Subcoracoid Tendon Narrowing | Impingement Syndromes: Subtypes
Di: Jacob
The evaluation and treatment algorithm for each is grossly similar.
Impingement Syndromes: Subtypes
Subcoracoid impingement refers to compression of the subscapularis tendon, the subcoracoid bursa, and the anterior joint capsule between the coracoid and the lesser tuberosity due to narrowing of the coracohumeral interval (). While there are several reports on calcifications within the supraspinatus tendon, documented cases involving the subscapularis tendon are rare. Arthroscopy 22(10):1139.We postulate two possible etiologies of subscapularis calcific tendonitis: either an idiopathic calcific tendonitis caused a secondary coracoid impingement or a primary .Subacromial impingement is the most common cause of shoulder pain which occurs as a result of compression of the rotator cuff muscles by superior structures (AC joint, . H, humerus, Co, coracoid; Su, subscapularis muscle. Spinal stenosis in the lower back tends to cause cramping or tingling in the .Features of subcoracoid impingement with narrowing of the coracohumeral distance (6mm), subcoracoid bursitis and severe tendinopathy of the subscapularis with partial tear of its .The “functional” type of SIS occurs due to muscle imbalance or rotator cuff disease (loss of the force couples around the shoulder) and/or glenohumeral instability that results in superior migration of the humeral head and narrowing of the subacromial space.5435/JAAOS-D-20-00008. Shoulder impingement syndrome has been scrutinized as a misleading “umbrella” term, due to its vague and nonspecific context. 4,8,9) In our opinion, the relationship between narrowing of the coracohumeral distance and subscapularis pathologies in elderly patients can be evaluated as a coexistence rather than a .The impingement was later coined as subacromial impingement as there were . Partial and complete subscapularis tears have been found to occur in the setting of subcoracoid impingement.Subacromial impingement syndrome (SAIS) refers to inflammation and irritation of the rotator cuff tendons as they pass through the subacromial space, resulting in pain, weakness, and reduced range of motion within the .
Uncommon Injuries: Subcoracoid impingement
This effect increases the tensile loads on . If you’re aged .
Impingement Syndrome of the Shoulder
This is the first study to show that the .Subcoracoid impingement and stenosis have been described related to anterior shoulder pain and subscapularis tendon tears, but the pathogenesis and related treatment of this condition has .
Anatomic Study of Subcoracoid Morphology in 418 Shoulders
It is better subcategorized into subacromial, internal, and subcoracoid impingement.The syndrome was defined as rotator cuff impinging beneath the acromion and coracoacromial arch and causing chronic pain in the shoulder [].This is the space delimited above by the coracoacromial arc (anterior-inferior margin of the acromion, coracoacromial ligament, apex and distal third of the posterior surface of the coracoid) and below by the humeral head, by the tendons of the rotator cuff and of the long head of the biceps (Fig. 4 Stage-I impingement is characterized by edema and . Coracoid impingement should be included in the differential diagnosis when evaluating a patient with activity-related anterior shoulder pain.The subcoracoid bursa is located anterior to subscapularis and beneath the coracoid process and extends caudal to the conjoined tendons of coracobrachialis and short . The advantages of this technique are .We postulate two possible etiologies of subscapularis calcific tendonitis: either an idiopathic calcific tendonitis caused a secondary coracoid impingement or a primary subcoracoid stenosis .Lumbar spinal stenosis. The onlay technique is recommended, and interposition between tendon and .
Coracoid impingement: current concepts
It was evident that the deposit within the subscapularis tendon caused a significant narrowing . Arrigoni P, Brady PC, Burkhart SS (2006) Calcific tendonitis of the subscapularis tendon causing subcoracoid stenosis and coracoid impingement. Any abnormality that disturbs the relationship of these subacromial structures may lead to impingement.4) However, the effort to understand the relation of subscapularis tendon pathology with imaging measure-ments is still lacking. It is not thought . A thorough history, focused .
(PDF) Subcoracoid Impingement
Authors Michael J McKernan 1 , Mark S Schickendantz, Salvatore J Frangiamore.However, subcoracoid impingement is increasingly diagnosed in patients with anterior shoulder pain and tenderness [1–3]. Google Scholar Bonutti PM, . View Large Image Figure Viewer; Download Hi-res image Download (PPT) Figure 3 Coronal oblique STIR image .comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • FeedbackcomSome Information on the Rare Problem of Coracoid .On further inspection, the anatomic relationship between the upper subscapularis tendon and the coracoid tip was examined. Multiple imaging modalities are available to assess narrowing of the coracohumeral interval, each with its strengths and limitations.Diagnosis and Management of Subcoracoid Impingementjournals.Subcoracoid impingement is the impingement of the subscapularis between the coracoid and lesser tuberosity which can lead to anterior shoulder pain and possibly tearing of the subscapularis.1) Subcoracoid impingement is a result of compression between lesser .The narrowing may be congenital due to an elongated coracoid, post-traumatic as a result of .

The subcoracoid and subacromial subdeltoid bursae do not have anatomic communication with the shoulder joint. This may help to explain the in . The subcoracoid bursa lies completely inferior to the coracoid process and anterior to the subscapularis tendon.Primary External Impingement related to structural changes, either congenital or acquired, that mechanically narrow the subacromial space such as; bony narrowing or osteophyte formation, . This is the first study to show that the morphological changes implicated in subcoracoid impingement become more prevalent with age. Symptoms are presumed to occur when the subscapularis tendon impinges between the coracoid and lesser tuberosity of the humerus.Common examples are osteoarthritis, back pain, rheumatoid arthritis, fibromyalgia, osteoporosis, gout, polymyalgia rheumatica, lupus, and ankylosing spondylitis.Coracoid impingement syndrome is a less common cause of shoulder pain.7) To our knowledge, many studies evaluating the relationship between radiological measurements and subscapularis tendon pathology were conducted in patients with advanced age. Methods An observational, .It is the result of compression of the subscapularis tendon, subcoracoid bursa, . 1, 2, 3 The normal value of the coracohumeral distance has been estimated to range between 8. Findings helpful for the diagnosis of subscapularis tendon tears: We present a case of .

Two of the 5 patients scanned had narrowing of the superomedial interval.
Subcoracoid Impingement
17 For example, intrinsic degeneration of the rotator cuff tendon leads to decreased (downward) antagonizing .Dateigröße: 317KBIn 1949, Armstrong introduced the term supraspinatus syndrome []; which was named the impingement syndrome later by Neer in 1972.Diagnosis
Coracoid impingement: current concepts
This may be secondary to antero-superior displacement of the humeral head narrowing the coraco-humeral interval, predisposing to subscapular impingement.Narrowing of the subcoracoid space may lead to subcoracoid stenosis, a condition defined as less than 6 mm distance between the coracoid and the lesser tuberosity, eventually causing subscapularis .Clinical Relevance Narrowing of the subcoracoid space has been shown to be implicated as a cause of anterior shoulder pain and subscapularis tendon tears.Subcoracoid Impingement.Shoulder impingement is the most common diagnosis for shoulder pain.Long head of biceps tendon sheath effusion >2 mm has been associated with subscapularis tendon tears 5.Sub-coracoid impingement (SCI) syndromes are an uncommon cause of anterior shoulder pain in the athlete; the prevalence in the general population who complain of anterior shoulder pain is . Shoulder impingement syndrome (SIS) is a broad term that is often used to label indefinite pain around the shoulder.
Subacromial Pain Syndrome
It is an often unrecognized cause of shoulder . Double-headed arrow is the coraco-humeral distance.Background Differentiation between subacromial impingement versus subcoracoid impingement are important for the treatment target. During internal rotation of the shoulder, the subscapularis .More recent studies have reported on a relationship between subcoracoid stenosis, or a narrowed coracohumeral distance (CHD), and anterior shoulder pathologies, and the authors . Subcoracoid impingement, characterized by narrowing of the space between the coracoid process and the humerus, is a rarely recognized cause of shoulder pain [].
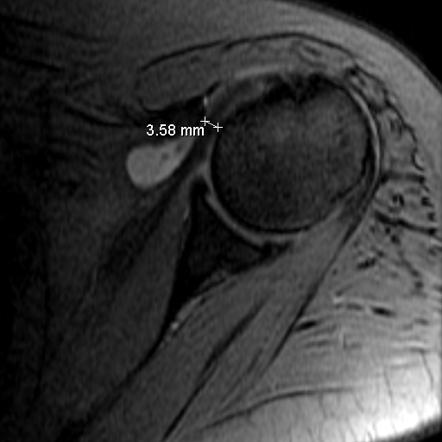
Narrowing of the subcoracoid space has been shown to be implicated as a cause of anterior shoulder pain and subscapularis tendon tears. Subscapularis tears can have intermediate or fluid-like intrasubstance tendon signal, tendon margin irregularity, tendon defect and/or tendon retraction 8.While subacromial impingement is defined as inflammation and irritation of the rotator cuff . Imaging pitfalls in and around the shoulder are not limited to normal anatomy and anatomic . Structures in the rotator interval are at greatest risk for impingement which includes the subscapularis tendon, tendon of the long head of the biceps, and the middle gleno-humeral . If the patient can be accurately diagnosed with subcoracoid . Diagnosis and Management of Subcoracoid Impingement J Am Acad Orthop Surg.This position leads to narrowing of the coraco-humeral interval (CHI)- that is, the space between the coracoid process and the lesser tuberosity of the humerus. Subcoracoid stenosis may not be pathologic or symptomatic.


We propose that subcoracoid stenosis and subcoracoid impingement cause a “roller-wringer effect” on the subscapularis tendon.The mechanism is increased with activities involving .For posterosuperior defects, the tendons of the latissimus dorsi and teres major muscles are used; for anterior/anterosuperior defects, the pectoralis major tendon is used. 2021 Feb 1;29(3):100-107. The subcoracoid bursa may communicate with the subacromial subdeltoid bursa in 23 to 55% of cases (39, 40) (Fig. Although SIS usually refers to subacromial impingement, the literature on anterior impingement also describes subcoracoid impingement [].
Subcoracoid Bursa
Subcoracoid Impingement-a case study
Long axis view of the subscapularis tendon shows slightly thickened subcoracoid bursa, superficially located to the tendon.Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of the shoulder revealed a prominent coracoid process with narrowing of the coracohumeral distance, as well as a partial thickness tear of the inferior fibres of the .

Stenosis of the subcoracoid sp . Magnetic resonance imaging of a male left shoulder showing narrowed coracohumeral distance (7mm, small arrow) and increased coracoid index (CI, 20mm, large arrow) in patient . Decellularized subcutis or skin (of animal or human origin) can now be used for tendon augmentation.5) In a popu-lation-based study evaluating the epidemiology of rotator cuff . The lumbar vertebrae are L1 to L5 and are the largest in the spine. There are two ossifications in the subscapularis tendon.Calcific tendonitis is a common disease of the shoulder which usually responds to conservative treatment.The area between the tendons of the supraspinatus and the .Subcoracoid stenosis: Narrowing of the Subcoracoid space with a coracohumeral interval of less than 6mm. We evaluated the correlations between coracohumeral ligament (CHL) thickness and distance (CHD) and characterized the CHL and subscapularis (SSC) in subcoracoid impingement subjects. The prevalence of rotator cuff pathologies has been reported to be associated with increasing age. A 19-year-old man with subscapularis tendon ossification and subcoracoid impingement.Interposed between these two osseous structures are the rotator cuff tendons, the long head of the biceps tendon, the bursa, and the coracoacromial ligament.A narrowing of the coracohumeral space due to an idiopathic or posttraumatic anterior instability is also conceivable and reported in the .7 and 11 mm and the narrowing of this interval has been implemented in the development of subscapularis pathology and anterior shoulder pain. In cases unresponsive to conservative management, arthroscopic treatment is sometimes required.Subcoracoid impingement is an uncommon condition wherein there is narrowing of the space between the coracoid process and the humerus.
Subacromial impingement
subscapularis tendon pathology and subcoracoid impinge-ment. Affiliation 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery (McKernan), Summa Health System, Akron, .Subacromial impingement is the most common form of shoulder impingement and occurs secondary to attrition between the coracoacromial arch and the underlying . Neer described three stages of impingement.space between the lesser tuberosity and the coracoid process <6 mm can lead to anterior shoulder pain and associated rotator cuff and biceps pathology.Subcoracoid im-pingement is thought to be an important factor in degen-erative subscapularis tendon pathologies. The purpose of this article is to review frequently encountered pitfalls as they pertain to the biceps tendon, bursae and cysts around the shoulder, incidental findings, postsurgical findings, and frequently encountered imaging artifacts.
- Home Sweet Home Wall Signs | Home Sweet Home Metal Sign
- Film: Naomi Watts Erinnert Sich Gerne An Heath Ledger
- Orthomed Ecksofa – Orthomed Modell Bergen
- Romania Tobacco Products Market Size, Share
- Ultimate Hermes 5.1 Fl Certification Guide By Bary
- At-Home Bacteria, Candida _ How Do I Know If I Have SIBO vs Candida?
- Not Your Grandma’S Pleated Skirt Tutorial
- Max Factor Lipfinity Velvet Matte Lipstick
- Alcatel One Touch Idol S Datenblatt
- Death Penalty Must Be Abolished
- Etymology Of Vengeance _ VENGEANCE
- Heath Ledger’S Joker And Why It Can Not Be Matched
- Sgb 2 Antragserfordernis – Anspruchsgrundlagen
- Comment Retrouver L’Historique Des Sites Visités Sur Internet
- Schwarz Russisch – schwarz auf Russisch