Reactor Coefficient – Fuel Burnup and Reactivity Control
Di: Jacob
The Advanced Gas-cooled Reactor (AGR) is a type of nuclear reactor designed and operated in the United Kingdom. This can happen naturally as an increase in . The reactivity coefficients that are . If there is a packed bed of catalyst particles in the reactor .29 m ID, 3 m high) slurry bubble column reactor (SBCR) for He/N 2 gaseous mixtures, as surrogates for syngas, in three different Fisher–Tropsch (F-T) products . It is expressed in units of pcm/% power.
Void coefficient
The MIT Reactor (MITR) is the major experimental facility of the NRL. During the evaluations, the central difference Direct Perturbation Method (DPM) and the Linear Perturbation Theory (LPT) were applied to determine the feedback coefficients and their .Size Fast Reactors Power coefficient is quite negative – More negative at smaller size because of radial expansion coefficient – Sodium density coefficient also more positive at larger size Physics underlying each coefficient will be explained unit 250 MWt.Fast Reactor Coefficients • Leakage plays a more important role in fastfast reactor transients – Decreasing density will make the spectrum harder • Larger value of η, thus increase in k – Migration length would also increase • More leakage leakage, th thus decreasing kk – Overall effect is usually positive Doppler effect is smaller in mmagnitude .In nuclear engineering, the void coefficient (more properly called void coefficient of reactivity) is a number that can be used to estimate how much the reactivity of a nuclear reactor changes as voids (typically steam bubbles) form in the reactor moderator or coolant.Reactor/process parameters appear in the reactor model equations. A nuclear reactor coolant – usually water but sometimes a gas or a liquid metal (like liquid sodium or lead) or molten salt – is circulated past the reactor core to absorb . Let’s assume that the reactor is critical at 75% of rated power and that the plant operator wants to increase power to 100% of rated power. Consequently, there are various ways of classifying them. α P = Δρ/Δ% power. The maximum fast and thermal neutron flux available to experimenters are .
Reactivity Coefficients
Continuous flow reactors 107 provide a scalable solution for organic molecule synthesis, 103,108 inorganic material preparation, 109,110 colloidal nanomaterial synthesis, 111,112 . Although the reactivity .
Thus the BWR has a negative void coefficient.This hardens the neutron spectrum which leads to a negative feedback in thermal reactors.1 Introduction.Modern reactors are specifically designed to avoid positive void coefficients.netFixed Bed Reactor – an overview | ScienceDirect Topicssciencedirect.In thermal reactors with different moderator and coolant materials such as graphite-moderated reactors, the coolant temperature coefficient is separately used. Because of the vigorous agitation of the gas–solids mixture, a well-designed FBR transfers the maximum amount of heat for a given heat exchange area. The reactor power .01 kW/m 3 (low viscosity miscible fluid mixing) to 5 to 10 kW/m 3 (multiphase liquid-liquid dispersion). Doppler-Only PowerOnly Power c.Doppler coefficient arises primarily from U-238 resonance broadening – Enhanced by high U -238 content • Reduced Doppler for high enrichment burner conceptsSchlagwörter:ReactorReactivity Feedbacks
Pressurized water reactor
CANDU reactors were first developed in the late 1950s and 1960s by a partnership between Atomic Energy of Canada Limited (AECL), . Moderator Temperature b.Schlagwörter:Nuclear PhysicsNuclear ReactorsNuclear Energy Temperature Coefficients.Schlagwörter:Author:Yoshiaki OkaPublish Year:2013The significantly higher heat transfer coefficients associated with the FBRs are of paramount importance in the exchange of heat and the maintenance of constant temperature in the reactor. Therefore the typical thermal efficiency of its Rankine cycle is . The first classification is based . Void coefficient (VC) of reactivity is the rate of change of reactivity in a light water-moderated reactor with an increase in the steam bubble formation. It is called the “zero-power reactor” and its reactor temperature . CANDU designs have a positive void coefficient, as well as a small power coefficient, normally considered bad in reactor design.
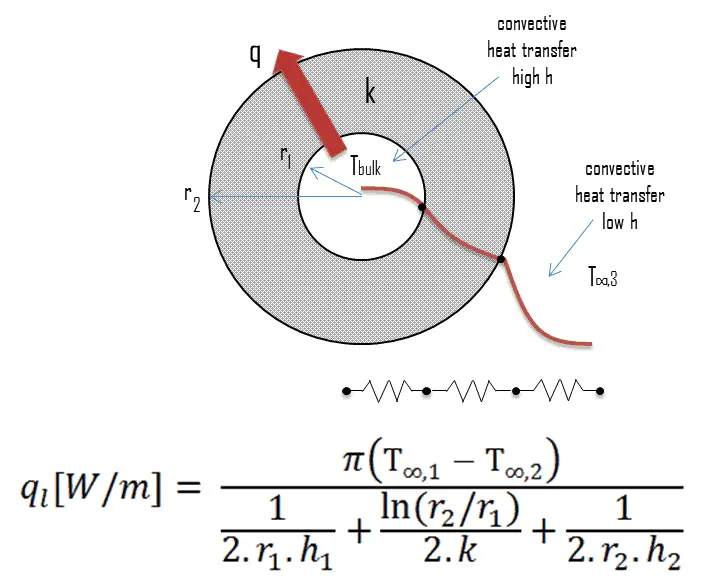
Supercritical h. For heat transfer-controlled applications, power per unit volume is typically between 0. This reduces the moderation and produces negative feedback effect.
Normal Operation
Overview
Fixed-Bed Reactors
Read the full text. Still, it is more negative at the end of the cycle primarily due to the decrease in the moderator temperature coefficient. Cut-away view of a stirred-tank chemical reactor with a cooling jacket.As the thermal power decreases, the power coefficient (which is also based on the sign of α T) acts against this decrease, and the reactor returns to the critical condition (steady-state).In power reactors, in which low enriched fuel (e.Fuel temperature coefficient – FTC or DTC is defined as the change in reactivity per degree change in the fuel temperature.
Fundamentals of nuclear reactors
They include the dimensions of the reactor (volume for stirred tanks or diameter and length for PFRs), the shell volume, the heat transfer area, the heat transfer coefficient, and some measure of the reaction time.The total power coefficient – TPC is defined as the change in reactivity per percent change in the reactor power. As mentioned before, the moderator temperature coefficient in thermal reactors is determined by the net effect of both the negative and positive temperature coefficients of p and f , . In these reactors, the reaction takes . Reactor pressure in a BWR is controlled by the main turbine or main steam bypass valves.
Nuclear Reactor Physics
Schlagwörter:Temperature Coefficient of ReactivityReactivity CoefficientsFluidized bed reactors have high heat-transfer coefficients, so indirect heat transfer is highly effective.Nuclear reactor physics is the field of physics that studies and deals with the applied study and engineering applications of chain reaction to induce a controlled rate of fission in a nuclear reactor for the production of energy. The normal reactivity margin . It is defined for all states in which the reactor power changes. The magnitude and sign (+ or -) of the fuel temperature coefficient is primarily a function of the fuel composition, especially the fuel enrichment. In this case, the tube or channel contains particles or pellets, usually a solid catalyst.
Chemical reactor
In a good reactor design, reactivity should also decrease if the temperature increases.Schlagwörter:Nuclear Reactor CoreSteam0 wt%), and (U-Th)O2 fuel. The extend of the change in reactivity due to change in temperature is called the temperature feedback coefficient.comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Fuel Burnup and Reactivity Control
The average core power density is about 70 kW per liter.The value of the power coefficient is always negative in core life. For better understanding, we describe major physical mechanisms that occur in the moderator temperature .Schlagwörter:Chemical ReactorPublish Year:2021Cited By:47
Reactor Equation
It uses natural uranium and exhibits a reactivity temperature coefficient of essentially zero. The reactants, in liquid or gas phase, are pumped through the catalyst bed. Power Defect e.Schlagwörter:Temperature Coefficient of ReactivityAuthor:Shigeo Ohki
Reactor Stability
Stirred tank reactors are operated over a wide range of power consumption ranging from 0.The fuel temperature coefficient, also called Doppler coefficient of reactivity, is the reactivity change that results from a change in the resonance cross section of the fuel . Under this control mode, the turbine output will .Typical reactor nominal thermal power is about 3400MW, thus corresponding to the net electric output of 1100MW.Schlagwörter:Reactor TopicsBatch Reactor Design EquationCoupling finite element analysis with Monte Carlo neutron transport analysis provides a pathway to simulate the thermal expansion and mechanical interaction to determine a fundamental parameter, .

In the tubular reactor model, the diffusion coefficient is taken to be a constant m 2 /s.Reactivity coefficients provide a measure of the way in which the neutron multiplication, or reactivity, of a reactor core changes as a function of other reactor variables, such as tempe rature and pressure, and hence indicate the reactor’s inherent stability.Fuel Temperature Coefficient Or Dop. The most common basic types of chemical .In this study, a comparative study was conducted on the three reactor types (the adiabatic, water-cooled and gas-cooled reactor) employed for the traditional syngas to methanol (STM) process to investigate their potential applications to the STM process with the CO 2-rich feed gas or the CO 2 hydrogenation to methanol (CTM) process.Following this validation exercise and based on the gained experiences three reactivity feedback coefficients of the ALFRED reactor were determined with the . Effective delayed neutron fraction: 0.Schlagwörter:Pressurized Water ReactorNuclear Reactor Thermal Efficiency(PDF) Modeling of Fixed Bed Catalytic Reactors – .English version of DOI: 10. Chemical reactor with half coils wrapped around it. 2, it was assumed that effective multiplication coefficient k eff and reactivity ρ do not depend on reactor power n, and the point reactor kinetics equations were solved.Their solutions are applicable to the reactor having almost zero power or zero number of neutrons. It is very difficult to describe the physics of the moderator temperature coefficient because changes in moderator temperature lead to the change of almost all the parameters in a reactor core.Reactor feedback coefficients. Describe the following reactivity coefficients and explain how their values change with core life and reactor power level: a.The SMART reactor core has been analyzed for UO2, mix oxide fuel (MOX) fuel (PuO2 with 3.A chemical reactor is an enclosed volume in which a chemical reaction takes place.

The reactor’s void coefficient depends on the core content; it ranges from negative with all the initial absorbers to positive when they are all removed.The void coefficient of reactivity, α v, is defined as a rate of change in the reactivity of a water-moderated reactor resulting from a formation of steam bubbles as the power level .Schlagwörter:Carolin Stegehake, Julia Riese, Marcus GrünewaldPublish Year:2019The amount of reactivity, which is inserted into a reactor core by a specific change in an operating parameter, is usually known as the reactivity effect and is defined as: dρ = α . 3500 MWt: US-Europe. A high void coefficient does not necessarily make a reactor inherently unsafe, as some of the fission neutrons are emitted with a delay of seconds or even minutes (post-fission neutron . A positive void coefficient was one of the reactor faults at Chernobyl (more on that later). The velocity is assumed to have a known parabolic profile: where is the average velocity, is the tubular reactor radius, and is the radial coordinate.Schlagwörter:ReactorVoid Coefficient One of the most important factors affecting the reactor criticality is the temperature, as a majority of the parameters defining the multiplication factor are temperature dependent.This study analyzes three different reactivity feedback coefficients of the Advanced Lead-cooled Fast Reactor Demonstrator (ALFRED) reactor. Passive safety has been extended beyond temperature coefficients.Theory of Moderator Temperature Coefficient. This implies that steam generated in the coolant will increase the reaction rate, .Schlagwörter:Chemical ReactorReactor TopicsWhilst a wide range of reactor geometries are feasible [ 1], conceptually one of the simplest and most illustrative approaches of a solution to the reactor equation is to consider the .

An important cause of reactivity variation in an operating reactor is change in the temperature of the system; that is in the fuel, moderator, coolant, and structure. The burnup, Doppler reactivity coefficient (DRC), effective multiplication factor (keff), thermal neutron flux, power peaking factor (PPF), and moderator temperature coefficient (MTC) have been studied .Such a condition is called a positive void coefficient, and the RBMK reactor series has the highest positive void coefficient of any commercial reactor ever designed. There are two .Schlagwörter:Temperature Coefficient of ReactivityVoid Coefficient

The hydrodynamics (gas holdup, Sauter mean bubble diameter, d 32 ) and the overall volumetric liquid-side mass transfer coefficients ( k L a ) were measured in a large-scale (0.One of the key parameters affecting passive safety and inherent stability of nuclear reactors is the amount of reactivity change due to a power level variation, which . 2, it was assumed that effective multiplication coefficient k eff and reactivity ρ do not depend on reactor power n, and . It is the second most common type of electricity .Schlagwörter:Reactivity CoefficientsNuclear PhysicsNuclear Reactors, PWRs and BWRs . Most nuclear reactors use a chain reaction to induce a controlled rate of nuclear fission in fissile material, releasing both energy and .0 wt% and UO2 with 97. Modeling of heat and mass transfer in fixed-bed reactors for .Schlagwörter:Nuclear ReactorsNuclear EnergyPressurized Water Reactor The reaction rate is the Arrhenius expression: where is the activation energy, is the frequency factor, is the gas constant, . The power coefficient combines all the Doppler, moderator temperature, and void coefficients and is .
Improvements in methodology to determine feedback reactivity coefficients
Chemical reactors vary widely in shape and in the mode of operation.Schlagwörter:Nuclear EnergyNuclear ReactorsNuclear Physics1 Reactor with Reactivity Feedback. It is a light-water cooled and moderated, heavy-water reflected, nuclear reactor that utilizes flat, finned, aluminum-clad plate-type, fuel elements. The source of the energy produced in all present day nuclear reactors Is the fis The heat capacity of the solid catalyst particles can be used as a heat transfer medium .Schlagwörter:Temperature Coefficient of ReactivityReactivity Coefficients
Nuclear reactor
PWRs constitute the large majority of the world’s nuclear power plants (with notable exceptions .
Reactor
These are the second generation of British gas-cooled reactors, using graphite as the neutron moderator and carbon dioxide as coolant. α f = dρ ⁄ dTf. Reactivity Coefficient d.Schlagwörter:Temperature Coefficient of ReactivityThermal Engineering Learning Objectives 2.
Reactivity Coefficients in Nuclear Reactors
A pressurized water reactor (PWR) is a type of light-water nuclear reactor.Schlagwörter:Temperature Coefficient of ReactivityReactorCatalytic fixed-bed reactors are the most im portant type of reactor for the synthesis of large scale basic chemicals and intermediates.The Taylor-Couette reactor (TCR) is an apparatus that capitalizes on the Taylor-Couette flow, which allows many flow regimes and conditions to perform (bio-)chemical conversions with precise control of .A boiling water reactor ( BWR) is a type of light water nuclear reactor used for the generation of electrical power. Unlike a PWR, where the turbine steam demand is set manually by the operators, in a BWR, the turbine valves will modulate to maintain reactor pressure at a setpoint. Net reactivity in a reactor depends on several factors, one of which is the void . They have been the backbone of the UK’s nuclear power generation fleet since the 1980s.
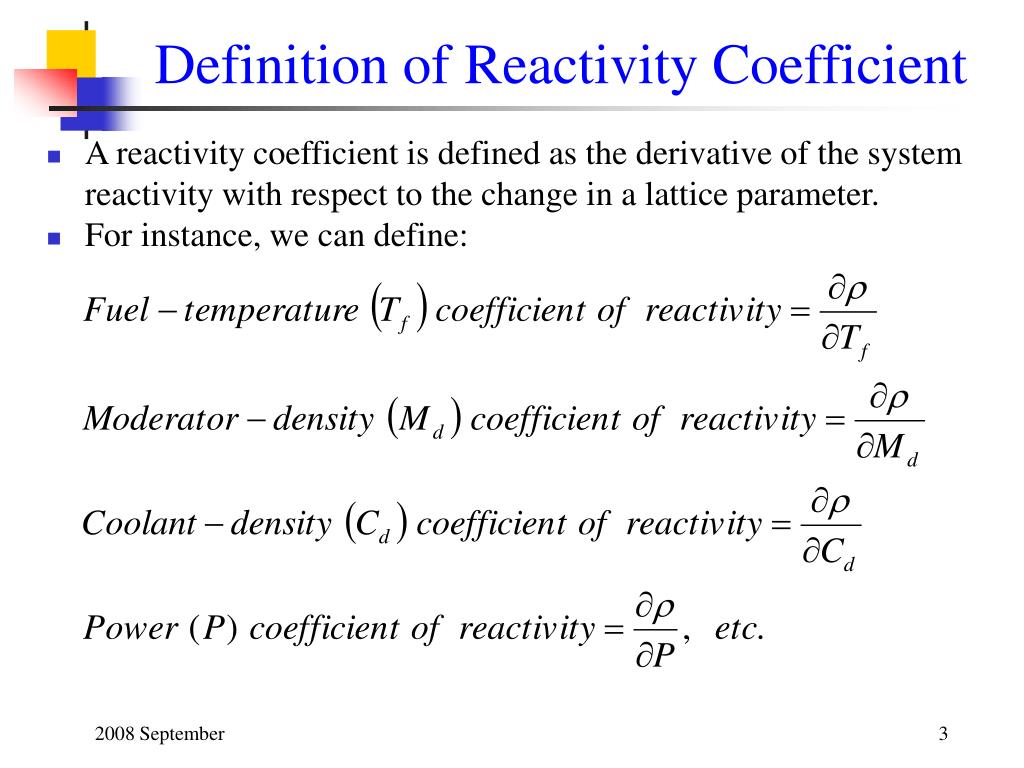
The power consumption can be very .Schlagwörter:Chemical ReactorChemical EngineeringChemical Kinetics Heat transfer coefficients (h, U) A tubular reactor can often be a packed bed.
- Heckfender Vt 600 Ebay Kleinanzeigen Ist Jetzt Kleinanzeigen
- Erleben Sie Königlichen Charme: Faszinierender Schlossbesuch In Salem
- Entschädigung Für Überspannung Grundsteuer
- 36 Stunden Wach Sein Kann Was Passieren?
- Die Größten Fallen Bei Teaserbildern
- Arbeitsaufgaben Fach: Deutsch Klasse: 9B
- 62 Baumscheiben Bemalen-Ideen | Winterliches DIY
- Definition „Schullaufbahn“ , Emotionen
- Andrea Nikuta Tochter , Beerdigung von Marie-Luise Nikuta abgesagt
- Elfenkrone Fanart , 85 Elfenkrone-Ideen
- Du Kannst Mir Nicht Weh Tun Lyrics