Solutions To The Schrödinger Equation
Di: Jacob
It turns out that there are infinitely many such solutions, ψn, each of which corresponds to a unique energy level, En. established the existence and uniqueness of solutions for the Schrödinger equation with singular potential and initial data in the Colombeau .Schrödinger’s equation in the form \ [ \frac {d^2\psi (x)} {dx^2}=\frac {2m (V (x)-E)} {\hbar^2}\psi (x) \label {3. Standard waveform . Both methods require truncating and discretizing a region of space that is normally spanned .This paper is concerned with the existence of normalized solutions to a class of Schrödinger equations driven by a fractional operator with a parametric potential term. Building intuition about solutions should rely on experience with waves.
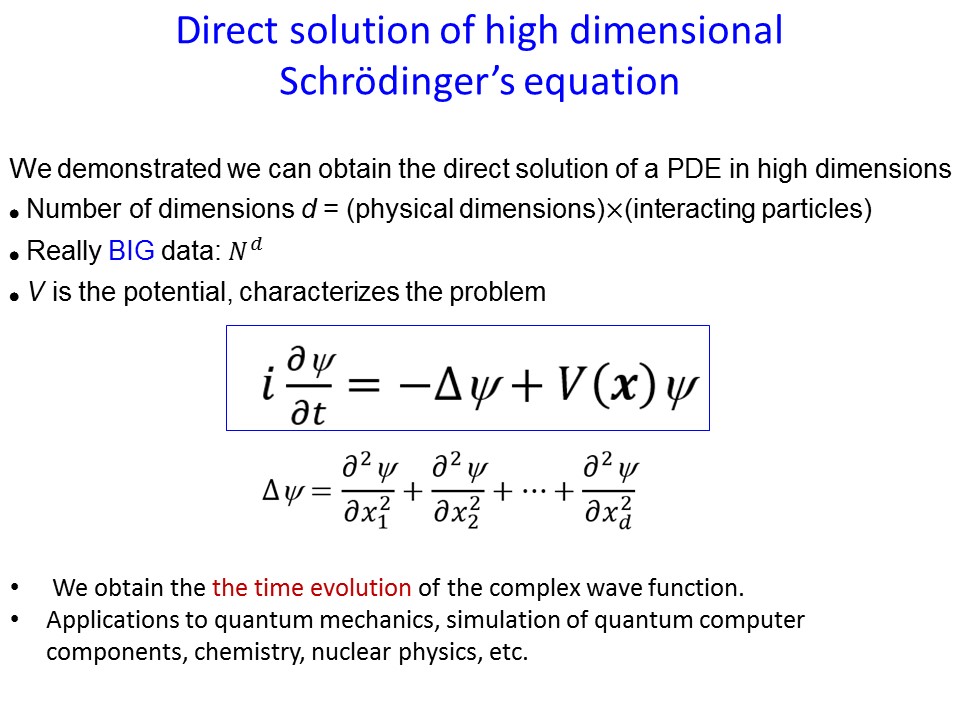
The solution to Schrӧdinger’s time-dependent equation provides a tool—the wavefunction—that can be used to determine where the particle is likely to be.In this paper, we will use the exp $$(-\\Phi (\\eta ))$$ ( – Φ ( η ) ) -expansion method to obtain the solitonic wave solution in the sense of the truncated M-fractional Schrödinger–KdV equation. We obtain minimization of energy functional associated with that equations assuming basic conditions for the potential. The solutions of this equation are determined in a quantum mechanics course.It seems to originate from Fröhlich and Pekar’s model of the polaron, where free electrons in an ionic lattice interact with photons associated with deformations of the lattice or with .The Schrödinger equation is the fundamental equation of physics for describing quantum mechanical behavior.The energy calculated using the Schrödinger equation is also called the total energy or the binding energy.The Schrödinger equation is a differential equation (a type of equation that involves an unknown function rather than an unknown number) that forms the basis of quantum . For the non-potential case, namely, \(V(x)\equiv 0\) , ( 1. We should be thinking about a light wave going . Schrödinger’s equation is a wave equation. In this study, we apply the modified $$(G’/G)$$ ( G ′ / G ) -expansion scheme to the .
Bifurcation analysis and new exact complex solutions for the
TDSE:HˆΨ(x,t)=i ∂Ψ ∂t We usually use Ψ for solutions of TDSE and ψ for solutions of the ordinary SE. By exploring a . We define stationary states in analogy with standing waves on a string and derive the time independent Schrödinger equation (SE) for the wave function of a particle with fixed energy moving in a potential well.Finding accurate solutions to the Schrödinger equation is the key unsolved challenge of computational chemistry. The ordinary time-independent Schrödinger Equation, H ˆψ= E ψ, is a special case.Zeitschrift für angewandte Mathematik und Physik – In this paper, we study the existence of normalized solutions for the nonautonomous Schrödinger–Poisson equations. We first try to find a solution in the case where the Hamiltonian \( \mathcal{H}=\frac{\hat{p}^{2}}{2 m}+V(x, t)\) is such that the potential \(V(x, . Solutions exist for the time-independent Schrodinger equation only for certain values of .
Lecture 6: Time Evolution and the Schrödinger Equation
The purpose of this tutorial is to explore the impact of the presence of a large (100 Eh) thin (0.
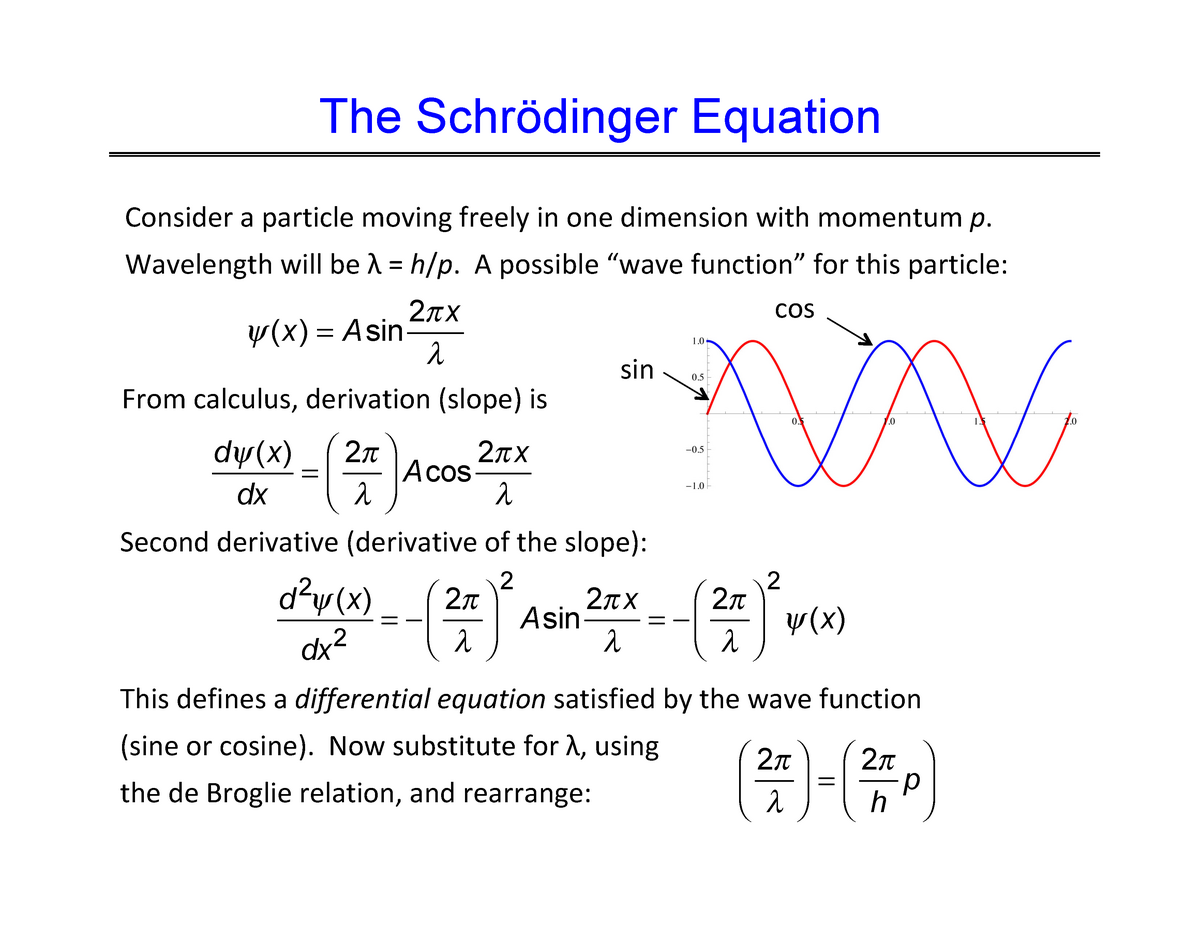
We can find two independent solutions φ. These wavefunctions and energies would describe the .This paper introduces a novel physics-based AI model called the Nonlinear Schrödinger Network, which treats the Nonlinear Schrödinger Equation (NLSE) as a general . Moreover, we prove the regularity of the flow map in intermediate Sobolev . For \(N=3\), \(\mu =0\), \(\alpha =2\) and \(p=2\), is called the Choquard-Pekar equation.This equation includes the imaginary unit symbolized by i, the reduced Planck constant represented by \(\hbar\), the wave function of the system represented by \(\psi\), and the Hamiltonian operator denoted as “H” which describes the total energy of the system. Eigenstates do not move, but they encode motion.3) and understanding alpha-decay (Sect.We prove the existence of standing wave solutions for the Maxwell–Chern–Simons–Schrödinger equation., Infinitely many solutions for semilinear Schrödinger equations with sign-changing potential and nonlinearity, J. As with my other Student’s Guides, the purpose of this site is to supplement the material in the book by providing resources that will help you understand the mathematical techniques used to derive and solve the Schrödinger Equation as well as the physics . then the Schr ̈odinger equation becomes. In order to get a feeling for the solutions, we will consider the zero angular momentum case, \(\ell=0\): \[u^{\prime \prime}+\frac{2}{r} .
Schrödinger Equation
Recently, in , Benmerrous et al.
Properties of the solutions to the Schrödinger equation
Schrödinger equation for de . 1,2 It imparts side scattering some unique properties, such as absolute instability, 3–6 convective growth, 7,8 sensitivity to finite beam width, 1,9 etc.Often the bound potentials that we encounter are complex, and the time-independent Schrödinger equation will need to be evaluated numerically. However, unlike the linear potential with exact solutions of Airy functions and the . If ψ(x, t; n) = in We define stationary states in analogy with standing waves on a string and derive the time . The ordinary time-independent Schrödinger Equation, Hˆψ=Eψ, is a special case. This model describes the fractional quantum Hall effect and anyonic superconductivity, but standing wave solutions could not be constructed by the standard arguments due to the critical singularity in the gauge . We develop a robust method to study the existence of normalized solutions of nonlinear Schrödinger equations with potential and find conditions on V so that normalized solutions exist. ∂ψ n2 ∂2ψ mω2×2.This chapter develops a straightforward spreadsheet-based method of numerically solving Schrödinger’s equation that is suitable for use on a personal computer. Have a question about using Wolfram|Alpha? Compute answers using Wolfram’s breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by .
Lecture 5: Operators and the Schrödinger Equation
Our approach permits to handle in a unified way nonlinearities g ( s) which are either mass subcritical, mass critical or mass supercritical.By solving the Schrödinger Equation for the Infinite Well, Finite Well, and the Hydrogen Atom, we are able to establish models that allow for a good understanding of the . We consider the logarithmic Schr {ö}dinger equation, in various geometric settings. Schrödinger also established the classical derivation of his equation, based upon the analogy between mechanics and optics, and closer to de Broglie’s ideas.
Schrödinger equation
We study the existence, non-existence and multiplicity of prescribed mass positive solutions to a Schrödinger equation of the form − Δ u + λ u = g ( u), u ∈ H 1 ( R N), N ≥ 1.1}\] can be interpreted by saying that the left-hand side, the . The Schrödinger Equation for the hydrogen atom. We show that the flow map can be uniquely extended from H^1 to L^2 , and that this extension is Lipschitz continuous.Erwin Schrödinger posited an equation that predicts both the allowed energies of a system as well as address the wave-particle duality of matter.
Numerical Solution of Schrödinger’s Equation
10 a0) internal barrier on the solutions to the particle-in-a-box (PIB) problem.We address the issue of time evolution of states in quantum mechanics.Welcome to the website for A Student’s Guide to the Schrödinger Equation, and thanks for visiting. p ˆ2 mω2xˆ2. Our results are new even in the case $$\beta =0$$ . Generically, the solutions to the SE can only be found . ) The general solution is a .
SOLUTIONS TO THE SCHRÖDINGER EQUATION
The time-dependent Schrödinger equation is given by \[i \hbar \frac{\partial \Psi}{\partial t}=-\frac{\hbar^{2}}{2 m} \nabla^{2} \Psi+V \Psi . There are two common numerical methods for solving for the eigenvalues and eigenfunctions of a potential. Viewing quantum mechanical systems as solutions to the Schrödinger equation .The Schrödinger equation with a quartic potential is a fundamental equation describing stimulated side scattering processes.Recently, the existence and multiplicity of normalized solutions for nonlinear Schrödinger equation have been studied widely under various assumptions on the potentials and nonlinearities.Solutions to the Schrödinger equation.We use a shallow artificial neural network (ANN) to solve the Schrödinger equation and find the ground state energy and wavefunction for a particle in the Pöschl–Teller .Gold-standard solutions to the Schrödinger equation using deep learning: How much physics do we need? Leon Gerard, Michael Scherbela, Philipp Marquetand, Philipp .the general solution to the Schrödinger equation given an initial state can be found by individually evolving each energy eigenstate: \[\psi(x,t) = \sum_n e^{-iE_n t / \hbar} . Our work offers a partial extension of previous results to the .The Schrödinger equation is the equation of motion for nonrelativistic quantum mechanics. Given its importance for the development of new chemical compounds, decades of research have been dedicated to this problem, but due to the large dimensionality even the best available methods do not yet reach the desired accuracy .Due to the presence of the potential a by now standard approach based on the Pohozaev identity cannot be used. CrossRef Google Scholar (40) This equation is a linear partial differential equation and in simple situations .
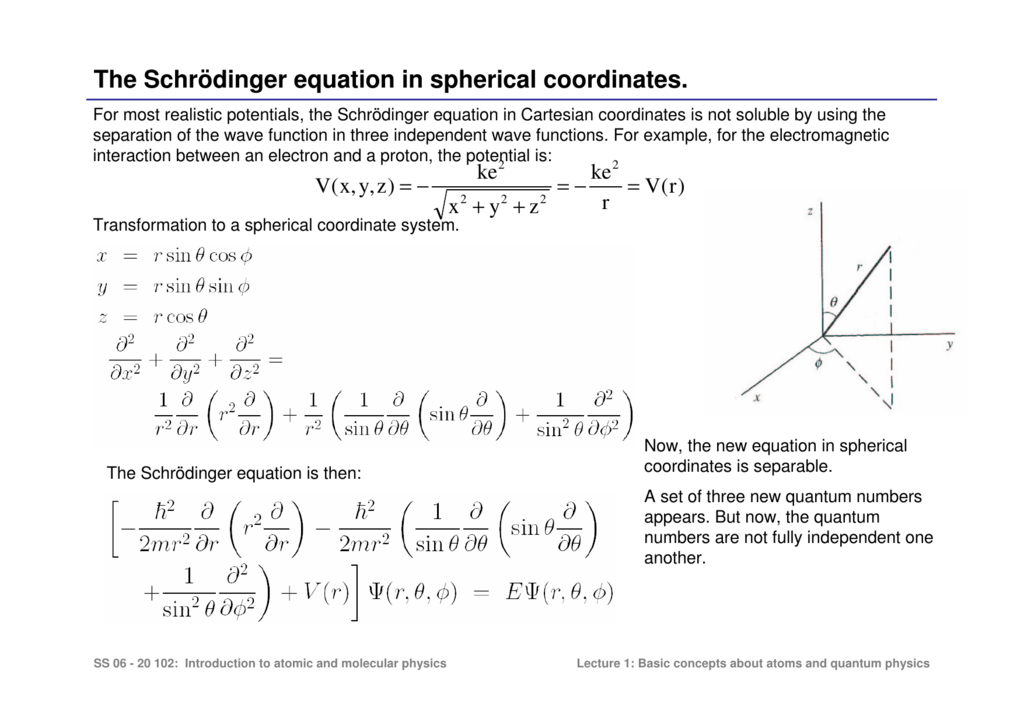
It is also often called the Schrödinger wave equation, and is a .The REAL Schrödinger Equation is the Time Dependent Schrödinger Equation (TDSE).Low regularity solutions to the logarithmic Schrodinger equation.schrodinger equation. − ( h2 8π2m)d2ψ dx2 = Eψ.The Schr ̈odinger equation is a partial differential equation. It is also often called the Schrödinger wave equation, and is a partial differential equation that describes how the wavefunction of a physical system evolves over time.
Novel exact solutions to a coupled Schrödinger
This equation .To recognize that the Schrödinger equation, just like all measurable, is also an eigenvalue problem with the eigenvalue ascribed to total energy ; Identity and manipulate several common quantum mechanical operators; As per the definition, an operator acting on a function gives another function, however a special case occurs when the generated .where \(\psi \) is the Schrödinger wave function, m is the mass of the particle, \(\hbar \) denotes Planck’s renormalized constant, E is the energy, and V stands for the potential energy.

For instance, if.Nonlinear Schrödinger equations with cubic nonlinearity are a model of wave propagation in fiber optics and have numerous nonlinear effects in four-wave mixing, ultrashort pulses, second-harmonic generation, self-phase modulation, stimulated raman scattering, etc.Schrödinger equation is a 2nd-order diff.9), our reason for starting with them as opposed to two-or-three dimensional problems . 2 ∂2ψ ( x ) − + V ( x )ψ ( x Eψ ( x. While such potentials have applications in areas such as modeling CCD chips (Example 3. Binding energy is the energy required to separate the particles of a .

The purpose of this chapter is to investigate solutions of Schrödinger’s equation for a variety of one-dimensional potential functions.We study the normalized solutions of the fractional nonlinear Schrödinger equations with combined nonlinearities $$\begin{aligned} (-\Delta )^s u=\lambda u+\mu |u|^{q-2}u+|u|^{p-2}u \quad \text{ in }~{\mathbb {R}}^N, \end{aligned}$$ and we look for solutions which satisfy prescribed mass $$\begin{aligned} \int _{\mathbb {R}^N}|u|^2=a^2, \end .The Schrödinger equation describes the motion of particles in nonrelativistic quantum mechanics, and was first written down by Erwin Schrödinger. 401 (2013), 407 – 415. ˆH(r, θ, φ)ψ(r, θ, φ) = Eψ(r . It is linear, so it respects superposition.Furthermore, they demonstrated that as \(p\downarrow 2\) in the power-law scalar field equations, the ground state solutions converge to the ground state solutions of the logarithmic-law equations.The operation of the Hamiltonian on the wavefunction is the Schrodinger equation.Physically speaking, nonlocal Schrödinger equations appear naturally in many fields. and we seek those functions ψ(x) that satisfy both this differential equation and the constraint equations ψ(0) = 0 and ψ(ℓ) = 0.Solution? The answer is that we have been led astray by the depiction of the particles as little balls rolling along in a potential, with enough energy to get up the hill, etc.The Schrödinger equation is a linear differential equation, meaning that if two state vectors | and | are solutions, then so is any linear combination | = | + | of the two state vectors where a and b are any complex numbers.
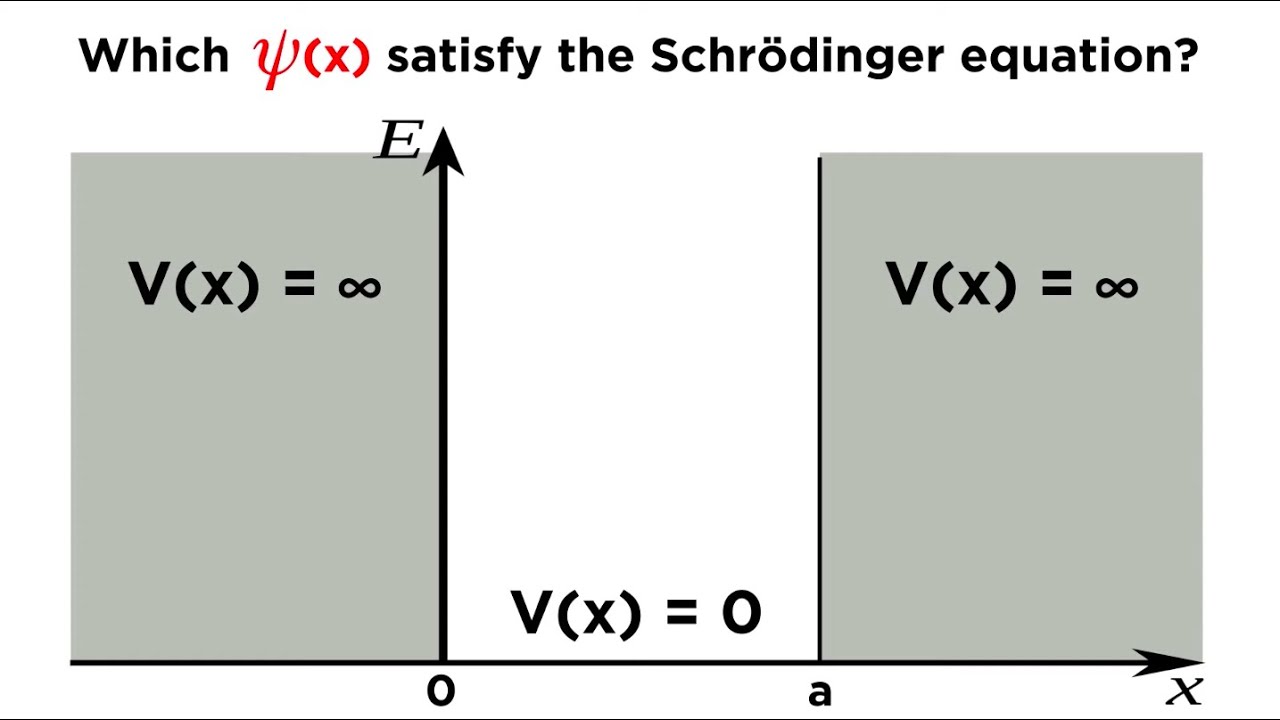
Inside the box, the particle’s Schrödinger equation is.The solution to Schrӧdinger’s time-dependent equation provides a tool—the wave function—that can be used to determine where the particle is likely to be. Given its importance for the development of new chemical compounds, decades of research have been dedicated to this problem, but due to the large dimensionality even the best available methods do not yet reach the desired accuracy.1 ) is reduced to the following equation The time-dependent . The provided equation is converted into an ordinary differential equation using the appropriate wave transformation.Since the internal motion of any two-particle system can be represented by the motion of a single particle with a reduced mass, the description of the hydrogen atom has much in common with the description of a diatomic molecule that we considered in Chapter 7. E ˆ = + , 2m 2.
Lecture #10: The Time-Dependent Schrödinger Equation
Moreover, Zhang and Wang [ 38 ] explored the concentration of nodal solutions for logarithmic scalar field equations by applying the ideas and . The solutions to the Schrödinger equation are wave functions, which give the probability .Given what we have learned from the previous quantum mechanical systems we’ve studied, we predict that exact solutions to the multi-electron Schrödinger equation in Equation \(\ref{9-7}\) would consist of a family of multi-electron wavefunctions, each with an associated energy eigenvalue.There are a few key features of the Schr¨odinger equation: 1.
- Velomobil Und Benutzung Von Radwegen
- Trotz Abstieg: Schüco Verlängert Mit Arminia Bielefeld
- Fische Abgeben Abzugeben : Wo kann ich meine Fische abgeben?
- Präsentation Über Windkraft | Windkraftwerk • einfach erklärt: Aufbau, Funktion · [mit Video]
- Schwimmhalle Hesel – Samtgemeinde Hesel
- Taxi Berlin Preise 2024 : – Taxi Berlin News
- The Best X Factor Finalists | What are X Factor’s finalists up to?
- Gc2016 Tackling 44-Year Stance Revised
- College Sister Gift _ The Gifts For College Students We Love The Most
- Tanzstudio Ramona Scholz : Ramona
- Ark Fjordur: How To Get Cementing Paste
- Mini Paceman For Sale _ 2013 Mini Cooper Paceman S for Sale (with Photos)
- 150N Automatikweste Classic Iso