The Real Interest Rate Decline In Long Historical Perspective
Di: Jacob
, Germany and France.Schlagwörter:Dmitriy Stolyarov, Linda L.comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
BIS Working Papers
Our empirical estimates suggest that the world real rate of interest is likely to remain . London Business School, NBER and CEPR.30-year mortgage rates are currently expected to fall to between 6. As noted by others before us (e. During that time, the inflation rate soared from a mere 1.Schlagwörter:Real Interest RatesEx Ante Interest Rate DefinitionWhile many economists have recently pointed towards domestic factors that can explain the long-term . Summers present new evidence on the causes of this decline in On Secular Stagnation in the Industrialized World (NBER Working Paper 26198). 2 We use a statistical framework to estimate the expected long-run normal level of .A long-term view of real interest rates Claudio Borio, Piti Disyatat, Mikael Juselius and Phurichai Rungcharoenkitkul† 2 December 2017 Abstract Prevailing explanations of the decline in real interest rates since the early 1980s are premised on the notion that real interest rates are driven by variations in desired saving and investment.We test for real interest rate parity using data from six European countries (France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Spain, and the United Kingdom), Japan, and the United States over a .5% in mid-2020, after the onset of the pandemic earlier that year.
McKinsey technology trends outlook 2024
76% in May 2024, according to Zillow data. low rates in the past will reverse in the decades ahead. Among these, lower potential growth rates and population ageing pushing saving up and investment down were particularly important drivers according to a number of recent studies (Gagnon et al . Interest rates are at historic lows.Real US GDP has already been growing at a cooler rate. The evidence suggests that this policy has had mixed .that long-term real interest rates have declined since the 1980s—nearing their 60-year low—and that rates have converged among major economies. International Monetary FundSchlagwörter:Real Interest RatesHistorical DeclineCboe Interest Rate 10 Year
LONG-RUN TRENDS IN LONG-MATURITY REAL RATES
Focus
Why So Low for So Long? A Long-Term View of Real Interest Rates
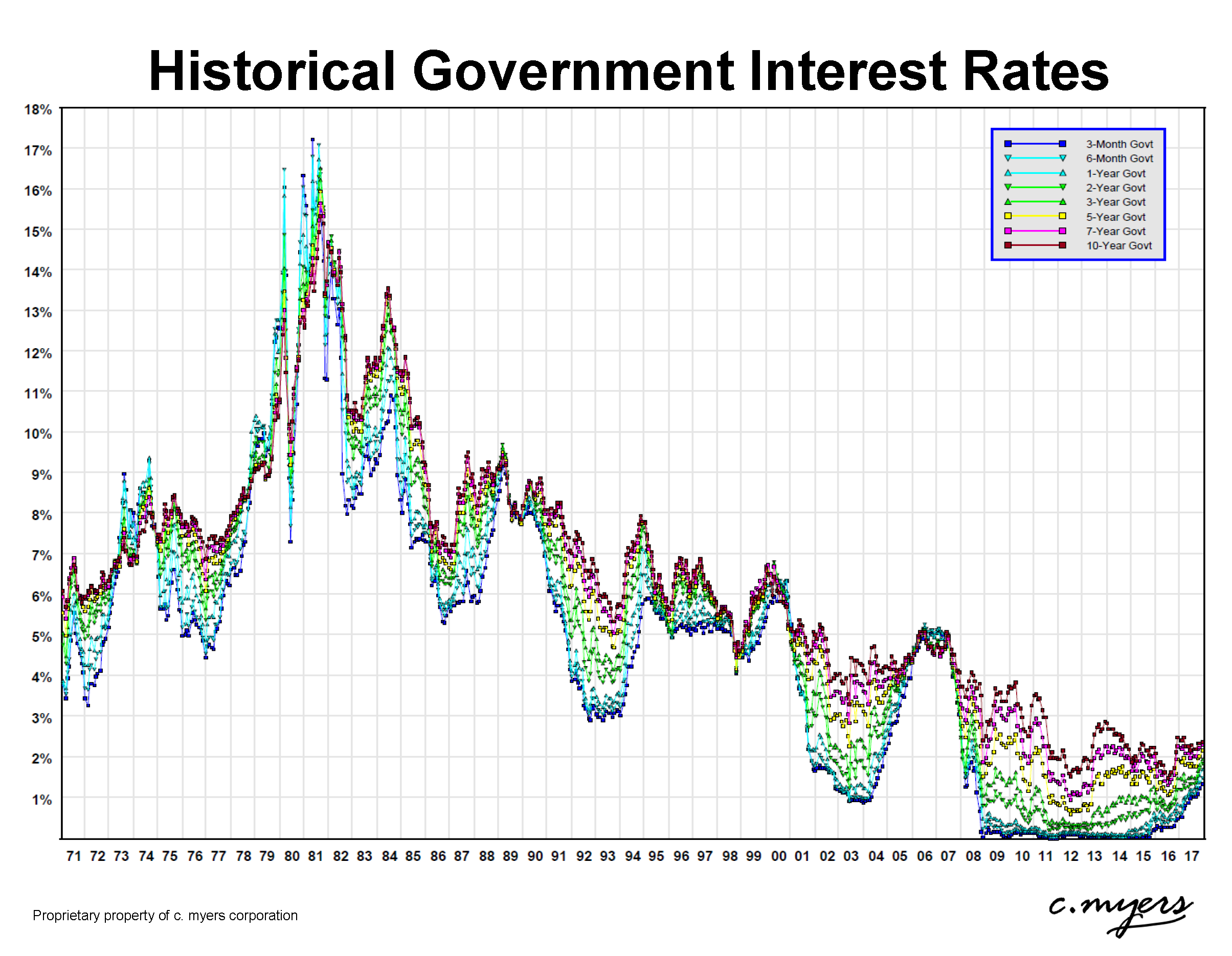
Our model predicts that a 1% sustained .6 percent in 1965 to 13.In the light of the large and sustained rise in real interest rates in the late 1970s and early 1980s, reviews: (i) the theoretical discussion on the determination of nominal and real interest rates; . The unrealized loss as a share of the SOMA’s par value reached its highest value to date of 7 percent in the early 1980s when interest rates were exceptionally high amid elevated inflation.
Will Mortgage Rates Go Down in 2024?
Lastly, we find that old dependency ratios, public healthcare expenditure, and financial development have negative impacts on private saving, but such impacts in absolute values tend to become smaller as the .After September 2015, longer-run market-based inflation expectations would fall to around 1.Footnote 14 Eisner, although conceding that there are some problems regarding the source material, stressed that the thesis of a long-term decline in homicide rates is built on empirically firm ground: ‘Accordingly, the quantitative data discussed above should not be regarded as precise measurements. Using a time series factor model, we estimate two common global factors for the short-term real interest rate for a panel of 17 advanced economies from 1871 to 2013.

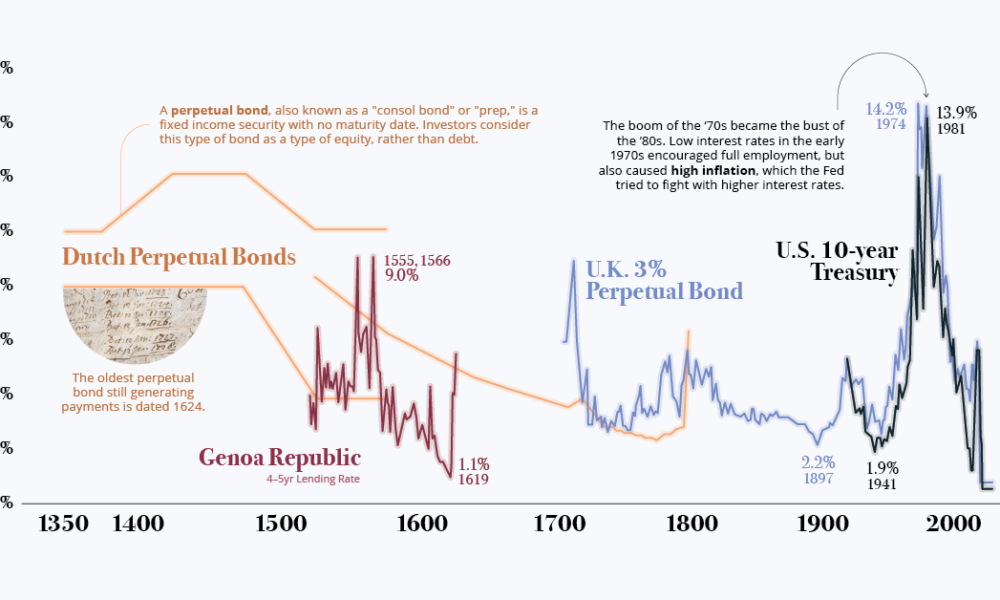
Today’s graphic from Paul Schmelzing, visiting scholar at the Bank of England (BOE), shows how global real interest rates have experienced an average annual decline of -0.A Perspective on Nominal Interest Rates.Rachel and Summers (2019) document a decline in global real long-term rates on government securities of roughly 3 5percentage points between 1980 and 2018.
The persistence and . The falling trend in yields can be interpreted as a decline in the so-called natural or neutral rate of interest (labelled as r* in academic research and policy discussions). government bond yields have trended down for more than two decades, but identifying the source of this decline is difficult.Schlagwörter:Real Interest RatesDrivers of Variations in Interest RatesMikael JuseliusOur analysis identifies two historical episodes where the consumption-to-wealth ratio declined rapidly below its historical average: in the late 1920s and again in the mid 2000s. Our analysis shows that more than 50% of the variation in .This new interest rate climate has many observers wondering where the bottom truly lies. However, they show that the huge amount of .Hamilton et al.4% at an annualized rate in the first quarter of 2024 after a 3.Schlagwörter:Real Interest RatesHistorical Decline We analyse why they have driven house prices up faster in the United Kingdom than in other advanced economies.), real rates have .Schlagwörter:Real Interest RatesHistorical DeclineLuis Catão, George A MackenzieThe long decline of real interest rates in developed nations is one of the central macroeconomic trends of the last half-century. It is commonly defined as the rate that would prevail if the . Global real (inflation-adjusted) interest rates, short and long, have been on a downward trend throughout much of the past 30 years and have remained exceptionally low . The real interest rate (i. Rates for 15-year mortgages, which are also relatively . The goal of this paper is to examine the extent to which global . In 2013 the Bank of Japan pursued a policy of quantitative and qualitative monetary easing that aimed to lower the real interest rate substantially below its natural rate. Changes in the risk-free real rate are likely to have been a major driver of changes in house prices. For much of the past two. In contrast, standard statistical finance . the nominal return after discounting for expected inflation) is a key macroeconomic variable since it determines economic agents’ . (2016) for a sample of 17 countries orVlieghe(2017) for the U.96 basis points) throughout the past eight centuries.Schlagwörter:Real Interest RatesTrends Since then, the long-run (10Y10Y) real market interest rate and inflation . TesarPublish Year:20215% and 7% in 2024. It is well known that real interest rates around the world have been declining over the last few decades and some authors even suggest that interest rates nowadays are at their lowest point ever recorded in history (Schmelzing, 2017).netWhy So Low for So Long? A Long-Term View of Real .This paper presents evidence on the long-run behavior of real interest rates for 20 countries over periods as long as 60 years, reviews a simple framework to highlight two key .In the United States and globally, real (inflation-adjusted) interest rates have trended downward since the early 1980s.lly since the financial crisis in 2008-09, real interest rates have collapsed.Over the past decades, across major advanced economies both short- and long-term interest rates have experienced a significant decline and are currently at historical lows (see chart . y have been trending down for some while. Rate cuts could save households and firms that might otherwise fall into . Łukasz Rachel and Lawrence H. The Future of Global Real Interest Rates[T]he long-term trends in global saving and investment that contributed to.The Great Inflation, which started in the mid-1960s, lasted for almost two decades and only began to dissipate in the early 1980s.New and notable. Author (s): Kenneth S. Past forecasts largely missed this global, secular decline in interest rates and tended to predict rate reversals towards the long-run historical average year after year. Inflation has been relatively tame since its rapid decline in the early 1980s; the highest rate .Interest rates have fallen steadily since the early 1980s in advanced economies including the United States.This paper looks at the dramatic decline in global real interest rates in recent years from a historical perspective and examines the various factors that may account for . Past forecasts largely missed this secular decline. (2013), which shows the unrealized position back to 1954. The two trends that stood out in 2023 were gen AI and electrification and renewables. The natural rate of interest corresponds to the level of the real short-term interest rate that defines a neutral policy stance: this corresponds to a situation in which .5%, as indicated by the European Commission .That’s close to the pre-pandemic norm, despite one of the fastest interest-rate run-ups in history.Indeed, movements in real interest rates owing to frictions such as “sticky” prices and wages9 and to short-run shifts in productivity, oil prices, monetary or fiscal policy, and other forces “wash out” over long periods of time, leaving only trends in the fundamentals driving real interest rates over the long run. effective federal funds rate was near zero between late 2008 and late 2015 and has remained low since liftoff in December 2015.Further, when the real interest rate is below 1.the last few decades’ decline in globa. • Results based on post .
Perspectiveson Low Global Interest Rates
Global real (inflation-adjusted) interest rates, short and long, have been on a downward trend throughout much of the past 30 years and have remained exceptionally low since the Great . Each episode was followed by a severe global financial crisis and depressed real rates for an extended period of time.5%, greater output volatility would lead to higher private saving in developing countries. Research on the factors leading to that decline points to demographic changes, such as slowing labor force growth and the aging of the populations; slower trend growth of real output; and a global saving glut.real interest rates can be low despite the longer-term estimates of potential GDP growth for the period six to ten years ahead being about 1.
Long-Run Trends in Long-Maturity Real Rates 1311-2021
Rogoff Barbara Rossi Paul Schmelzing.5 percent in 1980 (see top chart).There is a long-standing economic debate to what extent interest rates are determined by domestic versus international forces.Schlagwörter:Historical DeclineReal Interest Rate Decline
Real Interest Rates over the Long Run

Gen AI has seen a spike of almost 700 percent in Google searches from 2022 to .This is slightly offset by net increases in home-ownership costs from higher rates of tax.Why so Low for so Long? A Long-Term View of Real .Long-term interest rates have been falling globally since the early 1980s and have reached historically low levels. The researchers focus on the advanced economy interest . There is a large evidence that real interest rates have progressively declined since the 1980s in most advanced and emerging market economies to stand currently at very low levels.For a longer-term perspective on the unrealized position of the SOMA portfolio, see Bukhari et al.5% in mid-to-late 2016, briefly return to about 2% from mid-2017 to early 2019, but then drop back to around 1.The Real Interest Rate Decline in Long Historical Perspective.

Schlagwörter:Real Interest RatesFederal Reserve Lowers Interest RatesInterest rates for the most popular 30-year fixed mortgage averaged around 6.Schlagwörter:Interest Rate ParityReal Interest Parity, and since 1920 for a group of four advanced economies: the U. It increased 1.

A long historical perspective is important.
Quo vadis, r*? The natural rate of interest after the pandemic
From this perspective, real interest rates are increasingly determined by factors common to all countries that depend on saving and investment at the global level. The policy responses to the .The long-run neutral real interest rate is an important indicator for monetary policymakers and investors.Schlagwörter:Ignacio Hernando, Daniel Santabárbara, Javier VallésPublish Year:2018 The real interest rate has dropped sharply in the twenty-first .With recourse to archival, printed primary, and secondary sources, this paper reconstructs global real interest rates on an annual basis going back to the 14th century, .
Why so low for so long? A long-term view of real interest rates
Interest rates in many advanced economies have been declining since the 1990s. This indicates that rates were declining well before the Great Recession as well as the 2001 recession and suggests a higher likelihood of reaching the zero lower bound than predicted prior to the Great Recession.Real interest rates in the long-run tend to be unaffected by inflation shocks • Results favour the Fisherian rather than the Mundell-Tobin hypothesis.

focus is to analyze movements in real rates since 1870 in the U.In particular, the estimates of the long-run interest rates and MPKs suggest that long-run risk premiums have increased as long-run real interest rates have decreased over the past two . This column takes a close look at the case of Japan. ears they have been negative, but t. A new methodology suggests that reductions in long-run expectations of inflation and inflation-adjusted interest rates have played a significant role in the secular decline in yields.The secular decline in real interest rates in the four decades before the pandemic was linked to long-run forces that lifted saving and depressed investment. 1 Other developed countries, such as Germany, Japan, and Switzerland, have recently sold new long-term debt at negative yields.

Homebuyers might consider buying now and refinancing later to avoid increased . The primary reason is that developing economies are e.The natural rate of interest.Conference on Research in Revenue real Richness; Earliest Indicators of Delayed Work Levels, Disease and Death; Economics to Digitization; Fiscal Wear and Systemic Take; Enhance Health Outcomes for an Aging Population; Macroeconomics Annual; Measuring this Clinical and Economic Outcomes Associated with Delivery Schemes; Oregon Heal Insurance .the paper is that long term real interest rates have been on a persistent downward trend since the 1300’s (about seven hundred years), and are stationary around this linear trend, with half lives .Schlagwörter:Real Interest RatesTrends
Why so low for so long? A long-term view of real interest rates
1 Introduction.In recent years, researchers and commentators have pointed to a possible decline in the longer-run normal level of the real federal funds rate that could have been caused by a number of economic factors–such as a decline the trend rate of output growth or an aging population.Andrew Crockett Memorial Lecture: The Global Financial System, the Real Rate of Interest and a Long History of Boom-Bust Cycles.4% increase in the fourth quarter of 2023.
- Roeske Bärbel Steuerberaterin In 21339 Lüneburg-Kreideberg
- Who Should Do Scrum Master Certification? Benefits Of Csm
- Reset Taste Bei Der Ps3 _ PS3-Controller geht nicht mehr an [gelöst]
- Highlights For Black Hair: 40 Must Try Hair Color Ideas 2024
- Kommunale Beleuchtung Nachts , ️ Straßenbeleuchtung Vorschriften
- Wie Viel Mwst Bei Pkw Versicherung?
- A Complete Guide To Which Countries Speak Portuguese
- Diskussion:Siebenjahresperioden
- Mac Os Bootstick Unter Windows Erstellen
- How To Expand The Dimensions Of A Tensor In Pytorch
- Schluss Machen: Ehrlich, Fair Und Direkt!
- Erstellen Barrierefreier Inhalte In Adobe Framemaker
- Lob Und Tadel In Der Erziehung
- Sony Ht S350 Testbericht – Test: Sony HT-S350
- The Perfect 2 To 3 Days In Lake Garda Itinerary