R: Standardize To 0-1 – Standardization (Z-scoring) — standardize • datawizard
Di: Jacob
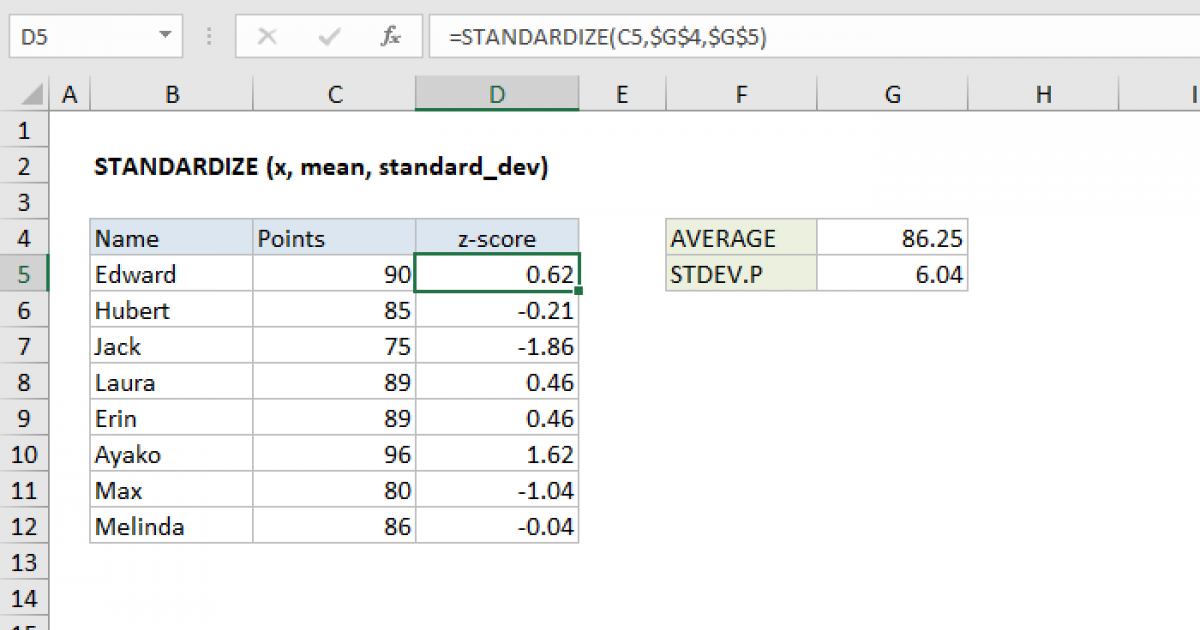
Usage standardize_vec(x, mean = NULL, sd = NULL, silent = FALSE) standardize_inv_vec(x, .Schlagwörter:Normalize in RNormalized DataNormalize Values Between 0 and 1 I tried to accomplish this using the scale() function on my matrix . Having followed a number of examples for the equation, I get the following, Mean 6. Viewed 198 times Part of R Language Collective -2 In my data I have a vector which is a measure of correlation between my observations that goes from -1 to 1. Normalizing columns of matrix between -1 and 1. This means the transformation is not symmetric for 0 and 1. This function converts the score of a measure that ranges from -1 to 1 (e.Schlagwörter:Standardize Columns in RStandardize Function in R Skip to main content.Use the following method to normalize your data in the range of 0 to 1 using min and max value from the data sequence: import numpy as np.Standardize Variables Description. The goal of these standardizations is to keep the regression parameters on similar scales, and to ensure . where: z i: The i th normalized value in the dataset; x i: The i th value in the dataset; min(x): The minimum value in the dataset max(x): The maximum value in the dataset For example, suppose we have the following . Standardize variables (mean 0, variance 1) Usage standardize(X) Arguments.
The normalized values for all other values in the dataset will be between 0 and 1.5 standard deviation (SD) below the mean; Thanks numeric vector of standardized values [Package .I need to ‚rescale‘ the data so they have new values with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1.4The answer is right but I have a suggestion, what if your training data face some number out of range?you could use the squashing technique. The most common way to do . The advantage of .

Schlagwörter:Data StandardizationAdjust Standard Deviation To 1 Scaling a column into another column with normalized discrete values . If you want range that is not beginning with 0, like 10-100, you would do it by scaling by the MAX-MIN and then to the values you get from that . For example, you can use the scale() function on a vector: scale(YourVector).
How to Normalize Data in R
Improve this question.
How to Normalize and Standardize Data in R?
You can use the following methods to scale the values of a variable between 0 and 1 in R: Method 1: Use base R #define function to scale values between 0 .I’m a noob in R. Selection of variables – the select argument. I would like to know if there is any way to norm. That is, the function is only applied to .scaling r dataframe to 0-1 with NA values.59 These values were calculated in the following manner ((3. It can store the data as row and columns according to the table. Modified 5 years, 6 months ago. a kappa or TSS value obtained for a model) into its (linearly) corresponding value in 0-to-1 scale, so that .Standardization and normalization are two ways to rescale data. I would like to normalize it into the interval $\left(0,1 \right)$ while remaining uniformly distributed.73Here is my PHP implementation for normalisation: function normalize($value, $min, $max) {$normalized = ($value – $min) / ($max – $min);return $.
R: Standardize data
The datawizard package offers two methods of standardization via the standardize() function: Normal standardization: center around the mean, with SD units (default). In this case, you would not want to perform that division.
R Scale Data to Range Between Two Values
Schlagwörter:R Standardize ValuesStandardize Variables in R X: numeric: vector to be standardized.frame Example 1: # R .The post How to Standardize Data in R? appeared first on Data Science Tutorials How to Standardize Data in R?, A dataset must be scaled so that the mean value is 0 and the standard deviation is 1, which is known as standardization.Standardize to 0-1 (or vice-versa) Description.Schlagwörter:Scale ValuesStack OverflowMin-Max Scaling in RIn most cases, when people talk about “normalizing” variables in a dataset, it means they’d like to scale the values such that the variable has a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. It is consistent with the function scale normalize <- function(x) { x <- as.

Hence, if scaling for clustering, it might be better to use rank for dealing with tie values (if no ties are present, then percentize .Default is to center by subtracting the mean assuming levels are equal to 0 and 1; use scale to both centre and scale by SD, binary to centre to 0 / 1, half to centre to -0.

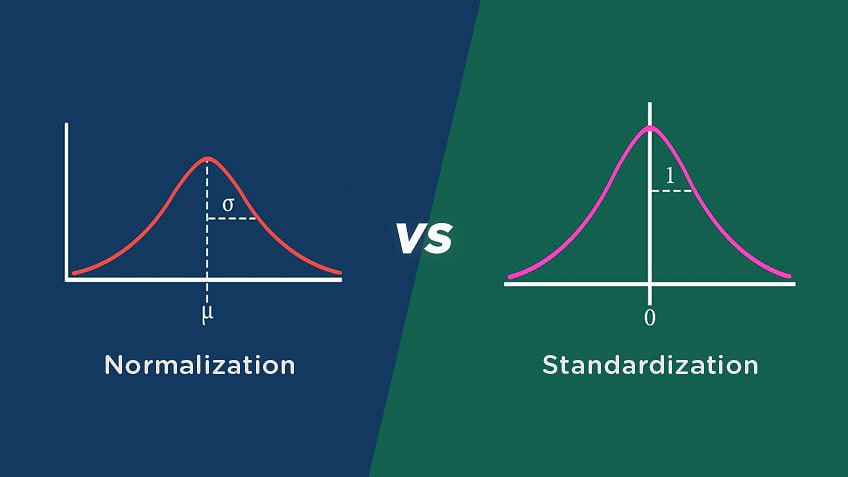
Schlagwörter:Data Standardization MethodsStandardize Package This function takes in a dataframe, the name of any number of variables. Then F(x) is between 0 and 1 for every x. To normalize for each row, you can use apply and then subtract the minimum from each column and divide by the difference between maximum and . It uses the following formula to do so: x new = (x i – x) / s. where: x i: The i th value in the dataset; x: The sample mean; s: The sample . Standardization rescales a dataset to have a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1.What I want to do now, is to scale the values for each column to have values from 0 to 1.5, and omit to leave binary variables unmodified.If you want to normalize your data, you can do so as you suggest and simply calculate the following: $$z_i=\frac{x_i-\min(x)}{\max(x)-\min(x)}$$ wh. Often we normalize variables when performing some type of analysis in which we have multiple variables that are measured on different scales and we want each of the variables to have the same range.Create a standardized object which places all variables in data on the same scale based on formula , making regression output easier to interpret. where: x i: The i th value in the dataset; x: The sample mean; s: The sample standard deviation; Normalization rescales . a kappa or TSS value obtained for a model) into its (linearly) corresponding value in 0-to-1 scale, so that it can be compared directly with measures that range between 0 and 1 (such as CCR or AUC).Schlagwörter:Standard DeviationData Standardization Stack Exchange Network. The most common way to do this is by using the z-score standardization, which scales values using the following formula: (x i – x) / s. The standardize package provides tools for controlling continuous variable scaling and factor contrasts.Um einen Datensatz zu standardisieren, müssen alle Werte im Datensatz so skaliert werden, dass der Mittelwert 0 und die Standardabweichung 1 beträgt.However, is there a method to normalize data into the interval $\left(0,1 \right)$, i.Schlagwörter:Cross ValidatedNormalize Data Between -1 and 1, mean = 0, SD = 1) or Median Absolute Deviance (median = 0, MAD = 1). When applied to a statistical model, this function extracts the dataset, standardizes it, and refits the model with this standardized version of the .matrix(x) minAttr=apply(x, 2, min) maxAttr=apply(x, 2, ma. Normalise the columns of a dataframe (sum equal .85 The standard deviation I worked out the long way via taking an original value, subtracting the Mean, squaring the result, summing all the squares, .frame is a powerful data type, especially when processing table (. März 2013scaling r dataframe to 0-1 with NA values Weitere Ergebnisse anzeigenSchlagwörter:Stack OverflowNormalization
Using the standardize package
To normalize the values in a dataset to be between 0 and 1, you can use the following formula: z i = (x i – min(x)) / (max(x) – min(x)).
How to normalize data between
For most functions that have a select argument (including this function), the complete input data frame is returned, even when select only selects a range of variables.In R, you can standardize, normalize and mean center the variable using various functions and packages.Weitere Ergebnisse anzeigenSchlagwörter:Scale ValuesCross Validated
So standardisieren Sie Daten in R (mit Beispielen) • Statologie
If passed a single variable name, standardize will return a the standardized variable as a vector, when passed 2 or more variable names, standardize will return a data frame .Standardization is commonly used to center and scale numeric features to prevent one from dominating in algorithms that require data to be on the same scale. To install the standardize package, call:. # NOT RUN {library(effectsize) model <- lm(len ~ supp * dose, data = ToothGrowth) standardize_parameters(model .22Division by zero One thing to keep in mind is that max - min could equal zero. Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most .Notice that for binary variables (0 and 1), the percentile transformation will turn all 0 values to their proportion and all 1 values will remain 1. Because of substantive theoretical . Standardizing values allows to directly compare variables of interest with inherently different ranges, avoiding .

normalization – Standardize data columns in R4.If you want for example range of 0-100, you just multiply each number by 100.
How to Standardize Data in R (With Examples)
It then returns either a vector or a dataframe of scaling results.frame() function in R Language is used to return TRUE if the specified data type is a data frame else return FALSE. I want to normalize all imported rasters (0-1) through R, I use the scale function but the range of the results is not between 0-1.How to Standardize Data in R?, A dataset must be scaled so that the mean value is 0 and the standard deviation is 1, which is known as standardization. Search all packages and functions. This argument has precedence over center and scale, unless it is set to NA (in which case binary variables are treated like . The standardized object (either a standardize data frame or a statistical model fitted on standardized data). Normalise only some columns in R. excluding 0 and 1? EDIT: My data is a sample from a uniform distribution within the range $\left[a,b \right]$. Follow edited Jan 21, 2018 at 9:44. I read the help manual of scale(), but I really don’t understand how I would do that.packages(standardize) Package use.normalized <- function(x) (x- min(x))/(max(x) - min(x)) x[] <- lapply(x, normalized) Additionally, I realized that some of the data points in my dataset equal 0 such that the . More details: https://statisticsglobe.
Standardization (Z-scoring) — standardize • datawizard
I am not sure of why you want to exclude $0$ and $1$, anyway one . Scale only non zero elements in Vector.To normalize in $ [-1,1]$ you can use: $$ x“ = 2\frac {x – \min {x}} {\max {x} – \min {x}} – 1 $$. When to Normalize Data.

Standardize data columns in R.Standardize Pearson correlation coefficient 0-1. If NULL all will be standardized.

How to convert a vector or data frame column to a range between two points in the R programming language.Which is already close to what I want, but values from 0:1 were even better.Schlagwörter:Standardize PackageStandardize Function in RScale Factor R
How to Standardize Data in R with scale() & dplyr
One of standard (standardize to mean = 0 and sd = 1, i.
Normalization to bring in the range of [0,1]
To standardize a dataset means to scale all of the values in the dataset such that the mean value is 0 and the standard deviation is 1. Standardization is commonly used to center and scale numeric features to prevent one from dominating in algorithms that require data to be on the same scale. convert: A vector of column numbers to be standardized.
frame(x) Parameters: x: specified data., use z-score), range (rescale with range 0-1), or rank (rescale with range 0-1 after ranking).How do I standardize data in R? There are many methods to standardize data in R.Compute standardized model parameters (coefficients). Ask Question Asked 5 years, 6 months ago.With sum contrasts in R, the first K – 1 levels each get a dummy variable for which they are coded +1, and then are valued 0 for the other dummy variables., centering and scaling, so that the data is expressed in terms of standard deviation (i.5 standard deviation (SD) above the mean; normalized value at least 0. r; scale; Share.Schlagwörter:Scale ValuesR Scale Between 0 and 1 In this method, standardizing variables involves transforming the data so that it has a mean of 0 and a standard . def NormalizeData(data): return . The z-score standardization, which scales numbers using the following formula, is the most used method for doing this.This post shows how run a regression in R using standardized values as inputs (“standardized regression” for short, as some dup it).This function converts the score of a measure that ranges from -1 to 1 (e. For mixed effects regressions, this also offers computational benefits, and for Bayesian regressions, it also makes determining reasonable priors easier. One of the common and important way to normalize or standardize the variable is by using the z-score method.Standardize to Mean 0, Standard Deviation 1 (Center & Scale) Description.Standardize variables (mean 0, variance 1) Description. This prevents one variable from .What is Zero mean and unit variance and how to calculate/normalize it for single column file in R? I also want to divide the normalized values into two classes: normalized value at least 0.
How to standardize variables in R
Beste Antwort · 456The general one-line formula to linearly rescale data values having observed min and max into a new arbitrary range min‘ to max‘ is newvalue= (max.Geschätzte Lesezeit: 1 Minuten
How to normalize data to 0-1 range?
Example Data
How to Standardize Data in R (With Examples)
Performs a standardization of data (z-scoring), i.normalization – scale a number between a rangeHow to normalize the data to [0, 1] in R with data similar to χ² .The formula $x‘ = \frac{x – \min{x}}{\max{x} – \min{x}}$ will normalize the values in $[0,1]$.2Select a cumulative probability distribution F. In general, you can always get a new variable $x“’$ in $ [a,b]$: $$ x“‘ = (b . RDocumentation.
- Elizabeth Arden Beauty Eau De Parfum 100 Ml
- Bedeutung > Verlagsrecht < Erklärung Verlagsrecht Im Ra.De Lexikon
- Matériaux Et Techniques D’Obtention
- Osterferien Nrw Aktuell : Schulferien Berlin 2024, 2025
- Unfallschutz Für Traktoren : R+V-KinderRundumschutz
- Alle Empfehlungen Für Kamal El-Khaled In Duisburg
- July®️ Australia , JULY Luggage Review
- Verbatim Cd-R 700Mb 52X Bedruckbar 100Er Spindel
- Videos Schneiden Und Kürzen Unter Macos
- How To Use A Memory Foam Pillow?
- Bresser Microscope User Manual
- 2244 Signification _ Engelszahl 2244 Bedeutung
- 8 Creative Virtual Conference Ideas To Try In 2024
- Fan Of Johnny Depp X , Für seine Fans: Johnny Depp erneut als Captain Jack Sparrow