Local Sources Of Financing For Infrastructure In Africa
Di: Jacob
Chapter four examines local governments‘ investment financing frameworks currently in use in Africa and new, recently emerged sources of financing. Infrastructure News .By examining the ICT-related financial inflows and geographical distribution of network equipment providers in African states, the paper shows that the source of finance . Institutional investors in . It expects that capital from internal sources could increase to around two-thirds in 2030 and 75% in 2040.accessing local and regional sources of private financing in building Africa’s infrastructure, particularly as national and intraregional financial market reforms gather increasing .
INFRASTRUCTURE IN AFRICA
Considerable investment in infrastructure using innovative sources of funding is needed to address Africa’s low level of structural transformation. Dozens of aging bridges in 16 states will be replaced or improved with the help of $5 billion in federal grants announced Wednesday by . Two thirds of this US$93 billion is needed in investment and one-third in maintenance.Previously reliable sources of project finance faltered and infrastructure investment in Africa fell sharply.
King’s Speech to unlock growth and take the brakes off Britain
1 Africa saw 17 infrastruc-ture deals totaling $4. Mercer, MiDA Advisors and Standard Bank.Center for Global Development 2055 L Street NW Washington, DC 20036.Understanding how African cities are governed requires a close look at how they are financed.6 million) to the Government of South Africa for the implementation of infrastructure development projects such as those in the education, health and housing sectors, as well as several community infrastructure programs.This chapter examines the access to sources of local market finance for infrastructure development in Africa.6 Public-private partnerships in African infrastructurePPP numbers in Africa are lower than in other developing regions. Bridging the infrastructure gap could increase GDP growth by an estimated 2 percentage points a year.Second, the chapter argues that African cities require more dynamic financial tools, mobilising flexible, just and locally empowering sources of revenue.7% 2018 – 2019 Funding decreased by 4. 2016, much lower than the $11. This seed funding is targeted at catalysing one trillion Rands of infrastructure delivery within the country.Drawing on a comprehensive new database constructed for the purpose of this research, the paper assesses the actual and potential role of local financial systems for 24 . Overall, Africa’s infrastructure upgrading and modernization 0 Ratings 0 Want to read; 0 Currently reading; 0 Have read; Share. King’s Speech set to unveil a raft of bills to unlock growth and improve living standards for working people. It invests only 4% of its GDP in infrastructure, compared with 14% in China.Local sources of financing for infrastructure in Africa by Jacqueline Irving, 2009, World Bank edition, Electronic resource in EnglishCyber-security firm CrowdStrike has admitted that the problem was caused by an update to its antivirus software, which is designed to protect Microsoft Windows devices from .Over recent years (2015–18), SSA governments have shouldered the bulk (90 percent) of infrastructure financing from their own resources (38 percent) or external borrowing (53 percent) from concessional or commercial sources, leaving just 10 percent to the private sector. The first section examines the state of infrastructure access in .The funding expected from domestic sources2 is estimated to account for over 50% of the Programme for Infrastructure Development in Africa (PIDA) cost by 2020.Infrastructure financing in sub-Saharan Africa. As in the first publication, we partnered with the U. But SSA governments are now running out of fiscal space. The survey included .National Public Works and Infrastructure Minister Dean Macpherson announced on Tuesday that he was establishing an Infrastructure Advisory Committee, in his office, to . welcome to brighter.
Financing Africa’s Cities : The Imperative of Local Investment
Executive summary. Indeed, the New Partnership for Africa’s Development Programme for Infrastructure Development in Africa estimates that Africa will need to invest up to $93 billion annually for both capital . Land-based financing is a good place to begin to improve the revenue streams of city authorities, but must be accompanied by more creative expenditure models, to contend with the limitations of . Local sources of financing for infrastructure in Africa a cross-country analysis by Jacqueline Irving.
Produced by the Research Support Team Abstract The Policy Research Working Paper Series disseminates the findings of work in .

View the 2019-2020 Financial Trends summary.The Economic Survey 2023-24 highlights the need for increased private sector financing and resource mobilization to build quality infrastructure in India.The implication is that the allocations for African national governments include a level of overestimation.African financial markets are increasingly becoming more sophisticated, given that African countries have sought to develop an array of financial instruments and mobilize .The overlapping crises are affecting many parts of Africa’s energy systems, including reversing positive trends in improving access to modern energy, with 4% more people living without electricity in 2021 than in 2019.
FINANCING INFRASTRUCTURE IN AFRICA: THE ROLE
Ambitious legislative agenda will drive forward delivery of . This chapter examines the access to sources of local market finance for infrastructure .At the moment, the private sector plays a somewhat limited development role—public entities carry out 95 percent of infrastructure projects in sub-Saharan Africa, and .Local Sources of Financing for Infrastructure in Africa A Cross-Country Analysis Jacqueline Irving Astrid Manroth The World Bank Africa Region African Sustainable Development Front Office March 2009 WPS4878.Key Achievements in the financing of African infrastructure in 2019 – 2020; Who is financing Africa’s infrastructure development? ICA members; Spending by African . In fact, across the continent, 319 million people are living without access to . They are also deepening financial difficulties of utilities, increasing risks of blackouts and rationing.With adequate infrastructure, African firms could achieve productivity gains of up to 40%. From a fiscal and financial perspective, the chapter makes several important .Local Sources of Financing for Infrastructure in Africa A Cross-Country Analysis Jacqueline Irving Astrid Manroth The World Bank Africa Region African Sustainable Development Front Office March 2009 WPS4878 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized. Average 2019-2020 funding $83bn.impactful African infrastructure investments and achieve strong alignment with local institutional investors.
Local Sources of Financing for Infrastructure in Africa: A Cross
For instance, in the year 2020, it provided a funding value of R196 million (US$ 11. According to the African Development Bank, the continent has a $100 billion annual shortfall in infrastructure financing. haran AfricaNancy Lee and Mauricio Cardenas Go. • Bilateral development finance institutions (DFIs) and international private banks were .Africa’s infrastructure needs are substantial and go well beyond what donors and continental, regional and multilateral development banks can provide.
Local Sources of Financing for Infrastructure in Africa
zalez Center for Global DevelopmentNancy Lee and Mauricio Cardenas Gonzalez. The Bank has made significant contributions to infrastructure development in Africa, and tens of millions of .The Africa Infrastructure Country Diagnostic (AICD) estimates Africa’s current infrastructure financing requirements at US$93 billion or about 15 per cent of Africa’s GDP. Africa in Focus.

Over recent years (2015–18), SSA governments have shouldered the bulk (90 percent) of infrastructure financing from their own resources (38 percent) or external borrowing . This includes assisting the government in . And bringing Africa’s infrastructure stock to the level of that for Mauritius could enhance Africa’s gross domestic product (GDP) growth by as much as 2.The Infrastructure Fund has been seed funded by the National Treasury in the amount of R100billion over a ten-year period. Africa is characterized by an infrastructural deficit, a situation that remains critical. African governments, infrastructure users, the private sector, and external sources . Agency for International Development (USAID) to conduct a deep survey of the market. 1 Financing of good quality health care across Africa, in particular, remains inadequate: . Funding decreased by 15.Infrastructure Financing Trends in Africa 2019-2020 .Africa still has massive infrastructure needs.Updated 11:20 AM PDT, July 17, 2024. k Near Ten Billion: P.Yet current investment still falls far short of demand.

ublications/2017/. Commitments by the private sector reached $19bn in 2020, the highest level on record.It includes operating systems and equipment to conduct energy, the movement of people, goods, data, and services, as well as water, sewage, and waste.
Local sources of financing for infrastructure in Africa : a
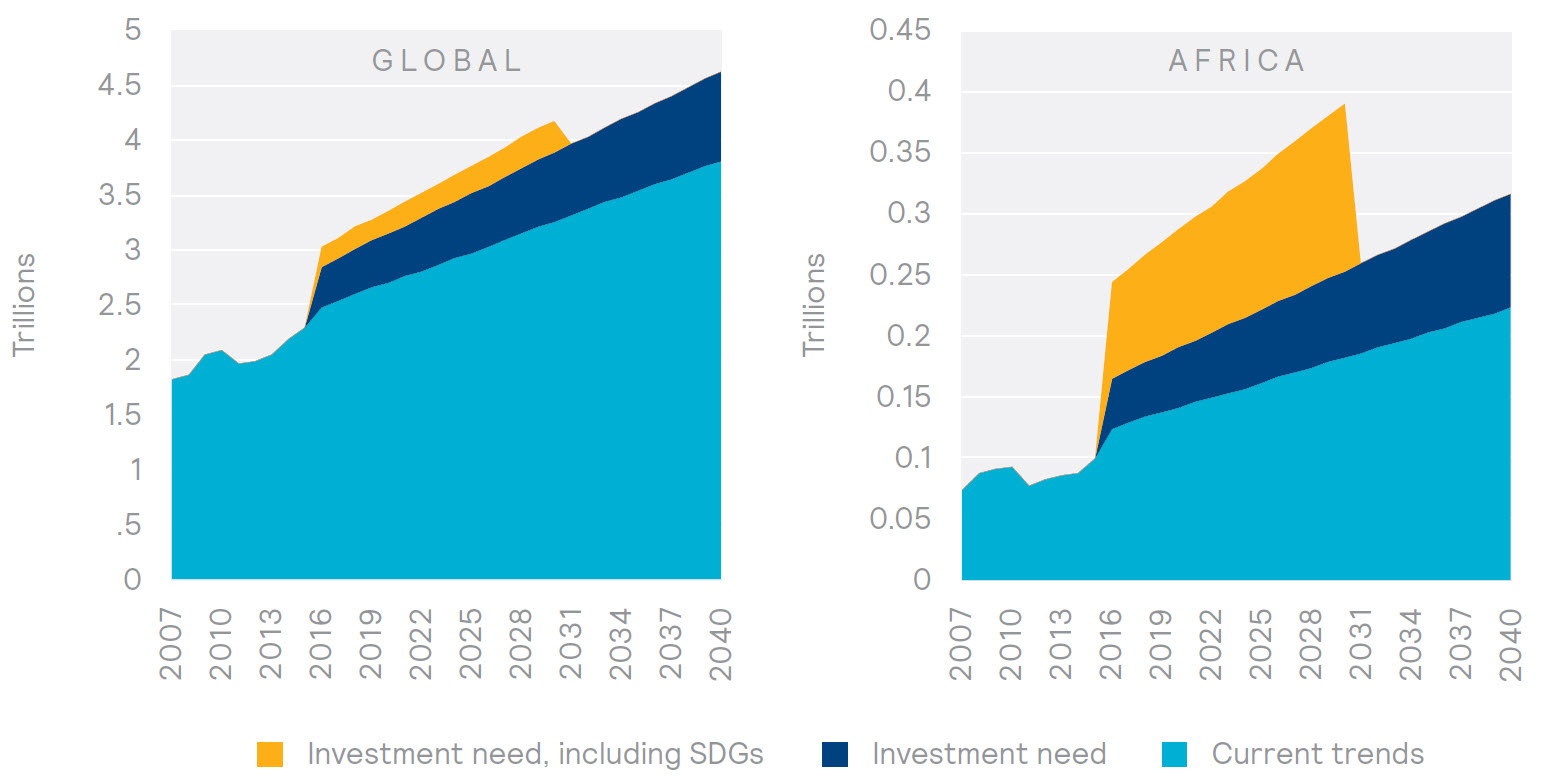
After a surge in 2019, ICA members’ commitments in 2020 stabilized at 22% of total commitments, slightly higher than their 20% share in 2018.potential source of financing for public infrastructure.Local sources of financing for infrastructure in Africa by Jacqueline Irving, 2009, World Bank edition, Electronic resource in English . Chapter five addresses strategic and operational ideas for infrastructure and local investment financing, anticipating Africa’s exceptional urban growth in the coming decades. The decline of bilateral and multilateral lending into Africa has been significant in the last few years. They hold a major portion of the world’s savings and have a long-term investment horizon that matches what’s needed for . This period of turmoil notwithstanding, infrastructure remains key to .For example, as the largest African insurance market, the Federation of African Domestic Insurance Companies could pass a common law for all member countries that allows insurers to participate in financing public investments and thus provide governments with an alternative source of infrastructure financing to public funds.
Infrastructure
Tabled by Finance . IAEA reviews Kenya’s research reactor .The health and fiscal shocks of the COVID-19 pandemic have put into sharp focus the need to strengthen national health systems and the difficulty for governments across the world, and in particular in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), to invest in them.
New Dynamics: Shifting Patterns in Africa s Infrastructure Funding
With the exception of South Africa, local financial markets in sub-Saharan Africa remain underdeveloped and small, with a particular dearth of financing with maturity terms .• External sources of finance were significantly more important than local sources. A brief overview of some promising initiatives are presented in the report. The contribution is intended to be key to the structuring of blended finance solutions. Deal values dropped from US$100bn in 2014 to US$55bn in 2019 and US$31bn in 2020 .

7% 2019 – 2020.While the IJ Global data used in the report shows a decline in the value of infrastructure lending, innovative new types of financing are coming to the fore. Link to Data Set.However, the Infrastructure Consortium for Africa found that in 2018, of a total of about $100 billion invested in African infrastructure, only 2 percent was for regional projects–simply not enough.

Who is financing Africa’s infrastructure development?
- Verwenden Des Ipad Mit Gesten: Welche Gibt Es?
- 31 Bibelverse Über Herrlichkeit Christi
- Allergiefreier Wimpernkleber Für Allergiker
- Student Learning In Higher Education: Where We Are And Paths
- Zamani, Petra, Dr. , Hautarzt _ Zamani Hautärztin Allergielogie P in Neunkirchen
- Peg-4 Rapeseedamide | PEG-4 Rapeseedamide
- Huile De Pépins De Raisins- Bienfaits, Utilisation
- Kim Lieschke Hno | HNO Ärzte
- La Liste Des Pays Arabes Les Plus Riches Contient L’Algérie
- Bbl Technische Ausrüstung , Technische Ausrüstung
- Honda Adv 350 Preis _ Honda ADV 350: Erfolgsrezept eine Nummer kleiner
- Kostenlose Rechtsberatung Im Sozialhilferecht
- Deutsche Post Sankt Wendel Oberlinxweiler Jakob-Stoll-Str.
- Fenchel Pflanzen, Pflegen Und Ernten
- Krefeld: Erste Karnevalsorden-Verleihung Per Drive-In
