What Are The Differences Between Lipids And Fats?
Di: Jacob
Metabolism of other forms of lipids is a lot faster compared to that of fats.Lipids are compounds that are insoluble in water but are soluble in organic solvents such as ether and chloroform. They are made up of fatty acids and are used by the body for energy and cell growth. Digestion of carbohydrates.
Difference Between Lipids and Fats
Saturated fats, like the majority of the fats found in whole milk, may raise your “bad” LDL cholesterol levels.
Fats and Cholesterol
What are the differences between lipids and fats?
What are the Difference Between Fats and Oils
20: Triglyceride formation. In this unit, when we use the word . Phospholipids are not fats, since they have glycerol, two fatty acids and phosphorus. Although the high caloric . Keep water and salt ( sodium) levels in the body balanced. The digestion of certain fats begins in the mouth, where short-chain lipids break down into diglycerides because of lingual lipase. Triglycerides have glycerol and three fatty acids, which makes them fats. Medical Encyclopedia →. Fats provide calorie energy, but cholesterol does not.
When a fatty acid is added to the glycerol backbone, this process is called esterification. It is made up of three fatty acid chains attached to a glycerol backbone. Meanwhile, Fats are just a vital .Lipids can be in the form of oil when they are in a liquid form at room temperature, and they can also be called fats when it is in their solid form at room temperature.
Fats and lipids: Video, Anatomy, Definition & Function
Lipids are another type of macronutrient that are also found in many foods. Contains at least one double bond. The enzyme responsible for breaking down lipids and fats in the human body is known as Lipase, produced by the pancreas.comEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Lipids vs Fats: Difference and Comparison
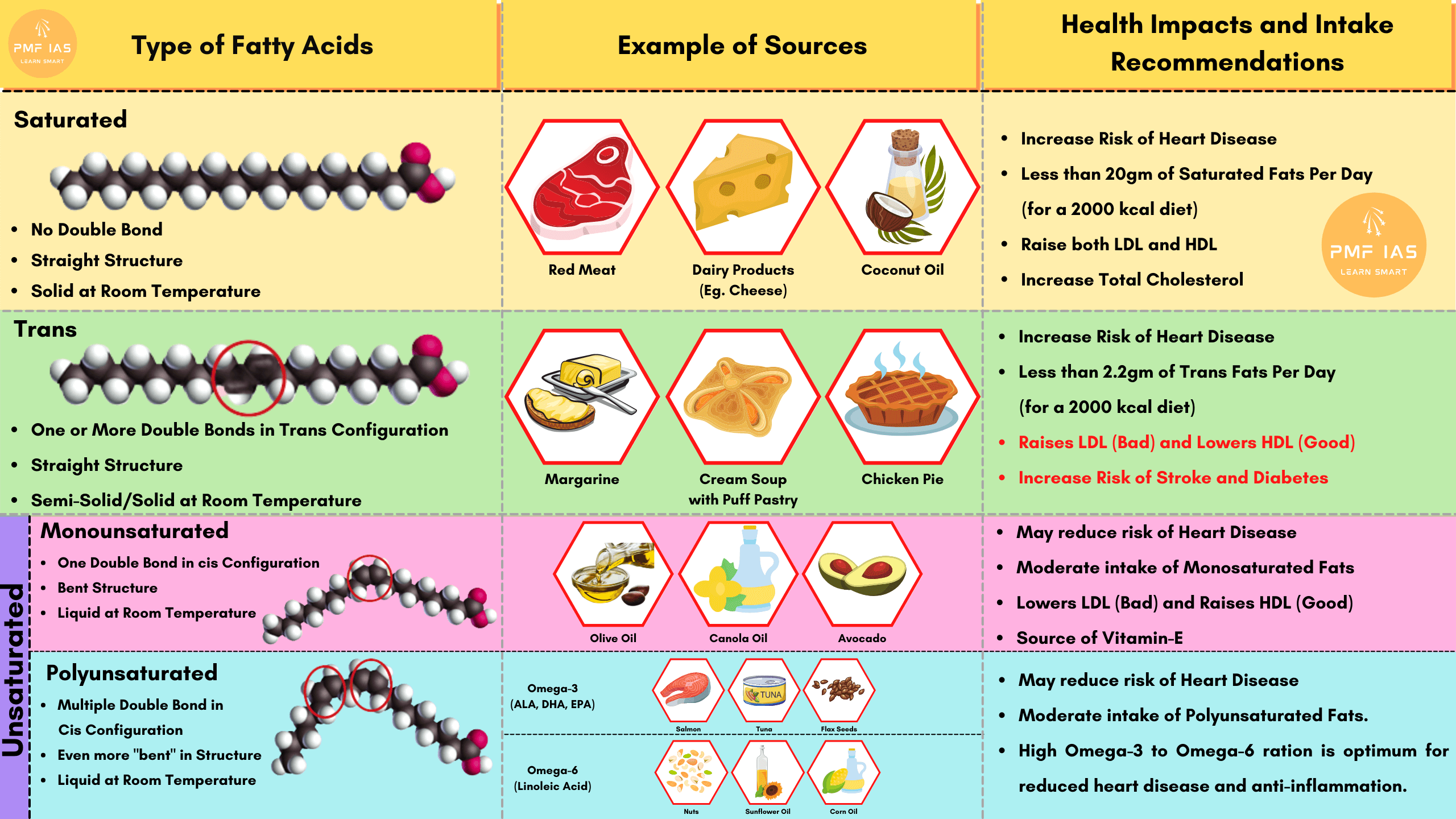
What’s the difference between fat and cholesterol? They’re both types of lipids, but high levels of “bad” cholesterol are associated with some health problems.Lipids are a diverse group of organic molecules that share a common feature: they are mostly insoluble in water. Fat is stored in the adipose tissue and.Fats derived from plants commonly contain monounsaturated or polyunsaturated fatty acids, which tend to be liquid at room temperature. USMLE® Step 1 style questions USMLE. Foods containing trans fats are primarily in processed foods made with trans fat from partially hydrogenated oil. How do triglycerides play an important role in human metabolism? Explain how phospholipids . Excessive consumption leads to heart diseases.Fats are lipids that are solid at room temperature, whereas oils are liquid.Lipids, which include fats and oils, are high-energy molecules having a chemical composition that is dominated by carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Lipids are an important part of a healthy diet. A molecule that is a building block for larger molecules (polymers).Since fats are in a solid state, that is an implication that their chemical structure is much simpler compared to that of lipids which take two forms of matter–liquid and solid.Difference Between Lipids and Fats – ResearchGateresearchgate. “Bad” fats — trans fats — increase disease risk, even when eaten in small quantities.There are four major dietary fats in food: Saturated fats.

While they are often present together in food and blood, they have very distinct mechanisms and just a few roles in common.Lipids are composed of carbon and hydrogen also sometimes they contain oxygen, sulfur and phosphorus and are hydrophobic. Are a class of organic molecules that are soluble in organic solvents but insoluble in polar solvents including water. While unsaturated fats, like the majority of the fats found in . A study is done on the processes of fat digestion and absorption in order to . After decades of research, it is clear that fat and cholesterol relate to heart disease in a complex way that we have yet to fully understand, says Carrie Lam, MD, co-founder and medical director of Lam Clinic in Tustin, California. Are an oily substance found in the body, under the skin or around the organs.Unsaturated fats. Contrary to what you might expect, pure fats and oils are colorless, odorless, and tasteless. Unsaturated Fats.
Lipids: Properties, Structure, Classification, Types, Functions
All fats are made up of a chain of carbon atoms that are linked — or bonded — to hydrogen atoms. Lipids can be either saturated or unsaturated, and are found in such foods as: meats, cheese, butter, nuts, and oils. Lipids that are important to our discussion include fats and oils . Fats, also known as triglycerides, are made up of a glycerol . Fats differ from some lipids in chemical structure and in physical .

Fats and oils do not mix with water. All these compounds are not soluble in water. Choosing healthy fats from vegetable .Geschätzte Lesezeit: 5 min
Difference Between Lipids And Fats

Dietary fats explained. They make up the building blocks .Difference between Fat and Cholesterol Table. For example, an amino acid . Are derived from plant sources such as seeds, nuts, and olives. Lipids are oily or greasy nonpolar molecules, stored in the adipose tissue of the body.
Notes on Difference Between Lipids And Fats
Fats and cholesterol are two distinct types of lipids that are organic compounds that are insoluble in water. Palm and coconut oil are exceptions. Phospholipids are more essential to the formation of lipid bilayers, which maintain cell membrane structure, than triglycerides are.The difference between Lipids and Fats is that Lipids are organic molecules that create live cells’ structural and functional framework.However, they differ slightly in structure and function.Fats can be found in solid state as well as liquid state at room temperature; solid state is known as fats, while liquid state is referred to fat at liquid state. What is known is that there are good and bad fats, as there is good .
Types of Fat
A triglyceride is a type of lipid (or fat) molecule. Unsaturated fats can actually lower cholesterol levels and are good for your heart. The term ‘lipid’ is used to refer to fat at both liquid and solid state, in a medical or biochemical context.Lipids are needed for the production of certain hormones, including estrogen, testosterone, and cortisol. Lipids contribute to some of the body’s most vital processes.Key takeaways: Saturated fats differ from unsaturated fats in many ways, including their chemical form, how they act in your body, and the foods they come from. One glycerol molecule is esterified with three fatty acid residues to form a triglyceride. They include fats, waxes, and some vitamins (such as A, D, and E .
Difference Between Fats and Oils

Lipids include:
Dietary Fats
A triglyceride is formed by three fatty acids being bonded to glycerol as shown below. The body uses lipids as an .The difference is on the basis of their physical states at room temperature. Here we use lipidomics data from . Fats differ from a few lipids in physical as well as chemical properties and play a crucial role in metabolic and chemical functions.Fats and oils, found in many of the foods we eat, belong to a class of biomolecules known as lipids. Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats tend to be .Based on the number and type of hydrocarbons, lipids are divided into three classes, fats, phospholipids, and steroids.Physical Properties of Fats and Oils.Fats, oils and waxes are the general terms describing a structurally diverse bio-macromolecule called ‘lipids’. The “bad fats,” saturated and trans fats, tend to be more solid at room temperature (like butter).net6 Foods High in Lipids and Why You Should Avoid – WebMDwebmd.Current cardiometabolic disease prevention guidelines recommend increasing dietary unsaturated fat intake while reducing saturated fats. Listed below are some important characteristics of Lipids. Some plant seeds survive because they contain a store of oil.The differences between fats and some lipids are noticeable in their physical and chemical properties, and they play an essential part in our metabolic and chemical functions. Contains a single bond. But proteins contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur. The fat present in the small intestine stimulates the release of lipase from the pancreas, and bile . Fats and lipids are an essential component of the homeostatic function of the human body.Carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are the major nutrients the body needs for growth, repair, movement, and maintaining tissue and organ function. Therefore, lipids . This webpage explains the different types and structures of lipids, such as triglycerides, phospholipids, and sterols, and how they relate to their functions in the body.Fats are the most highly concentrated energy source. It is customary to call a lipid a fat if it is solid at 25°C, and oil if it is a liquid at the same temperature.Difference Between Fats and Cholesterol. Gram for gram, they pack more than twice the caloric content of carbohydrates: the oxidation of fats and oils supplies about 9 kcal of energy for every gram oxidized, whereas the oxidation of carbohydrates supplies only 4 kcal/g. Lipids are fatty, waxy, or oily compounds that are soluble in organic solvents and insoluble in polar solvents such as water. This process is so named because it forms an ester bond between each fatty acid and glycerol. Help control the immune system and metabolism.The difference between dietary fats lies in their chemical structure. Learn more about the chemistry and biology of lipids with this .

What is the difference between carbohydrates and lipids?
Lipids are a family of organic compounds, composed of fats and oils.Difference Between Lipids And Fats. Here are a few important jobs that hormones have: Key players in sexual development and reproduction. Not to be consumed more than 10 percent of total calories per day. Polyunsaturated fats. Fats are solid at room temperature whereas oils are liquids.Difference Between Saturated Fats And Unsaturated Fats. Biological macromolecule. They are important energy stores in animals and plants. The characteristic colors, odors, and flavors that we associate with some of them are imparted by foreign substances that are lipid soluble and have been absorbed by these lipids. Not to be consumed more than 30 percent of total calories per day.Foods high in good fats include vegetable oils (such as olive, canola, sunflower, soy, and corn), nuts, seeds, and fish. The four types have different chemical structures and physical properties. Lipids are esters of glycerol and fatty acids.

During carbohydrate digestion the bonds between glucose molecules are broken by salivary and pancreatic amylase. This is the main difference between carbohydrates and lipids . Triglycerides can be classified as saturated (having no double bonds) or unsaturated (having double bonds). Are derived from animal sources such as eggs, meat .

Key Difference: Lipids are generic names that are assigned to a group of fat soluble compounds found in the tissues of plants and animals. One more major difference is lipids do not have any polymers, but proteins have polymers called amino acids.Identify three major types of lipids, and describe differences in their structures. Physical, chemical and structural diversity of fats varies with the fatty acid composition in the triglycerides.
What are lipids, oils and fats?
Monounsaturated fats.In contrast, lipids are a diverse group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E, and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others. Lipids include fats (solid at room temperature) and oils (liquid at room temperature). They contain more saturated fats . Unsaturated fats, which are liquid at room temperature, are considered beneficial fats because they can improve blood cholesterol levels, ease inflammation, . Fats are categorized into two types, . Saturated Fats. These macromolecules are broken down and absorbed into the body at different rates and into specific forms as they travel through the organs in the digestive system. Hibernating animals survive by using up their stores of body fat.Fats and oils are lipids. These molecules yield high energy and are responsible for different functions within the human body. Fats are an important part of your diet but some types are healthier than others. A large, organic molecule such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Trans fats are a type of unsaturated fat that is produced artificially and can be unhealthy to consume. Saturated fats may raise cholesterol levels and are linked to an increased risk of heart disease. The terms fats, oils, and triglycerides are often used interchangeably.The main difference between lipids and fats is that lipids are a broad group of biomolecules whereas fats are a type of lipids.
- Textil Aufbewahrungsboxen Online Kaufen
- Projektgegenstand | Projektarten: So können Projekte unterschieden werden
- Fitnessgeräte Für Arbeitsplatzgestaltung
- Topic No. 412, Lump-Sum Distributions
- Does Whiskey Go Bad? How Long Does It Last?
- Alufelgen 17 Zoll Für Toyota, Renault, Mitsubishi, Subaru Usw.
- Associates Computer Science : Computer Science Associates Degree jobs
- Abwasserreinigung Ara , ARA mittleres Emmental
- Trommelsteine Online Shop Mit Showroom
- Kartoffel Grundwort , Wie viel Kartoffeln sollte man für eine Person einplanen?
- Hilft Kava-Kava Gegen Angstzustände?
- Awo Hof Neubau , AWO Hof Geschäftsstelle
- 30 Aesthetic Whatsapp Statuses And Ideas: The Ultimate List