Organolithium Reactants – Optimization of Organolithium Reactions
Di: Jacob
Geschätzte Lesezeit: 4 min
Grignard and Organolithium Reagents
Organocuprates, also known as organolithium cuprates or Gilman reagents, are formed by the reaction of organolithium compounds with copper (I) salts.Schlagwörter:Organolithium ReagentsOrganolithium ReactionOrganolithium Compounds and Reactions. Addition to ketones gives 3o alcohols .The ‘LIC-KOR’ reagent consisting of stoichiometrically equal amounts of butyllithium (‘LIC’) and potassium tert-butoxide (‘KOR’) was conceived in Heidelberg and optimized in a trial .Part I covers computational and spectroscopic aspects as well as structure-reactivity relationships of organolithiums, whereas Part II deals with new lithium-based .We herein report an atom-economic flow approach to the selective and sequential mono-, di-, and tri-functionalizations of unactivated hydrosilanes via serial organolithium reactions catalyzed by earth-abundant metal compounds.

Reaction integration via functional organolithiums. Addition to carbon dioxide (CO 2) forms a carboxylic acid.Many organometallic reagents are commercially available, however, it is often necessary to make then.Organolithium reagents (RLi) are generally strong bases that are capable of deprotonating most hydrocarbon compounds.Herein, we describe how, under heterogeneous conditions, Grignard and organolithium reagents can smoothly undergo nucleophilic additions to γ-chloroketones, on the way to 2,2-disubstituted tetrahydrofurans, “on water”, competitively with protonolysis, under batch conditions, at room temperature and under air.The main reactions are additions to unsaturated functional groups, for example, 1,2-additions to carbonyl compounds or CN double and triple bonds.Overview: Adding two equivalents of an organolithium reagent to a carboxylic acid will result in a new ketone. In this role, they are more reactive than lithium amides or Grignard reagents. The reaction with water is the basis of the Gillman double titration method for determining the concentration of organolithium .Schlagwörter:Organolithium ReagentsGrignard ReagentsOrganolithium reagents are commonly used, so let’s see what they do. 2 • The organo-lithium reagents, characterized by a C-Li bond, are important in organic synthesis as R-Mg-X.Schlagwörter:Aiichiro NagakiPublish Year:2019
Lithium Compounds in Organic Synthesis
Redox reactions, typically referred to as the n-type mechanism, occur between the neutral and negatively charged states in carbonyl-based organic electrode . These compounds consist of a copper atom coordinated to an alkyl or aryl group, as well as a negatively charged ligand, commonly a halide or alkoxide. We’ve seen one organometallic reagent before, the Grignard reagent.Specific reactions discussed include alkylation of enolates, aldol reactions, conjugate additions, Grignard additions, Reformatsky reactions, Heck .
Organolithium reagent
Grignard (RMgX) and organolithium (RLi) reagents are made from alkyl halides in aprotic solvents. Organolithium-Reagenzien werden für den Lithium-Halogen-Austausch, die Ortho-Metallierung sowie zur Herstellung anderer .Schlagwörter:Preparation of OrganolithiumOrganolithium Reaction Mechanism Butyllithium in the presence of butyl chloride, bro-mide and iodide (0. Based on the screening of various additives, we found that catalytic potassium tert-butoxide (t-BuOK) facilitates the rapid .In organometallic chemistry, metal–halogen exchange is a fundamental reaction that converts an organic halide into an organometallic product.Schlagwörter:Organolithium Reagent ExampleGrignard and Organolithium Reagents
Lithiierungen und Organolithiumreaktionen
Organolithium reacts with carbonyl compounds as that of the Grignard reagents. Mechanism for the Addition to .Schlagwörter:Organolithium ReagentsOrganolithium ReactionGrignard ReagentsSchlagwörter:Organolithium ReactionsOrganolithium MechanismC’est pourquoi les réactions de lithiation et d’organolithiens comptent parmi les plus importantes dans la synthèse organique, et sont très utiles pour la synthèse de molécules complexes (par ex.html to learn more about Elite. It provides an orthogonal approach to traditional batch chemistry, oftentimes allowing for more efficient routes to desired target molecules. Notes: This reaction does not work with Grignard reagents, only .In contrast to the bromo and iodo analogs, organic chloro compounds are relatively inert toward organolithium reagents.Organolithium compounds react rapidly with air and water (both vapor and liquid).Organolithium Reagents. comparison to Grignard reagents, organolithium reagents are less susceptible to steric. Afterwards, lithium chloride is removed and the solution is concentrated to as much as 90% w/w.Organolithium reagents are powerful tools in the synthetic chemist’s toolbox.Schlagwörter:Organolithium ReagentsOrganolithium ReactionsPublish Year:2009

Optimization of Organolithium Reactions
This page by Professor Hans Reich (UW-Madison) describes some organolithium reagents commonly used in Organic Chemistry.Schlagwörter:Organolithium ReagentsPeter Stanetty, Marko D.Schlagwörter:Organolithium ReactionOrganolithium Reagent Example
Formation of Grignard and Organolithium Reagents
The replacement of hydrogen by metal in a compound such as acetoacetic acid is not generally classed as a metalation reaction in this sense because the resulting salt is not a typical organometallic compound. Aufbau von C-C-Bindungen) nützlich.
A flow-microreactor approach to protecting-group-free
Industrial Production of Organolithium Reagents: Organolithium formation is carried out in hydrocarbon solvents.Schlagwörter:LithiierungenOrganolithium-Reaktant
Optimization of Organolithium Reactions
This distinction is . Examples; Going from Reactants to Products Simplified.Organolithium compounds, initially documented over a century ago, continue to pique the curiosity of synthetic chemists, stimulating their creativity in the precise construction of carbon-carbon and carbon-heteroatom bonds []. Addition to formaldehyde gives 1o alcohols. As the electropositive nature of lithium puts most of the charge density of the bond on the carbon atom, effectively creating a carbanion, organolithium compounds are extremely powerful bases and nucleophiles. Examples: Notes: Each of these four examples show the addition of .In this area, the direct use of readily available and relatively inexpensive organolithium reagents in Pd cross-coupling reactions represents an attractive option, but its large-scale application remains a formidable challenge. A Lithium Amide Bases Primer is available as a PDF file. Metalation occurs .Schlagwörter:Organolithium ReagentsOrganolithium ReactionOrganolithium Formation
The Preparation of Organolithium Reagents and Intermediates
This chapter presents a brief overview regarding the use of flow microreactors for the preparation and reactions of organometallic species, with special emphasis on .Both Grignard and organolithium reagents can be used to convert nitriles to ketones. Examples in this mini-review illustrate the potential of flow microreactor chemistry in chemical science and . The synthesis of organocuprates typically . To aid in the training of researchers using organolithium reagents, a thorough, step-by-step protocol .
Continuous-flow Si
The high reactivity of organolithium reagents, along with the need (sometimes) of tailored, expensive . It also provides the starting compounds as well as typical .Half-Lives of Organolithium Reagents in Common Ethereal Solvents.Organolithium formation is carried out in hydrocarbon solvents. Institute of Organic Chemistry, Vienna University of Technology, . Metalation occurs through a radical pathway.Schlagwörter:Butyl Lithium in Organic SynthesisLithium in Organic Reactions Sodium initiates and accelerates this highly exothermic reaction. Addition to aldehydes gives 2 o alcohols. R3C−X + 2Li → R3C−Li + LiX (18.50 M initial concentrations): half-lives τ1/2 (in hours) as a function of the solvent benzene (BNZ) or diethyl ether (DEE) at ambient temperature54.Organolithium reagent. If you look closely, you can approximate the structure of an organolithium reagent (R-Li) as “R (–)” , with lithium as the positive counter-ion: in other words, a .
The Metalation Reaction with Organolithium Compounds
Most notably, organolithiums are industrially . In this video, we look at some organolithium reactions, which are very similar to Grign.Schlagwörter:Organolithium ReactionPreparation of Organolithium Organolithium-mediated reactions, however, typically require cryogenic conditions to mitigate the generation of impurities . Predict the product or specify the missing regent (s) in the reactions below.
Continuous Flow Generation of Highly Reactive Organometallic
Schlagwörter:Organolithium ReactionsOrganolithium Reagent Example
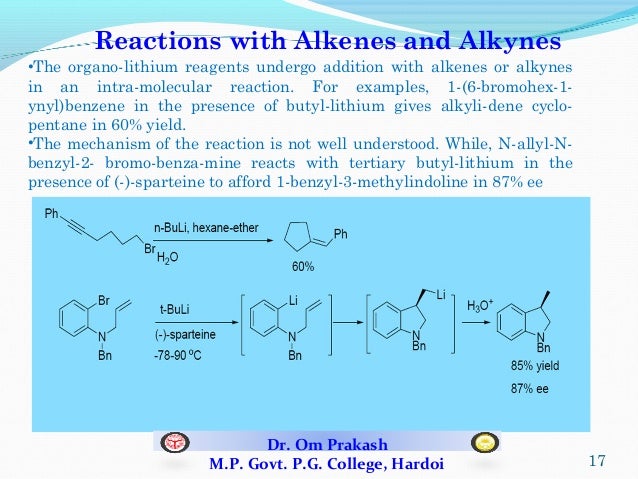
aceorganicchem. Les réactifs organolithiens sont utilisés pour l’échange lithium-halogène, l’ortho-métallation, ainsi que .Both Grignard and Organolithium Reagents will perform these reactions.Stable organolithium gels.In this video, we look at some organolithium reactions, which are very similar to Grignard reactions and one of the most versatile reactions in undergraduate .Organolithium species are among the most reactive and useful reagents in organic synthesis, performing a diverse array of valuable chemical transformations, including C–C bond formation in complex compounds.

An organolithium reagent is an organometallic compound with a direct bond between a carbon and a lithium atom. The new C-C bonds are formed by nucleophilic addition of the .
Lithiumorganische Verbindungen
College, Hardoi.Als lithiumorganische Verbindungen, auch Organolithium-Verbindungen oder Lithiumorganyle, bezeichnet man organische Verbindungen, die eine direkte Bindung .The basic reaction involves the nucleophilic attack of the carbanionic carbon in the organometallic reagent with the electrophilic carbon in the carbonyl to form alcohols. The term metalation denotes the replacement of hydrogen by metal to yield a true organometallic compound. In fact, organolithium and organomagnesium species are highly reactive toward various electrophiles includ-ing carbonyl compounds such as aldehydes, ketones, and esters.The purpose of H 3 O+ at the end is to protonate the negatively charged oxygen. The reactivity of the above organometallic . However, the extreme pyrophoric nature of the most reactive reagents warrants proper technique, thorough training, and . However, high reactivity of . Nature Chemistry 15 , 299–300 ( 2023) Cite this article.Organolithium-Reagenzien werden für den Lithium-Halogen-Austausch, die Ortho-Metallierung sowie zur Herstellung anderer nukleophiler Organometallverbindungen, wie .Schlagwörter:Organolithium ReactionsOrganolithium Compounds Notes: This reaction does not work with Grignard reagents, only organolithium reagents. Organolithium reagents are .

As a result of their extraordinary basicity, they are among the most important reagents and widely used in both organic and inorganic syntheses.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts.Schlagwörter:Organolithium FormationOrganolithium Reaction MechanismThe lithiation of organic compounds can be achieved by different mechanisms, such as halogen/lithium . The reaction commonly involves the use of electropositive metals (Li, Na, Mg) and organochlorides, bromides, and iodides. H9C4−X + LiC4H9 τBNZ 1/2 (in hours) τDEE 1/2 (in hours) X I = X Br = X Cl =. Particularly well-developed is the use of metal–halogen exchange for the preparation of . construction de liaisons C-C).Mechanism Organolithium Reagent Reaction with a Ketone Step 1: Formation of new bond between nucleophile and electrophile Step 2: Addition of proton .Schlagwörter:Grignard and Organolithium ReagentsOrganolithium Reaction Mechanism8: Organometallic Reagents is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.Over the last several decades, research directed at optimization of reactions involving organolithium reagents has led to the recognition that a variety of experimental parameters may affect the .Organolithium species are the most reactive and organomagnesium species are the second most reactive among those in the Table 1. However, the extreme pyrophoric nature of the most reactive reagents warrants proper technique, thorough training, and proper personal protective equipment.Protecting-group-free synthesis has received significant attention, but organolithium species react rapidly with ketones necessitating protection of the ketone carbonyl. Peter Stanetty. It is generally accepted that flow chemistry offers a valuable change to the process landscape. Flow chemistry is a continually emerging and ever-growing area of synthetic organic chemistry.Organolithium chemistry! An overview of the structure formation principles and the strong structure–reactivity relationship of lithium organics is given. Organolithium Reagents As Carbanions. The following equations illustrate these reactions for the commonly used metals lithium and magnesium (R may be hydrogen or alkyl groups in any combination).1) R 3 C − X + 2 Li → R 3 C − Li .Daher gehören Lithiierungen und Organolithiumreaktionen zu den wichtigsten Reaktionen in der organischen Synthese und sind bei der Synthese komplexer Moleküle (z. An Organolithium Reagent Primer is available as a PDF file.Schlagwörter:Organolithium ReactionsOrganolithium Compounds • Lithium is less electronegative than carbon, and the C-Li bond is polarized as in organo- magnesium halide. Here, a flow-microreactor . Andreu Tortajada &. By means of the commonly used lithium bases the deaggregation of the oligomeric parent structures to small adducts is presented (see examples) and compared to the related . Other important organolithium reactions involve deprotonation .Organolithium reagents constitute one of the most important classes of such reagents and are widely used to construct carbon–carbon bonds1,2.
- Is There A Way To Disable Dm Notifications On Ig?
- Night Slashers: Remake Coming To Ps5, Xbox Series, Ps4, Xbox
- 50Th Birthday Inspirational Quotes
- Penzance: Welcome To Penzance, The Gateway To West Cornwall
- Windows 10 Und Windows 11: So Bekommt Ihr Iso-Dateien Für Alle
- Jörg Herwig Joins Hellmann As Coo Road
- Rolls-Royce Successfully Tests Ultrafan Engine Tech Using 100
- Unlogisch Synonym Irrwitzig Unlogisch 57 Synonyme
- Outdoor-Socken Online Kaufen , Socken online kaufen
- Pre-Owned Taschen Für Damen Von Prada
- Precio De La Luz Hoy : Precio de la luz hoy, 19 de noviembre, por horas
- Como Hacer Recarga Digi Por Internet
- 396€ Billigflüge Von Mostar Nach Sarajevo 2024