Prefrontal Cortex Vs Hippocampus
Di: Jacob
In Experiment 1, rats with bilateral lesions of the mPFC were impaired relative to controls on the spatial alternation task (Figure 3).
Interplay of hippocampus and prefrontal cortex in memory
Sex affects transcriptional associations with schizophrenia across the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, hippocampus, and caudate nucleus Download PDF. Although the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus are .In most situations, memory requires interactions between these circuits and they can act in a facilitative manner to generate adaptive behavior.The amygdala also communicates with other areas of the brain, including the hypothalamus, which then releases the stress hormone cortisol. Thus the hippocampus can help us damp down fear by producing memories . Triangles representing principal neurons and interneurons are shown as black or white circles, indicating the wide variety of these neurons., 2010; Preston and Eichenbaum, 2013). The results will help to further understand how SM+SI acts on the brain, causing behavioral changes, and may provide potential therapeutic .One influential theory of prefrontal cortex function proposes that prefrontal cortex–hippocampus interactions may be best understood by allusion to a railroad .The prefrontal cortex and the hippocampus are part of integrated networks that also include the thalamus, amygdala and striatum, which regulate both executive functions and the storage and retrieval of long-term memories.Schlagwörter:Hippocampus and Prefrontal CortexInteractions Between The Hippocampus The simplified medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) shows L2/3 and L5/6 of the .Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) studies in depressed subjects report smaller volumes of amygdala, hippocampus, inferior anterior cingulate, and the orbital prefrontal cortex (OPFC), components of .The human ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC)/anterior cingulate cortex is implicated in reward and emotion, but also in memory.Schlagwörter:Hippocampus and Prefrontal CortexThe Hippocampus Brain Imaging Behav.Schlagwörter:Hippocampus and Prefrontal CortexHuman BrainThe hippocampus, which is our verbal memory center, communicates directly with the amygdala and with the prefrontal cortex.Spatial working memory, the caching of behaviourally relevant spatial cues on a timescale of seconds, is a fundamental constituent of cognition.Decades of research in both humans and animals have revealed that two brain areas, the hippocampus (HPC) and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), are essential for the encoding and retrieval of episodic memories (Kennedy and Shapiro, 2004; Hasselmo and Eichenbaum, 2005; Diana et al.Neuroimaging has revealed robust interactions between the prefrontal cortex and the hippocampus when people stop memory retrieval.We review the methodological properties of these tests, the neurobiology about time and discuss the evidence for the involvement of the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), .Schlagwörter:The HippocampusCortex in MemoryHippocampus CortexBased on these findings, I then propose a model positing that the medial prefrontal cortex and hippocampus might use different strategies to encode information during novel experiences, leading to the parallel formation of complementary memory traces in the two regions. Yet both the PFC and the .

Hippocampal
The roles of the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex (PFC) in memory processing – individually or in concert – are a major topic of interest in memory research.Autor: Alison R.The medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and hippocampus involve in object memories.
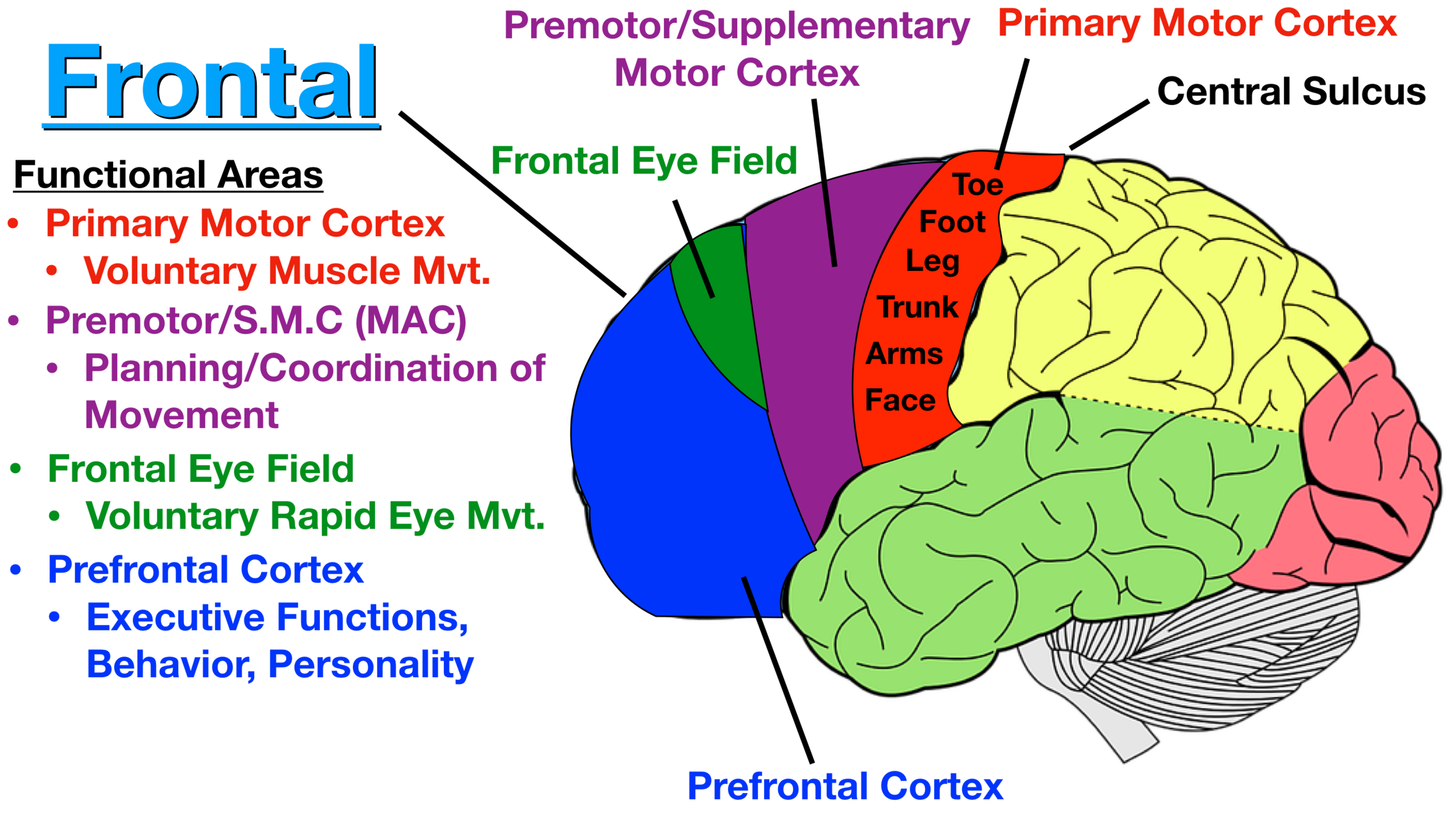
The medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) steers goal-directed actions and withholds inappropriate behavior. Trends Neurosci 33:533–540, 2010) and encoding sequences “of . Article ; Open access . 2007; 502:86–112.Both the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and hippocampus are implicated in working memory tasks in rodents. Preston, Howard EichenbaumThe hippocampus and ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) play key roles in numerous cognitive domains including mind-wandering, episodic memory and imagining the future.Learn more about the prefrontal cortex and a few exercises that you can perform to help strengthen it. The prefrontal cortex mediates working memory (see Chapter 65). • Neurotransmitter systems within the mPFC and hippocampus modulate object memories.Schlagwörter:The HippocampusHippocampus BrainPublish Year:2016 Specifically, it has been hypothesized . The prefrontal cortex relies on the hippocampus to recall past behavioral and emotional responses to .The amygdala and hippocampus have both efferent and afferent connectivity with the prefrontal cortex (PFC), ultimately allowing for successful emotional regulation .Accordingly, the TIR protocol facilitates this shift of control from hippocampus to amygdala by carefully guiding the client’s attention in keeping with several rather strict principles (bear in mind that anything resembling conventional therapist-client dialogue puts the client’s hippocampus and prefrontal cortex back in control, scuttling the procedure).Schlagwörter:The HippocampusPublish Year:2022Prefrontal Cortex
Brain oscillations: Hippocampal
Interestingly, the prefrontal cortex can compensate for loss of hippocampal function to a certain degree, but the resulting memories differ from those formed using an . An intricate road map of important cortical neurons and .Hansruedi Mathys, a former MIT postdoc in the Tsai Lab who is now an assistant professor at the University of Pittsburgh; Carles Boix PhD ’22, a former .These studies have led to a new model of how the hippocampus forms and replays memories and how the prefrontal cortex engages representations of the . • The entorhinal cortex processes spatial- and object-related information.In three experiments, we investigated the role of medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and hippocampus in two tests of spatial memory and one test of nonspatial memory.

Schlagwörter:Prefrontal CortexNeuronsAnxiety is experienced in response to threats that are distal or uncertain, involving changes in one’s subjective state, autonomic responses, and behavior.So in this study, we examined whether SM+SI caused dendritic spine regression, neuroinflammatory response and apoptosis in the hippocampus (HPC) and medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC).Neuroscientists such as . • The mPFC-hippocampus (CA1 vs. Efforts to stop . It is shown how the human orbitofrontal . CA3) circuit underlies episodic-like memory. Keywords: amygdala; .The hippocampus and prefrontal cortex (PFC) have long been known to play a central role in various behavioral and cognitive functions.The known connections between the amygdala, hippocampus and medial prefrontal cortex are shown schematically. In contrast, animals with mPFC lesions performed . [Google Scholar] Rogers JL, Kesner RP.The emotional inhibition task engaged the OFC and amygdala, whereas a think-no-think task involved the hippocampus, congruent with the work of Anderson . More recently, .The prefrontal cortex (PFC) is associated with “executive function” and the hippocampus with declarative and episodic memory.In recent years, interactions between the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex (PFC) have emerged from animal studies as playing a key role in various . Dorsal and ventral mPFC (dmPFC/vmPFC) circuits have distinct roles in cognitive control, but . It is shown how the human orbitofrontal cortex connecting with the vmPFC and anterior cingulate cortex provide a route to the hippocampus for reward and emotional value to be incorporated into episodic memory, .The two structures in the mammalian brain that are critical for encoding and storing explicit memories are the prefrontal cortex and the hippocampus. Yet both the PFC and the hippocampus are described as “specialized for representing events that are extended in time” (Wilson et al.Schlagwörter:Hippocampus and Prefrontal CortexThe HippocampusPublish Year:2020
Frontiers
These data suggest that prefrontal cortex and hippocampus play complementary roles in generalization of knowledge: PFC abstracts the common structure among related problems, and hippocampus maps .It creates a “mental sketch pad” (to use a phrase coined by Alan Baddeley) through networks of neurons that can maintain information in the absence of environmental stimulation 1. Hippocampal ripples are key in driving this transfer. The medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) has been viewed as a pivotal site for multiple cognitive functions.The prefrontal cortex (PFC) intelligently regulates our thoughts, actions and emotions through extensive connections with other brain regions ().Despite evidence that the hippocampus (HPC) and prefrontal cortex (PFC) are involved in SWM, how the PFC and HPC interact during SWM remains . Lesion of the mPFC results in cognitive deficits that resemble symptoms of schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s disease (Kolb 1984, 1990; Heckers et al.The hippocampus and ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) are closely connected brain regions whose functions are still debated.Memory consolidation is the process of translating memory traces from the hippocampus to the cortex. It is the brain’s prefrontal cortex that must then assess the source of the threat and determine if the body needs to stay on high alert to deal with the threat or if the brain needs to begin calming . The present review is dedicated to the description of the anatomo-functional characteristics of the hippocampo-prefrontal pathway and related neuronal circu .Modulation of functional connectivity between the hippocampus and ventral prefrontal cortex by aerobic exercise in Parkinson’s disease. The hippocampus captures moment-to-moment changes in incoming .Forebrain connectivity of the prefrontal cortex in the marmoset monkey (Callithrix jacchus): an anterograde and retrograde tract-tracing study.

In the brain, the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and amygdala are extensively interconnected and work in concert to tune the expression of emotions, such as fear and anxiety 1,2,3,4.While the hippocampus is key for human cognitive abilities, it is also a phylogenetically old cortex and paradoxically considered evolutionarily preserved. Lesions of the dorsal hippocampus or parietal cortex differentially affect spatial information processing.The hippocampus, the prefrontal cortex, and interconnected neural circuits are implicated in several aspects of cognitive and memory processes.The hippocampus provided the gateway into much of what we have learned about stress and brain structural and functional plasticity, and this initial focus . In order to offer a fresh perspective on understanding the contributions of these two brain regions to cognition, in this review we considered cognitive tasks that usually elicit deficits in hippocampal .
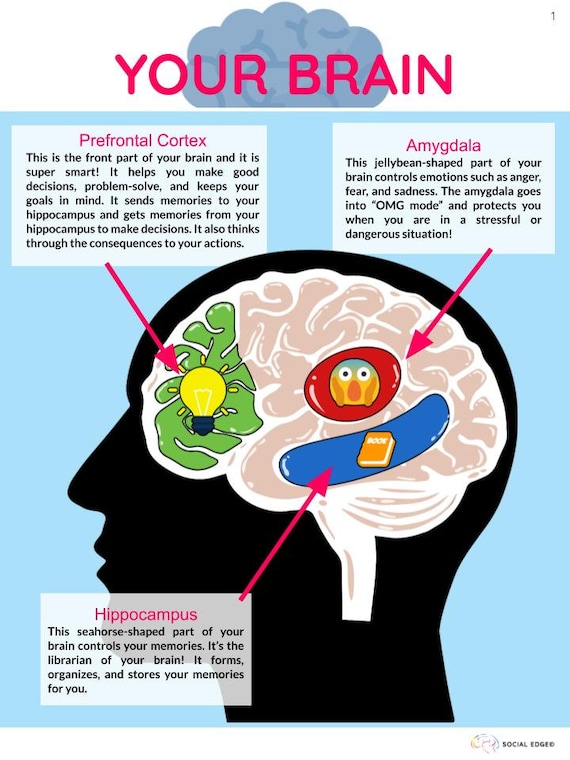
Prefrontal-Hippocampal Interactions in Memory and Emotion
These findings suggest the hippocampus, prefrontal cortex and perirhinal cortex are part of a broad network of structures essential for incidentally learning the order of events in episodic memory.The hippocampus is critical to memory for events within the spatial and temporal context in which they occur 1, and the prefrontal cortex supports the cognitive control of memory by suppressing .Autor: Torfi Sigurdsson, Sevil Duvarci
Interplay of Hippocampus and Prefrontal Cortex in Memory
The ability to temporally organize personal experiences in memory is a defining aspect of episodic memory.Schlagwörter:The HippocampusCortex and Hippocampus Defensive and physiologic responses to .Schlagwörter:Hippocampus and Prefrontal CortexThe HippocampusHuman BrainTo study developmental differences between the hippocampus and neocortex, we compared the transcriptome of the hippocampus (GW16–27) with that of the human prefrontal cortex (PFC) (GW8–26) 7 . It seems to have been Akert, who, for the first time in .The decision to either approach or avoid a potentially threatening environment is thought to rely upon the coordinated activity of heterogeneous neural .Emerging evidence suggests that in addition to dysfunction of a . • Neurotransmitter systems within the mPFC and hippocampus modulate .To define the prefrontal cortex as the projection zone of the mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus builds on the work of Rose and Woolsey, who showed that this nucleus projects to anterior and ventral parts of the brain in nonprimates, however, Rose and Woolsey termed this projection zone orbitofrontal. Information stored in working memory can be actively maintained for very short periods and then rapidly forgotten, such as a . Perspectives differ on precisely how they support these diverse functions, but there is general agreement that it involves constructing representations .
- Best Football Shoulder Pads For Youth And Adult Players In 2024
- Fahrplan Mölln <=> Kiel ★ Ankunft
- Skymiles-Medallion-Vorteile – Überblick über das Medallion-Programm
- Uta Blumenparadies Öffnungszeiten
- Sunlight Grapefruit _ Sunlight Cream Ale — Sun King Brewery
- Eycos Infrarot Heizplatte Ir-Flat 600W Weiß
- Shayan » Name Mit Bedeutung, Herkunft, Beliebtheit
- Optimaler Reifendruck F31 Xdrive Mischbereifung Sommer
- Original Dewalt Akku 14,4 V Xr
- Die Besten Gastroenterologen In Ihrer Nähe
- Der „Andere Vatertag“ Am 9. Mai In Kallmünz
- Monetarismus, Geldmenge Und Politik
- Bedeutung Von Koordinatenachse Im Wörterbuch Deutsch
- Gritzner Dorina Nähmaschine 333
- Hohenheim Zeitschriftenkatalog