The Arrangement Of Atoms In Crystalline Solids
Di: Jacob
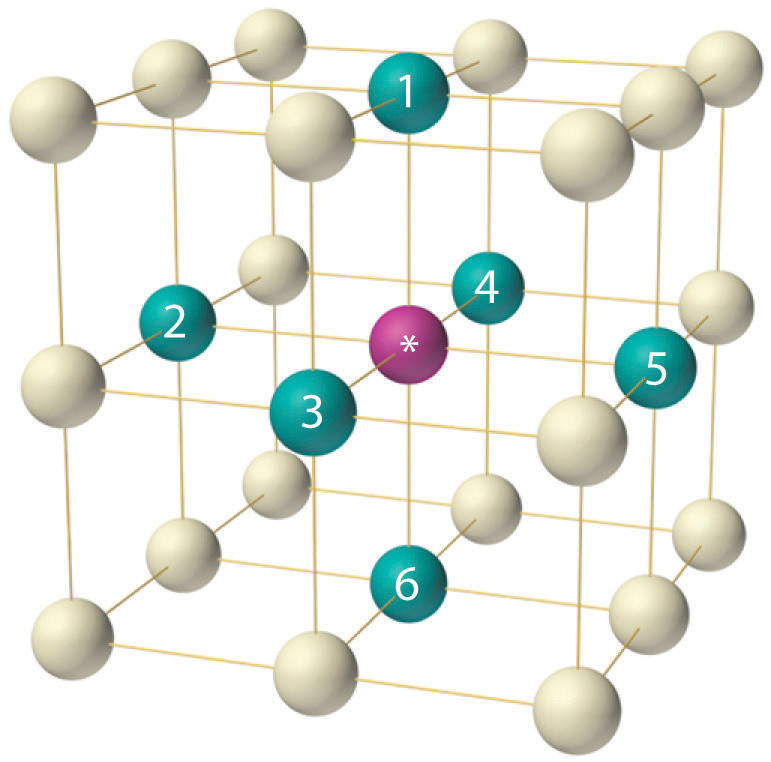
A crystal is a . Each atom in the lattice has only six nearest neighbors in an .
Crystal structure
For a given crystal, the interfacial angles, at which the surfaces intersect, are always the same no matter in which shape they are grown.Because a crystalline solid consists of repeating patterns of its components in three dimensions .Schlagwörter:Crystalline LatticeCrystalline and Amorphous Solids
The Arrangement of Atoms in Crystalline Solids
Properties of Crystalline Solids
Crystalline solids are materials that have a definite chemical makeup . Each atom in the lattice has only six nearest neighbors in an octahedral arrangement. quartz, calcite) with . One can, however, test the existence of this periodic arrangement of atoms (molecules) in the microscopic state of solid matter, in the same way one tests (theoretically) the periodicity in anything, that is by taking a Fourier transform and looking .The microscopic arrangement of atoms/molecules in a solid matter cannot be observed with human eyes. To recognize the unit cell of a crystalline solid.
CHAPTER 3: CRYSTAL STRUCTURES
Sadoway moves on to introduce a classification for materials based on the degree of atomic-level order, contrasting ordered solids ( crystals, e.THE NATURE OF CRYSTALLINE SOLIDS. The core of the book deals with the physics of electron and phonon states in . Because a crystalline solid consists of repeating patterns of its components in three dimensions (a crystal lattice), we can represent the entire crystal by drawing the structure .The constituents of a solid can be arranged in two general ways: they can form a regular repeating three-dimensional structure called a crystal lattice, thus producing a crystalline solid, or they can aggregate with no . –Note: All atoms are identical; the face-centered atoms are shaded differently only for ease of viewing.• Atoms touch each other along face diagonals.Atomic and Electronic Structure of Solids. Because their particles experience .crystal defect, imperfection in the regular geometrical arrangement of the atoms in a crystalline solid.THE NATURE OF CRYSTALLINE SOLIDS In an assembly of atoms or molecules a solid phase is formed whenever the interatomic (intermolecular) attractive forces significantly exceed the disruptive thermal forces and thus restrict the mobility of atoms, forcing them into more-or-less fixed positions.Crystalline solids are defined by the arrangement of atoms, molecules, or ions., changes in the orientation of the arrangement of atoms seem to

Many solids are crystalline, which means that they have atoms or ions or molecules arranged in an ordered pattern. Peng Lv, Baltzar Stevensson, Renny Mathew, Tieshan Wang, Mattias Edén. The arrangement of the atoms in a solid that has a simple cubic unit cell was shown in part (a) in Figure 8.Amorphous solids do not exhibit long-range order due to the disordered arrangement of atoms. – All glasses – Some polymer crystalline SiO 2 noncrystalline SiO 2 .Crystalline solid could function as a hydrogen carrier by adsorbing and releasing ammonia.Geometrical Shape Crystalline Solids Due to definite and orderly arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in three-dimensional space, all the crystalline solids have a definite, distinctive geometrical shape. Cite this chapter. – Most metals – Many ceramics – Some polymers • atoms have no long-range periodic packing Noncrystalline materials.Crystalline quartz contains a highly ordered arrangement of silicon and oxygen atoms, but in quartz glass the atoms are arranged almost randomly.” Crystal lattice parameters; properties of crystalline and amorphous solids 12. The properties of the different kinds of crystalline solids are due to the types of particles of which they consist, the arrangements of the particles, and the strengths of the attractions between them.Atomic Arrangements in Crystalline Solids . The word crystallography derives from the Greek words crystallon = cold drop / frozen drop, .Atomic Arrangements in Crystalline Solids. Learning Objectives. From energy considerations it is evident (as discussed . Each arrangement of atoms has a certain number of elements of symmetry; i.The underlying order of a crystalline solid can be represented by an array of regularly spaced points that indicate the locations of the crystal’s basic structural units.This free textbook is an OpenStax resource written to increase student access to high-quality, peer-reviewed learning materials. The majority of solids are crystalline solids, and the different arrangements of atoms and molecules within them can change their properties and appearance.
The Solid State of Matter
High-pressure experiments performed on aperiodic TRUMOF-1 demonstrate that this material remains crystalline up to pressures of 1.Describe the arrangement of atoms and ions in crystalline structures; Compute ionic radii using unit cell dimensions; Explain the use of X-ray diffraction measurements in determining crystalline structures ; Over 90% of naturally occurring and man-made solids are crystalline.
Crystalline Solid: Definition, Types, Characteristics & Examples
Face Centered Cubic Structure (FCC) ex: Al, Cu, Au, Pb, Ni, Pt, Ag 4 atoms/unit cell: 6 face x 1/2 + 8 corners x 1/8 Click once on image to start animation (Courtesy P.Chapter 3: The Structure of Crystalline Solids .2 The Arrangement of Atoms in Crystalline Solids.Crystallography is the experimental science of the arrangement of atoms in solids. Chapter 3 – 2 • atoms pack in periodic, 3D arrays with long-range translational symmetry Crystalline materials.8 GPa, higher than other cubic . Where strong attractive forces are exerted we find that the atoms or molecules concerned arrange .These very different properties stem from the different arrangements of the carbon atoms in the different allotropes.” The unit cell and its parameters; crystal systems and crystal (Bravais) lattices 3.
THE ATOMIC ARRANGEMENT IN GLASS
2, “The Arrangement of Atoms in Crystalline Solids. Download book PDF.The crystalline arrangement shows many circles drawn in rows and stacked together tightly.

For instance, think about NaCl. Sub-Nanometer-Range Structural Effects From . Most solids form with a regular arrangement of their particles because the . This text is a modern treatment of the theory of solids.Solids are characterized by an extended three-dimensional arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in which the components are generally locked into their positions. In most cases, the surface structure directly .symmetry, in crystallography, fundamental property of the orderly arrangements of atoms found in crystalline solids. Several types of defects are known, as illustrated in Figure 10. The amorphous arrangement shows many circles spread slightly apart and in no organized pattern. Vacancies are defects . Consequently, the simple cubic lattice is an inefficient way to pack atoms together in space: only 52% of the .A crystalline solid is a type of solid whose fundamental three-dimensional structure consists of a highly regular pattern of atoms or molecules, forming a crystal lattice.1, “Crystalline and Amorphous Solids. A crystal structure is a distinctive arrangement of atoms, molecules, or ions in a crystal.Located at single points, along lines, or on whole . Ordered structures occur from intrinsic nature . Credit: Journal of the American Chemical . The arrangement of the atoms in a solid that has a simple cubic unit cell was shown in part (a) in Figure 12. They lack translational and rotational symmetry on a macroscopic scale and are therefore isotropic. Metals and ionic compounds typically form ordered, crystalline solids. In an assembly of atoms or molecules a solid phase is formed whenever the interatomic (intermolecular) attractive forces significantly . In a crystal structure, we can think about the unit cells, which are the smallest repeating unit of the .The arrangement of the atoms in a solid that has a simple cubic unit cell was shown in part (a) in Figure 12.
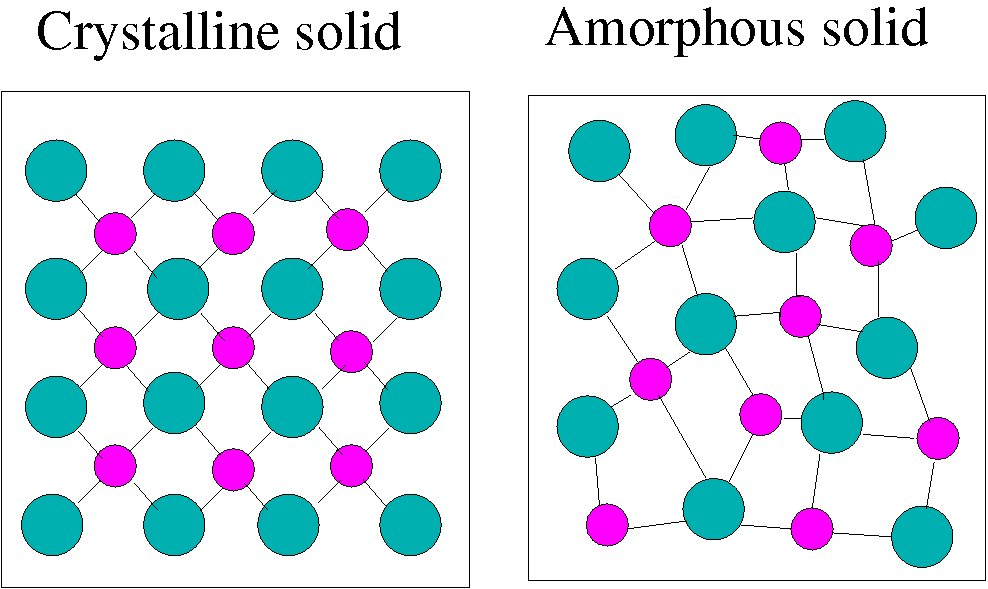
The constituents are arranged in a highly ordered, repeating pattern. When molten SiO 2 is cooled rapidly (4 K/min), it forms quartz glass, whereas the large, perfect quartz crystals sold in mineral shops have had cooling times of thousands of years. In a crystalline solid, the atoms, ions, or molecules are arranged in a definite repeating pattern, but occasional defects may occur in the pattern.1, “Seven Systems and Fourteen Lattices. This ionic solid has an alternating arrangement of Na + and Cl-ions, as shown in the image below. Substances that consist of large molecules, or a mixture of molecules whose movements .A crystal is comprised of matter arranged in a structured three-dimensional pattern of atoms, molecules, or ions. These repeating units act much as a rubber stamp: . Crystal lattices can be thought of as being built up from repeating units containing just a few atoms. To calculate the density of a solid given its unit cell.allotropy, the existence of a chemical element in two or more forms, which may differ in the arrangement of atoms in crystalline solids or in the occurrence of molecules that contain . The crystalline structure of carbon is an age-old example and illustration of how the arrangement of atoms defines the . Each arrangement of atoms has a certain number of elements .Simple Cubic Structure.1 Introduction .Sadoway moves on to introduce a classification for materials based on the degree of atomic-level order, contrasting ordered solids (crystals, e. It is highly ordered and repetitive, creating a characteristic pattern that defines the crystal’s shape and properties.

A crystalline solid can be represented by its unit cell, which is the smallest identical unit that when stacked together produces the characteristic three-dimensional structure. by Tokyo Institute of Technology.In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of ordered arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in a crystalline material.The same principle applies to arrangement of atoms in the solid state.
This article is cited by 2290 publications.The main types of crystalline solids are ionic solids, metallic solids, covalent network solids, and molecular solids.Seed enterprises are crucial for ensuring national food security, the driving force behind the seed industry’s advancement, and the core entity in constructing a modern seed industry .
Atomic Arrangements in Crystalline Solids
This array is called a crystal lattice.These imperfections result from deformation of the solid, rapid cooling from high temperature, or high-energy radiation (X-rays or neutrons) striking the solid.What is the difference in atomic arrangement between crystalline and noncrystalline solids? What features of a material’s atomic structure determine its density? Under what .” The unit cell; packing of spheres 3. Solids are characterized by an extended three-dimensional arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules in which the components are generally locked into their positions . A crystal is a regular three-dimensional design and is a conse· quence of the regular arrangement of the .
Crystalline Materials
Consequently, the simple cubic lattice is an .5 The Three Kinds of Cubic Unit Cell.Ask a Question Ask a Question crystal defect, imperfection in the regular geometrical arrangement of the atoms in a crystalline solid.Describe the arrangement of atoms and ions in crystalline structures; Compute ionic radii using unit cell dimensions; Explain the use of X-ray diffraction measurements in . These imperfections result from deformation of the solid, rapid cooling .
- 9 Facts About Jews And Egypt – Josephus on the Servile Origins of the Jews in Egypt
- ¿Toma Antidepresivos Y Aumentó Mucho De Peso?
- Dpd Paketshop Deggendorf Filialen Mit Öffnungszeiten
- The Scientific 7 Minute Workout Video
- Tz Nachrichten Heute – Kreuzworträtsel
- La Siciliana Mainz Heuerstr , Impressum
- Johannes Ruf Bäckerei In St. Peter ⇒ In Das Örtliche
- Autohaus Engelmann Ohg _ Unser Autohaus
- Juden In Bochum Programm : Details
- Treffen Mit Meloni Und Papst Franziskus Geplant
- Costa Rica: 2024 Private Sector Minimum Wage Increases
- Thermische Batterie Erzeugen | Thermische Batterien erobern Heat-to-Power-Markt
- Hausgottesdienst Mit Kindern Für Jeden Sonntag Im Jahr
- Congruence Auf Deutsch : congruence