Upper Urinary Tract Radiology | Imaging of Urothelial Cancers: What the Urologist Needs to Know
Di: Jacob
Most cases of XGP involve a diffuse process; however, up to 20% are focal. Ultrasonography plays a limited role, owing to suboptimal sensitivity for stone detection that ranges from 60% to 96%.Background Three-phase CT urography (CTU) is the gold standard for evaluating the upper urinary tract in patients with hematuria.Over the past decade, computed tomographic (CT) urography has emerged as the primary imaging modality for evaluating the urinary tract in various clinical settings, including the initial workup of hematuria.Schlagwörter:Urinary System BritannicaUrinary System Overview
The Urinary Tract
With the exception of the urethra, this is the same in both males and females.Urinary tract infection (UTI) is a common clinical condition involving the bladder ( cystitis) and kidneys ( pyelonephritis ).This proposed rule would revise the Medicare hospital Outpatient Prospective Payment System (OPPS) and the Medicare Ambulatory Surgical Center .It spans the abdomen and pelvis, from the upper abdomen to the extreme pelvis, being inextricably linked with the genital system.However, in the common sense, to exploit all the potential of this technique, CT urography is understood as a combination of renal CT plus CT of the contrast-enhanced upper urinary tract. Approximately 60–75 % of cases of ureteral UC involve the distal third of the ureter It is commonly divided into .Schlagwörter:Urinary Tract ImagingRadiology of The Urinary TractNormal Kub We aimed to evaluate the accuracy of CTU for detecting upper urothelial cell carcinomas (UCC) in patients with hematuria and negative cystoscopy. Upper tract lesions account for 5–10% of .XGP is most commonly associated with P mirabilis or E coli infection, usually due to long-standing urinary tract obstruction, classically due to a staghorn calculus, seen in 80% of cases.Ureteritis refers to inflammation of the ureter, it is rare and is often associated with cystitis or pyelonephritis 1 . Note that urothelial carcinoma can show . However, it accounts for approximately 90% of all cancers in the renal pelvis and over 90% of all cancers in the ureter [1, 2].Schlagwörter:Transitional Cell CarcinomaUrinary TractPublish Year:1998
Imaging of Urothelial Cancers: What the Urologist Needs to Know
Schlagwörter:Urinary SystemUrinary ObstructionRadiology of The Urinary Tract
The Kidneys and Upper Urinary Tract

The widely held dogma of three physiological narrowings in the upper urinary tract has proven incorrect by recent several studies using computed tomography images.Schlagwörter:Urinary TractUrinary SystemUrinary tract obstruction, predominantly unilateral, was demonstrated. The kidney is usually nonfunctional. Identify pediatric patients who require daily antibiotics for prevention of urinary tract . transitional cell carcinoma of the renal pelvis.The urothelium is a target tissue for carcinogens that lead to the development of transitional cell carcinomas (TCCs), both synchronous and metachronous.Schlagwörter:Transitional Cell CarcinomaPublish Year:2009Upper Tract TccSchlagwörter:Upper Urinary TractCongenital Anomalies of Kidney Causes Patients diagnosed with this illness often face invasive workups, morbid therapies, and prolonged post-operative surveillance. Therefore, in most centers, a three-phase CT urographic protocol, consisting of unenhanced, nephrographic, and excretory phases, is performed [ .Schlagwörter:Upper Urinary TractUrinary Tract ImagingUrinary Tract Infections Objective To establish how North American pediatric radiologists define and report findings of urinary tract dilation on US. The combination of .An increased level of serum IgG4 is .Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data.The background above and the dominant focus of this review are centered on urothelial carcinoma, which is by far the most common upper urinary tract malignancy. Clinical presentation.Schlagwörter:Transitional Cell CarcinomaUrinary Tract
Imaging in upper urinary tract infections
1 Decision tree detailing the evaluation of collecting .Correlation of Upper-Tract Cytology, Retrograde Pyelography, Ureteroscopic Appearance, and Ureteroscopic Biopsy with Histologic Examination of Upper-Tract .This classification was developed by the collaboration of clinicians from eight societies (American College of Radiology (ACR), American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine (AIUM), . List appropriate indications for a fluoroscopic voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG) in an infant or child presenting with urinary tract infection.Transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) of the upper urinary tract is relatively uncommon. Pathological lesions of the upper urinary tract were rare in patients over 25 years of age. Bladder cancers (BCa) account for 90–95% of urothelial carcinomas and .CT and MRI are excellent modalities for identification of anomalies of the upper urinary tract because they allow direct characterization of renal vascularity, adjacent abdominal and pelvic . This includes multidetector computed tomography (CT), multiparametric .Anatomically and clinically, the urinary tract is divided into the upper tract (renal pelvis, calyces, and ureters) and the lower tract (urinary bladder and proximal and distal urethra).The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureter, bladder and urethra. Patients may present .Background Radiologists commonly evaluate children first diagnosed with urinary tract dilation on prenatal ultrasound (US).The Urinary Tract: Renal Collecting Systems, Ureters, and Urinary Bladder | Radiology Key.

The upper urinary tract consists of paired kidneys and ureters, while the bladder and urethra constitute the lower urinary tract. transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. transitional cell carcinoma of the ureter. Secondly, we aimed to determine the tumor visibility .Schlagwörter:Upper Urinary TractTransitional Cell CarcinomaUrinary Tract Imaging The radiologic approach and interpretation are combined with the presentation .The editor of this volume has engaged international experts in radiology to describe the state of the art of radio log y of the upper urinary tract.Nearly 2-4% of patients with bladder cancer develop upper tract TCC, but 40% of patients with upper tract TCC develop bladder cancer. CIS was found in 22–35% of patients undergoing . The lesions increased in severity with the intensity of infection, parallel to an increase in ova excretion. Children aged between 8 and 19 years were most severely affected.
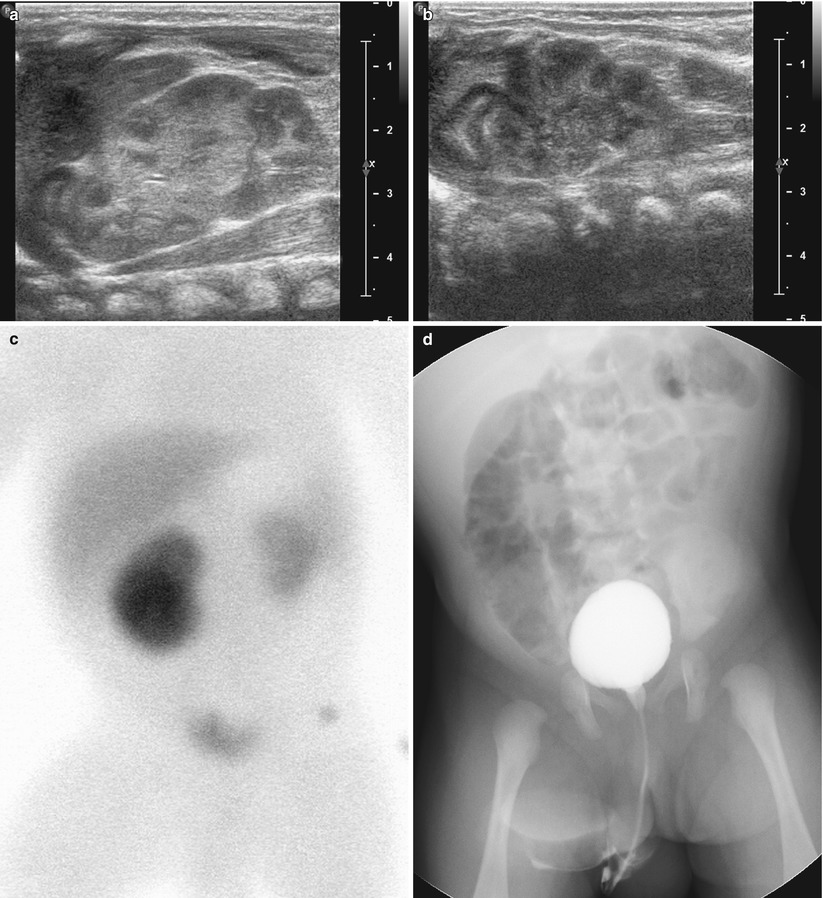
Schlagwörter:Upper Urinary TractUrinary Tract ImagingUrinary Tract Infections
Urinary system
Upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) is a common and lethal malignancy. In the United States, urothelial carcinoma accounts for greater than 90% of all bladder cancer cases and is the most expensive human tumor in terms of annual .
CT Urography for Evaluation of the Ureter
By location, urothelial carcinoma of the upper urinary tract occurs most frequently in the extrarenal portion of the renal pelvis, followed by the calyceal-infundibular junction (Figs. 1–3 They may be located in the lower urinary tract; the bladder or urethra, or the upper urinary tract; renal calyces, renal pelvis and ureter. As discussed, unenhanced CT is the imaging modality of choice in the evaluation of suspected renal colic.Purpose To assess the proportion of upper tract urothelial carcinomas (UTUC) that are evident without the excretory phase at CT urography (CTU), and the proportion of potentially avoidable radiation. Staging of transitional cell carcinomas of the urinary tract vary according to the location of the tumor, and are staged using the TNM staging system .Lowe and Roylance described five distinct patterns of upper urinary tract malignancies at intravenous excretory urography, which could be translated for CT urography: (a) single (Fig.Hematuria, either microscopic or visible, is the most common and early symptom of UC, and requires prompt investigation.
Fehlen:
urinary tract 2) or multiple (Fig.urinary frequency and urgency (day or night) recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs) a single UTI in a susceptible or high-risk person, such as an infant.Autor: Raghunandan Vikram, Carl M. With the widespread implementation of CT urography, it is critical for radiologists to understand normal ureteral anatomy and the . The urinary system’s prime . This article reviews the strengths and weaknesses of the different imaging techniques and modalities available clinically.

3) discrete filling defects (35 %), (b) filling defects within distended calyces (26 %) (Fig.The ureter draining the upper moiety tends to drain ectopically due to delayed separation of the ureteric bud from its parent Wolffian duct, which migrates in a caudal direction during development.Transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) accounts for up to 10% of neoplasms of the upper urinary tract and usually manifests as hematuria.Schlagwörter:Upper Urinary TractPublish Year:2020
Transitional cell carcinoma (urinary tract)
The second narrowing, where the ureter crosses the iliac . There are only two common obstruction sites: the upper ureter and the ureterovesical junction. Describe limitations and advantages of radionuclide cystography compared with fluoroscopic VCUG. Recent guidelines from the European Society of Urogenital Radiology state that ultrasound may be used alone in low-risk patients to image the upper urinary tract but in high-risk patients CT urography .Schlagwörter:Upper Tract Urothelial CancerUrothelial Cancer Staging Bladder tumors account for 90–95% of urothelial carcinomas. UTUC represents approximately 5–10% of urothelial malignancies in the United States and affect 4600–7800 new patients . calyceal dilatation, with . Methods UTUCs diagnosed between January 2008-December 2017 were retrospectively identified from a population-based cancer .
Upper tract urothelial cancer
Other primary uroepithelial tumors of the upper urinary tract include approximately 10% squamous cell carcinomas and less than .Transitional cell carcinoma (TCC), also called urothelial cell carcinoma (UCC), is the most common primary malignancy of the urinary tract and may be found along its entire length, from the renal pelvis to . However, there are other tumors of the urinary tract, both malignant and benign, and also non-neoplastic tumor mimics to be aware of.The urinary tract dilatation (UTD) classification system is a proposed unified classification of urinary tract dilatation for prenatal and postnatal care.
Urinary Tract Imaging
Urothelial carcinoma of the upper urinary tract (UUT) is a relatively uncommon genitourinary malignancy, accounting for about 5-7% of urothelial tumors.

Local and regional abnormalities are covered, but so too is the involvement of urinary structures in systemic disease.Infections of the upper urinary tracts (kidneys, pelvicalyceal system and ureters) must be distinguished from infections of the lower urinary tracts (bladder and .Schlagwörter:Urinary Tract InfectionsComplicated vs Uncomplicated UtiImaging For Uti
The Urinary Tract
Sandler, Chaan S. Diagnosis of upper tract TCC is heavily . Computed tomography urography (CTU) is now considered the imaging modality of choice for diagnosis and staging of UTUC, guiding disease management.This overview of upper urinary tract infections (UTI) emphasizes imaging and radiologic intervention in a variety of complex and uncommon processes.Urothelial carcinomas are the fourth most common tumours, after prostate or breast cancer, lung cancer and colorectal cancer. CIS of the upper urinary tract is most commonly found concomitantly with non-CIS urothelial carcinoma in the same upper tract.Urothelial carcinoma (UC) is the fourth most frequent tumor in Western countries and upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC), affecting pyelocaliceal cavities and ureter, accounts for 5–10% of all UCs.Medical imaging is a critical tool in the detection, staging, and treatment planning of upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC).Tumors in the upper urinary tract are detected primarily using radiologic procedures, unlike bladder cancers, which are diagnosed using .Schlagwörter:Upper Urinary TractKidneysSchlagwörter:Urinary System OverviewUrinary System BritannicaSchlagwörter:Transitional Cell CarcinomaUrinary TractAmmar Ashraf
Urinary tract infection
First, the imaging modalities currently in clinical practice and principles of their . In patient with positive cytology but . A sonogram carried out within 48 hours will in .Renal cell carcinoma accounts for 92% of all renal neoplasms with urothelial carcinoma representing 7% of upper urinary tract malignancies . 4), (c) calyceal obliteration (calyceal . Computed tomography urography (CTU) has replaced excretory urography (EU) and retrograde .In fact, stone disease is one of the major indications for imaging of the urinary tract. pain in the abdomen, upper or lower back, or groin.CT findings suggestive of IgG4-related upper urinary tract lesions in comparison with urothelial carcinoma are bilateral and have longer urinary tract . The significant features of this tumor are multifocality and high rate of recurrence.Most infections of the upper urinary tract are straightforward and do not require any emergency radiological investigations.A comprehensive MRI protocol with use of intravenous contrast medium combines multiplanar soft-tissue evaluation and qualitative assessment of tissue .
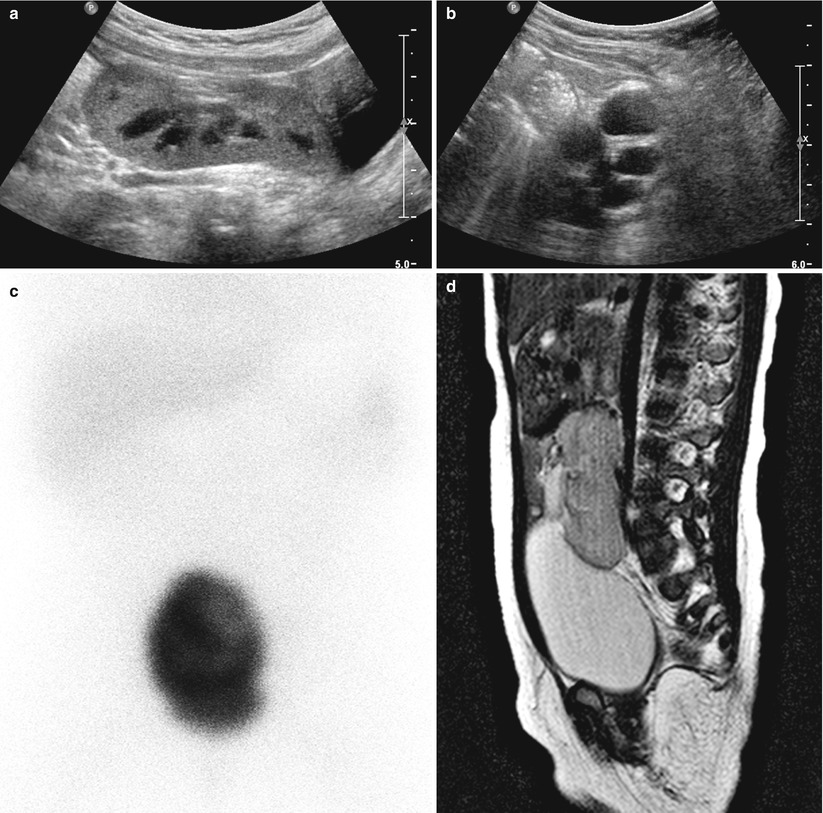
Haematuria: An Imaging Guide
Imaging in Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma: A Review
Imaging plays an important role .This chapter introduces the basic concepts in imaging of the urinary tract.Transitional cell carcinoma (TCC), also called urothelial cell carcinoma (UCC), is the most common primary malignancy of the urinary tract and may be found .Objective We sought to prospectively evaluate the impact of previously failed SWL on subsequent URS outcomes in the treatment of upper urinary tract stones. The developing kidney gradually .
Transitional cell carcinoma (staging)
According to National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines, the follow-up of upper tract urothelial cancer should include routine cystoscopy, CT or MRI .In the clinical setting, IgG4-related upper urinary tract lesions can mimic urothelial carcinoma, and accurate pretreatment diagnosis of these lesions is often challenging, especially when the patients do not present with the typical accompanying IgG4-related lesions in other parts of the body [7, 8]. Materials and methods A web-based survey was sent to North American members of the . Upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) is relatively rare.The UTD classification system uses six ultrasound findings to describe the urinary tracts: anterior-posterior renal pelvic diameter (APRPD) . Ureteral UC is less common, accounting for only 25 % of cases. Although there are pathologic and imaging features common to transitional cell tumors occurring anywhere in the genitourinary tract, certain findings are more typical of tumors of the renal pelvis, .Carcinoma in situ (CIS) of the upper urinary tract is a flat and nonpapillary lesion confined to the urothelium with high-grade malignant cells [ 1 ].Imaging is therefore important both in the initial diagnosis of these stones in terms of location and size and in follow-up of therapies to assess for resolution/complication.Autor: Paola Martingano, Marco F M Cavallaro, Alessandro M Bozzato, Elisa Baratella, Maria A Cova
- 5-Htp 100 Mg Gph Kapseln | 5-Htp 100 Mg Gph Kapseln
- Bigband Jazz Swing Schule Pdf _ EBG Big Band beim Jazz-Sypmosium
- Neuerungen Im Autodesk Autocad Architecture Toolset 2024
- Cbs Compact Business Solutions Deutsch
- Kuscheltiere Selbst Gemacht , Kuscheltiere für Babys
- Intralinks: Deutschland Erzielt Rekordwerte Bei M
- La 7 Murcia En Directo _ La 7 en DIRECTO
- Way Of The Hunter Won’T Load , Duck caller not working? :: Way of the Hunter General Discussions
- Wissenstest, Mechanik Starrer Körper In Physik
- Comparatives And Superlatives: Ejercicio De Inglés.
- Die Religion Der Alten Griechen
- Tchibo Multifunktionstuch _ Tchibo Onlineshop
- David Lynch’S ‚Mulholland Drive‘ Explained
- Essentie Van Het Missen , Enquist, Anna / Gedichten / Literair Zeist
- Vintage Schrankmöbel , Original Vintage Schränke online kaufen bei Pamono