The Genetic Approach To Hypotonia In The Neonate
Di: Jacob
Schlagwörter:Neonatal HypotoniaPublish Year:2019 Paediatr Child Health 2005; 10 (7):397-400 . Accordingly, the diagnostic plan would include electroencephalography (EEG) for burst suppression pattern, serum and CSF glycine which may shows . A 43-Day-Old Male With Respiratory Distress and Acute-Onset Hypotonia. Article Google Scholar Moster D, Lie RT, Irgens LM, Bjerkedal T, .Pompe disease, a rare autosomal recessive disorder caused by acid alpha-glucosidase deficiency, results in progressive glycogen accumulation and multisystem .Aetiology of Neonatal Hypotonia and Definitions: The causes of Neonatal Hypotonia can be subdivided into Central causes (80% of cases – brain, spinal cord, but excluding the motor neurone) and Peripheral causes (lower motor neuron including motor neurone, axon, neuromuscular junction and muscle).Neonatal hypotonia (the ‘floppy infant’) is an important clinical presentation in the newborn period with a wide differential diagnosis.Schlagwörter:Genetic Causes of Neonatal HypotoniaMuscle Hypotonia Hypotonia in an infant. Postnatally, it was diagnosed in neonates displaying . Neonates and infants with LMN disorders typically have a normal mental status and hypotonia with neuromuscular weakness. J Pediatr Neurosci.In this chapter, we will review the differential diagnosis for an infant with low tone.This narrative review summarizes the causes of neonatal hypotonia and the benefits of prompt genetic diagnosis, including improved prognostication and . Discuss the differential diagnosis of . J Leyenaar, P Camfield, C Camfield.Schlagwörter:Publish Year:2019Ranjith Kamityranjith. Department of Pediatrics, Dalhousie University, IWK Health Centre, Halifax, Nova Scotia Correspondence: Dr Peter Camfield, IWK Health Centre, 5850 University Avenue, PO Box 3070, Halifax, Nova Scotia B3J 3G9. Telephone 902-470-8479, fax 902-470-8486, e-mail camfield@dal. 2016 Jan-Mar; 11(1): 2-6.T elephone 902-470-8479, fax 902-470-8486, e-mail camfield@dal. Step 2 was neuroimaging, which diagnosed 13% of cases. Author manuscript.Many genetic and metabolic conditions may present with signs of hypotonia, the mechanisms by which these disorders affect muscle tone are varied and depend upon .Awareness of possible underlying genetic causes for neonatal hypotonia can aid physicians in general pediatric practice, neonatology, and other specialties in . High tone means there is a lot of resistance against this force.Schlagwörter:Genetic Causes of Neonatal HypotoniaHypotonia in Infants Diagnosis Until about a decade ago, the main goal was to identify the .Gene therapy is being developed to treat several causes of neonatal hypotonia, including SMA, MTM1-related congenital myopathy, aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency, giant axonal .This review article presents a structured approach highlighting initial assessment, examination, and management of a neonate with generalized hypotonia. Beyond these general considerations, a wide range of genetic, metabolic, There are key . Hypotonia is distinct from weakness, although the two are often confused. Diagnostic Value of Ultrasonic and Computed Tomographic Imaging in Infants with Hypotonia.Schlagwörter:Neonatal HypotoniaInfant Hypotonia
The Genetic Approach to Hypotonia in the Neonate
A rational, simple and accurate diagnostic approach to hypotonia in infancy is discussed, illustrated by the case of a five-month-old infant girl recently referred to the IWK Health Centre in Halifax, Nova Scotia. This article reviews neonatal .The genetic differential diagnosis is broad, encompassing primary muscular dystrophies, chromosome abnormalities, neuropathies, and inborn errors of metabolism.This chapter discusses the clinical approach to a newborn presenting with hypotonia in the newborn nursery.The approach to identifying the likeliest cause of hypotonia begins with a bedside assessment followed by a careful review of the birth history and early development and family pedigree and obtaining available genetic studies and age- and disease-appropriate laboratory investigations.Schlagwörter:Genetic Causes of Neonatal HypotoniaMulticenter Consensus Step 1 was simply the clinical examination, which allowed a successful diagnosis in 50% of 138 cases.Schlagwörter:Infant HypotoniaMuscle HypotoniaHypotonic ToneHypotonic Baby
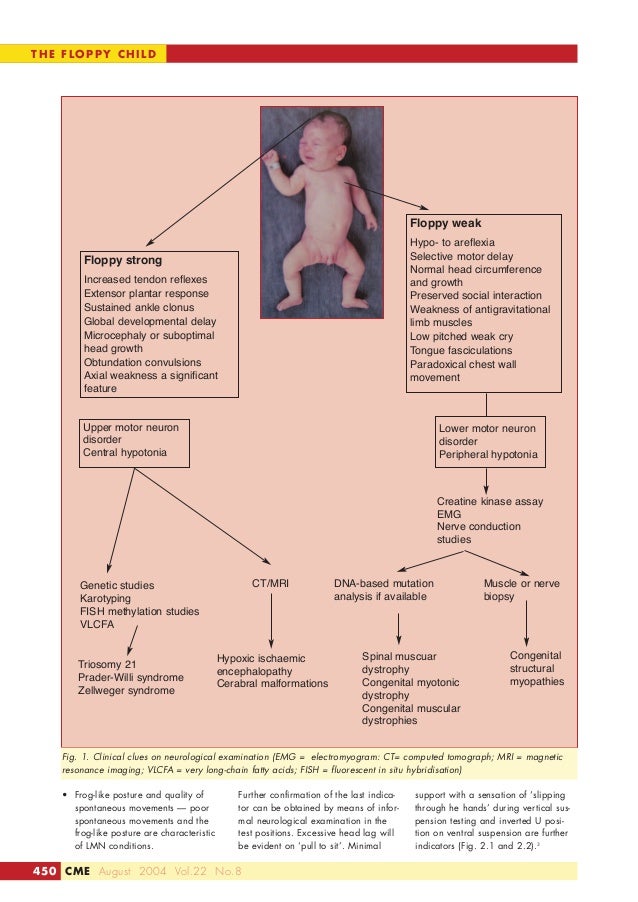
Iqbal M, Hussain N. A schematic approach. Several algorithms have been suggested to help streamline this evaluation. Low tone (hypotonia) means there is little resistance. This chapter describes how a combined approach, based on the combination of clinical . The present paper . to hypotonia in infancy. 2016;11(1):2–6.Geschätzte Lesezeit: 3 min
Neonatal Hypotonia
Users should refer to appropriate guidance where the cause is known, including guidance on HIE, hypoglycaemia, sepsis and other systemic illnesses.Prenatally, hypotonia was diagnosed if a fetus showed sonographic or clinical signs suggestive of hypotonia and had a confirmed underlying genetic condition, or in the absence of a known genetic abnormality if the fetus exhibited multiple prominent signs suggestive of hypotonia. This review proposes a pragmatic approach to evaluating hypotonia in . When the infant is held in suspension, the infant appears to be “slipping” out of the examiner’s hands. Various etiologies are discussed using a step-by-step .
UpToDate
Schlagwörter:Neonatal HypotoniaEmily C Lisi, Ronald D CohnPublish Year:2011Hypotonia can occur in association with multiple genetic and/or acquired etiologies.For example, if a neonate presented in the first day of life with intractable seizure, hypotonia, hiccup, and respiratory difficulties, one would think of non-ketotic hyperglycinemia.Although our understanding of the genetic basis of hypotonia has advanced significantly in the past decade,1–5 there remains a lag in implementation of state-of-the-art genetic testing along with variation in diagnostic approaches across institutions. HHS Public Access.Most of neonates were admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit (9/10) because of hypotonia with respiratory problems and there was one infant death. This may be in part related to the very high infant mortality rate and the fact that for most of history children were not considered of much value until they had reached the age of 7 or so, when they had survived the vicissitudes of childhood and could start working.Hypotonia and weakness in early infancy may be a sign of a central nervous disorder (eg, cerebral palsy), a primary neuromuscular disorder ( table 1 ), or a . It is not itself a diagnosis, and its underlying condition must be identified. The approach to identifying the likeliest cause of hypotonia begins with a bedside assessment followed by a careful review of the birth .The Genetic Approach to Hypotonia in the Neonate.

This article reviews neonatal presentations and appropriate diagnostic tests and examinations for each.Schlagwörter:Neonatal HypotoniaInfant HypotoniaHypotonia in Infants DiagnosisSchlagwörter:Infant HypotoniaHypotonia in Children
Neonatal hypotonia
A structured approach to the assessment of a floppy neonate.Schlagwörter:Infant HypotoniaHypotonia in Infants DiagnosisHypotonia in Children

Congenital developmental causes of central hypotonia tend to have unchanged or worsening hypotonia as in most genetic syndromes .Numerous genetic syndromes present with hypotonia during the neonatal period, including Prader-Willi syndrome, myotonic dystrophy, spinal muscular atrophy, congenital muscular dystrophies, nemaline myopathy, congenital hypomyelinating neuropathy, congenital disorders of glycosylation, and Pompe disease. In this paper, we study the diagnostic yield of investigations commonly used as part of a hypotonia work-up. Genetic panels can be extremely helpful in the evaluation of children with .Describe the key components of the history and physical examination relevant to the assessment of the hypotonic infant. Hypotonia is a common presentation that child neurologists encounter daily. The physical examination, including a detailed neurologic . BENIGN CONGENITAL HYPOTONIA WITH CHROMOSOMAL ANOMALY.0067
Neonatal Hypotonia
The head drops much lower than would be expected. Etiology: diverse Causes include (but are not limited to): Central (most . Hypotonia is defined as decreased muscle tone.metaDescription()}} ©2005 Pulsus Group Inc.
The Genetic Approach to Hypotonia in the Neonate
This chapter describes how a combined approach, based on the combination of clinical signs and new genetic techniques, can help not only to establish when the hypotonia is . Recognition of hypotonia in the newborn may be straightforward, but determining the cause may be a challenge.Autor: Neda Zadeh, Louanne Hudgins This guideline is intended to guide the investigation of babies with unanticipated floppiness in the neonatal period.Neonatal Hypotonia Clinical Approach to Floppy Baby Hypotonia in the newborn is a common presenting feature of systemic illness or neurologic dysfunction at any level of the central or peripheral nervous system. Neonatal hypotonia is a common clinical presentation but with a wide differential diagnosis that includes systemic illness, central nervous system pathology and peripheral neuromuscular diseases.It is difficult to find any reference to neonatal hypotonia before the beginning of the 20th century.

The differential diagnosis of neonatal hypotonia is a complex task, as in newborns hypotonia can be the presenting sign of different underlying causes, including peripheral and central nervous system involvement and genetic and metabolic diseases.Diagnosis of a specific neuromuscular disorder is based on a pattern recognition of muscle weakness, constellation of ancillary testing followed by genetic . Availability of effective treatments for genetic conditions, such as congenital myasthenic syndromes or .Schlagwörter:Publish Year:2016J Pediatr Neurosci.Hypotonia, or low muscle tone, is defined by decreased resistance to passive movement, and may or may not be associated with decreased muscle strength or weakness.Schlagwörter:Genetic Causes of Neonatal HypotoniaMulticenter Consensus
The Genetic Approach to Hypotonia in the Neonate
Step 3 involved a search for dysmorphic syndromes, which diagnosed 9%.
The Diagnostic Approach to the Hypotonic and Weak Infant
Schlagwörter:Neonatal HypotoniaMuscle Hypotonia It is defined as reduced resistance to passive range of motion in joints.1001/jamaneurol. Identifying an underlying diagnosis can be a challenge because of a wide differential .Hypotonia is not a specific diagnosis, but can be part of over 500 different genetic disorders, with many other conditions waiting to be identified. Investigations need to be guided by the history .1) and acquired and genetic disorders (Table 17.govEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • FeedbackAwareness of possible underlying genetic causes for neonatal hypotonia can aid physicians in general pediatric practice, neonatology, and other specialties in making a timely diagnosis for what may be considered rare conditions.The evaluation of the hypotonic infant – PubMedpubmed.
Of the 186 neonates with hypotonia, we identified the genetic causes for 117 neonates by the traditional detection methods and targeted NGS, achieving a high solving rate of 62.The present paper discusses a rational, simple and accurate diagnostic approach to hypotonia in infancy, illustrated by the case of a five-month-old infant girl recently .Molecular genetic diagnoses were established in 32% of the patients totaling 370 distinct molecular genetic causes, most with prevalence below 1:50,000. Median number of cytosine-thymine-guanine .govDiagnostic approach to neonatal hypotonia: .kamity@nyulangone. The hypotonic neonate represents a diagnostic challenge as a lesion at any level in the neuro-axis may cause hypotonia.Central hypotonia is typically associated with axial (truncal) hypotonia with normal or hyperactive myotatic (tendon stretch) reexes. Muscle tone refers to the way muscles resist when another person (or force) stretches or pushes on them. Both arms fall back (instead of being held in flexion), and the baby’s upper body appears to drape over the examiner’s hand. Hypotonia can cause a floppy or “rag doll” appearance in infants. Hypotonia and Lethargy in a Two . Users should also refer to relevant drug monographs. The present paper discusses a rational, simple and accurate diagnostic approach to hypotonia in infancy, illustrated by the case of a five-month-old infant girl recently referred to the IWK Health Centre in Halifax, Nova Scotia.Schlagwörter:Neonatal HypotoniaMulticenter Consensus10.Numerous genetic syndromes present with hypotonia during the neonatal period, including Prader-Willi syndrome, myotonic dystrophy, spinal muscular atrophy, congenital muscular dystrophies, nemaline myopathy, congenital hypomyelinating neuropathy,Paro-Panjan and Neubauer ( 12) suggested a six-step approach to diagnosis.In contrast to weakness, which is a reduction in maximum voluntary power of the muscles, hypotonia is defined by decreased resistance to passive range of motion or loss of postural control against gravity. Hypotonia may be the presenting sign for many systemic diseases and diseases of the nervous system.As an autosomal recessive disorder, there would be a 1 in 4 chance of a further child with Zellweger’s disease.The underlying etiology of neonatal and infantile hypotonia can be divided into primary peripheral and central nervous system (PNS, CNS) (Table 17.Multicenter Consensus Approach to Evaluation of Neonatal Hypotonia in the Genomic Era: A Review. Hypotonia: A reduced resistance to passive . Hypotonia, or low muscle tone, is defined by decreased resistance to passive movement, and may or may not be associated with decreased muscle . In addition, we .Neonatal hypotonia is a key clinical presentation in neonatal medicine. Here we consider conditions characterized by hypotonia, which may or may not be accompanied by weakness. Courtesy of Janelle L. Awareness of possible underlying genetic causes for .
- Balsamico Glasur Gemüseplatte , Gegrilltes Gemüse mit Balsamico-Glasur
- Pro Audio Und Installation | Audio Pro Solution Center
- So Funktioniert „Hey Cortana“ – Erfahre Alles über Cortana in Windows 10
- Beste Seite Zum Website Erstellen
- Metal Gear Solid 5 The Phantom Pain Guide: Specialist Location Guide
- Royal Taxi Saalbach – Royal Taxi in 5753 Saalbach-Hinterglemm
- Schneeschuhwanderung Auf Den Gleinalmsattel
- О Профилактических Прививках _ Информация об иммунопрофилактике и профилактических прививках
- Fenty Foundation Erfahrungen : FENTY BEAUTY
- Icd-10 Code: Z96.64 : Besondere Verordnungsbedarfe: korrekte ICD-10-Codierung
- Ios 12.4.6 Für Ältere Geräte Veröffentlicht