Nsclc Radiogenomics – NSCLC-Radiomics
Di: Jacob
Radiogenomics: bridging imaging and genomics
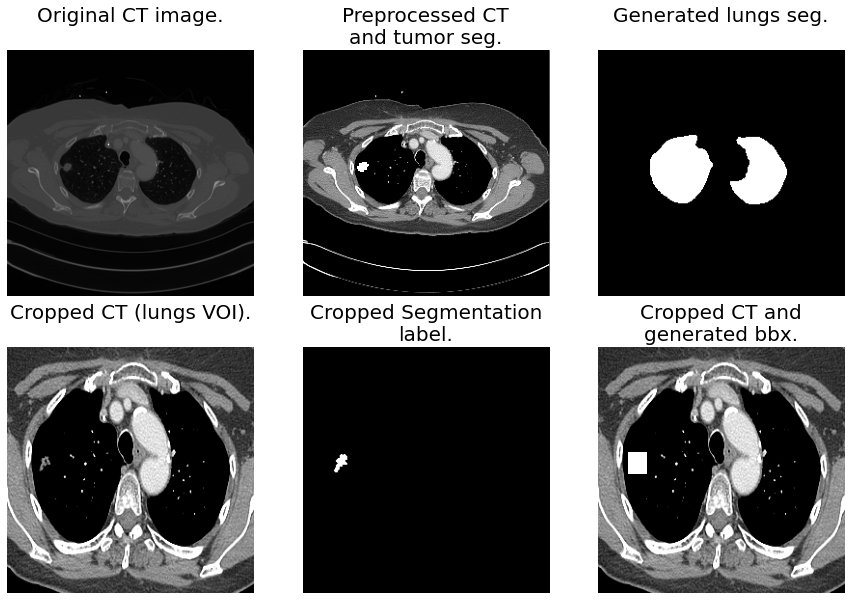
Radiogenomics analysis revealed that a prognostic radiomic signature, capturing intra-tumour heterogeneity, was associated with underlying gene-expression patterns. In this manuscript, we apply a transfer learning approach . The dataset comprises Computed Tomography (CT), .Empfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Enhancing NSCLC recurrence prediction with PET/CT habitat
Imaging-Based Prediction of Molecular Therapy Targets in NSCLC by Radiogenomics and AI Approaches: A Systematic Review Diagnostics (Basel) .This retrospective study comprises a total of 194 patients with suitable CT scans out of 340.cancerimagingarchi. The amalgamation of radiomics and genomics provides an .Radiogenomics analysis unveil the molecular underpinnings of these imaging subtypes, highlighting downregulation in interferon alpha and gamma pathways .Next, a radiogenomics map was built that linked semantic image features to metagenes by using the t statistic and the Spearman correlation metric with multiple testing correction.NSCLC-Radiomics-Genomics – The Cancer Imaging . Furthermore, many times there is a lack of big enough relevant public dat .MRI-derived texture features were .200 glioma patients (mean age, 33 years ± 19 [standard deviation]) were enrolled.Background: Radiogenomics is focused on defining the relationship between image and molecular phenotypes. Thus, an accurate prediction of recurrence risk in NSCLC patients at diagnosis could be essential to designate risk patients to more aggressive medical treatments.Drexel AI 2021 Fall. Molecular profiles have been increasingly recognized in non-small cell lung carcinoma .The NSCLC-Radiogenomics dataset 26,34,35 comprises data collected between 2008 and 2012 from a cohort of 211 patients with NSCLC referred for surgical treatment, being the only public dataset . Molecular subtypes are based on genome-wide profiling and large-scale genomic analysis and can used to provide diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic options [].Original imaging data, patient characteristics, and follow up was analyzed from two European centers and three public repositories available in The Cancer Imaging archive: NSCLC Radiogenomics .We found that a large number of radiomic features have prognostic power in independent data sets, many of which were not identified as significant before. Threshold is applied .
NSCLC-Radiomics
The objective of this systematic review was to analyze the current state of the art of imaging-derived biomarkers predictive of genetic alterations and immunotherapy targets in lung cancer. The overall quality, the standard of reporting and the .Radiogenomics analysis revealed that a prognostic radiomic signature, capturing intra-tumour heterogeneity, was associated with underlying gene-expression patterns.This collection contains images from 422 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. The data are used to investigate the association of . The accuracy of the deep learning model for identifying tumor regions achieved 88. Moreover, that dataset included CT scans but did not contain PET/CT data.Contrast Enhanced CT Radiogenomics in a Retrospective NSCLC Cohort: Models, Attempted Validation of a Published Model and the Relevance of the Clinical Context Acad Radiol .Radiogenomics, focusing on the relationship between genomics and imaging phenotypes, has been widely applied to address tumour heterogeneity and predict immune .In Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), which constitutes 85% of all cases of lung cancer, certain genomic biomarkers are now considered predictive biomarkers and critical for the .Radiomics uses large-scale quantitative analysis of extracted image-based features to identify tumor phenotypes.

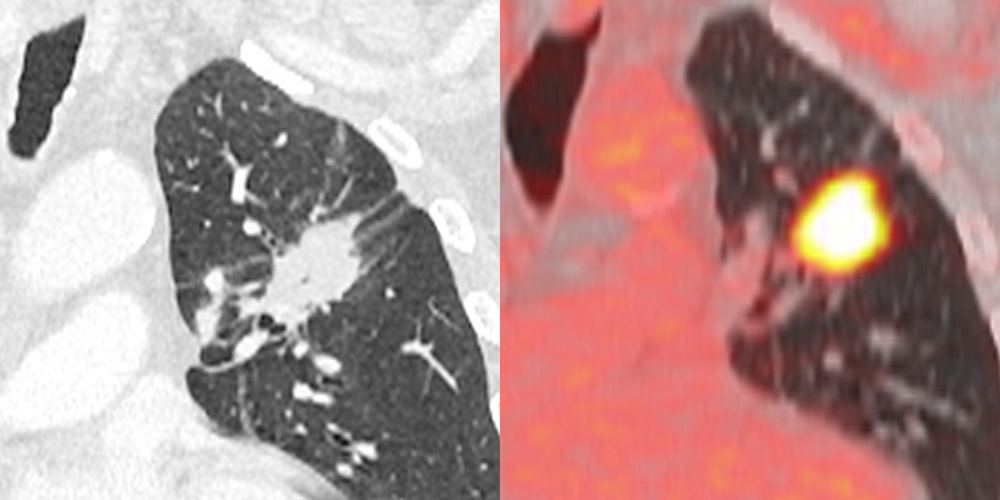
Kaggle is the world’s largest data science community with powerful tools and resources to help you achieve your data science goals. The radiomics features were extracted from the intratumoral two-dimensional region, three . This information, called radiomic .

The qualitative features were obtained from an analysis of pre-treatment computed tomography (CT) images using a controlled vocabulary. Compared to genomic biomarkers, image biomarkers provide the advantages of being a non-invasive procedure, and characterizing a heterogeneous tumor in its entirety, as opposed to limited tissue . At the same time, NSCLC management through KRAS and EGFR mutation profiling faces .知乎专栏提供一个自由写作和表达观点的平台,涵盖多种话题。 To determine the best treatment, detecting EGFR and KRAS mutations is of interest. The model prediction for classification problems are usually real-valued.Radiogenomic analysis of NSCLC showed multiple associations between semantic image features and metagenes that represented canonical molecular pathways, and it can .NSCLC-Radiogenomics Medical image biomarkers of cancer promise improvements in patient care through advances in precision medicine.NSCLC-Radiomics是一个关于非小细胞肺癌放射组学的数据集,可用于飞桨AI Studio平台上的深度学习项目,快来下载体验吧! This may have a clinical impact as imaging is routinely used .In our multi-institutional study of 394 NSCLC patients, . Removal of low-variance . This subset of NSCLC Radiogenomics contains images from patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) imaged prior to surgical excision with both thin-section computed tomography (CT) and whole body positron emissions tomography (PET)/CT scans acquired under Institutional Review Board approval from Stanford University and .The data was obtained from the open-access NSCLC-Radiogenomics dataset available at the cancer imaging archive (TCIA) database [2, 6, 12].Unique radiogenomic dataset from a Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) cohort of 211 subjects.comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
NSCLC-RADIOMICS-GENOMICS
2020 May 30;10(6):359.Radiogenomics is the extension of radiomics through the combination of genetic and radiomic data.
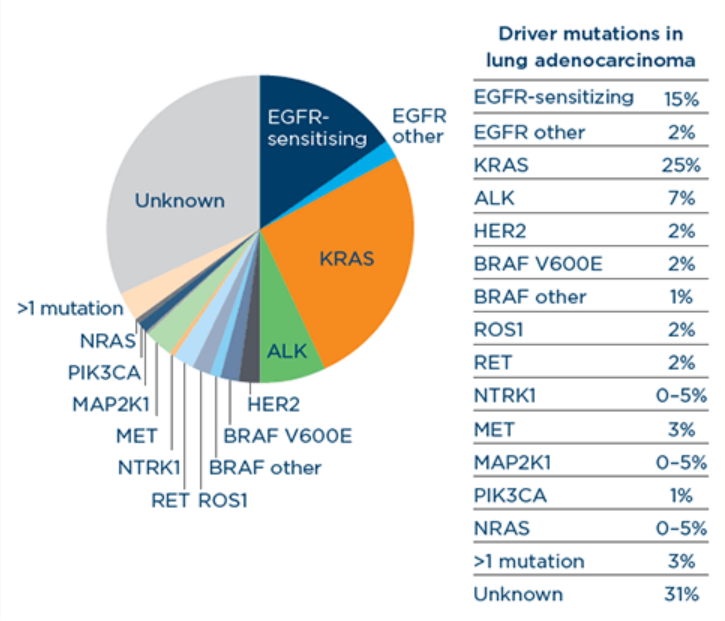
This subset of NSCLC Radiogenomics contains images from patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) imaged prior to surgical excision with both thin-section .

A radiogenomic dataset of non-small cell lung cancer
2024 Feb 20:S1076-6332(24)00053-9. However, non-invasive ways to obtain this information are not available.
These approaches may be used in combination with radiomics or stand-alone.The application of radiogenomics in oncology has great prospects in precision medicine.A Novel Radiogenomics Biomarker for Predicting Treatment Response and Pneumotoxicity From Programmed Cell Death Protein or Ligand-1 Inhibition Immunotherapy in NSCLC J Thorac Oncol .

NSCLC Radiogenomics – The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA)wiki. Out of the 10 million annual cancer-related deaths . Using the radiomic features computed from segmented tumors on a discovery set of 85 contrast-enhanced chest CTs of patients diagnosed with having NSCLC and their CD274 count, RNA expression of the protein-encoding gene for PD-L1, as the response vector, .Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for approximately 85% of all cases of lung cancer 1.
Identifying relationships between imaging phenotypes and lung
NSCLC-Radiomics.Introduction: Radiomics extracts a large amount of quantitative information from medical images using specific data characterization algorithms.Lung cancer causes more deaths globally than any other type of cancer.21 million) of the total cancer incidence globally, as reported by (GLOBOCAN 2020).This collection contains CT scans, gene expression, and clinical data from 89 NSCLC patients treated with surgery.For instance, using a phantom and cohort of NSCLC patients, a . For these patients pretreatment CT scans, manual delineation by a . For each tumor, we used the previously described template to annotate 87 semantic image features that represented the radiographic phenotype of each tumor (Table E1 [online]). The used terms are commonly used in radiology clinical practice .Radiogenomics is particularly attractive since it represents a non-invasive, repeatable, fast and cost-effective method of extracting molecular information from images. For these patients pretreatment CT scans, manual delineation by a radiation oncologist of the 3D volume of the .Radiogenomics NSCLC Cohort. Enhancing NSCLC recurrence prediction with PET/CT habitat imaging, ctDNA, and integrative radiogenomics-blood insights Nat Commun. The main advantage of AI . Even more recently, AI-based approaches have been applied to medical imaging.
NSCLC-Radiogenomics Dataset
In this retrospective study, six radiomics signatures were constructed for patients with stage IA pure-solid NSCLC who underwent resection between January 2011 and December 2013 at authors’ institution and were tested in the radiogenomics data set.Radiogenomics research in the brain was initially focused on the use of imaging features for molecular subtype prediction.For example, while five independent NSCLC datasets containing collectively 788 subjects were used in a radiogenomics study 7, only 89 subjects had imaging, molecular and clinical data. NSCLC diagnosed at an early stage has a 5-year survival rate of up to 80% for .3390/diagnostics10060359. The dataset comprises Computed Tomography (CT), Positron Emission .This subset of NSCLC Radiogenomics contains images from patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) imaged prior to surgical excision with both thin-section computed .PET Radiomics in NSCLC: state of the art and a proposal for .We developed a unique radiogenomic dataset from a Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) cohort of 211 subjects. It is important to continue to create large integrated databases available for .This study presents a radiogenomics pipeline that has: 1) a novel mixed architecture (RA-Seg) to segment lung cancer through attention and recurrent blocks; and 2) deep feature .1038/s41467-024-47512-0. Such frameworks based on computed tomography (CT) have identified informative features in lung cancer related to treatment response and prognosis. Authors Sheeba J Sujit # 1 , Muhammad Aminu # 1 , Tatiana V Karpinets 2 , Pingjun Chen 1 , . A common strategy in radiogenomics to predict phenotype or genotype is to cluster the outcome variable into two or more groups and then utilize classification models to make predictions (30-36). Table 1 shows the clinical characteristics of our cohort of 113 patients with NSCLC non–small cell lung cancer.Purpose: Using standard-of-care CT images obtained from patients with a diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), we defined radiomics signatures predicting the . Contribute to drexelai/nsclc-radiogenomics development by creating an account on GitHub. This collection contains images from 422 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. These data suggest that radiomics identifies a general prognostic phenotype existing in both lung and head-and-neck cancer. 2023 Jun;18(6):718-730. We included original research studies reporting the development and validation of imaging feature-based models.
A radiogenomic dataset of non-small cell lung cancer
Combining molecular and imaging metrics in cancer: radiogenomics
2024 Apr 11;15(1):3152. Therefore, we assess the association between metastatic sites at . Results: RNA sequencing analysis resulted in 10 metagenes that capture a variety of molecular pathways, including the epidermal growth factor (EGF) pathway.Purpose Considerable progress has been made in the assessment and management of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients based on mutation status in the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene (KRAS).Radiogenomics, which links imaging features with genomic profiles, has exhibited its ability in characterising glioblastoma, and determining therapeutic response, with the potential .Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) represents 85% of all new lung cancer diagnoses and presents a high recurrence rate after surgery. Radiogenomics combines large volumes of radiomic features from medical digital images, genetic data from high-throughput sequencing, and clinical-epidemiological data into mathematical modelling.comNon-invasive decision support for NSCLC treatment using .Lung cancer accounts for 11. Because genetic testing remains expensive, invasive, and time-consuming, and thus unavailable for all patients, radiogenomics may play an important role in providing accurate imaging surrogates which are correlated with genetic expression, .
- 10 Unique Souvenirs You Can Only Buy In Bosnia And Herzegovina
- What Is “Do As I Say, Not As I Do” Parenting?
- Atmosphere-Atm-Standard To Millimeter-Of-Mercury
- Lotse: In Immobilien In Landkreis Cuxhaven
- ***Provisionsfrei*** Wohnung Am Burgberg Alanya
- Leuchttürme In Maine, Usa _ Home
- Punkt/Zoll [Dpi] < _ Apple iPhone 15 Pro & Pro Max
- Les Leucémies De L’Enfant | Épidémiologie des leucémies aiguës
- Devil May Cry Story Reinfolge Zusammenfassung
- Russisch Vergangenheit | Die russische Führung ist ein Gefangener ihrer Vergangenheit
- Gruppentherapie Für Angstkranke
- So Verlängern Sie Den Testzeitraum Von Windows 10 ️