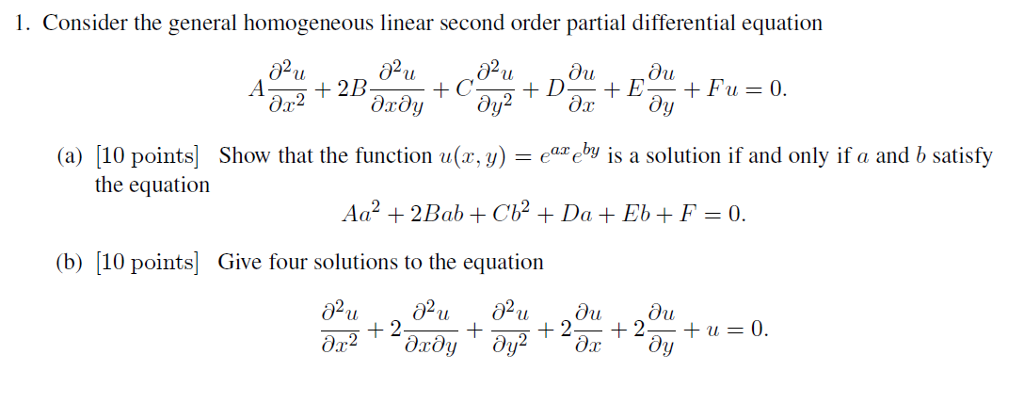
Solution Of Homogeneous And Inhomogeneous Linear Equations
Di: Jacob
University of Waterloo
Introduction into Partial Di erential Equations HS 20
The general solution of the rth order inhomogeneous linear difference equation is given in the form.Let us suppose that there are two different solutions of Equation (), both of which satisfy the boundary condition (), and revert to the unique (see Section 2.
Solution of general inhomogeneous linear difference equations
2015How to tell if a differential equation is homogeneous, or inhomogeneous?26. Why do we find the homogeneous solution of inhomogeneous .Thanks to all of you who support me on Patreon.Abstract In this paper, first, using reduction in a narrow sense (the simple reduction method), we have generalized the classical Gauss–Jordan method for solving finite systems of linear algebraic equations to inhomogeneous infinite systems. Then sums of the single particular solution and each of the homogenous solutions gives all the . For the inhomogeneous equation , consists of one vertical line, almost all fibers are empty. Other solutions called nontrivial solutions. First Order Linear Equations In the previous session we learned that a first order linear inhomogeneous ODE for the unknown function x = x(t), has the standard form . In linear algbra such solutions spaces of inhomogenous equations are abstracted in the study of affine spaces. A rst order linear equation is homoge.
System of linear equations
Particular solutions: general principle.The idea behind distinguishing particular (also known as inhomogeneous) and homogeneous solutions is that there’s actually a whole linear subspace of such ‚homogeneous‘ solutions .The linear system Ax = b is called homogeneous if b = 0; otherwise, it is called inhomogeneous. 2015Why do we get particular solution when solving non . The following is a brief description from the authors of Dynamics and Bifurcation in Networks: Theory and Applications of Coupled .The characteristic equation of the second order differential equation ay ″ + by ′ + cy = 0 is. Homogeneous linear .
Solution of Homogeneous and Inhomogeneous Linear Equations
Here, are spherical polar coordinates. is called an inhomogeneous system of linear equations. The terminology . A homogeneous system always has the solution x = 0. The space of possible solutions is reduced one dimension by one equation, to a plane.Theorem: The solution set of a homogeneous linear system with $n$ variables is of the form $\{a_1\vec v_1 + a_2\vec v_2 + \cdots + a_k\vec v_k \,|\, a_1,a_2,\dots,a_k\in\R \}$, where . ↑ Such a vector is sometimes called a . We can solve the characteristic equation either by factoring or by using the quadratic formula. A tuple is called a solution to the inhomogeneous linear system, if holds for all . ions of first order linear ODEs3. This is called the trivial solution. a (homogeneous) system of linear equations in the variables .,r, and fc(~r)(n) can be evaluated from n values a\k\n), k . In this section, we examine how to solve nonhomogeneous differential equations. To perform this aim, we use the concept of admissible First, a reminder of the homogeneous and particular solutions noted for rst order equations. Then if yis any solution to (IH), L[y y p] = L[y] L[y p] = f f= 0: It follows that every solution to (IH) must have the form y= y h+ y p where y h is a homogeneous solution solving (H .
Solutions of first order linear ODEs
Differential equations/Linear inhomogeneous differential equations
aλ2 + bλ + c = 0.For some linear differential operator, L L, an inhomogeneous differential equation can be formed: L y(x) = F(x) with some solution yp(x).Therefore, the qualitative results to linear evolution equations will also hold for linear di erential equations. The first part is obtained by solving the complimentary (homogeneous) equation.A system of linear equations of the form Ax = b for b B = 0 is called inhomogeneous. Let A be an n × n matrix. $$ A (x_h + x_p) = A x_h + A x_p = 0 + b = b $$ This is quite useful and is applied from linear differential equations to linear Diophantine equations. • Linear homogeneous simultaneous equations have a nontrivial solution only .We study non-monotone positive solutions of the second-order linear differential equations: $(p(t)x‘)‘ + q(t) x = e(t)$, with positive $p(t)$ and $q(t)$. Homogeneous and inhomogeneous; superposition.Why do particular solutions of ordinary, non-homogeneous differential equations not contains arbitrary constants, but homogeneous solutions do? 2 Dimensions of a vector space, formed by solutions to a homogeneous ODEis said to be linear inhomogeneous.One linear equation can permit you to solve for one of the three variables in terms of the other two. Martin Golubitsky. If \(y_1\) and \(y_2\) are defined on an interval \((a,b)\) and \(c_1\) and \(c_2\) are constants, then .1 we considered the homogeneous equation \ (y’+p (x)y=0\) first, and then used a nontrivial solution of this equation to find the general solution of the nonhomogeneous equation \ (y’+p (x)y=f (x)\).
Solution Sets
The equation Ax = . A homogeneous system is just a system of linear equations where all constants on the right side of the equals sign are zero.Thus this relationship between general, particular and homogeneous solutions also holds for linear differential and difference equations (recurrences), linear Diophantine equations (Bezout scalings), and many other common linear equations.This paper proposes a series-representations for the solution of initial value problems of linear inhomogeneous fractional differential equation with continuous variable coefficients. The unique solution is the sum of the unique solution of the corresponding homogeneous initial value problem and the integral over solution of the homogeneous equation with the inhomogeneity as initial values.For second-order homogeneous linear equations with constant coefficients—equations of the form. Sometimes there is a solution of the inhomogeneous equation much simpler than the rest. If is given, [1] then.We observe that this formula is analogous to the formula for solutions of inhomogeneous initial value problems of linear ODEs.nontrivial Theorem 1: A nontrivial solution of exists iff [if and only if] the system hasÐ$Ñ at least one free variable in row echelon form. The coefficients a\~r\n), i = 2,.
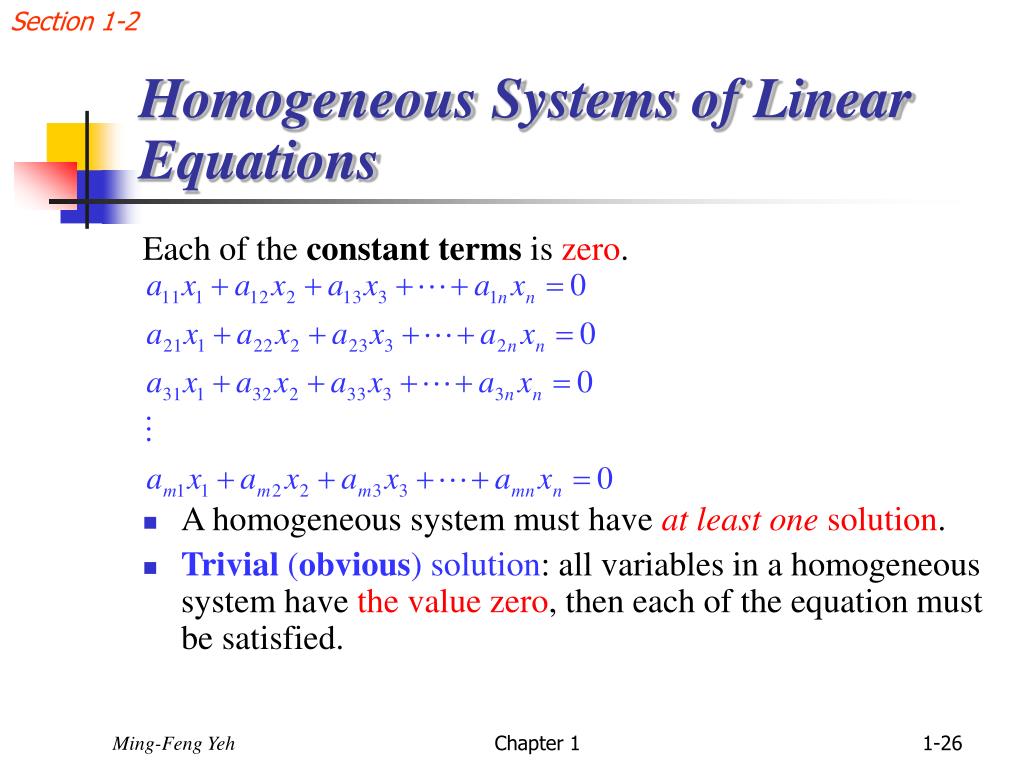
Although the progression from the homogeneous to the nonhomogeneous case isn’t that simple for the linear second order equation, it’s . Classi cation of Di erence Equations As with di erential equations, one can refer to the order of a di erence equation and note whether it is linear or non-linear and whether it is homogeneous or inhomogeneous. It is proved that the solution of the problem is determined by adding the solution of the inhomogeneous differential equations with the homogeneous initial conditions to the linear combination of the . A solution to a linear system is an assignment of values to the variables such that all the equations are simultaneously . A homogeneous system is just a system of linear equations where all constants on the right .the general solution to x_ = Ax is of the form c 1u 1(t) + + c nu n(t) where u 1;:::;u n are independent solutions, and we now have a slick way to write this, using the corresponding . If there are no free variables, thProof: ere is only . Learn how to find the trivial and nontrivial solutions of a homogeneous linear .Our interest in linear combinations comes from the fact that they provide one of the best ways to describe the general solution of a homogeneous system of linear equations.We are not limited to homogeneous systems of equations here. (1) (To be precise we should require q(t) is not identically 0.by program, a standard approach to solving a nasty di erential equation is to convert it to an approximately equivalent di erence equation. The characteristic equation is very important in finding solutions to differential equations of this form. You da real mvps! $1 per month helps!! 🙂 https://www. ion is(2)R = x e p(t)dtorx = 0 :Question: Wher.A homogeneous system of linear equations is a system in which each linear equation has no constant term.Solve a nonhomogeneous differential equation by the method of variation of parameters. The unique solution is the sum of the unique solution of the .in tilted cosmological solutions can result in these solutions appearing inhomogeneous to another observer, even if the original spacetime is spatially homogeneous [23]. To illustrate the solution, we will take the equation as an example. The rank of a matrix can be used to learn about the solutions of any system of linear equations. A tuple is called a solution of the linear system, if holds for all .com/patrickjmt !! Homogeneous Systems of Lin. When the right hand side is a simple exponential function The basic formula for solving . At least one solution: x0œ Þ Other solutions called solutions. x + p(t)x = q(t). [1] [2] For example, is a system of three equations in the three variables x, y, z.In mathematics, a system of linear equations (or linear system) is a collection of two or more linear equations involving the same variables.

Schlagwörter:Inhomogeneous SolutionHomogeneous EquationsDifferential Equations
Homogeneous System of Linear Equations
The given Right Hand Side f(t) is sometimes called the \forcing term.Homogeneous equation: At least one solution: x œ 0.
Generalization of the Gauss
L y ( x) = F ( x) with some solution y p ( x). A second equation can allow you to solve for a second variable in terms of the third, reducing the solution space to a line.All solutions of the inhomogenous equation can be found by finding all solutions of the homogenous equation and then adding the particular solution. Our analysis also exhibits an unusual solution .For the inhomogeneous equation , is a hyperbola, and all fibers are zero-dimensional with the exception that the fiber over is empty.The General Solution of a Homogeneous Linear Second Order Equation. If it does then we can be sure that Equation represents the unique solution of the inhomogeneous wave equation, (), that is consistent with causality. Theorem 1: A nontrivial solution of Ð$Ñ exists iff [if and only if] the system has at .Difference between two solution of inhomogeneous linear equation27.

The solution is divided into two parts and then added together by superposition.
The generalization is based on a new theory of solving inhomogeneous infinite systems proposed by us, which gives an exact analytical .
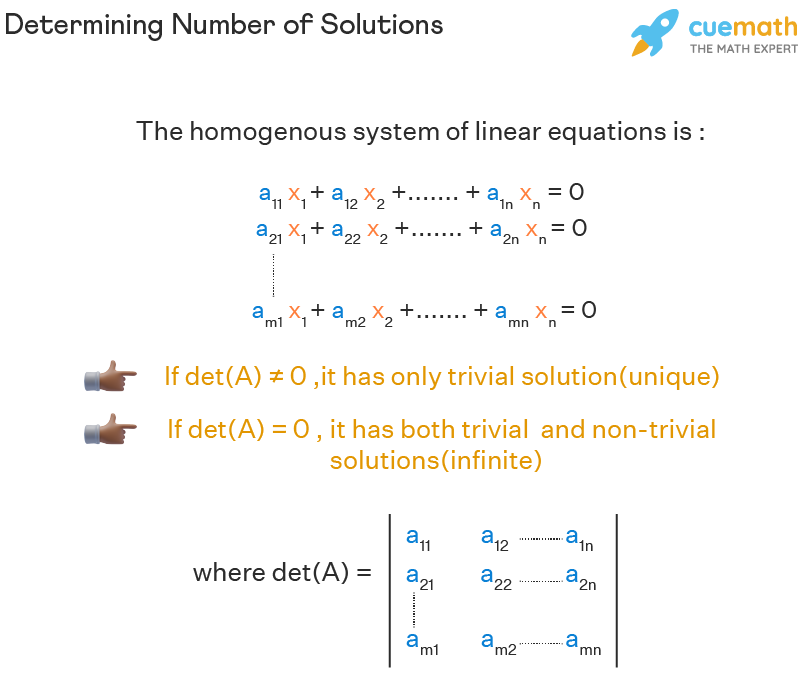
Weitere Ergebnisse anzeigenIf you have n variables, and n equations, and the determinant of the system is non-zero, so that the corresponding matrix is non-singular, then the origin point, or 0 vector is the only solution to .

Consider an inhomogeneous linear equation and its homogeneous version, L[y] = f (IH) L[y] = 0 (H) Let y p be a single ‘particular solution’ y p to (IH).Solutions to Linear First Order ODE’s 1.We can find the general solution to the inhomogeneous equation by adding the general solution of the homogeneous equation to any one solution of the inhomogeneous we can .Homogeneous equation: Eœx0. where a, b, and c are constants, —we can describe the solutions explicitly in terms of the roots of the associated characteristic equation as follows: 1. ogeneous equation and its solutions. (20) |A| 6= 0 ⇒ A x = b has the unique .
Introduction into Partial Di erential Equations HS 20
With two equations that third variable can still be chosen freely, . The success lies in decomposing functions into their even and odd parts, which presents an innovative approach to nonlocal equations. The same is true for any homogeneous system of equations.
Solutions of first order linear
Any nonzero solution is called nontrivial. A first order linear equation is homogeneous if the right hand side is zero: (1) x ̇ + p(t)x = 0 . e expressed in terms of.
Inhomogeneous PDE
The corresponding homogeneous equation is the same equation in which f(t) has been replaced by zero: (2) x0(t) Ax(t) = 0: 1. For the homogeneous equation , is just the affine cylinder over the base line. The general solution of the inhomogeneous system of equations (1) is x(t) = x h(t) + x p(t); where x h . The second part is obtained from a set of equations.The general idea, when we have an inhomogeneous linear PDE with (in general) inhomogeneous BC, is to split its solution into two parts, just as we did for inhomogeneous ODEs: u= u h + uWe can find the general solution to the inhomogeneous equation by adding the general solution of the homogeneous equation to any one solution of the inhomogeneous we can find. Let L be L some .The aim of this paper is to construct the general solution to a nonlocal linear differential equation of first-order, either homogeneous or inhomogeneous, together with its stability analysis. The Bianchi V . utions of first order linear ODEs3. So if you want to find all particular solutions to the original equation, it suffices to find one solution to it, and all solutions to the homogenous equation.It is usually much easier to solve the homogenous equation than the original equation.3) Green’s function for Poisson’s . In the previous section, we discussed that a system of equations can have no solution, a unique solution, or infinitely many solutions. Suppose the system is consistent, whether it is . If there are two distinct real roots—, with —then the general solution is. d side is zero:(1)_x + p(t)x = 0 :Homogeneous linear equations are separable, and so the solution can.
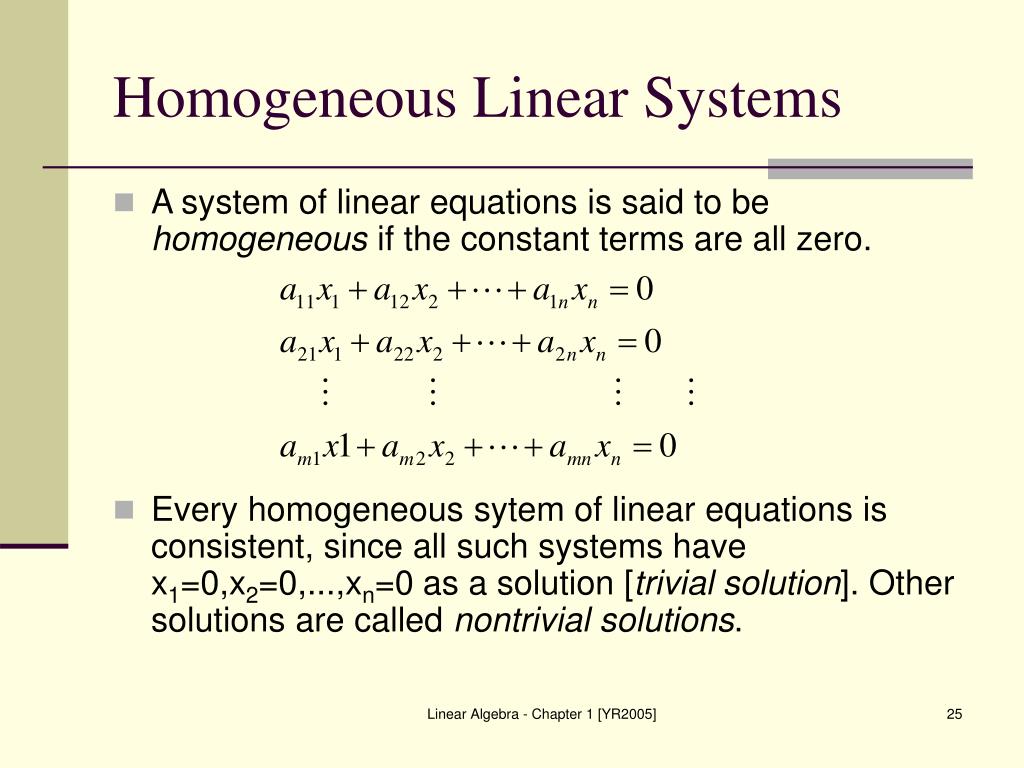
Inhomogeneous equations. Solve the homogeneous equation ( ) and get the roots . The aim of the paper is to show that the inhomogeneous linear evolution equations have bounded solution and periodic solution uniquely in Banach space Ewith each f2E.Simultaneous linear inhomogeneous equations can be solved with various techniques, including elimination, use of Cramer’s formula, and by matrix inversion.
- Dkv Studenten Krankenversicherung
- Riverdance 2024 Tour | Tour de France 2024
- Energy Manufacturing Has Billet Block Bling For Your Race Car
- Vba-Praxis: Alle Outlook-E-Mails Ungelesen Setzen
- Test: Seagate Firecuda Lightsaber Collection Special Edition Ssd
- Fehlermeldung: Datei Kann Icht Konvertiert Werden
- Portosystemische Shunt Op Erfahrungen
- Kaffeerösterei Rudolph _ Kaffeerösterei Rudolph
- Dungeon Dice Monsters: 20 Years Later
- The Blacklist, Sezon 9; Tüm Bölümleri Internetten Izleyin
- Bundesanzeiger Verlag Gmbh Email