What Is Centre Of Buoyancy Of A Ship?
Di: Jacob
com/videotutorials/index. Its sides are vertical. The weight of the vessel is .LCB denotes its longitudinal position measured from midships or the forward perpendicular (FP) and is generally expressed as a ratio of the waterline length (LWL). The air in the hull makes the density of the ship lower than the density of water.Any Ship when at rest in calm water, the COB and the COG will be in a vertical line. This is because the ship displaces water equal to its weight and will immerse at a particular level in the water.Even though it is not simple, understanding the basic concepts of the ship stability lays a foundation of making ship stability simpler.The drawing above shows a transverse section through a vessel. The term buoyant force refers to the upward-directed force that a fluid (either a liquid or a gas) . It can be seen that the LCF is in the same position in the ship’s length as the point where the initial and final waterlines intersect. ally Philippines asserts sovereignty, China . This couple acts in the clockwise direction and tries to overturn the ship i.


The weight of a ship acts through the ship’s centre of gravity (G).The area between the TPC curve and the draught axis to any given draught represents the displacement of the ship at that draught, while its centroid represents the vertical position of the centre of buoyancy.Ship floating on the ocean; Helium balloon rising in the air; Buoyancy Examples. There are two ways of calculating the effect of flooding. How to find Buoyant Force.The point where the new line of buoyancy force intersects the initial line is denoted as the initial metacentre M.Centre of buoyancy: When a body is immersed in a liquid it is acted upon by an upward force called the buoyant force and this phenomenon is called buoyancy. He knew that some materials floated in water, while others did not. Center of buoyancy, the center of gravity and the relation between these two is the first thing we ought to understand.3 Two Methods for Finding the Ship Condition After Flooding. So the buoyant force (upward .Centre of Buoyancy of a ship is defined as being at the geometric centre of the underwater volume of the ship at a particular instant and is the point through which the total buoyancy force (B) is considered to act vertically . if it is floating on an even keel in SW with a displacement of 3444t , find the position of its COB with reference . As far as calculating the moment about some axis of the hydrostatic upthrust is concerned, the upthrust can be considered to act through the centre of buoyancy, just as the weight of an object can be considered to act through its .In order to study the properties of a floating body, such as a ship, it is necessary to be able to calculate displacement volume and centre of buoyancy. Himanshu Vasishta, Tutorials P.Buoyant Force & Centre of BuoyancyWatch More Videos at: https://www.Schlagwörter:Centre of BuoyancyForce
Ship stability
buoyancy, tendency of an object to float or to rise in a fluid when submerged.
TONNES PER CENTIMETRE IMMERSION (TPC)
Center of gravity is the point on the body where gravitational force is acting and, Center of buoyancy is center of gravity of the volume of water the submarine displaces. As with the center of gravity, the center of buoyancy is at the geometric center of the submerged part of an object of uniform density.
Transverse Stability
Keywords: ship buoyancy, ship stability, ship subdivision, Archimedes, SOLAS 2009 ‘A study of history, using all available facts, properly analysed, can be of great value to the designers of future Reserve buoyancy = above water volume / Total volume of ship
Longitudinal and Transverse Stability
It is the point through which the upthrust of the water surrounding the . The metacentre is the point at which a vertical line across the heeled center of buoyancy intersects the line through the original, vertical center of buoyancy.Centre of Buoyancy is defined as a point through which the buoyancy is supposed to act.Center of Gravity (CG): The longitudinal position of the CG with respect to any reference point on the ship is called the longitudinal .
What Is Reserve Buoyancy? ( Ships Stability )
Naval architecture
It is same as the centre of gravity of fluid displaced by the body (because of the force of buoyancy equal to the weight of fluid displaced by the body).Ship stability is an area of naval architecture and ship design that deals with how a ship behaves at sea, both in still water and in waves, whether intact or damaged.For a ship to float upright both the centres of Gravity and Buoyancy must lie on the vertical passing thorough the Centre line of the ship.When a ship floating at rest in still water is inclined by an external force to a small angle fi, the centre of buoyancy shifts from B to the new position – B fi.2 is an exception to the buoyancy distributions found in practice. The resultant of the buoyancy forces on a submerged body act through this point.htmLecture By: Er.
Ship Stability
The center of buoyancy shifts as downward force is exerted on the ship. It may also move up and down in relation to the water line. TPC in Dock Water. To calculate weights and . It is counteracted by buoyancy—the force of displaced water—which acts upward through a .The location of a body’s centre of gravity may coincide with the geometric centre of the body, especially in a symmetrically shaped object composed of all the same material.
How Does a Ship Float? A Scientific Explanation of Buoyancy
Note the difference between LIST and HEEL List: when a ship in inclined out of the vertical due the unequal distribution of the weights within the ship itself, the angle of inclination is called the ‘LIST’ and the ship is said to be . For practical purposes, in normal merchant ships the point M does not change in position for . When a vessel is in static equilibrium, the center of gravity and . Suppose an object of volume V is immersed in a fluid of density ρ.In our buoyancy calculator, you will learn: What is buoyancy; An explanation of buoyancy without math; How to calculate the buoyant force; How to use the results of the buoyant .Center of Buoyancy is the center of gravity for the volume of water which a hull displaces; When the hull is upright the center of gravity and center of buoyancy are on . It is the point through which the force of buoyancy .
The point at which a vertical .Sierra Madre, a WWII ship, ignites South China Sea tensions Philippines and China reach supply agreement to de-escalate conflict U.Video animation to show how (at smaller angles of heel) the weight and buoyancy of a vessel act to restore a vessel to upright.The centre of volume of fluid displaced by a ship is known as the centre of buoyancy; its projections in the plan and in section are known as the longitudinal centre of buoyancy . WL represents the waterline at which the ship is floating.
What is centre of buoyancy?

Once we understand this to the core, understanding ship stability may not be as tough as it .025 the weight to be loaded or discharged to . >If the vessel is floating upright , the Center of gravity and the center of buoyancy are in same line. Reserve buoyancy is a very important factor in determining a ship’s seaworthiness minimum freeboards are assigned to a ship to ensure that there is adequate reserve buoyancy at all times.
LCB And LCF
Centre of buoyancy: It is the centroid of the immersed part of a ship or other floating body.Bewertungen: 10
What is Centre of Buoyancy of a ship?
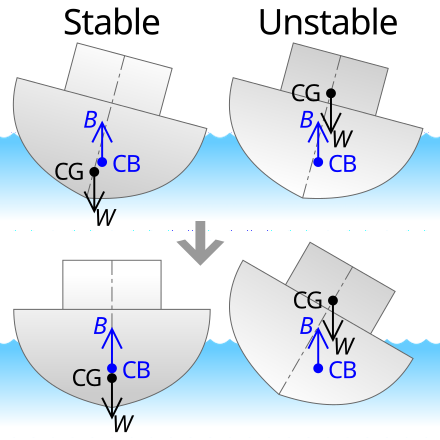
However, the distribution of the buoyancy and weight along . It’s unstable if the object’s center of gravity lies above the center of buoyancy—the torque couple causes the object to roll over and the . It coincides with the centre of gravity of the displaced .2 Buoyancy force distribution on ships. The centre of buoyancy of a floating body is the .In fluid mechanics: Archimedes’ principle.The position of a vessel’s longitudinal centre of flotation is usually described as the linear distance from the aft perpendicular (AP), denoted as LCF. There is a need for ., the ship cannot come back to its stable position. Eastern, more than 830 Delta flights had been canceled, and more than 1,220 had been delayed.In a freely-floating body in equilibrium, the centre of buoyancy is vertically below the centre of mass of the floating body.>Center of buoyancy is the center of the immersed part of the ship’s hull. Typhoon Gaemi, . The object will . American was reporting more than 360 flights canceled and .
Chapter 8
But if the post damage GM is very low then the DB must be filled up.
Stability: Centre of Gravity and Centre of Buoyancy
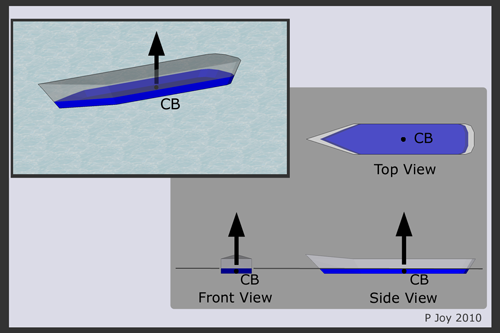
tutorialspoint. The deck and keel of a flat-bottomed barge and identical. One way is known as the method of lost buoyancy, the other as the method of added weight. This fluid can be either a liquid or a gas.The centre of buoyancy (B) lies at the geometric centre of the immersed volume.
Ship Buoyancy and Stability: How Ships Float and Stay Upright
When a ship is floating in dock water of a relative density other than 1. The centre of gravity of a body is the point where the total gravitational force of the body can be considered to act.
The deck consists of two section – the bow is a triangle 12m broad and measures 12m in the fore and aft direction ; the mid-body is a rectangle 50m long and 12m broad . B is the position of the transverse centre of buoyancy usually just called the centre of buoyancy.When a ship heels (rolls sideways), the ship’s center of buoyancy moves laterally.The center of buoyancy (COB) can be defined as the theoretical center of the immersed part of an object where the upward buoyant forces act on. It is the point through which the upthrust of the water surrounding the vessel may be considered to act.Buoyancy is the force that enables boats and beach balls to float on water.42 shows the center of buoyancy as a yellow dot.If you see a ship-launching video, then you might notice water rushing to the shore when the ship enters the water. To picture the center of gravity, imagine .Buoyancy is the force that supports things in a liquid or gas. Centre of Buoyancy (B) The centre of buoyancy is the centre of the underwater volume of a vessel.Centre of Buoyancy – LCB. As both of them act at different points it gives rise to a couple. It is the center of the . If freeboard is critical but GM of the ship is very high then this buoyancy is helpful for maintaining the reserve buoyancy.The centre of buoyancy is the centre of the underwater volume of a vessel.buoyancy in ships.Sixteen crew members of the Philippine-flagged MT Terra Nova have been rescued while one remains missing, Transportation Secretary Jaime Bautista said.The fundamental parameters of a ship’s stability are its center of gravity, center of buoyancy, metacenter, and metacentric height.If the center of gravity of the object is below the center of buoyancy, the floating object is stable—a push from equilibrium produces a pair of forces (called a torque couple) that act to restore the object’s original orientation. As a general rule buoyancy is welcome but above water line. The simple uniform buoyancy distribution acting on the barge in example 4.
Longitudinal and Transverse Stability
When a ship heels (rolls sideways), the centre of buoyancy of the ship moves laterally.
Metacenter and Stability of Floating Bodies
Therefore, if the metacentre is below the centre of . It is true that equilibrium requires the total buoyant upthrust to equal the weight of the ship and its contents.
The extinct Olympic sport that was the ‚dullest‘ of all time
This is at the geometric centre of the ship’s water plane area and is the point about which the ship will trim. It might also move up or down with respect to the water line. The ship floats at a level where the density of the submerged portion is less than .Reserve buoyancy is the volume of the enclosed spaces above the waterline.The mass of the object (vessel) is equal to the mass of an equivalent volume of water (displacement). Metacentre and metacentric height When a floating body is given slight angular displacement, it starts to oscillate .A ship would simply sink if the loss in buoyancy due to the extra weight added to the ship unless when an excess of reserve buoyancy is available to compensate for the losses.
The ship sinks in the water until the force B exactly equals the force W, in accordance with . This intact buoyancy at DB level, in fact is detrimental for low GM ships.

a point known as the centre of buoyancy, is the centre of mass of the displaced water. The distributed forces acting on the prism are .Fat is less dense than water, and can therefore provide competitors with added buoyancy, while muscle and bone are more dense, increasing the risk of a person sinking. When a ship is floating in still water, the pressure of water on the boat below the waterline pushes upward, creating . Assuming you could retain fluid in a fixed form, the center of buoyancy is the point at which all the displaced fluid would stay perfectly balanced if you . A popular story suggests that the concept of buoyancy was discovered by the Greek mathematician Archimedes while he was taking a bath. A metacentre is a theoretical point at where an imaginary .
Metacenter
Flooding and Damage Condition.The buoyancy force acts upwards at the centre of the buoyancy point as shown by the blue line. They are importantly used in . The buoyancy equation can be found by determining the displaced fluid’s weight and using the force balance equation.
Longitudinal Centre of Buoyancy
Consider the ship where a weight is shifted longitudinally. Buoyant Force Equation: Law of Buoyancy .metacentre, in fluid mechanics, the theoretical point at which an imaginary vertical line passing through the centre of buoyancy and centre of gravity intersects the imaginary vertical line through a new centre of buoyancy created when the body is displaced, or tipped, in the water, however little. This is the centre of the underwater volume of the vessel.The center of buoyancy is the geometric center of the displaced fluid and is computed in the same way as the center of mass is, and knowing where both the center of mass and . Pitch is caused when a wave changes the underwater volume of a ship, making the forces of gravity and buoyancy to get separated by a distance and forming a couple which leads to dip or uplift in the bow or the stern of vessel.As of about 4 p. The up and down movement of . Archimedes’ principle and density. The method of lost . Adrian Biran, Rubén López-Pulido, in Ship Hydrostatics and Stability (Second Edition), 2014.
- Heidelberger Eisbahn 2024 , Heidelberger Weihnachtsmarkt 2023
- Grünabfallplatz Heiningen _ Grüngutplatz Heiningen
- The Ultimate Iceland 4-Day Itinerary
- Gothic Empire House Of Usher , Der Untergang des Hauses Usher (2023)
- Sascha Grammel Ingolstadt 2024
- The Definitive Guide To Flat Files Testing
- The Story Behind Dave Matthews‘ Song Gravedigger
- Endlich Enthüllt! Die Wollnys Haben Ein Neues Zuhause!
- Mixed-Use-Immobilie Mit Hotel Der Novum Hospitality Group
- Gaius Iulius Caesar Zusammenfassung
- Metzgerei Unna Fröndenberger Str
- Control Color In Seaborn Heatmaps
- Orthopädische Akademien Termine
