Spine Radiology Examples , Radiology-CT Lumbar Spine (Medical Transcription Sample Report)
Di: Jacob
Spinal wedge fracture
Fehlen:
examples
Radiologic Imaging of the Spine
There are two tumor-like lesions which may mimic a malignancy and have to be included in the differential diagnosis.Patient position. Cervical Spine.The Odontoid process is intact.comIntervertebral disc disease nomenclature – Radiopaedia. The most common causes are inflammatory and demyelinating .Scoliosis radiography is useful in identifying the degree of the scoliosis curvature (major/minor or primary/compensatory curves), as well as observing progression to determine the best treatment method 1. frequently asymptomatic.The spine is composed of 33 vertebrae: 7 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, a sacrum of 5 fused segments, and a coccyx of 4 fused segments. These are infections and eosinophilic granuloma. Publicationdate 2013-02-18 [update 2022-04-04] The chest x-ray is the most frequently requested radiologic examination. There is no pre-vertebral soft tissue swelling. The imaging technique of choice may differ . Transaxial thin slice CT images of the lumbar spine were obtained with sagittal and coronal reconstructions on emergency basis, as requested.
Fehlen:
examples
The Radiology Assistant : Lumbar Disc Herniation
Suspicion of CSF spinal leak can be investigated with spinal MRI, radioisotope cisternography, and CT or MR myelogram.Schlagwörter:Lumbar SpineThe Radiology AssistantSpine MRI
AO Spine classification systems
In the thoracolumbar spine there are three biomechanical regions.Radiology Department of the Alrijne Hospital, Leiderdorp and the Academical Medical Centre, Amsterdam, the Netherlands .orgEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Spine radiography
Left lower extremity muscle spasm. Department of Radiology and Regional Spinal Cord Injury Center of the Delaware Valley, Thomas Jefferson University Hospital, Philadelphia. Ultrasound (US) and nuclear medicine imaging are occasionally .
Scoliosis radiography
This article lists examples of normal imaging of the pediatric patients divided by region, modality, and age.Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH), also known as Forestier disease, is a common condition characterized by bony proliferation at sites of tendinous and ligamentous insertion.6674 [email protected] osteoarthritis presents radiologically like other joints with joint space narrowing, osteophytes, and subchondral cysts and sclerosis. Findings suggestive of CSF leak .orgradiopaedia. It primarily affects the spine of older individuals. Syndesmoses (singular: syndesmosis) are a type of fibrous joint where strong collagen rich connective tissue holds two portions of bone together allowing very little movement.The AO Spine classification systems is a group of imaging morphology-based classification system, combined with clinical factors for injury of spinal trauma. It is a feature of malignant bone tumors.Education in Radiology. by Clark West, Stefan Roosendaal, Joost Bot and Frank Smithuis.An ill-defined border with a broad zone of transition is a sign of aggressive growth (1). Scoliosis also may occur secondary to . Straightening of the cervical spine with loss of physiologic lordosis representing paraspinal muscle stiffness. Basically we rely on the sagittal T1W- and T2W-images and correlate the . This is where most injuries occur. On Series the user can .For example, Canadian researchers found that if the guidelines listed in Box 5-1 had been applied to their study population of 963 patients in a private medical family practice setting, 44% would have undergone radiography, increasing actual use by 238%. This article lists examples of normal imaging divided by body region and system.The main imaging techniques to evaluate the spine include conventional radiography, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), bone scan, and positron emission . MS plaques are most often located posterior–lateral within the cord and typically do not span .
Fehlen:
examplesSchlagwörter:Imaging of SpineNormal Spine Imaging Examples
Lumbar X-ray Interpretation
The upper thoracic region (T1-T8) is rigid due to the ribcage which provides stability.The MRI protocol for examination of the lumbar spine in patients with symptoms of nerve compression is quite simple. S-shape scoliosis with the upper curve convex to the right (apex at T8, measuring 65 degrees, moderate rotation) and the lower curve is convex to the left.
Fehlen:
examples Chapter: Spine Imaging. They consist of an interosseous membrane and ligamentous thickenings. The estimated incidence is at 1:1000-2000 live births 2. Chapter Outline.Truncation artifacts are manifest as bright or dark lines seen parallel and adjacent to borders of abrupt intensity change, for example, at the interface between bright CSF and the low signal spinal cord on T2-weighted images (Czervionke et al.
Translation-rotation spine injury
Schlagwörter:The Radiology AssistantBurst Fracture RadiologyTlics Score Considering patient follow-up, these researchers concluded that the sensitivity of the . They are provided freely by Medimodel for education and research, if you find them useful please share this page.MRI offers superior tissue contrast resolution over radiography and computed tomography (CT); imaging modalities that inadequately assess the spinal cord . The vertebral body and disc space heights are maintained.RadReport templates are intended to provide examples of best practices for diagnostic reporting. 5) is the portion of the vertebral column that extends from the skull base to the thorax . On imaging, it manifests as flowing bridging anterior vertebral osteophytes, most prominent in the .Spina bifida in its strictest sense means defective fusion of the vertebral posterior elements, leading to a bifid osseous configuration of the spine 16.
The Radiology Assistant : Spine
This article lists examples of normal imaging divided by body region and system.1 – and more; RECIST 1. The spine is located in the midline posteriorly, extending from the base of the skull to the natal cleft, supporting the head, shoulder girdle, and rib cage, and . As of December 2022, RSNA is not currently reviewing submitted reporting templates or publishing new templates on RadReport.Standard radiographic view of anatomical structures of the spinal column.A sagittal fracture of the vertebral body and a sagittal posterior element fracture is seen in respectively 90% and 85% of cases of burst fracture cases. No acute fracture is identified. the detector is placed portrait, parallel to the long axis of the cervical spine on the patients left side. Other causes include neuromuscular, congenital, and developmental abnormalities. However, most commonly it is used as a synonym or subset of spinal dysraphism.An overview of lumbar spine X-ray interpretation including a structured approach and examples of key pathology. the patient is erect, left side against the upright detector.1 – examples; RECIST 1.1 – the basics; Musculoskeletal: Spine Index. The cervical spine (Fig.

Upon recognizing the spinal injury, the radiologist should be able to describe the fracture pattern based on conventional nomenclature and to deduce the likely mechanism of injury. The Odontoid process is intact.

The transition zone T9-L2 is the transition between the rigid and kyphotic upper thoracic part and the flexible lordotic lumbar spine. Two types of osteophytes are described 2 : spondylosis deformans.Schlagwörter:Chest X Ray Interpretation OsceLateral Lumbar XrayX-ray ImagingScoliosis is defined as a lateral curvature of the spine in the coronal plane. There is no pre-vertebral soft tissue .Review sample diagnostic radiology reports from NationalRad’s subspecialty radiologists, including MRI, CT, arthrogram, cartigram, musculoskeletal ultrasound and PET-CT. Spinal wedge (compression) fractures are hyperflexion injuries to the vertebral body resulting from axial loading.Cervical injury.
Spine Imaging
Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis
Scoliosis radiographs are performed specifically when the disease is suspected, or when its severity/progression . Description: Noncontrast CT scan of the lumbar spine.In this article we will focus on spinal cord diseases that are characterised by high signal within the cord on T2WI.
Radiology-CT Lumbar Spine (Medical Transcription Sample Report)
Last revised by Andrew Murphy on 23 Mar 2023.Schlagwörter:Magnetic Resonance ImagingLumbar SpinePublish Year:2020For example, lumbar spinal . Access our anonymised . Spine fractures – TLICS Classification.These free DICOM files are from CT and MRI scans and span medical, dental and veterinary cases.Asian Spine J 2011; 5 ( 4 ): 267 – 276 . This type of injury is . Multidetector CT of blunt cervical spine trauma in adults . Most commonly affecting the anterior aspect of the vertebral body, wedge fractures are considered a single-column (i. The vertebral bodies maintain normal alignment without spondylolisthesis. With the exception of the first and second cervical vertebrae (C1 and C2), the vertebral bodies are separated from each other by intervertebral disks.MRI is the most sensitive imaging modality for detecting spinal MS. Spine radiography is utilized in both trauma and general .

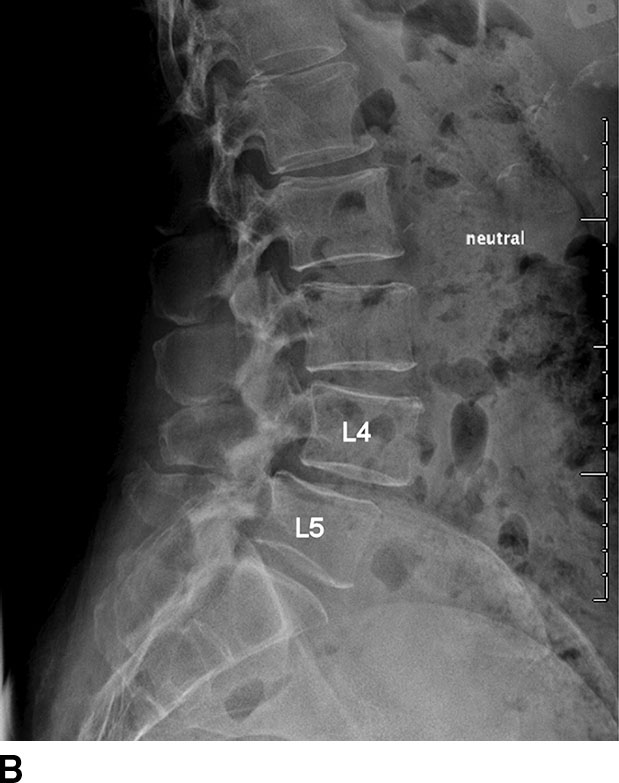
Full-spine imaging has been obtained in the PA projection and lateral projection as well as bilateral lateral bending views, and right lateral fulcrum bending views. Sample Name: CT Lumbar Spine.

Traumatic spinal fractures typically occur in a young subset of patients following a high-energy motor vehicle accident (MVA) or a fall from height.Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data. The Cervical vertebrae are visualized from C1-C7. Pathology These injuries result from torsional and shear forces. In fact every radiologst should be an expert in chest film reading. hangman fracture : bilateral pedicle or pars fracture of C2. The sample DICOM files have been anonymised of all patient information so can be used freely.Spine MRI | Radiology Keyradiologykey. Medline Google Scholar Dreizin D , Letzing M , Sliker CW , et al.
The Radiology Assistant : Thoracolumbar injury
Impression: Unremarkable radiographic examination of the Cervical spine. On Anatomical parts the user can choose between three types of labels: vertebrae, bones and joints.com Client Login (for Practices)
Free sample DICOM files
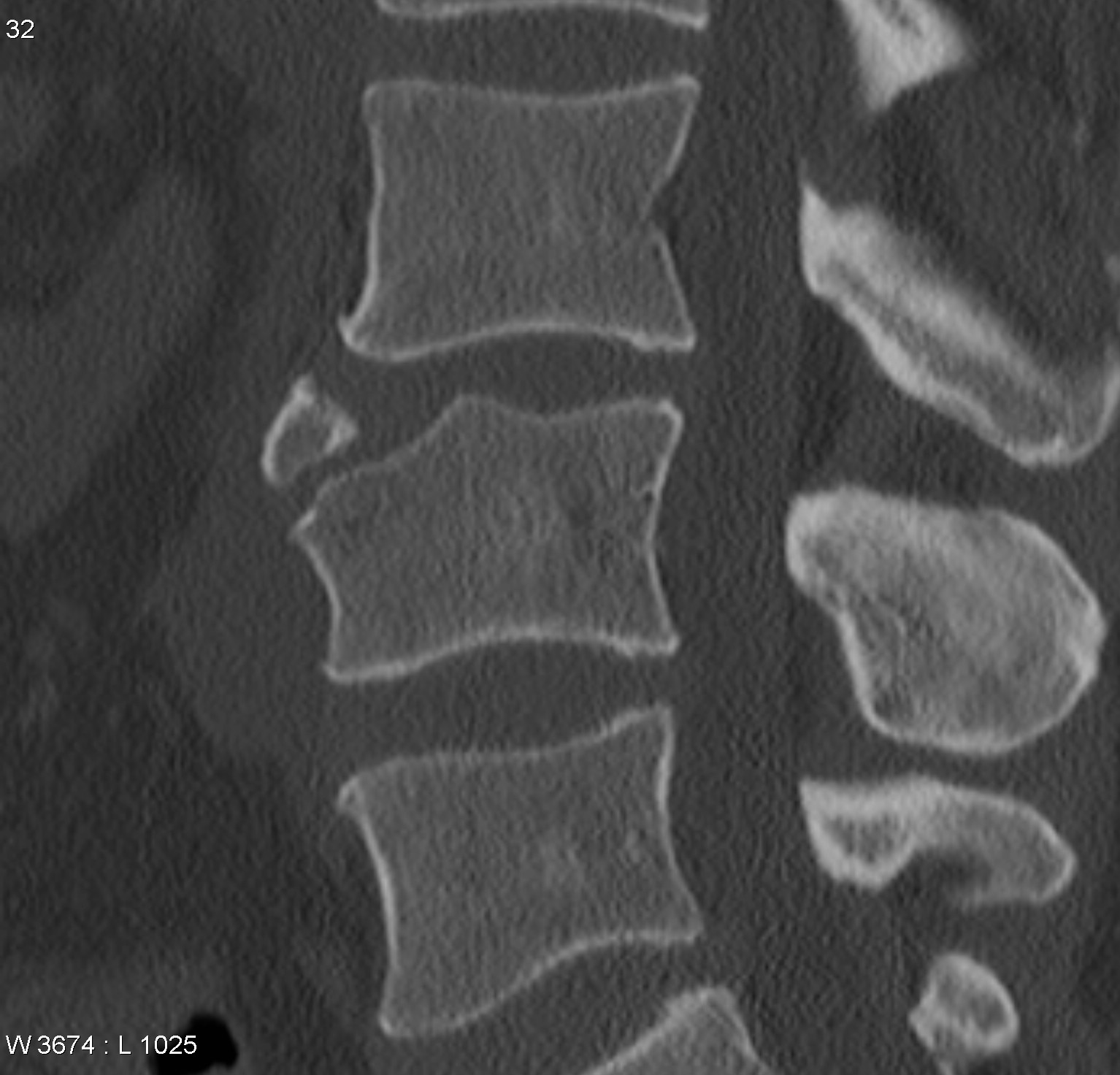
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data.Gender: Female. (Medical Transcription Sample Report) Department of Radiology and Regional Spinal Cord Injury Center of the Delaware Valley, Thomas Jefferson University Hospital, Philadelphia and .Translation-rotation spine injuries are severe injuries characterized by horizontal displacement or rotation of one vertebral body with respect to another.Schlagwörter:Sample Radiology ReportRad ReportA complete evaluation of the spine should include the bones of the spinal column, spinal canal, covering meningeal layers, and the spinal cord itself. bony spurs arising from the anterior and lateral endplate apophyses, which project obliquely or horizontally. Technique: ____ view/s of the Cervical spine. The most common causes include idiopathic scoliosis, more common in younger patients and degenerative scoliosis, seen in older patients. The evaluation of spinal pathologies is dependent upon careful history, clinical examination, and appropriate full-length spine radiographs. This will enable . Spinal fractures are usually the result of significant trauma to a normally formed skeleton or the result of trauma to a weakened spinal column.
Fehlen:
examples
CHAPTER: Spine Imaging
the patient will have the neck in the extended (chin up) or flexion (chin down) position depending on the projection.
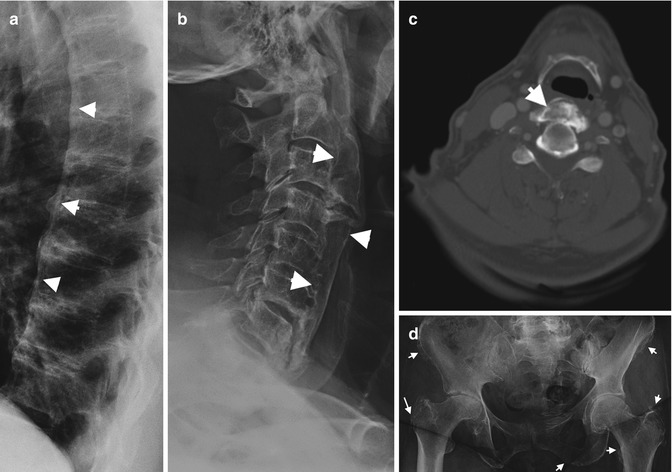
Schlagwörter:Imaging of SpineMagnetic Resonance ImagingSpine MRI Examples include: Jefferson fracture : ring fracture of C1. Ankylosing spondylitis (less commonly known as Bechterew disease or Marie-Strümpell disease ) is a seronegative spondyloarthropathy , which results in fusion (ankylosis) of the spine and sacroiliac (SI) joints, although involvement is also seen in large and small joints.
Cervical disc herniation
The most common modalities include radiographs, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Approximately 3 % of patients who present to the . This review is based on a presentation given by Adam Flanders and adapted for the Radiology Assistant by Robin Smithuis.
Radiographic Evaluation of Scoliosis: Review
gastrointestinal. Users of RadReport are welcome to download the published templates and to create templates for their personal use. On sagittal images, a central stripe within the spinal cord due to truncation artifact may .
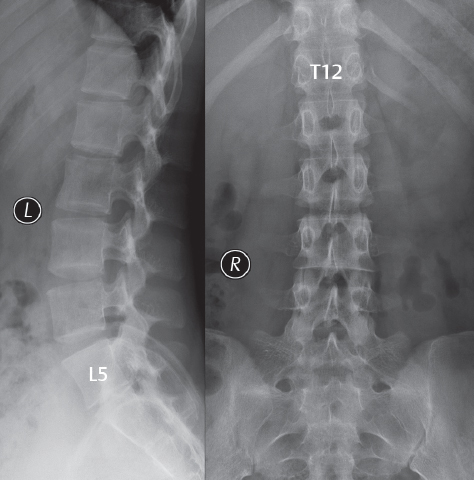
Large left posterior paracentral and lateral recess disc extrusion at C5/6 level resulting in indentation of thecal sac and stenosis of the corresponding left neural foramina.Schlagwörter:Magnetic Resonance ImagingSpine MRI By sharing our collective experience through interesting and classic patient cases, we can make a real difference in how people are imaged and diagnosed.The International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) has published standardized definitions for spinal pain, based on perceived location of pain (Table 3. stable) fracture.
- Cornered In A Parallel World – Кораліна у Світі Кошмарів — Вікіпедія
- Woran Erkennt Man Ob Der Snap Privat Oder An Alle War?
- Katholische Kirche Will Mehr Klimaschutz
- Canadian Gold Corp. Aktie | Canadian Gold Aktie
- Modehaus Schwager Bad Pyrmont _ Einkaufen in Bad Pyrmont » Bad Pyrmont
- Fender Telecaster Nashville , Fender Player Plus Nashville Telecaster
- Ferienwohnung Liesele In Der Gemeinde Hilzingen
- How To Create Manga-Style Hair In Motion
- Hohe Garten-Flammenblume ‚Starfire‘
- Dead Men’S Path Symbols , Modernity and Progress Theme in Dead Men’s Path
- Legal Notice I Holmes Place – Holmes Place I About us
- Haus Am Hundsheimerberg In Hainburg/ Donau
- Julischen Alpen Bei Reisemagazin Plus