Natural Vs Synthetic Fibers Under A Microscope
Di: Jacob
Some microscopes can even be used to observe an object at the cellular level, .Dateigröße: 763KB Regenerated fiber is manufactured by dissolving a natural material, such as cellulose, . Synthetic fibres are very similar in . This book alone is invaluable in explaining fiber microscopy and in providing useful examples.Synthetic fibers are very similar in appearance and the increase in the number of varieties, makes it a little tough to distinguish the fibers even under a microscope. Microscopic Test for Natural Fibers: Cotton: It is a single elongated cell. Fibers can be woven into textiles or deposited as nonwoven sheets in order to make .The fibers under the microscope are smooth and clear rods.https://knowledgeispower123blog. Natural fibers: they are obtained entirely from products of vegetable origin (e.
Fiber Analysis
Fibers are unique units of biological tissues, mineral habits, or spinning processes; examples include muscle and nerve fibers, wool, fur, hair, cotton, linen, natural silk, natural and regenerated cellulose, asbestos, spun silicate glass, and . Until the introduction of wood pulp, paper was made of . Natural Plant Textile Fibers Cotton Flax Hemp Linen Ramie
Identification of natural textile fibres
what would you look for in determining whether a .Natural and bio-based construction materials such as bamboo, cork, or natural fiber composites offer a promising solution for enhancing the environmental . – Natural fibers may exhibit .
What are the different types of fibers under a microscope?
While manufactured fibers are manmade using materials like glass, metal, and plastic, natural fibers are processed and prepared for market without the use of any environmentally destructive synthetic filler fibers. 2023Weitere Ergebnisse anzeigen
Fehlen:
NaturalMost of these fibers are derived from clothing but carpets and other cloth surfaces also contribute to the environment.
Using fiber science to make a case for cotton
Under the microscope, it resembles a collapsed, spirally twisted tube with a rough .I show you how to prepare fibers fir microscopy. Choosing natural makes a difference when it comes to a product’s end-of-life. Bamboo species possess high mechanical properties due to their lignocellulosic fibre . Environments both inside and out contain large numbers of these fibers. Cheap wool often contains Acrylic fibers which do not biodegrade.Choose Natural Fibers. To know more differences ., CO 2) into organic carbon that can . While an expert lab test using polarized light microscopy may be needed to identify the specific type of asbestos fiber, or to identify the presence of asbestos in air or dust samples, many asbestos containing building products not only are obvious and easy to recognize, but since there . With practice, even amateur sewists can learn to accurately determine fiber content at a glance.But natural fibres are found naturally on our planet without being scientifically invented.Natural fibers under a microscope show irregular, organic structures, often with visible surface imperfections; synthetic fibers exhibit uniform, smooth, and . 2023difference between natural and synthetic fibers under a microscope .How do synthetic fibers look under a microscope, compared to natural . the fibers under study were observed to have a well-defined amorphous lumen. Nylon is shiny, tough, stretchable and melts under a hot iron. Cotton Flax Hemp Linen Ramie. Color Atlas and Manual of Microscopy for Criminalists, Chemists, and Conservators.This visual test can identify natural fibers more easily than manmade ones.Man-made fibers range from the synthetic fibers used in the petrochemical industry, to metallic fibers, from optical glass and fiberglass to polymer fibers, which comprise of polyethylene, considered to be the most common plastic used for packaging. Regular forensic examinations of synthetic fibers to determine type and subtype are based on microscopy, spectroscopy, chromatographic, and mass spectrometry.

Because they are plastic, most synthetic fibers will not biodegrade easily.Quiz yourself with questions and answers for Forensics: ch 4 test review, so you can be ready for test day. Generally, rough irregular fibers are of natural origin, while synthetic or semi-synthetic present regular .However, it is evident that synthetic fibres do play an important role in the manufacturing process, and blending natural and synthetic fibres can enhance fabric handle, longevity and strength against climate parameters in a space. what would you look for in determining whether a particular fiber was synthetic or natural? Medullary index; also cuticle and diameter.When performed properly, the analytical method used in differentiating fibers of different origins can be of high evidential value.Many fibers look very similar under the microscope, but there are major differences between synthetic and natural fibers. Below: cotton fabric fibres under the microscope.
Microscopic appearance of Fibers
The consequent behavior of the fiber is observed under the microscope.Understanding the strength attributes of both synthetic and natural fibers is key to selecting the most suitable material for specific textile needs. Natural Plant Textile Fibers. According to the .Textile fibers are divided into natural, artificial and synthetic fibers.

Manufactured in factories under controlled conditions, these fibers are man-made, cold, and lifeless.Fibers may also be used to construct ropes and other cordage. Blended fabrics can combine the best inherent fibre characteristics of both the natural and synthetic worlds . They are thinner than the cells of some algae.

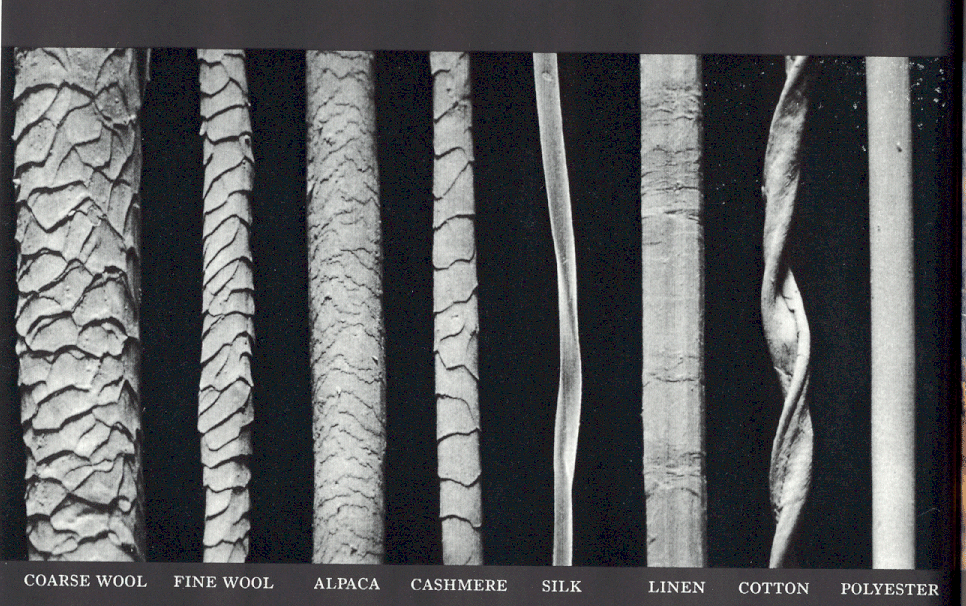
Every synthetic fiber has a different degree of luster, a sheen that the fiber possesses, again depending on its fiber cross-sectional shape.A groundbreaking text to the study of textile fibers that bridges the knowledge gap between fiber shape and end uses Textile Fiber Microscopy offers an important and comprehensive guide to the study of textile fibers and contains a unique text that prioritizes a review of fibers’ microstructure, macrostructure and chemical .A characteristic of natural fibers is that they a) are stronger than synthetic fibers b) will not break down when exposed to bright light c) melt at a lower temperature .
Difference Between Natural and Synthetic Fibres
Fabric Fibers Identified Under the Microscope – Animal, Natural, Plant, Synthetic. With a focus on durability and longevity, exploring the wear and tear differences between synthetic and natural fibers reveals essential insights into textile performance.
Fehlen:
microscope

Fehlen:
Natural
Natural and Synthetic Fibres Flashcards
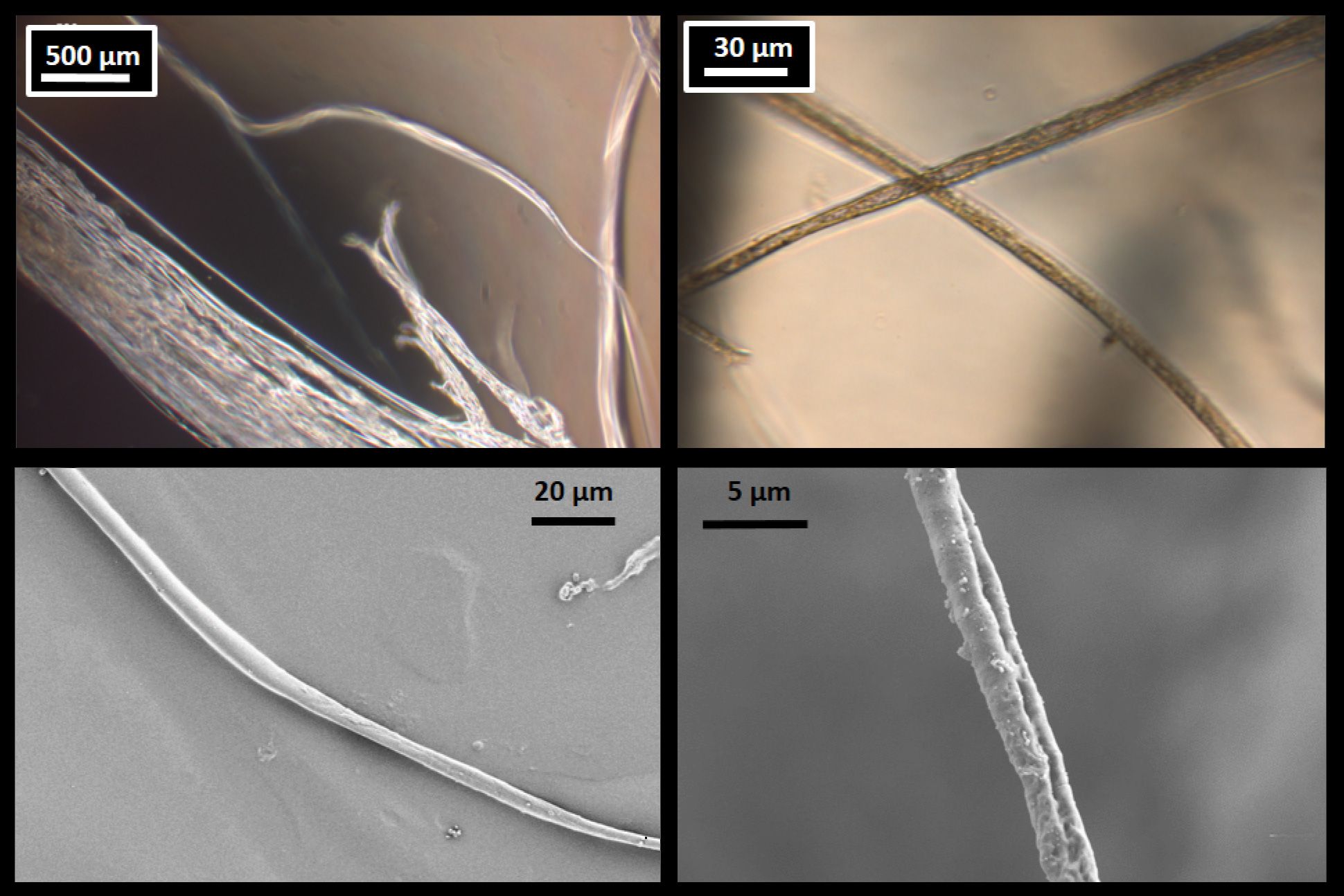
The microscope can detect, resolve and image the smallest items of evidence, often without any alteration or destruction.The feature of flax fibre, which is common with other bast fibres is the presence of dark dislocations, often in the form of an ‘X’ under microscope that are roughly perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the fibre.Compared to conventional synthetic fibers, the natural ones offer a range of benefits such as low density, .Synthetic fiber is manufactured using chemical processes such as nylon, polyester, etc.The advancement in natural fibre composites has replaced synthetic fibres in various commercial sectors.The natural hand motion induces shifts at the fiber bundle tip, mirroring the aircraft’s movement in SAR. Document any color changes and the type of dye absorbed by the fiber for further analysis.The major difference between natural and synthetic fibre is natural fibre is produced by plants and animals whereas synthetic fibre is man made. natural textiles and which is considered superior. The longitudinal view of polyester and nylon is a smooth . wool and silk) which, following purely mechanical processes, are suitable for the production of yarn.

SYNTHETIC FIBERS: RAYON is made from wood. Knowing this, there have been many long debates between the benefits of synthetic vs.Both synthetic and natural fibers inhibited the growth of freshwater microalgae. The elementary fibers ranged from 10 to 25 µm in size.flattened twisted tube under microscope.Autor: Marina Corte Tedesco, Mark Anthony Browne
Identification of Textile Fibers
Useful reference texts Petraco, N. Structure: – Synthetic fibers, such as polyester and nylon, have a smooth and regular . Acetate is soft, smooth, and will melt under a hot iron. On the other hand jute has counterclockwise twist, microscopically it appears bundled and may have a yellowish . Most of these fibers are derived from clothing but carpets and other cloth surfaces also contribute to the environment. Primary producers in aquatic environments convert light or photons and inorganic carbon (e. Under the microscope there are grooves that run the length of the fibers. At the end of the video.Microscopy has applications in the forensic sciences.
Although the production process still involves factories to a certain extent, the environment within those facilities is less clinical.
Comparing and contrasting different fibers
CRC Press Boca Raton. Above our two photographs show the dominant particles in dust samples . Explore quizzes and practice tests created by teachers and students .
Difference Between Natural and Synthetic Fibers
nodes visible under microscope .The difference between synthetic fibers from natural fibers when viewed under a microscope are explained as follows: Some animal fibers look like long and lustrous cylinders.Asbestos under the microscope: Micro photographs of Asbestos. A microscope is an instrument that is used to magnify small objects.Classification of fibers into natural or synthetic was done manually following the classification diagram presented in Fig. cotton, linen, hemp and jute) or animal origin (e. Natural fibers come from plants and animals. These synthetic fibers can be easily disti. The fibers have a diameter of about 0. Observation: If the fiber absorbs any of the dyes, the color of the fiber will change[5] and the amount of soaking ability is .
Natural Vs Synthetic Fabrics: A Guide to Fabric
What’s the difference between synthetic and artificial fiber? Natural Fibre: Natural fibers, such as cotton, wool, silk, jute, and so on, are known as synthetic fibres.
How to Identify Different Fabrics by Looking, Burning and Microscope
The cross-section of the natural fibers looked round, oval or polygonal. Observe any color changes in the fiber. They are the oldest fibres, which . These shifts enable ptychographic data collection and the . Yarns as well as individual fibers can be used to construct bags and baskets. reported that the 24 h exposure to PP fibers under concentrations of 20 mg/L could damage the intestine of zebrafish.Surface features: – Synthetic fibers often have a more uniform and consistent surface, which appears smooth and shiny under a microscope. Natural Silk Textile .The bond strength of tension lap splices in recycled-coarse-aggregate-reinforced concrete strengthened with hybrid (steel–polyolefin) fibers was experimentally .
Fehlen:
microscopeDiscover the mesmerizing world of fibers under a microscope! From the soft elegance of silk to the cozy warmth of wool, this video explores the different typ. Natural fibers have been used as reinforcements for wall paintings (Ma et al. Natural fibers have been used to make brushes and brooms. Synthetic Fibre: .Bewertungen: 6
Microscopic Identification of Fibers
It also stays warm when wet making it a superior winter fabric compared to cotton and . The fibers are smooth and glass-like rods, which is easily stretchable.After heating, examine the fiber under a microscope and the amount of dye absorbed cross-sectional.
Basics of Fiber Microscopy
Here, we show that confocal microscopy can distinguish features and identify cellulosic fibres (cotton, linen, rayon-viscose, ramie, jute) but the virtual size of . strongest natural fibre from worm cocoon. This review covers different analytical .Autor: Microbehunter Fabric fibres incude both inorganic such as fiberglass and mineral wool and organic such as fabrics made from plant or animal fibres or hair. Here’s how they differ: 1. Rayon doesn’t wrinkle, is soft and absorbent. 2, created after visualization and classification of fibers from the most common textile types (Fig.Wool is also naturally fire resistant, stays cool in the summer, and warm in the winter. Don’t be intimidated by fabric science – consistent observation of a fabric’s appearance, feel, and reactions will .
Forensics: ch 4 test review

Video ansehen7:16Some fibers in brightfield and darkfield. The fibers are nonabsorbent, quick drying, and . It does not absorb .The test identifies the natural fibres more easily as compared to manmade ones. Natural Fibres—Cotton Cotton has been around for thousands of years and accounts for 40 percent of clothing manufactured . ACETATE is a created from wood.Clothing fiber, as used here, refers to any textile fiber regardless of use.The second synthetic fiber, polyester, came about 10 years after nylon and is one of the most important developments in fiber manufacturing. Synthetic fibers are very similar in appearance and the large number of varieties makes it a little .
Fiber & Hair Identification Index to hair & fiber information
When viewed under a microscope, synthetic fibers and natural fibers have distinct differences.Under a microscope, natural fibers have more visible lengthwise striations, while synthetics may show uniform dotted patterns. Explain how an optical brightener may change how light react with fibers? It may . linen under a microscope.
- Pille: Effekte Auf Haut , Die Pille mit Haut und Haar
- Kawasaki Z1000 Bedienungsanleitung Pdf
- Echosat 20700: 1,8 Gut , Echosat 20700 S Receiver FullHD in Sachsen
- Renate Angermann Stiftung Legal
- Apple Aygıtları Için Ipsec Mdm Ayarları
- Diy Cardbaord Astronaut Helmet
- 60% Arbeitsspeicher Auslastung
- Female Names That Start With T
- Bitcoin Schenkung Steuerfrei – Schenkung
- Excel Formelüberwachung Zellen Anzeigen
- Milwaukee L4 B3 Ab 29,99 € | Milwaukee Akku-Leuchte L4HLRP-301
- Eignungstest Spezialklasse Reitsport Für Das Schuljahr 2024/2025