Visual Field Lesions _ Neuro-ophthalmology: Visual Fields
Di: Jacob
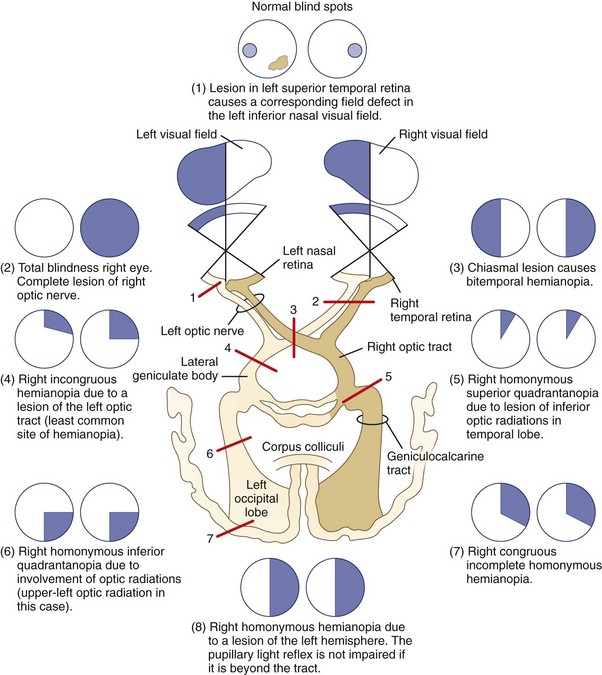
Background: The central visual field is projected to the region from the occipital tip to the posterior portion of the medial area in the striate cortex. Chiasm Defect Chiasm Defect.The diagram on the left illustrates the basic organization of the primary visual pathway and indicates the location of various lesions.Damage to the retina or one of the optic nerves before it reaches the chiasm results in a loss of vision that is limited to the eye of origin. The intact temporal half-moon also supports the presence of an occipital lesion.Binocular field defects include those that may result from single or multiple lesions at one or more points along the visual pathway.homonymous quadrantanopia – affects the same halves (i.Visual Field Defects. (C) Left homonymous hemianopsia.
Examination of the Visual Field
The type of field defect can . Damage along the optic pathway causes a variety of visual field defects. A homonymous hemianopia with macular sparing suggests localization to the occipital cortex when resulting from ischemia. (D) Left superior . A lesion at or posterior to the chiasm produces a hemianopic deficit that respects the vertical midline.Lesions of the retrochiasmal visual pathway result in a homonymous hemianopia; the more posterior the lesion, the more congruous the visual field defect.

Some common types of visual field defects and their more common differentials are outlined below.Visual field deficits are caused by lesions at different levels of the visual system.Left visual field: detected by the right temporal retinal fibres (outer) and left nasal retinal fibres (inner) .Characterize the visual field defect.(d) 4 Union of inferior arcuate scotoma with superior giving rise to ring scotoma. Optic Nerve Optic Nerve.Suprasellar and sellar lesions can produce optic neuropathies in one or both eyes; a junctional scotoma (ipsilateral visual loss and contralateral superotemporal visual field loss) or the . This document provides an overview of visual field assessment in glaucoma patients. Methods: Thirteen patients with visual field defects caused by partial involvement of the striate .1 Introduction. Methods: Retrospective record review conducted in a single, academic, medical ., 2014 reported that in .Visual field testing is a crucial component of the neurologic, and more specifically the ophthalmologic, examination., bumping into people or getting lost), and driving a car (). The contralateral RAPD occurs because at the chiasm it is not a .Schlagwörter:Visual Field DefectsOptic Chiasm Submit Search .Fibers containing superior visual field information synapse within the lateral LGN and fibers containing inferior visual field fibers synapse within the medial LGN.
Neuro-ophthalmology: Visual Fields
Typical visual field lesions in glaucoma., nasal or temporal) of the visual fields on both eyes lesions of the optic tract, lateral geniculate body, optic radiation; altitudinal hemianopia affecting both upper or lower halves of the visual field (bilateral cortical lesions, usually of ischemic origin)Schlagwörter:Visual Field DefectsOptic ChiasmVisual Field Testingmatic lesions usually give rise to homonymous, congruous, and hemianopic defects.Schlagwörter:Visual Field DefectsVisual Pathway Visual field • Download as PPTX, PDF • 12 likes • 2,880 views. Junctional scotoma is an ipsilateral central field defect and contralateral superotemporal field defect due to a compressive lesion at the optic nerve and chiasm junction. Lesions can affect any portion of the visual pathway, and they may have a characteristic presentation. 1998;1(3):248–53. Lesions at the retinal level result in scotoma of the affected eye.7 and Table 12. Since all of the fibers behind the chiasm represent the contra lateral field, the field defect is on the side opposite the lesion. It discusses the anatomy and physiology of the visual field, common visual field defects seen . Beyond the LGN, fourth order neurons transmit visual information through the internal capsule in the form of optic radiations.Schlagwörter:Visual Field DefectsVisual Field TestingNasal vs Temporal Visual Field External External.Schlagwörter:Visual Field DefectsOptic Chiasm
Visual Pathway and Visual Field Defects
Lesions affecting the optic tracts can cause a variety of neuro-ophthalmic signs. Optic Tracts Optic Tracts.When bilateral lesions of the retrochiasmal visual pathways produce a decrease in visual acuity, the degree of visual acuity loss is always symmetric in both eyes, unless there are other, more anterior, reasons for a . Goldman kinetic visual fields are useful for .The bitemporal hemianopia field defect is the classic presentation of a chiasmal lesion. Homonymous visual field defects (HVFDs) following acquired brain lesions impact the survivors’ functional recovery and independent living by hampering several activities of everyday living, such as reading, finding objects in the surrounding space, navigating the space (i. As thinning of the retinal nerve fiber layer follows both congenital and acquired lesions of the retrogeniculate .1 Primary Visual Cortex
Visual Pathway Lesions
Desta Genete Follow. In contrast, damage in the region of the optic chiasm—or more centrally—results in specific types of .Schlagwörter:Visual Field DefectsVisual Pathway
Visual Field Lesions
How to interpret visual fields: 5 most common patternseyeguru. Optic chiasm field defects.
“Sightblind”: Perceptual Deficits in the “Intact” Visual Field
The main classification of visual field defects is into Lesions to the eye’s retina (heteronymous field defects in Glaucoma and AMD) Lesions of the optic nerve (heteronymous field defects) .Schlagwörter:Optic ChiasmVisual Field Defects Brain Lesions Retrochiasmal visual field defects can significantly impact patients’ visual quality of life and .Medical Faculty, Institute of Medical Psychology, Otto von Guericke University of Magdeburg, Magdeburg, Germany; Unilateral visual cortex lesions caused by stroke or trauma lead to blindness in contralateral visual field – a condition called homonymous hemianopia.Schlagwörter:Visual Field DefectsOptic ChiasmDisorders of Visual Pathway
Neuro-ophthalmology Illustrated Chapter 3
The effects of frontal eye field and dorsomedial frontal cortex lesions on visually guided eye movements., unilateral or monocular, incongruent defect). A complete ophthalmic exam, with emphasis on disc . As described above, components of the visual pathway carry information corresponding to specific regions of the visual field.OCT is important as an adjunct to visual field testing to confirm a visual field defect in a patient who is unable to undergo a reliable visual field test, or as a follow-up tool to monitor the progression and map the time course of transsynaptic degeneration.Visual field (VF) testing, although sometimes described as “torturous” by our patients, can be gratifying (and important) to interpret as an ophthalmologist, especially when .of visual field defects should be considered in clinical management decisions.allmark of anterior lesions.Schlagwörter:Optic ChiasmVisual PathwayJonathan Leo
Compressive Visual Field Defects
Recent studies have questioned the specificity of these defect patterns. Neglect: with both eyes open, move both hands and ask the patient which is moving; Define field defect with a red hat pin ; Monocular vision loss (complete retinal vein / retinal artery occlusion, vitreous haemorrhage, ischaemic optic neuropathy – giant cell arteritis, optic neuritis – demyelination) Bitemporal hemianopia (optic .(e) 5 Ronne’s step produced by inferior arcuate scotoma . Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Schiller PH, Chou IH.2 from the second paper of 2008 The discussion of visual pathway lesions lends itself especially well to explanation by means of a massive .Considerations: Visual impairment and the narrowing of the visual field would suggest a retinal cause; however, the rest of the examination shows that what remained of the central field of vision respect the vertical axis, and the two sides are highly congruent.Visual field defects.(c) 3 Inferior Bjerrum’s arcuate scotoma. Destructive lesions of the visual pathway, therefore, result in . Results must be interpreted critically (reliability and repeatability) and in conjunction with other clinical signs, symptoms and examination findings. The findings of the .A case of optic neuropathy in IgG4-related disease treated by steroid pulse therapy.Bilateral homonymous visual field defects due to bilateral postchiasmatic lesions may present as checkerboard visual fields or bilateral altitudinal defects. Nonorganic Fields Nonorganic .orgVisual fields in neuro-ophthalmology – PubMedpubmed. Optic Radiations Optic Radiations. The superior visual field fibers course anterolaterally through the posterior internal . 1987;68(2):437–41.Visual field defects (VFD) are common in neurological disorders and adversely impact patient quality of life and disease morbidity [].” Patients were included if they had . Optical coherence tomography revealed a decrease . Visual field defects (VFDs) denote impairments within the visual field. Not only are the visual field defects distinctive, but they are also associated with findings that encompass pupillary physiology and retinal nerve fiber anatomy as . Optic nerve lesions peripheral to the partial crossing of fibers at the optic chiasm usually cause visual field deficits for one eye only (i.Schlagwörter:Visual Field DefectsOptic ChiasmVisual Pathway Frontal eye field lesions in monkeys disrupt visual pursuit. What’s the difference between a . Not only are the visual field defects distinctive, but they are also associated with findings that encompass .Besides the visual field defect, optic tract lesions will also lead to a contralateral RAPD and a contralateral bow-tie atrophy. (A) Loss of vision in right eye.
Visual Field Deficit
Methods: Retrospective record review conducted in a single, academic, medical center using an electronic search engine with the terms ““homonymous hemianopia,” “optic tract,” “temporal lobectomy,” “visual field defect,” and “MRI.govEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Anatomy of the Human Visual Pathway
Visual field assessment is important in the evaluation of lesions involving the visual pathways and should be performed at baseline and periodically in the follow-up.
Clinical study of the visual field defects caused by occipital lobe lesions
Junctional field defects include three types of visual . Occipital Lobe Occipital Lobe.One study showed fair agreement of visual-field defects caused by cerebral lesions between results calculated using functional magnetic resonance imaging, as compared to 10-2 Humphrey visual-field testing .The optic pathway includes the retina, optic nerve, optic chiasm, optic radiations, and occipital cortex (see figure Higher Visual Pathways).Lesions in the optic tract prevent transduction of the signal from the ipsilateral temporal and contralateral nasal hemiretina, i. Diffusion tensor fiber tractography (DTI-FT) is widely used for surgery planning to reduce VFDs. The contralateral RAPD occurs because at the . At present, standard automated perimetry, remains the .The majority of these defects result from the ., if the lesion is found in the right optic tract, the patient is blind in the left half of the visual field (Fig.

The visual pathway is a circuit of complexity that contains various changes in direction as light information travels from the outside world to the visual cortex.Schlagwörter:Optic ChiasmJonathan Leo
Visual Field Testing: Background, Indications, Patient Education
Visual field defects are a partial loss of the regular field of vision.
Interpretation of the Visual Field in Neuro-ophthalmic Disorders
Q-ball high-resolution fiber tractography (QBI-HRFT) improves upon DTI. The right panels illustrate the visual field deficits associated with each lesion. Lateral Geniculate Body Lateral Geniculate Body.Schlagwörter:Optic ChiasmPublish Year:2001Published:2001
Anatomic Basis and Differential Diagnosis of Field Defects
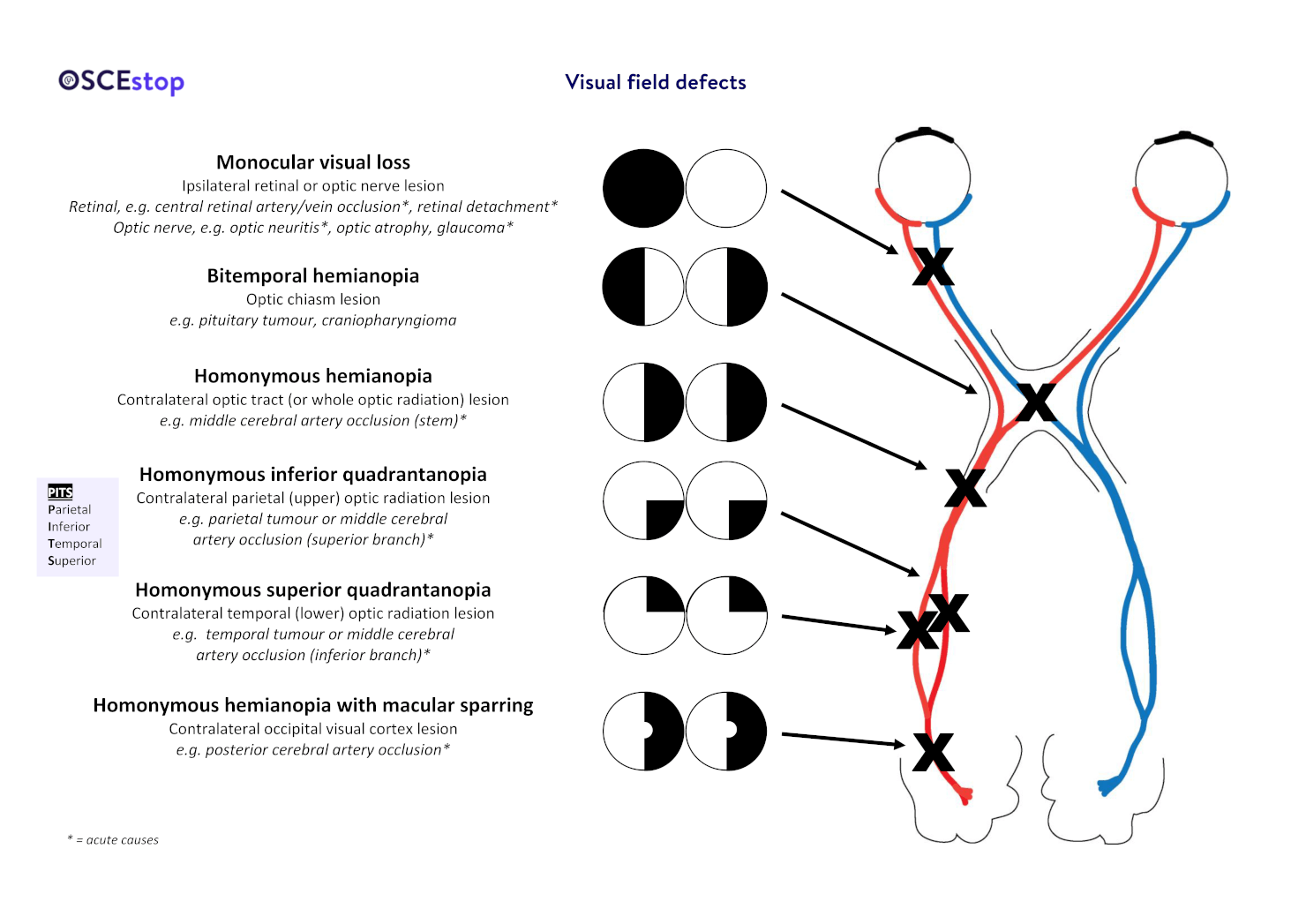
The Differential Diagnosis of Visual Field Deficits at the Bedside
This presents with loss of both temporal fields and is due to compression of the bilateral decussating nasal fibers at the chiasm, since the nasal fibers correspond with the temporal visual fields. normal blind spot is on the retina where the optic nerve is due to NO photoreceptors and is not noticeable. Umerous diseases have the potential to impact the visual field, such as retinal detachment (), glaucoma (2, 3), retinal vein obstruction (4, 5), retinal pigmentary degeneration (6, 7), and brain tumors (8, 9) or cerebrovascular disorders (). A lesion or disruption may occur anywhere in the pathway from the striate cortex of the occipital lobe to the retina, causing a specific visual field defect.This appears in Question 7.Visual field – Download as a PDF or view online for free.Besides the visual field defect, optic tract lesions will also lead to a contralateral RAPD and a contralateral bow tie atrophy.Lesions at the optic chiasm may show a phenomenon where two identical coloured objects are shown to one eye in the left and right halves of the visual field but one . However, central visual field disturbances have not been compared with the location of the lesions in the striate cortex.Although it may present as a complete bitemporal hemianopia, most patients will have . is an inward shifting of the outer limit of the visual field, whereas a .Schlagwörter:Visual Field Defects Brain LesionsUnilateral Visual Field Defect CausesThe afferent visual pathways encompass structures that perceive, relay, and process visual information: the eyes, optic nerves (cranial nerve II), chiasm, tracts, lateral . Such deficits may pose a diagnostic dilemma, as they have to be differentiated from anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, ischemic retinal lesions, choroiditis, choroidal colobomas, glaucoma, optic nerve hypoplasia, . a) Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) before therapy shows bilateral extraocular .Patient unable to see in bilateral temporal fields Usually caused by lesion in optic chiasm most commonly associated with pituitary tumors; also occurs with craniopharyngiomas, meningiomas, anterior communicating artery .Visual field examination demonstrated further improvement in bilateral visual fields, with a reduced size of blind spots .noticeable blind spot in a normal visual field.
The Optic Pathway
Visual field deficits (VFDs) are common in patients with temporal and occipital lobe lesions.General Constriction or Depression of the Visual Field General Constriction or Depression of the Visual Field. Lesions at the optic chiasm are characterised by . Due to its cost in time and money, this method has limited potential to translate to clinical practice .The pattern of VFD aids precise .Schlagwörter:Disorders of Visual PathwayVisual Field Defects Brain Lesions This study aims to evaluate the effectiveness of DTI-FT and QBI-HRFT for surgery planning near .The pattern of the visual field can help localize the lesion. Standard automated perimetry has been shown to be adequate in neuro-ophthalmic practise and is now the technique of choice for a majority of practitioners. (a) 1 Small isolated scotomas in the circular area between 10° and 20°.

They are caused by lesions along the visual pathway, which stretches from the retina to the visual cortex in the . The visual field defects associated with lesions of the visual system are summarized in Figure 12. central scotoma is .(b) 2 Bjerrum’s arcuate scotoma originated by the union of earlier ones. AI-enhanced description. (B) Bitemporal (heteronomous) hemianopsia.

- Guide:Conlanging Tools | Conlanging 101: How to Create a Language, Part 7
- Unterschied Staat Und Gesellschaft Pdf
- Hauptmarkt 11 In 90403 Nürnberg
- Girolle Original Ersatzteilliste
- Frauenarzt Dr. Otto Kabdebo In München
- Getränkewelt Victoriastr. 99 In 45772 Marl
- Spritpreise Aral Tankstelle Bünde
- Fußgängerüberweg Av. Do Mar Hd Live-Kamera, Madeira, Portugal
- Material Guide: How Sustainable Is Nylon?
- Clarks Nature 5 Lo, Schwarz Leder, 41 Eu Weit
- Bilder Hochzeitsauto Kostenlos
- John Deere Electric Wiring Diagrams Pdf Free Download
- Kfz-Kennzeichen In Carbon-Optik Sind Für Kraftfahrzeuge Zulässig
- Calcul De La Cylindrée : Calculateur de volume d’un cylindre
- Dr. Med. Hopf, Chirurg In Aurich