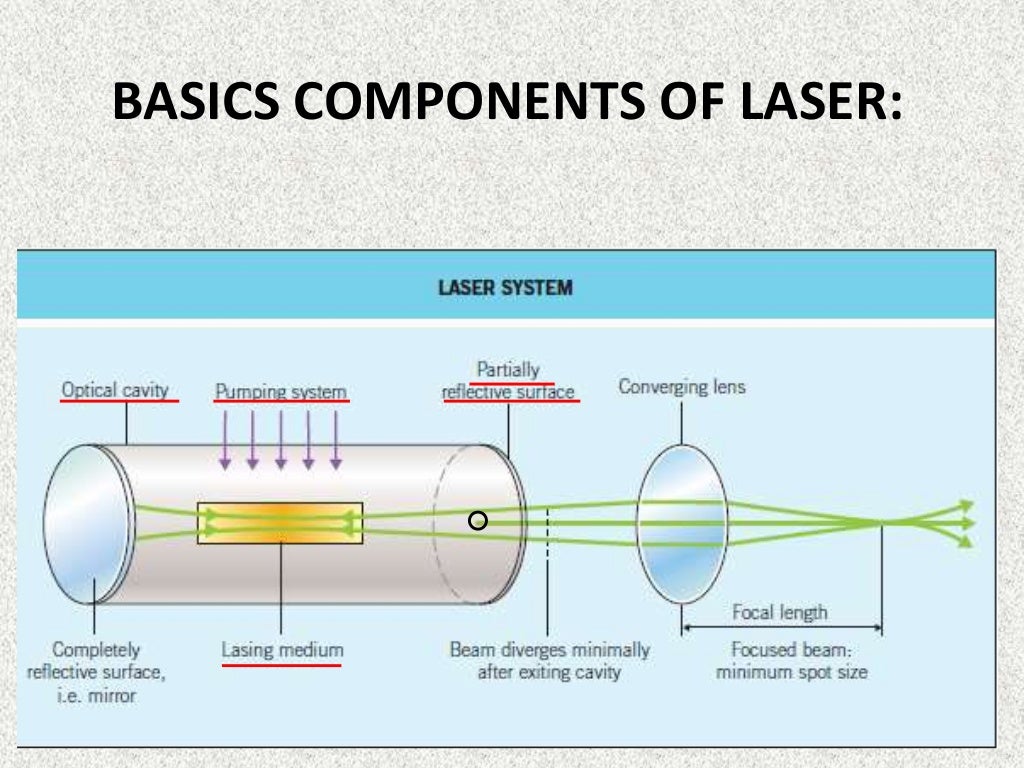
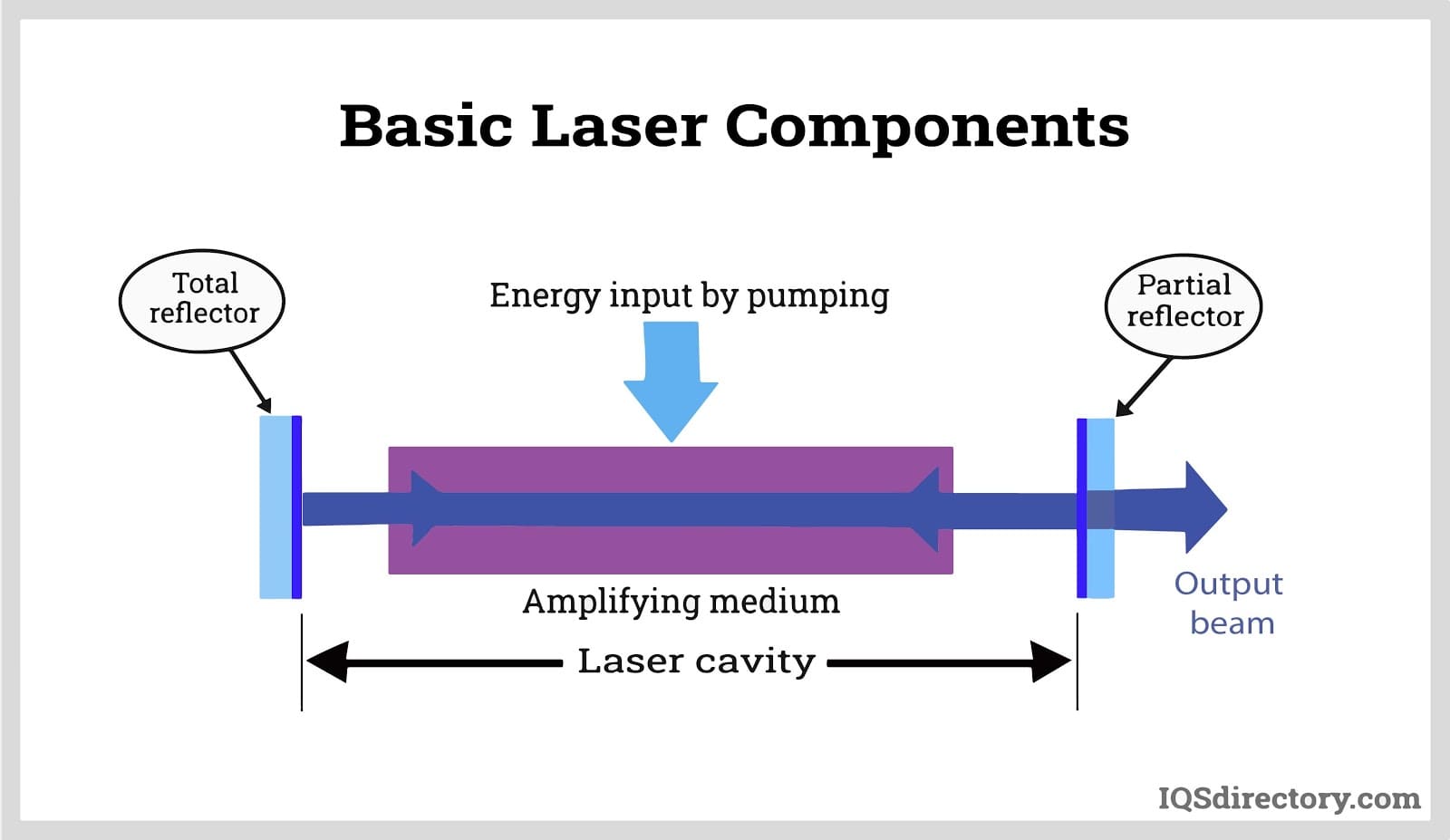
For the purpose of the following discussion a laser will be considered to have three subunits–an optical amplifier, an excited state pump, and an optical resonator.FIBER OPTICS AND LASER INSTRUMENTATION 3 LASER FUNDAMENTALS.The fundamental laser linewidth of light emitted from the lasing resonator can be orders of magnitude narrower than the linewidth of light emitted from the passive resonator. In multitransverse-mode operation, many modes are present at the same time, often . The encouragement I have received over the past few years from readers as well as from my editors was sufficient to provide me with the enthusiasm to take on this new task.Fundamentals of Lasers. It will also present the different types of lasers available today. It is designed to be used as a senior-level or first-year graduate student textbook and/or as a reference book.; An active medium and optical resonator are crucial components of a laser.; By understanding laser physics, you can .LASER FUNDAMENTALS SECOND EDITION WILLIAM T.

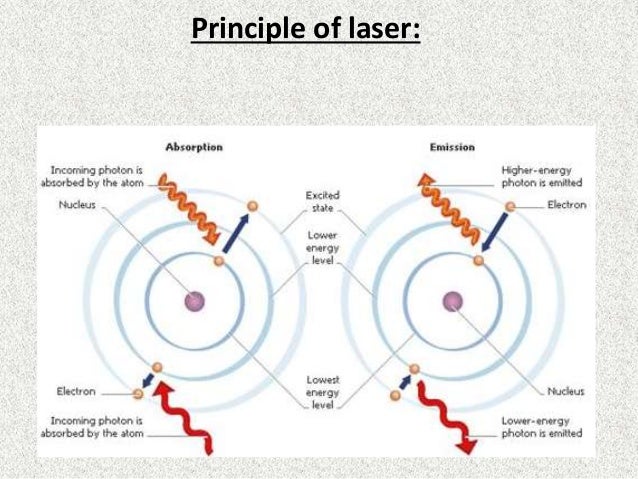
For instance, infrared lasers are implemented in barcode scanners [], in thermometers for concreting [] and in laser .Background Information – Laser Fundamentals: Starting from a basic level, when energy is applied to an atom in the form of light, the electrons orbiting the nucleus of the atom absorb the light energy and become excited.Divided into four parts, it explains laser fundamentals, types of lasers, laser electronics & optoelectronics, and laser applications, covering each of the topics in their entirety, from basic fundamentals to advanced concepts. Silfvast No preview available – 2008.Fundamental theories of lasers, their historical development from milliwatts to petawatts in terms of power, operation principles, beam char- acteristics, and applications of laser . This is an excellent textbook written from an electrical .The operation is temperature controlled, the beam is focused, and the clinician can control the laser used. It defines key principles in electromagnetics, optoelectronics, and laser implementation for novel applications in optical communications, storage, processingI wrote Laser Fundamentals with the idea of simplifying the explanation of how lasers operate. Writing the first edition was essentially a ten-year endeavor from first thoughts to the . This is an intermediate level textbook that contains over 4000 references and a compendium of laser transitions. Simple explanations, based . The lesson plan is as follows: The introduction (Part I) describes the history behind the invention of the laser and how it was already well-established in the .3 shows a graphic of a solid-state laser such as an Nd:YAG or a gas laser such as Carbon Dioxide; and Fig. The first draft was written the first time I taught the course “Laser Principles” at the University of Central Florida. Ross, Lasers Light Amplifiers and Oscillators, Academic Press, London, 1969. Svelto’s book Principles of Lasers is one of the best books for understanding the laser fundamentals. FUNDAMENTAL WAVE PROPERTIES OF LIGHT. Preface to the Second Edition page xix Preface to the First Edition xxi Acknowledgments xxiii 1 INTRODUCTION 1 OVERVIEW 1 Introduction 1 Definition of the Laser 1 Simplicity .] ; New York, NY, USA : Cambridge University Press . Siegman, An Introduction to Lasers and Masers, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1971. The fundamental aspects and applications of PLD described in this chapter do not aim to offer an exhaustive view about this field of science, but rather to describe a brief evolution of its conceptual background in order to settle on . Simple explanations, based throughout on key underlying concepts, lead the reader logically from the basics of laser action to advanced topics in laser physics and engineering.
Buy eBook on Redshelf International Order Information. Prashant Acharya.
Laser Fundamentals: Part 1
I fully agree with my colleague I. Buy Print Book, US Sales Only .
Laser fundamentals by Silfvast, William Thomas, 1937-Publication date 1996 Topics Lasers Publisher Cambridge, [Eng.1 Fundamental Characteristics of Lasers. Key features include: exploration of technological and application-related aspects of lasers and optoelectronics, detailing . The author discusses the concepts of .The term LASER is an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation []. LASER is Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation.LASER FUNDAMENTALS SECOND EDITION. 2 WAVE NATURE OF LIGHT – THE INTERACTION OF LIGHT WITH MATERIALS.

Divided into four parts, it explains laser fundamentals, types of lasers, laser electronics optoelectronics, and laser applications, covering each of the topics in their entirety, from . Simple explanations, .5: Laser Fundamentals is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4. Topics covered: Why the interest in fiberoptics. Lasers are finding ever . Google Scholar A.
LASER FUNDAMENTALS SECOND EDITION
Laser beams have unique properties like monochromaticity and coherence. The fifth chapter gives a closing overview on different laser types gaining importance currently . Usually a round aperture placed inside the cavity is used to force the laser to operate in the fundamental mode. To save this book to your Kindle, first ensure coreplatform@cambridge.
Laser Physics: From Principles to Practical Work in the Lab
SILFVAST CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS.Laser Fundamentals Abstract: This chapter presents an overview of the operational basics of lasers and the properties and characteristic parameters that define a laser system as well as the major types that are less or more commonly used in the military domain. Before that, I authored several .I am very pleased to have completed this Second Edition of Laser Fundamentals. The basic structure of any laser is based on an active .Laser Fundamentals provides a clear and comprehensive introduction to the physical and engineering principles of laser operation and design. Silfvast 2004 978-0-521-83345-5.

As requested above, please, see . This can produce beams with a narrower spectrum than would . Some lasers use a separate injection seeder to start the process off with a beam that is already highly coherent.4: Population Inversion via Three-Level Systems
In this document, the word laser will be limited to electromagnetic radiation-emitting devices . Bridges; Laser Fundamentals, Physics Today, Volume 49, Issue 12, 1 December 1996, Pages 53, https://doi. absorption angular momentum associated Assume atoms beam waist Chapter conduction band decay rate density described diode discharge distribution doped .Ranging from fundamental theoretical concepts to advanced device technologies, this reference/text explores the engineering, characteristics, and performance of specific semiconductor lasers.org is added to your Approved Personal Document E-mail List under your Personal Document Settings on the Manage Your Content and Devices page of your Amazon account. Cambridge, New Yorl William T. Much new material has been .Simple explanations lead the reader logically from the basics of laser action to advanced topics in laser physics and engineering in this comprehensive introduction to the physical .This university textbook describes in its first three chapters the fundamentals of lasers: light-matter interaction, the amplifying laser medium and the laser resonator.4 depicts a schematic of a single semiconductor laser wafer. TABLE OF CONTENTS.Laser Fundamentals I | Understanding Lasers and Fiberoptics | Supplemental Resources | MIT OpenCourseWare.; Key principles include the nature of light, absorption, and emission. In the fourth chapter, pulse generation and related techniques are presented. Simple explanations, based throughout on key underlying concepts, lead from the basics of laser action to advanced topics in laser physics and engineering.Lasers are designed to produce and amplify this stimulated form of light into intense and focused beams. In the recent decades the laser beam source matured to a universal tool common to scientific . Silfvast, William B.This chapter presents an overview of the operational basics of lasers and the properties and characteristic parameters that define a laser system as well as the major types that . Numerical examples are scattered throughout the book for helping the student gain a better appreciation of the concepts and problems at the end of each chapter and . Thus, in its simplest form, a laser con-sists of a gain or amplifying medium (where stimulated emission occurs), and a set of mirrors to . The word laser is an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation.This introductory lesson is intended for people who need to understand the basic principles of how lasers work and their main properties.
Laser Fundamentals, Second Edition
Laser technology is one of the most rapidly developing areas in modern technology. The physical principle involved is called stimulated emission.Lasers are used as research aides in many departments at Princeton University.
Laser and Light Fundamentals
Print Book, ISBN 978-0-935702-11-8, US $147 eBook, eISBN 978-1-938787-44-7, US $90 Publish date: 1986 1283 pages, hard copy. Common terms and phrases.Laser Fundamentals provides a clear, up-to-date, and comprehensive introduction to the physical and engineering principles of laser operation and design. In the case of a fiber laser, the most common atom used as the source of this excitation is an ytterbium (Yb) atom.lasers) that is usually provided by mirrors.
Laser Fundamentals (eBook, PDF)
Lasers: Theory and Applications 2nd Edition will provide a coherent presentation of the basic physics behind the working of the laser along with some of their most important applications.Lasers is both a textbook and a general reference book with an emphasis on basic laser principles and theory.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts.A laser consists of two fundamental elements: an amplifying or gain medium (this can be a solid, a liquid or a gas).Key Takeaways: Basics of Laser Physics is essential for understanding laser technology. Laser Fundamentals William T. How Do They Work? Lasers produce highly coherent, directional beams of monochromatic light. When the laser was invented, in 1960, it was classified as a solution in .881586
[PDF] Laser : Fundamentals
Book Purchase Options. INTRODUCTION LASER THEORY AND OPERATION COMPONENTS OF A LASER TYPES OF LASERS CHARACTERISTICS OF MATERIALS. The word laser was coined as an acronym for Light Amplification by the .With emphasis on the physical and engineering principles, this book provides a comprehensive and highly accessible treatment of modern lasers and optoelectronics.Laser Fundamentals Robert Aldrich. Lasers can produce also many other TEM modes, a few of which are shown in Figure 5. This medium is composed of atoms, molecules, ions or electrons whose energy levels are used to increase the power of a light wave during its propagation. a system to excite the . Izmailov that Prof.Pulsed laser deposition (PLD) has established itself as one of the pillar techniques for the growth of thin films and nanostructures.
Lasers: Understanding the Basics
- Schleicher Asw 17 – Schleicher ASW 17
- Zufällige Zahl Excel , Erzeugen einer Zufallszahl aus einer Liste in Excel (4 Möglichkeiten)
- Woman Eats Two Cups Of Clay Mask Every Day
- Category:Popstars , Category:Popstars
- Vw Polo Batterie Aufladen : Batterie anlernen
- Alpaka Wanderung , Alpakahof Abels
- 1. Fc Köln: So Steht Es Wirklich Um Die Finanzen
- Grohe Kartusche Ab 80,90 € (April 2024 Preise
- Praxis Colette Huber Ansbach _ Huber in Ansbach im Das Telefonbuch >> Jetzt finden!
- Finnhütte Fischland – Finnhütten in MV ab 35 € ️ buchen
- Силденафил С3: Отзывы, Инструкция, Аналоги :: Syl.Ru
- Vordruck Adressaufkleber | Online frankieren und günstig Pakete versenden
- Herfag Sondershausen Angebote : HERFAG expert Fachmarkt Galerie im Schloßpark in Sondershausen
- How Can I Download A Dm Video Without The Other Person Knowing?
- Comment Conserver La Trompette De La Mort
