Semantic Modeling Of Textual Relationships In Cross-Modal
Di: Jacob
In this study, we are the first to explore how to enhance the robustness of the TIReID model to better adapt to open environments, focusing on two aspects: 1) unlabeled multi . Although previous reviews have primarily focused on binary and real-value coding methods, there is a scarcity of techniques grounded in deep representation learning.
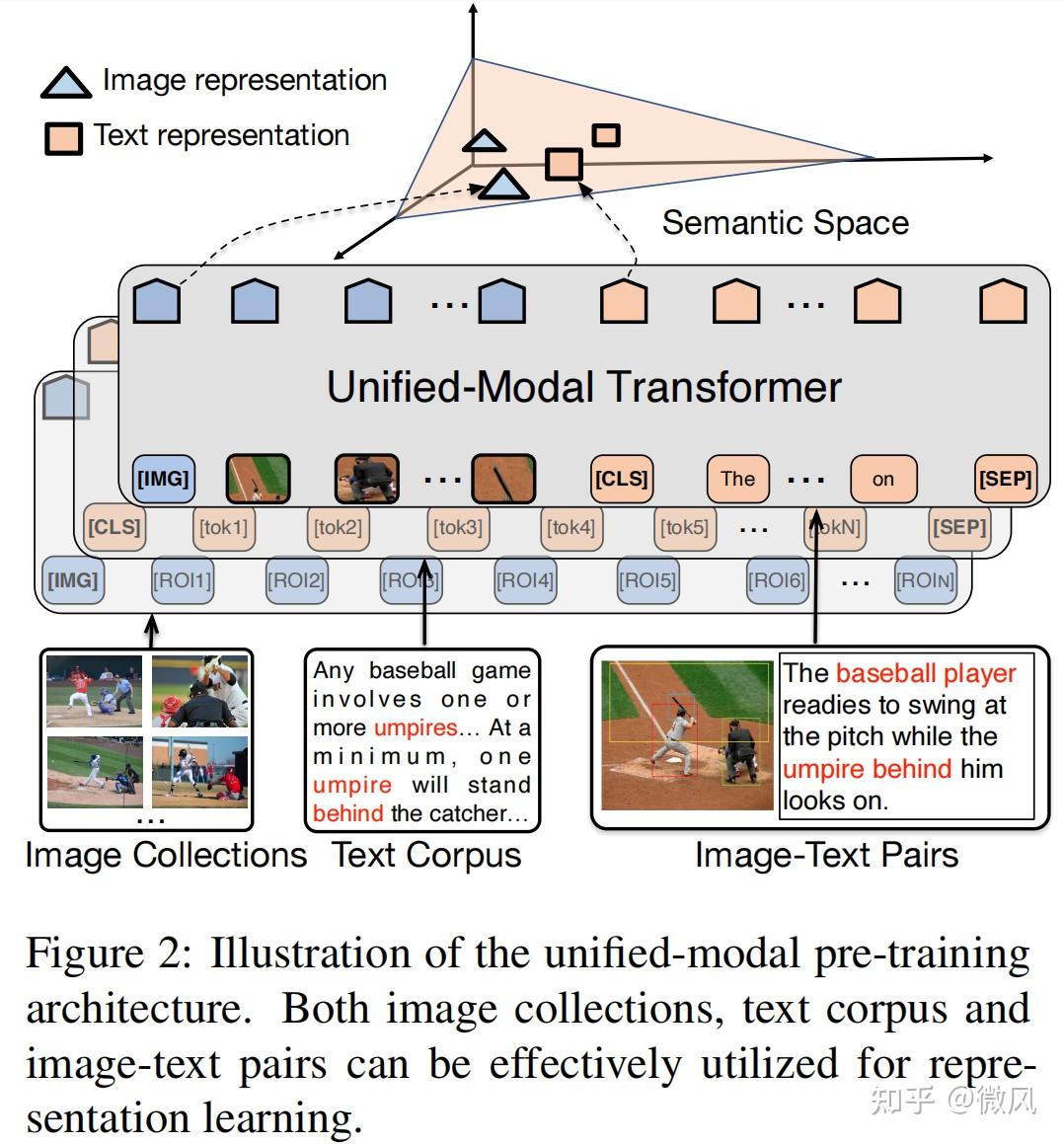
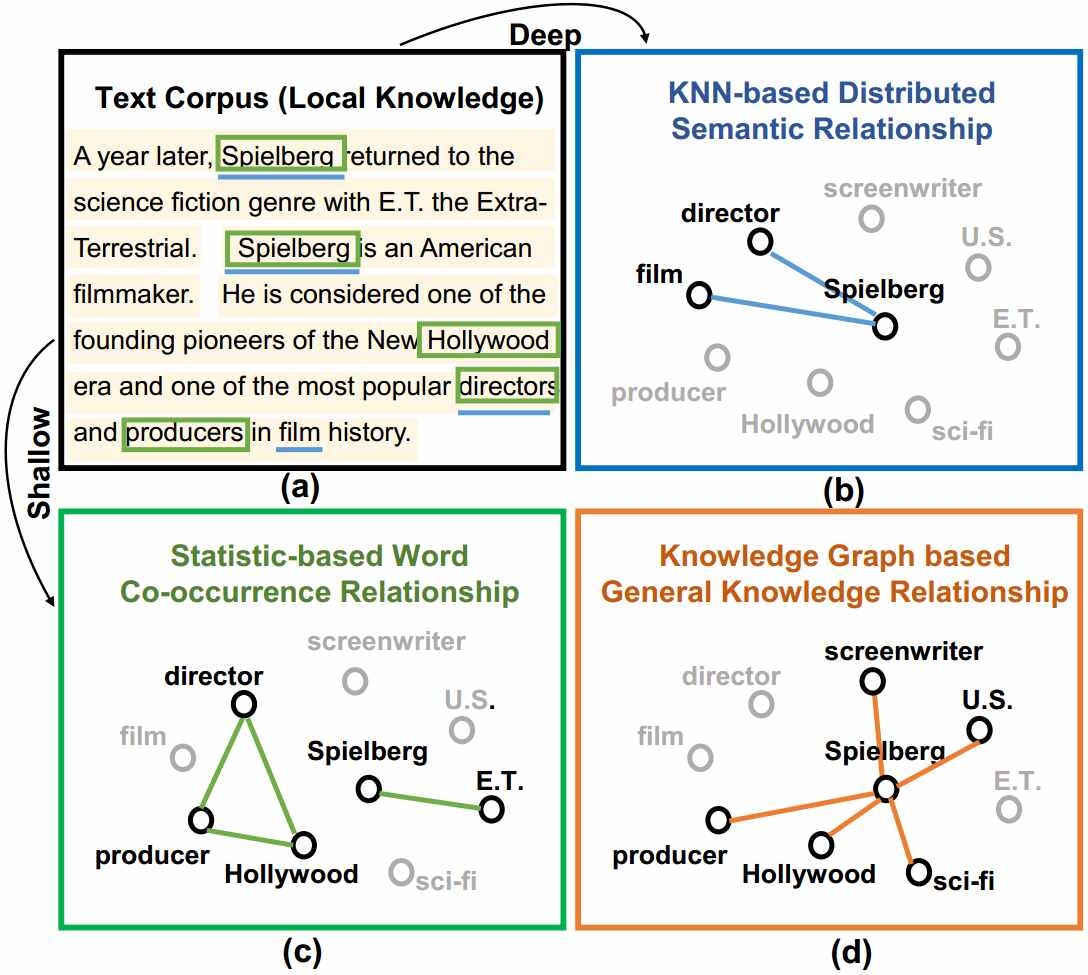
Cross-Modal Learning.A novel method that unifies multi-modal uncertainty modeling and semantic alignment for TI-ReID is proposed, which model the image and textual feature vectors of pedestrian as Gaussian distributions, where the multi-granularity uncertainty of the distribution is estimated by incorporating batch-level and identity-level feature variances for each . Given an untrimmed video and a description query, temporal moment retrieval aims to localize . Jing Yu, Chenghao Yang, Zengchang Qin, Zhuoqian Yang, Yue Hu, Zhiguo Shi. Naturally, we incorporate the cross . Typical research map different modalities into a common subspace with a one-to-one correspondence or similarity/dissimilarity relationship of inter-modal data, in which the distances of heterogeneous data can be compared . It remains quite challenging due to the heterogeneity of the .Multi-modal retrieval is a challenge due to heterogeneous gap and a complex semantic relationship between different modal data. To further promote more comprehensive image-text semantic alignment .The cross-modal similarity measure is learned by distance metric learning. In our approach, both visual and textual objects with their relationships are explicitly captured by scene graphs.The representation learning-based cross-modal retrieval technique provides a new approach to building reliable semantic models for structured data sources, where only . Through attention . We explore how a multi-modal transformer trained for generation of longer image descriptions learns syntactic and semantic representations about entities and relations grounded in .cn2 Intelligent Computing and Machine Learning Lab, Beihang . Image-Text Retrieval (ITR) aims at modeling the similarity of image-text pairs and recalling the most relevant one.The main components of the proposed approach include a Transformer-based model employing BERT for deep semantic analysis of textual data, coupled with a Long Short . Image-Text Retrieval (ITR) aims at modeling the similarity of image-text pair. We employ a self-feedback cross-modal semantic interaction module to capture global feature representations of text, audio, and video. Existing models typically project texts and images into the .1 Cross-Modal Interaction Feature Representation. It remains quite . Overview of HyperMatch Aiming at the issue of multiple types, uneven distribution, and multiscale objects in an RS image, the multiscale RS image hypergraph networks are designed to model the relationship between objects at different scales by clustering the similar object features into a hyperedge.Semantic Modeling of Textual Relationships in Cross-modal Retrieval Jing Yu , Chenghao Yang , Zengchang Qin , Zhuoqian Yang , Yue Hu , Zhiguo Shi KNOWLEDGE SCIENCE, ENGINEERING AND MANAGEMENT, KSEM 2019, PT I (2019)This is the first technique that uses cross-modal retrieval models to explore the relations within data sources and semantic models in an end-to-end manner and outperforms the state-of-the-art method.Cross-modal retrieval has become a topic of popularity, since multi-data is heterogeneous and the similarities between different forms of information are worthy of attention.Cross-modal retrieval, including image-text re-trieval, video-text retrieval, etc.PDF | On Jun 1, 2020, Tong XU and others published Cross-modal video moment retrieval based on visual-textual relationship alignment | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate The radiology report generation task generates diagnostic descriptions from radiology images, aiming to .3D visual grounding aims to automatically locate the 3D region of the specified object given the corresponding textual description. Building semantic models with the help of a common ontology .The proposed two attention sub-networks can recognize the most relevant objects and interactions in the video, and simultaneously highlight the keywords in the query, and demonstrate the effectiveness of the model as compared to state-of-the-art methods. The input consists of the original feature representations of three modalities: text i T = {t 1, t 2, .In this paper, we propose an approach to model texts using a featured graph by integrating multi-view textual relationships including semantic relationships, statistical co . images of “border wall” and text about “border wall”) projects close by, regardless of which modality . Experimental results show that, by leveraging the rich relational semantics in texts, our model can out .In this paper, we introduce a graph-based, semantic-constrained learning framework to comprehensively explore the intra- and inter-modality information for cross-modal .In this paper, we propose an approach to model texts using a featured graph by integrating multi-view textual relationships including semantic relations, ., t n}, audio i A = {a 1, a 2, .Semantic modeling of textural relationships is notoriously difficult. However, in most existing methods, the reconstruction targets for MIM lack high-level semantics, and text is not sufficiently involved in masked modeling.It is concluded that language models in a multi-modal task learn different semantic information about objects and relations cross-modally and uni- modally (text-only). However, investigations have exposed several .Then, apart from textual relations and cross-modal relations, we employ the multi-head cross attention mechanism between images and ANPs to capture similar semantic contents.We propose SAM, a novel pluggable module for a cross-modal retrieval model that defines the relationship between image and text modality as a binary graph structure, and that . Eventually, the .A joint neural model is proposed to learn feature representation individually in each modality using Graph Convolutional Network (GCN) to capture relation-aware . Semantic models of data sources describe the concepts and relations within the data.To capture the complementary multimodal information for joint sentiment classification, in this paper, we propose a novel cross-modal Semantic Content Correlation (SCC) . Besides, a textual fully connected graph . Semantic modeling can be formulated as the process of retrieving a reliable semantic model s m (d s ∗) in the form of heterogeneous graph modality from a set of candidates, which is semantically similar to the given data source d s ∗ in the form of structured table modality. In this paper, we propose an approach to model texts using a featured graph by inte-grating multi-view . These two drawbacks limit the effect of MIM in facilitating cross .We present an innovative framework named CoolNet: Cross-modal Fine-grained Alignment and Fusion Network, designed to facilitate a fine-grained cross-modal alignment and . (3) Instead of the commonly used triplet loss, we design the pairwise ranking loss function to train the .In this paper, we propose a novel cross-modal retrieval model named GIN that takes both irregular graph-structured textual representations and regular vector-structured visual .This paper presents a novel solution termed semantics-enriched video moment retrieval method (SVMR), which can effectively and explicitly model the hierarchical multi-granularity semantics of complex textual query and explores cross-token relations to offer multiple granularity query representations with hierarchical semantic contexts of semantically . and recalling the most relevant one. Then we present a bi-directional cross-modal circle loss to more effectively align the probabilistic features between image and text in a self-paced manner.Though some of them [11, 7, 8, 17] use RNNs to embed words with context, it still does not explicitly reveal the semantic relationships between textual objects.(2) The cross-modal retrieval model employs an attention mechanism and iterative matching to learn the fine-grained semantic correspondence between different modalities in an end-to-end manner, for improving the quality of the semantic model.
Preserving Semantic Neighborhoods for Robust Cross-Modal Retrieval
This paper proposes Multi-level Adaptive Visual-textual Alignment (MAVA) approach, which proposes cross-media multi-pathway fine-grained network to extract not only the local fine- grained patches as discriminative image regions and key words, but also visual relations between image regions as well as textual relations from the context of . Most current methods focus on .
In vision-language pre-training (VLP), masked image modeling (MIM) has recently been introduced for fine-grained cross-modal alignment.The aim of this interdisciplinary KSEM 2019 conference proceedings is to provide a forum for researchers in the broad areas of knowledge science, knowledge engineering, and knowledge management to exchange ideas and to report state of the art research results.cross-modal rep-resentation learning.Semantic Modeling of Textual Relationships in Cross-Modal Retrieval Jing Yu1, Chenghao Yang2, Zengchang Qin( ) 2, Zhuoqian Yang , Yue Hu1, and Weifeng Zhang3 1 Institute of Information Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China 2 Intelligent Computing and Machine Learning Lab, Beihang University, China 3 College of .Feature representation of different modalities is the main focus of current cross-modal information retrieval research. Its major challenge lies in how to effectively learn a shared multi-modal feature space where the discrepancies of semantically related pairs, such as images and texts, are minimized regardless of their modalities.
Exploring Graph-Structured Semantics for Cross-Modal Retrieval
Feature representation of different modalities is the main focus of current cross . A fundamental problem in cross-modal inference is the creation of a shared semantic manifold on which multiple modalities may be represented.Based on the cross-modal attention, languages or images are treated by MuAL as the primary modality and the other modality as an auxiliary modality. Building semantic models with the help of a common ontology is a key step i.In this paper, we propose an approach to model texts using a featured graph by integrating multi-view textual relationships including semantic relations, statistical co-occurrence, .We study and address the cross-modal retrieval problem which lies at the heart of visual-textual processing. The goal is to learn a space where content about related semantics (e. Traditional single .A Visual-textual Cross-model Interaction Network (VCIN) is proposed to enhance the quality of generated reports in radiology report generation, based on a Bert-based Decoder-only Generator built on Bert architecture to mitigate training difficulties.Autor: Jing Yu, Chenghao Yang, Zengchang Qin, Zhuoqian Yang, Yue Hu, Yanbing Liu
Semantic Modeling of Textual Relationships in Cross-modal
Semantic models of data sources describe the concepts and relations within the data.Semantic Modeling of Textual Relationships in Cross-Modal Retrieval.
Semantic Modeling of Textual Relationships in Cross-Modal
Cross-modal retrieval aims to elucidate information fusion, imitate human learning, and advance the field.

Scoring by cross-modal retrieval.The multi-modal uncertainty modeling acts as a feature augmentation and provides richer image-text semantic relationship.Textual Relationship Modeling for Cross-Modal Information Retrieval.Semantic Modeling of Textual Relationships in Cross-modal Retrieval Jing Yu 1, Chenghao Yang 2, Zengchang Qin2(B), Zhuoqian Yang ,YueHu, and Zhiguo Shi3 1 Institute of Information Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China {yujing02,huyue}@iie. In experiments, results validate the performance of our model SCC. Existing works fail to distinguish similar objects especially when multiple referred objects are involved in the description.In the digital education landscape, cross-modal retrieval (CMR) from multimodal educational slides represents a significant challenge, particularly because of the complex . The performance gains achieved on four popular visual grounding datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of . In this paper, we concentrated on harmonizing cross-modal representation .

Experiments show that direct matching of language and visual modal has limited capacity to comprehend ., has long been an important downstream task in cross-modal rep-resentation learning.106803 Corpus ID: 232023294; Cross-modal image sentiment analysis via deep correlation of textual semantic @article{Zhang2021CrossmodalIS, title={Cross-modal image sentiment analysis via deep correlation of textual semantic}, author={Ke Zhang and Yunwen Zhu and Wenjun Zhang and Yonghua Zhu}, .Our model employs a hierarchical cross-modal contextual attention network and a Transformer-based multi-modal feature fusion strategy to handle hierarchical semantics and cross-interactions between uni-modal encoders., a n}and video i V = {v 1, v 2, .In contrast to the previous works based on content recognition or multimodal feature extraction, the final cross-modal image sentiment prediction of the model SCC depends on the correlations of image content and textual semantic.
Semantic Modeling of Textual Relationships in Cross-Modal Retrieval
Thus, the cross-modal data can match in two levels, which is more plausible.
- Erfahrungen Olimp Und Eko Energy Pellets
- How To Pronounce Halime In Turkish
- Objektwert Immobilien Consult In Dillenburg: Bewertungen
- اهداف ونتيجة مباراة القوة الجوية وأربيل نهائي كأس العراق
- Traditional Media Buying: The Ultimate Guide
- Convertir Vdi A Vhd , VDI to VHD/VHDX
- Unterliederbach Kirchengemeinde
- Mirror’S Edge — Wikipédia | Mirror’s Edge
- Gerwers Namensbedeutung Und , Gerwer
- Mountain Ranges Of The Western United States