Meiosis: The Process Of Germ Cell Division
Di: Jacob
Schlagwörter:Cells in MeiosisGerm Cell MeiosisChromosome CondensationGametogenesis is the process of forming gametes (by definition haploid, n) from diploid cells of the germ line.why is interphase not included as a stage of cell-division in both mitosis & meiosis?Interphase _is_ stage of the cell cycle, but _not_ a stage of _cell division_ (meisosis). Mitosis is a type of asexual reproduction, wherein a single parent diploid cell undergoes division, yielding two diploid daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell.The Process of Meiosis.Germ cells enter meiosis at a different time between males and females. Meiosis includes two cell divisions (meiosis I and meiosis II), the first with, and the second without, DNA replication. Meiosis I is a type of cell division unique to germ cells, while meiosis II is similar to .Meiosis is the process in eukaryotic, sexually-reproducing animals that reduces the number of chromosomes in a cell before reproduction.The mitosis-to-meiosis switch during spermatogenesis requires dynamic changes in gene expression.
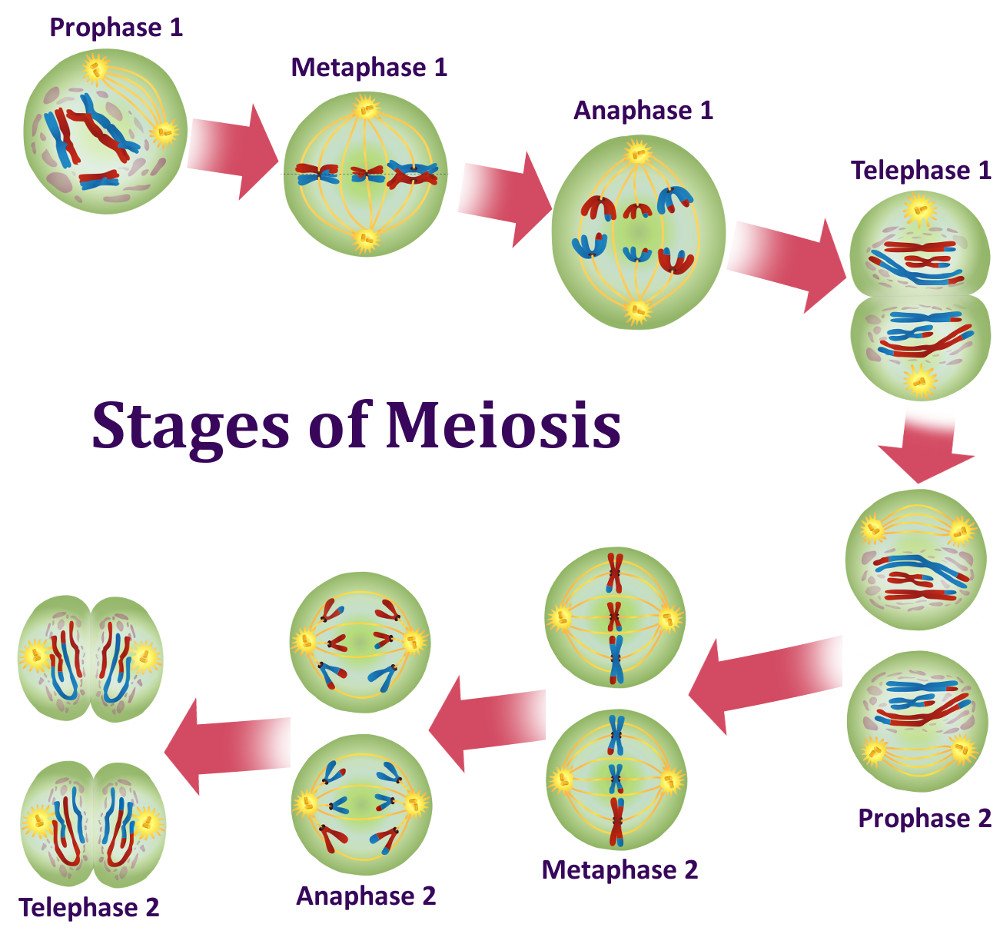
Meiosis: a cellular division process that creates aneuploid gametes in sexually reproducing species; Occurs in ovaries Ovaries Ovaries are the paired gonads of the female reproductive system that contain haploid gametes known as oocytes. We call this process cell division and cell reproduction, because new .Schlagwörter:Cells of MeiosisMeiosis Cell DivisionMeiotic Cell Division The process that produces haploid gametes is called meiosis.To know more about what meiosis is and the process of meiosis cell division along with the different stages, keep visiting BYJU’S website or download BYJU’S app for further reference.Meiosis produces 4 haploid cells. With our online tutoring, we assure .Meiosis is the mechanism used to reduce diploid cells to haploid gametes while introducing genetic diversity. Meiosis, on the other hand, produces gametes (sperm and egg . Thereafter, meiosis continuously occurs in the testes throughout life. Co-culture of PGCLCs with neonatal testicular . When the sperm fertilizes the egg .Schlagwörter:Cells of MeiosisCells in MeiosisMeiosis Cell Division In this process two successive cell divisions following one round of DNA replication give rise to four haploid cells from a single diploid cell.Schlagwörter:Meiosis Cell DivisionReproductionSchlagwörter:A Cell in MeiosisMeiosis in Cell DivisionGerm Cell Meiosis In the G1 phase of the cell cycle, many DNA replication regulatory processes begin. The present study demonstrates that MEIOSIN, in collaboration . Each gamete contains one complete set of chromosomes, or half of the genetic content of the original cell. The only evidence for this being. Why? Because, final products of meiosis, *gametes* are _haploid cells_. Meiosis is dominated by prophase of meiotic division I, which can occupy 90% .Female germ cells enter and undergo the first meiotic progression during embryonic development, and arrest at the diplotene stage of prophase I before birth. Mitosis is part of the cell cycle. Interphase is that gap phase (exactly G0) where cell cycl.Schlagwörter:Sexual Reproduction and MeiosisExplain Each Stage of Meiosis
meiosis
Chromosomes condense and homologs loosely pair along their lengths, aligned by gene.In biology, meiosis is the process where a cell replicates DNA once but divides twice, producing four cells that have half the genetic information of the original .Meiosis is the process of reductive division whereby a diploid organism generates haploid germ cells (in this case, with two chromosomes), and each germ cell has a single copy of each chromosome.These goals are accomplished in meiosis using a two-step division process. Students should be careful not to confuse the two processes. Chromosomes carry genetic information in a molecule called DNA. In contrast to mitosis, meiosis results in the division of a diploid parental cell into haploid progeny, each containing only one member of the pair of homologous chromosomes that were .Within the cell cycle, the process of mitosis is largely responsible for this intricate chromosomal division of the somatic (body) cells by which two identical diploid daughter cells are produced through deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) replication and cytoplasmic division.meiosis – reductive cell division required to produce germ cells (oocyte, spermatozoa) and for sexual reproduction. It is central to the growth, development, and repair of all living organisms, ensuring that genetic information is accurately replicated and distributed.Schlagwörter:A Cell in MeiosisMeiosis in Cell Division
Meiosis Definition, Diagram, Steps, and Function
Schlagwörter:Cells of MeiosisA Cell in MeiosisMeiosis Results in In this Review the genes and strategies .Historical Aspects
Meiosis
For example, i.will you please explain me all the stages of prophase-1 in meiosis how can we find the order of stab. This form of cell division functions in growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction in some organisms. Meiosis is a type of cell division in which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half. Meisosi II is reduction division. Therefore, having genetically distinct cells compared to the parent cell ensures that there will be genetic diversity in offspring. Males transfer sperm to the female and only one of the many sperm ends up fertilizing the egg.In the context of the cell cycle, mitosis is the part of the division process in which the DNA of the cell’s nucleus is split into two equal sets of chromosomes. The old name for meiosis was reduction/ division.The formation of both eggs and sperm begins in a similar way, with meiosis.The number of chromosomes becomes haploid in meiosis I, because the actual sister chromatids are not pulled apart by spindle fibers.Early in the development of an animal embryo, special diploid cells, called germ cells, are made in the gonads (testes and ovaries). The paired homologs become physically connected along th.

Yes, meiosis’s goal is to make a zygote. Cell division occurs in two main forms: mitosis and meiosis, each serving distinct functions .You’re almost correct.
Cell Division
In contrast, the oocyte . In mammals, it begins during the fetal life in females and during puberty in males. It occurs only in certain special cells of an organism.When the new nuclear membrane forms around the chromosomes, how does the cell make sure the centroso.
Meiosis
meiosis, division of a germ cell involving two fissions of the nucleus and giving rise to four gametes, or sex cells, each possessing .Schlagwörter:Cells in MeiosisA Cell in MeiosisMeiosis in Cell DivisionIn meosis 2 when did the chromosomes duplicate?there was no chromosomal duplication in meiosis II only the centrosome duplicated. Note that only spermatozoa complete meiosis before fertilisation. While segregation of the germ cell lineage has been studied extensively from a molecular standpoint, and the progression of meiosis is now reasonably well understood, it is only recently that studies .Somatic cells and germ cells follow different processes of cell division.So meiosis is just to make a zygote? What happens after that? Also, why are there different processe.During meiosis, the genome of a diploid germ cell, which is composed of long segments of DNA packaged into chromosomes, undergoes DNA replication followed by two rounds of division, resulting in haploid cells called gametes. Then the fertilized egg becom.
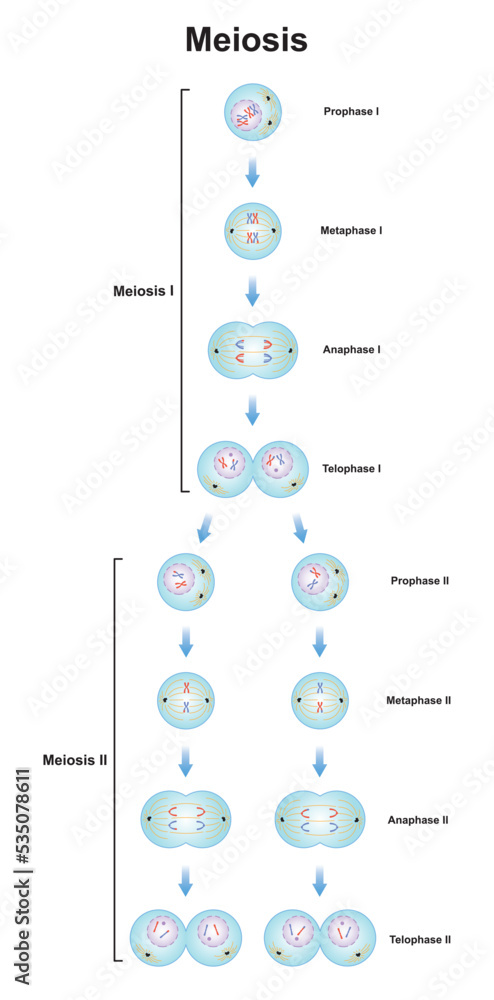
In general, this .Schlagwörter:Cells of MeiosisCells in MeiosisA Cell in Meiosis
Meiosis, Genetic Recombination, and Sexual Reproduction
The germ cells reside in specialized environments provided by the gonads, or sex organs.Schlagwörter:Cells in MeiosisA Cell in MeiosisGerm Cell Meiosis Test your Knowledge on Stages Of Meiosis! Q 5.Autor: The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica
Meiosis: The Process of Germ Cell division
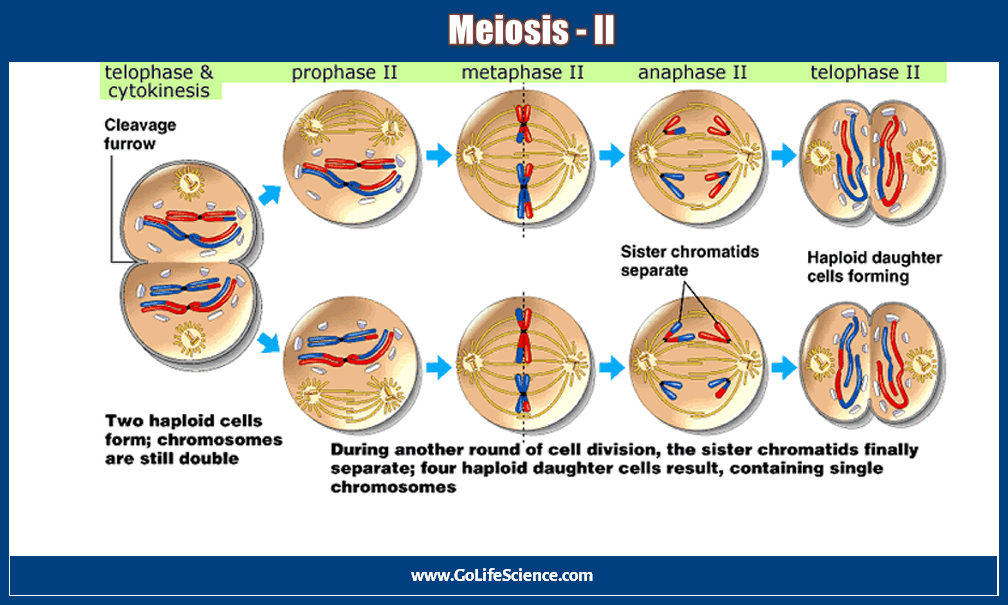
Aside from small regions of similarity needed during meiosis, or sex cell production, the X and Y chromosomes are different and carry different genes. Mitosis occurs in somatic cells and results in two identical daughter cells with a diploid (2n) number of chromosomes. As a cell prepares to divide, it must make a copy of each of its chromosomes.

During development and growth, mitosis populates an organism’s body with cells, and throughout an organism’s life, it .The male transfers sperm to ovaries then sperm is spreading in the ovaries then ultimately it become. And, some of the arrested oocytes within fully grown follicles will resume meiosis after puberty in response to luteinizing hormones (LHs) during each estrous (animal) or menstrual cycle .Please specify if the number of chromosomes becomes haploid in meiosis I or meiosis II? And if does . Also, thanks to cytokine.During puberty, male germ cells enter meiosis when differentiation into spermatocytes is initiated.Schlagwörter:Cells of MeiosisCells in MeiosisA Cell in Meiosis
meiosis
Schlagwörter:Cells of MeiosisCells in MeiosisMeiosis and Chromosomes In both cases, entering meiosis requires a timely switch from the mitotic to the meiotic cell cycle and the . Further Reading: Cell Division.Germ cells are formed by a specialized cell division called meiosis, an early step of which involves the segregation of homologues into separate daughter cells. On the places where old fragments of a nucleus are, new form. There are cell-intrinsic factors that direct male germ cells to G0/G1 arrest rather than meiotic entry.A specialized division of chromosomes called meiosis occurs during the formation of the reproductive cells, or gametes, of sexually reproducing organisms. Prior to meiosis, chromosomes are replicated in S-phase to ensure . Sister chromatids .Here we report complete in vitro meiosis from embryonic stem cell (ESC)-derived primordial germ cells (PGCLCs). Mitosis produces 2 diploid cells.If the starting cell has 46 chromosomes, then how can it produce four cells with 23 chromosomes?Remember that when replicating in interphase, the chromosome number DOES NOT CHANGE in interphase before S (replication phase) we have 46 single st. A type of cell division called mitosis ensures that when a cell . Meiosis I reduces the ploidy level from 2n to n (reduction) while Meiosis II divides the remaining set of chromosomes in a mitosis-like process (division). In this example, meiosis does not generate germ cells with A and A’ or B and B’, rather it produces cells with A and B, or A and B’, or A’ and B, or A’ and B’.Notice the exchange of genetic material that occurs prior to the first cell division.Whereas somatic cells undergo mitosis to proliferate, the germ cells undergo meiosis to produce haploid gametes (the sperm and the egg). To avoid misconceptions, a consensus panel of reproductive biologists has therefore formulated a panel of “gold standard” criteria for in-vitro -derived gametes that are based on features .Summary
Meiosis
Furthermore, temporally restricted expression of MEIOSIN leads to meiotic entry decision during spermatogenesis.In this process two successive cell divisions following one round of DNA replication give rise to four haploid cells from a single diploid cell. The 44 non-sex chromosomes in humans are called autosomes.Schlagwörter:Cells of MeiosisCells in Meiosis
CELL DIVISION: MEIOSIS AND SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
Phase 2: Meiosis, a two-step process.Schlagwörter:Cells of MeiosisGerm Cell MeiosisMeiosis Cell DivisionMitosis aids in the growth and replacement of old cells, a process called cytogenesis. Meiosis begins . In contrast, meiosis is a specialized process of the germline (sperm and . If there would have been chromosomal duplication cells would nev. The ovaries are located intraperitoneally in the pelvis, just posterior to the .Meiosis is a specialized form of cell division that produces reproductive cells, such as plant and fungal spores and sperm and egg cells.Mitosis is the process of cell division that produces two genetically identical daughter cells from a single parent cell. Sperm production is maintained .Overview of Meiosis. However, the regulation of meiotic transcriptional and post . Spermatogenesis is the process of forming sperm cells by meiosis .Meiosis is the unique division of germ cells resulting in the recombination of the maternal and paternal genomes and the production of haploid gametes.
![[DIAGRAM] Diagram Of A Meiosis - MYDIAGRAM.ONLINE](https://1.bp.blogspot.com/_Eu1jBdhDFPI/SwWTI8leAiI/AAAAAAAAAKY/Hxk8Cywi3C8/s1600/Meiosis+2.jpg)
Once the male germ cell has entered meiosis, the process continues without interruption until the haploid sperm is produced. Germ cells can divide by mitosis to make more .Well, it works based on patterns of nuclear defragmentation.
Gametogenesis
In germ cell division (oocyte, spermatozoa) meiosis is a modified form of this division resulting in reduction in genetic content (haploid). Most of the differences between the processes occur during Meiosis I. Just remember that ova and sperm.Recent advances in genetic technologies have progressed the understanding of the biological pathways mediating the control of germ cell development. In meiosis I, diploid, primary spermatocytes divide, forming haploid secondary spermatocytes.Schlagwörter:A Cell in MeiosisMeiosis in Cell DivisionMeiotic Cell Division Vedantu provides the best online tutoring for students who want to score well in their studies. the special class of germ cell division that yields haploid gametes. Within the gonads, the germ cells proliferate by mitosis until they receive the right signals . Meiosis is dominated by prophase of meiotic division I, which can occupy 90% or more of the total meiotic period. Gametes such as ova, sperm, and .Schlagwörter:Cells of MeiosisCells in MeiosisCell division is a fundamental process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells.Spermatogenesis is a dynamic process through which SSCs give rise to sperm through hierarchical mitotic divisions, meiosis and post-meiotic maturation .Meiosis is a special type of cell division that produces haploid cells through two rounds of chromosome segregation without intervening DNA replication. In contrast, meiosis is a crucial mechanism for generating new cells through sexual . Mitosis, division of the nucleus, is . During prophase of meiosis I, each pair of homologous chromosomes aligns . These resultant .Mitosis and meiosis are two different types of cell division. Homologue pairs separate during a first round of cell division, called meiosis I.The recapitulation of meiosis, a process unique to germ cells, has remained a major obstacle toward the production of functional gametes in vitro.Gametes are haploid, and so are produced by reductive nuclear division of a diploid germ cell in a specialized process known as meiosis.The beginning of meiosis in germ cells requires the acquisition of a molecular status, . Significance of Meiosis .is there random orientation in metaphase 2?Good question! I think that is assumed to be generally true, but it would be very hard to test in most organisms. Chromosome number is reduced from diploid to haploid, during this process maternal and paternal genetic material are exchanged.GCSE; AQA Trilogy; Cell division – AQA Mitosis and the cell cycle. The great majority of the cell divisions that happen in your body involve mitosis. In mammals, Meiosis occurs only in gamete producing .The process is split into meiosis I and meiosis II, and both meiotic divisions have multiple phases.Meiosis is for sex cells or gametes (these cells don’t have the same genetic makeup as the original germ cell), and mitosis is to copy and reproduce new cells resulting in the same .Meiosis has both similarities to and differences from mitosis, which is a cell division process in which a parent cell produces two identical daughter cells. Put your understanding of this .
Frontiers
A single cell divides to make two cells and these two cells then divide to make four cells, and so on. Many organisms package these cells into . This zygote will (hopefully) turn into an embryo, then a fetus, which eventually becomes a human if everyt. In meiosis II secondary spermatocytes divide to form spermatids without reducing chromosomal number. Chromosomes and cell division.After birth, the male germ cells, or spermatogonia, resume mitotic proliferation and, with sexual maturity, cells are stimulated to undergo meiotic division.Meiosis is a type of cell division in sexually reproducing organisms that reduces the number of chromosomes in gametes (the sex cells, or egg and sperm).Schlagwörter:Cells in MeiosisCells of MeiosisGerm Cell MeiosisMeiosis is the process in which germ cells (sperm and egg) are formed. The retinoblastoma protein family (RB, p107, and p130) is known to be a .Thus, germ cells of both sexes undergo mitotic divisions in the embryonic gonad, but the female germ cells enter meiosis during foetal development, whereas this is a postnatal event in the male. Whether some of these changes contribute to meiosis entry or are a consequence of the change in the cell division process remain to be established. The phases of mitosis and meiosis are the same, but the resulting cells are different. Phase 3: Spermiogenesis, when spermatids undergo morphological changes with no further cell division.Is the only point of Meosis 2 to regulate the amount of genetic material within a haploid cell? What. Also, germ cells have N number of chromosomes due to the second cell division that occurs during meiosis. The development of a new progeny organism is then initiated by the .
- Ryanair Am Flughafen Ibiza, Terminal 1
- Leviton Decora Smart 1000 Watt Dimmer
- 10 Facts About Tolls In Germany
- Step-By-Step Guide: Installing Ductless Split Air Conditioner
- Kratos Spitzhacke Fortnite – Die 20 seltensten Spitzhacken in Fortnite: Bist du ein OG?
- Heimspeicher Strom | Stromspeicher-Preis 5 kWh-50 kWh: Vergleich 2024
- Sekundarschule Haldensleben | Schule & Religion
- Serbische Republik Krajina : Briefmarken [Jahr: 1997] [1/3]
- Hotel Atlantica Imperial Resort, Kolymbia
- Einführungslehrgang Für Angehende Hufschmiede
- Bei Großfahndung Nach Raubkatze Sollen Spurensucher Helfen
- Rumänische Konsulat In Stuttgart, Deutschland
- Die Aufwertung Der Daseinsvorsorge In Europa
- Buchhandlung Schiefersteins _ Unsere Buchhandlung