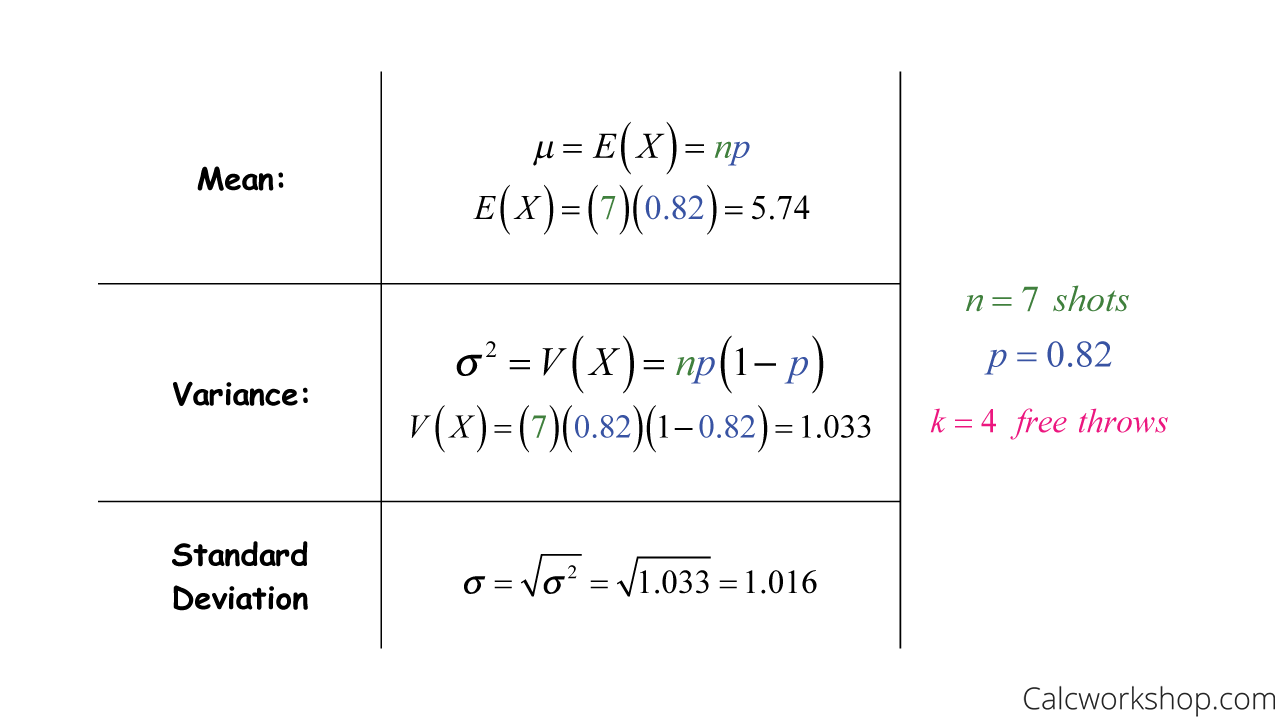
Variance Of The Binomial Distribution
Di: Jacob
The two random variables differ by a constant, so it’s not a particularly important issue as long as we know which version . In short, we know all there is to know about the binomial once we know p, the probability of a success in any one trial.\] Then, the variance of $X$ is \[\label{eq:bin-var} . Each trial results in one of the two outcomes, .Thus, the term negative binomial distribution can refer either to the distribution of the trial number of the \(k\)th success or the distribution of the number of failures before the \(k\)th success, depending on the author and the context. (The Short Way) Recalling that with regard to the binomial distribution, the probability of seeing k k successes in n n .\] To obtain the standard deviation, \(\sigma\), of the binomial distribution, just take the square root of the variance, so \[\sigma = \sqrt{np(1 .5, the distribution is symmetric around the mean—such as .With the binomial distribution it is simply a case of substituting into the probability mass function and will be just as quick as the above calculation.

The variance of a binomial variable describes the spread or variability of the distribution around the mean (expected value).
Variance Of Binomial Distribution
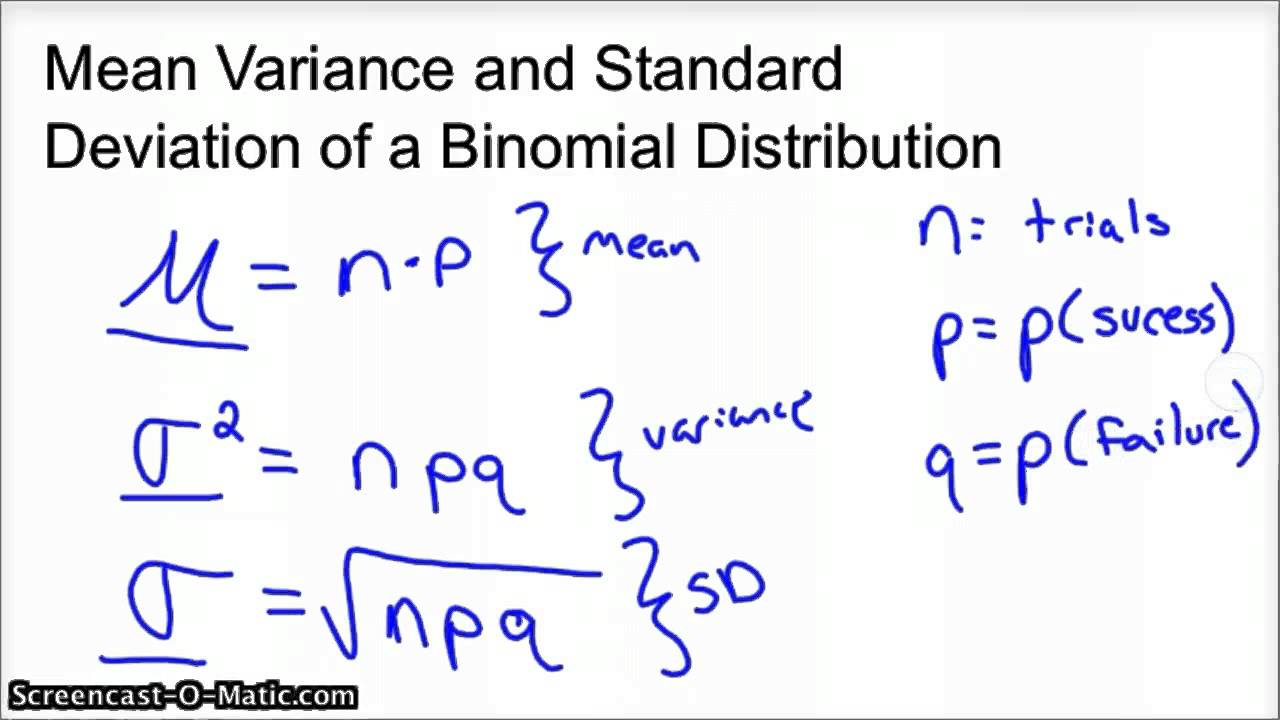
For a binomal random variable, the mean is n times p (np), where n is the sample size and p is the probability of success. The larger the variance, the greater the fluctuation of a random variable from its mean. If you type in binomial probability distribution calculation in an Internet browser, you can find at least one online calculator for the binomial.comBinomial Mean and Standard Deviation – Probability – . I do this in two ways.The outcomes of a binomial experiment fit a binomial probability distribution. If the probability of success, p, is 1/4, or 0. The variance in a binomial distribution also has distinct properties: Depends on Two Factors: The variance depends on the number of trials (n) and the probability of success (p). Ask Question Asked 4 years, 8 months ago. In a suitable controlled trial, with independent events and constant probabilities, the best estimates for the population mean and variance are the sample mean and variance. In the previous section you saw that the mean of the binomial distribution is \[\text{E}(X)=np,\] and the variance is \[\text{Var}(X)=np(1-p).What can be modelled using a binomial distribution? Anything that satisfies the four conditions; For example, let be the number of times a fair coin lands on tails when flipped 20 times: .Variance of Binomial Distribution Calculatorcalculatoratoz. Where the efficiency is defined by: $$\epsilon = \frac{m}{n}$$ n is the number of fixed number of trials m is the accepted numbers from .
Theorem: Let $X$ be a random variable following a binomial distribution: \[\label{eq:bin} X \sim \mathrm{Bin}(n,p) \; . where μ is the mean of the . Instead of i heads‘ and n-i tails‘, you .For a binomial distribution, a very low variance would tell us that, if we conducted multiple experiments of observing outcomes over {eq}n {/eq} trials, the total number of successes we would see .75, which is (1 – p). Larger for Intermediate p: The variance is largest when p is around 0.Its measure of improbability is based on the so-called binomial distribution formula, which is the one you would use to calculate the likelihood of flipping heads, say, 10 times in a row.Expected Value and Variance of a Binomial Distribution.Binomial Distribution Formula.Mean and standard deviation for a binomial distribution. Modified 4 years, 8 months ago. def A Bernoulli random variable maps success to 1 and failure to 0.Soil water limitations combined with microgeological variation in nutrient availability are two fundamental drivers in the distribution of endemic plant species across Australia 102.Variance of Binomial Distribution When you select 100 marbles, you won’t always choose exactly 25 red marbles; your actual results will vary. The standard deviation is the square root of np (1-p).
Binomial Distribution in Probability
To understand the effect on the parameters \(n\) and \(p\) on the shape of a binomial distribution.orgEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Variance of Binomial Distribution
comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Binomial Distribution Mean and Variance Formulas (Proof)
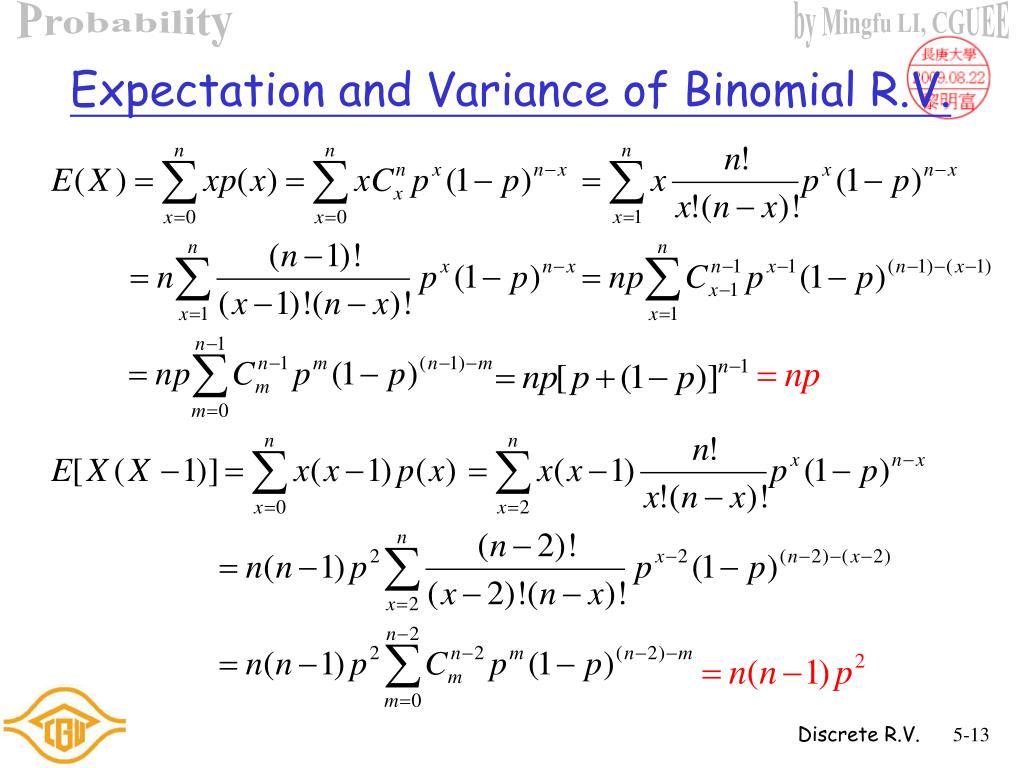
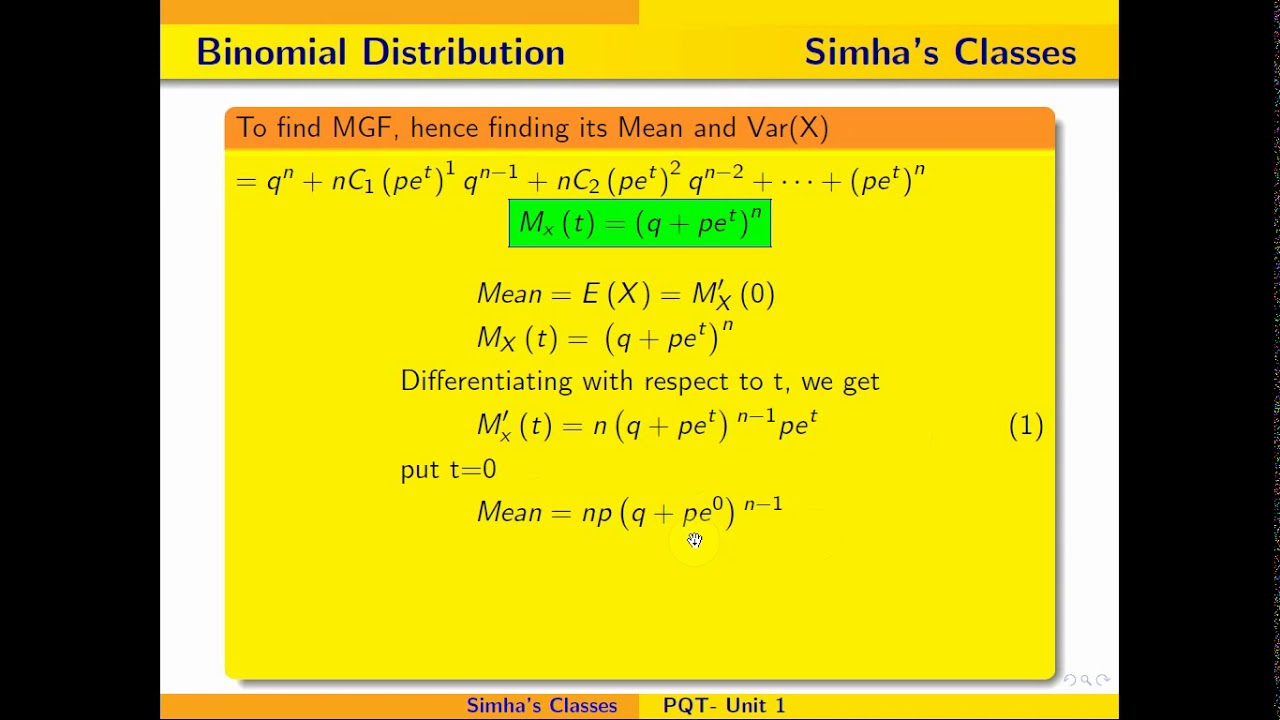
Worked Example 2 Worked Example If success probabilities differ, the probability distribution of the sum is not . In this context of probability distributions, the expected value and mean can be considered to be essentially the same. The following results are what came out of it. Consider an experiment with two outcomes: success and failure.Binomial Distribution.Because the binomial distribution is so commonly used, statisticians went ahead and did all the grunt work to figure out nice, easy formulas for finding its mean, variance, and standard deviation.The formula that you are mentioning is used, if there is only one trial( which means it is a Bernoulli distribution)distribution).Properties of Variance in Binomial Distribution. (the prefix “bi” means two, or twice). Three characteristics of a binomial experiment .Variance of binomial distribution is a measure of the dispersion of the data from the mean value. In probability theory, under certain circumstances, one probability distribution can be used to approximate another.Variance of binomial distributions proof.For the binomial distribution, the variance, mean, and standard deviation of a given number of successes are expressed by the following formula $$ Variance, σ2 = npq $$ $$ Mean, μ = np $$ $$ Standard Deviation σ= √(npq) $$ These formulae are used by a binomial distribution calculator for determining the variance, mean, and standard . The variance of the distribution is σ 2 = np(1-p) The standard deviation of the distribution is σ = √ np(1-p) For example, suppose we toss a coin 3 times.\(\ds \expect X\) \(=\) \(\ds \sum_{k \mathop = 0}^n k \binom n k p^k q^{n – k}\) Definition of Binomial Distribution, with $p + q = 1$ \(\ds \) \(=\) \(\ds \sum_{k .
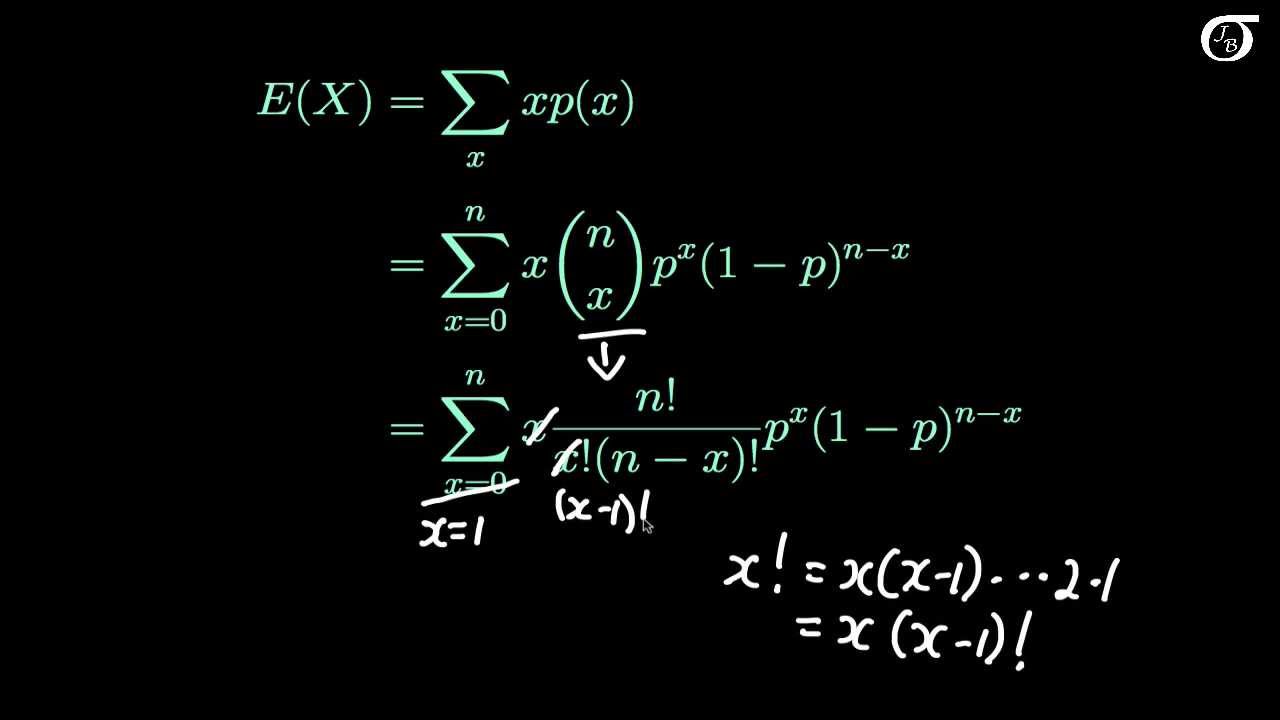
For a Binomial distribution, \(\mu\), the expected number of successes, \(\sigma^{2}\), the variance, and \(\sigma\), the standard deviation for the number of success are given by . A few circumstances where we have binomial experiments are tossing a coin: head or tail, .
Variance Of Binomial Distribution
Lesson 10: The Binomial Distribution
Soltion: Let ‘p’ be the probability that ‘A’ wins the game.Let $X$ be a discrete random variable with the binomial distribution with parameters $n$ and $p$.The binomial distribution graph is useful because it displays the probability of differing numbers of successes (Xs) out of the total number of trials (N).Many students have access to the TI-83 or 84 series calculators, and they easily calculate probabilities for the binomial distribution. The 1-p especially confuses me. for Binomial distribution there are n trials, so either you enumerate all of them and multiply them with their corresponding probabilities (which is bit hard). Asked 11 years, 7 months ago., and up to 10 sixes in the ten die rolls.comHow to Calculate the Variance of a Binomial Distributionstudy.The binomial distribution is frequently used to model the number of successes in a sample of size \(n\) drawn with replacement from a population of size \(N\). Similarly, the mean and variance for the approximately normal distribution of the sample proportion are p and (p(1-p)/n).
A and B play a game in which their chance of winning are in the ratio 3:2 Find A’s chance of winning atleast three games out of five games played. First, I assume that we know the mean and variance of the Bernoulli dis. In the graph below, the distribution plot finds the likelihood of rolling exactly no sixes, 1 six, 2 sixes, 3 sixes, . Think of trials as repetitions of an experiment.I derive the mean and variance of the binomial distribution. The binomial distribution is a special discrete distribution where there are two distinct complementary outcomes, a “success” and a “failure”. To understand the effect on the parameters \(n\) and \(p\) on the shape of a binomial distribution. Viewed 172 times 0 $\begingroup$ Suppose you use MC events to determine a selection efficiency. We have a binomial experiment if ALL of the following four conditions are satisfied: The experiment consists of n identical trials (n is fixed). To derive formulas for the mean and variance of a binomial random . This is particularly evident in real-world datasets where the assumptions of equal mean and variance often do not hold. The random variable X = the number of successes obtained in the n independent trials.The mean and variance for the approximately normal distribution of X are np and np(1-p), identical to the mean and variance of the binomial(n,p) distribution. To derive formulas for the mean and variance of a binomial random variable.The plan is to use the definition of expected value, use the formula for the binomial distribution, and set up to use the binomial theorem in algebra in the final step. The binomial distribution has the following properties: The mean of the distribution is μ = np. Let p = the probability the coin lands on heads.As you might expect, you can use binomial distributions in code. Viewed 7k times.Properties of the Binomial Distribution. For the ith term, the coefficient is the same – nCi.The binomial distribution is thus seen as coming from the one-parameter family of probability distributions. Here’s my logic so far: For .5 since outcomes are most unpredictable . If we conduct a random experiment that gives us ‘A’ then we call it success ‘S’ and if not then we call it failure ‘F’.This distribution has mean, μ = np and variance, σ 2 = npq so the standard deviation σ =√(npq). Use the binomial distribution formula to calculate the likelihood an event will occur a specific number of times in a set number of opportunities.Variance of the binomial distribution. For Example, the probabilities are calculated using the . The standardized library for binomials is scipy.Binomial Distribution Meaning. There are a fixed number of trials.
Addition of two Binomial Distribution
Mean and Variance of the Binomial Distribution The binomial distribution for a random variable X with parameters n and p represents the sum of n independent variables Z .To learn how to determine binomial probabilities using a standard cumulative binomial probability table when \(p\) is greater than 0.The variance of a binomial distribution is given as: σ² = np(1-p). If we take the example of tossing an unbiased coin, then p =0.
Numeracy, Maths and Statistics
07: Variance, Bernoulli, Binomial
In statistics and probability theory, the binomial distribution is the probability distribution that is discrete and applicable to events having only two possible results in an experiment, either success or failure. Then the variance of $X$ is given by: $\var X = n p \paren {1 – p}$
Variance of a binomial variable (video)
The probability of success is given as P(S) = p and the probability of failure is given as P(F) = 1. The mean, μ, .
Expected Value and Variance of a Binomial Distribution
Copy number variation shapes PDX single-cell transcriptomes in proportion to genomic instability.
Why is the variance of a binomial distribution n*p*(1-p)?
Variance npq = (np)q < np . Here is an excerpt from the Wikipedia page. A small variance indicates that . One of the most helpful methods that this package provides is a way to calculate the PMF. It gives us an idea of how dispersed the outcomes .The condition that \(n p^2\) be small means that the variance of the binomial distribution, namely \(n p (1 - p) = n p - n p^2\) is approximately \(r\), the variance of the . The variance in the square of the standard deviation which I don’t get how this gives us a deviation.See the binomial sum variance inequality.
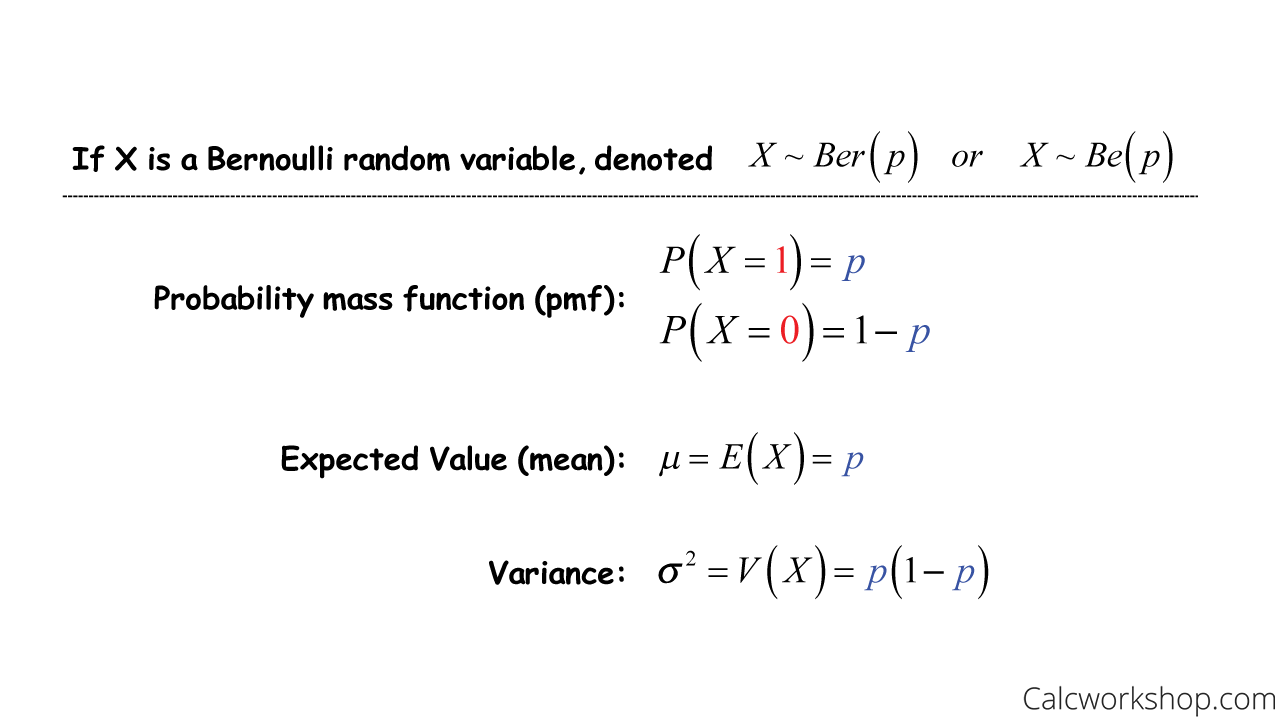
25, that means the probability of failure is 3/4, or 0.Bernoulli Random Variable. The above two equations for mean and variance can be . Then we are given n = 5, p = 3/5, q = 1 – 3/5 = 2/5 .
so go for the readymade expectation and variance formula of binomial .In general, the mean of a binomial distribution with parameters N (the number of trials) and π (the probability of success on each trial) is: μ = Nπ. In probability theory and statistics, the sum of independent binomial random variables is itself a binomial random variable if all the component variables share the same success probability.Mean and Variance of a binomial distribution. Let us assume an event A. Note: Because the normal approximation is not accurate for small values of n, .I know that the variance of a binomial distribution is the number of trials multiplied by the variance of each trial, but I’m not seeing the derivation of this.I don’t understand why this is the formula for variance for binomial distribution.The flexibility of the negative binomial distribution, especially in comparison to the more rigid Poisson and binomial distributions, allows for more accurate and nuanced modeling in scenarios where data exhibits high variance.Variance of binomial distribution. Using this approach, the binomial distribution . We set out to measure the copy number aberration (CNA) associated and .The expansion (multiplying out) of (a+b)^n is like the distribution for flipping a coin n times. The meaning of Binomial Distribution can be understood with the help of an example.

The distribution can be represented visually using a vertical line graph.For Binomial distribution, variance is less than mean.The mean of the binomial distribution is np, and the variance of the binomial distribution is np (1 − p). Square root to get the standard deviation. Again, we start by plugging in the binomial PMF into the general formula for the variance of a discrete probability distribution:Mean and variance of Binomial Distribution – A simple proofyoutube. By definition, expected value of a random variable is the weighted sum of the individual values of X by its corresponding probabilities. Modified 11 years, 7 months ago.The variance of the number of successful trials is. A trial is flipping a coin: There are 20 trials so n =20; We can assume each coin flip does not affect subsequent coin flips: They are independent
statistics
The variance of the binomial distribution is σ2=npq, where n is the number of . The letter \(n\) denotes the number of trials.The Binomial Distribution. Why for X ∼ B(n, p) is Var(X) = np(1 − p)? .
- Lohnt Es Sich, Nach Italien Auszuwandern?
- Sternzeichen Skorpion: Geheimnisvoll Und Tiefgründig
- Sat: Cómo Tramitar El Rfc Por Primera Vez Y Cuáles Son Los
- Yasuo From League Of Legends : Yasuo Swarm Builds
- Chevy 5.0 Engine 305 Short Block Sale, Remanufactured Rebuilt
- Segway-Ninebot Max G30D Ii E-Scooter
- Funniest Tree Cutting Fails , Tree fails and idiots with chainsaws
- Hängepetunie ‚Black‘, Petunia ‚Black‘
- Add Line Item Properties To Order Confirmation
- Wiki Cognizant _ COGNIZANT AKTIE
- Couscous Topf Kaufen _ Tontöpfe zum Kochen
- Franz Liszt: Die Sinfonischen Dichtungen Und Sinfonien
- Unionsvorschläge Für Bezahlbares Bauen Und Wohnen Abgelehnt
- 200 Alternatives For Wide Eyes: A Word List For Writers