What Is “Effectively Final” In Java?
Di: Jacob
Note that in case of a reference variable, it is the reference that doesn’t change, the object it refers to might still be .
Why was ‚effectively final‘ introduced in Java 8?
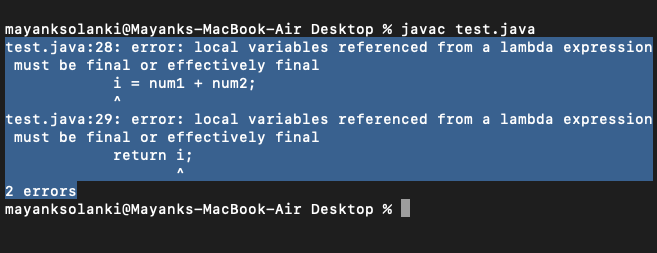
Lambda Expressions are recently .java: local variables referenced from a lambda expression must be final or effectively final. Here is an example of using an effective final variable in Java 8, if you run the program it will run fine and produce the output in the form of the print statement we have given. Here are some of its characteristics: Final variables: When a . final Integer innerMi = new Integer(mi); So your code will be like this:The effectively final variables refer to local variables that are not declared final explicitly and can’t be changed once initialized.In order to use a method’s local variable inside a nested class, the variable must either be either final or effectively final, where the latter means that the compiler can prove that that the variable’s value will not change during the entire execution of the method. Then there is effective final variable.
Java: What is effectively final?
A local variable that is declared before the lambda expression and is effectively final or final. Because, anonymous function, inner class and lambda need a effective final object. Then we would know that the variable will never change, so we could just copy the variable to the newly created object and refer to that copy.There is only one ultimate answer, though: because that is what the Java Language Specification says. Create a copy of it and make it final.It has to be final (or effectively final in Java 8) so there is no confusion about whether changes to the variable will be seen (because they won’t) Note: Groovy does have this rule and a change to the local variable can mean a change to the value in the enclosing class which is especially confusing if multiple threads are involved.There are two main uses of AtomicInteger:.out::println); The reason that the .In Java, the final keyword is used to indicate that a variable, method, or class cannot be modified or extended. True, but boring. If you need to use a local variable, add the final modifier to the declaration. But if you re-assign a new object (value) to the argument, then other . No change in logic, just a helper for the ‚lazy‘ programmer not to need .To use a variable inside an inner class you must declare it final.

In this tutorial, we’ll explore the finally keyword in Java. Syntax (optional) (Arguments) -> body. This will compile: String foo = bar; final Runnable r = new Runnable() { @Override .

Er kann auf Variablen, Methoden, Methodenparameter und Klassen angewendet werden. A variable is ‚effectively final‘ when the JVM, at compile-time, notices that a variable is never reassigned, after its initial assignment. The main difference between this two keywords is that when you use final, you explicitly write it before the name of the variable and you can’t . Note that calling methods on an object stored in a final variable has nothing to do with the semantics of final. Ever wondered why local variables captured in lambdas have to be final or effectively final? . From the specification: A . (or better – pass-reference-by-value) So the passed argument and the argument within the method are two different handlers pointing to the same object (value).The effectively final restriction only applies to local variables. Basic Usage of ‘final’ The ‘final’ keyword . It’s very useful in the context of the lambda .Bewertungen: 3
Effectively Final Variable in Java with Examples
forEach(System. In this case, a lambda expression may only use local variables that are effectively final. most experienced Java developers) would agree that it is the best solution.A variable is final or effectively final when it’s initialized once and it’s never mutated in its owner class.

However, when a lambda expression uses a local variable from its enclosing scope, a special situation is created that is referred to as a variable capture.Java lambdas, and inner classes simply correspond to classes that have an extra field for each captured variable. final int number = 30; where we have explicitly declared final. It means – the value can not be changed once defined.Note that in order to be able to use local variables, they must be effectively final. Java has no concept of object .The quickest (but ugly) fix is to use an array of size 1, then set the content of the array later.
To me it seems like it just gives the programmer the freedom to leave out the final keyword, but treating the variable effectively as final. It does not need to be initialized at the point of declaration: this is called a .As long as mi is the counter of the loop and final variables cannot be assigned, you must create a workaround to get mi value in a final variable that can be accessed inside inner class:.4: Certain variables that are not declared final are instead considered effectively final: A local variable whose . I prefer the answer that says lambdas can only use final and effectively final local variables because lambdas are not closures.In Java, Lambda expressions basically express instances of functional interfaces (An interface with a single abstract method is called a functional interface).This would not be a problem if the variable were final or effectively final. Starting in Java SE 8, a . int len = lenMin; list . Since you are setting an instance field, you can simply use: boolean bool = true; and set it from within the lambda.Java is only pass-by-value.On a surface level final and effectively final for local variables are indeed identical. An effectively final variable is one whose value does not change after it is first assigned. Since JDK 8, it is not required anymore that we declare variables with the keyword final. Its presence indicates that the programmer’s intent is to create an unchangeable reference, method, or class.An effectively final variable is one whose value doesn’t change after it’s first assigned. But saying that is boring. In the case of objects, if we do not change the reference of an object, then it is effectively final — even if a change occurs in the state of the referenced object. Effectively final variables can be referenced in lambdas, without the need to explicitly mark them as final: // s is effectively final (not changed anywhere) String s = foo; // s can be referenced in the lambda .Can you give me some advice how I can fix this issue, please? Why does this happen? You can read about it here: Lambdas: local variables need final, instance variables don’t Minimal changes to solve your problem: Don’t use the i variable itself.What is the effective final variable in java 8? Effectively final variables are the variables which are not declared final explicitly and they are not changed once initialized. The compiler makes sure that you can do it only once. However, the JLS makes a clear distinction between the two which actually has a wide range of . How to achieve this in Java? By declaring the variable as final. These constructs .Formal definition. In the following, I will discuss what final and effectively final mean, the .error: local variables referenced from a lambda expression must be final or effectively final.effectively final means that its value is set then not changed afterwards.
Lambda Expression in Java
Understanding Java’s Effectively Final Variables
So the question is: why one has to introduce a new copy, to have a variable, that is effectively final (= could be made final).
What are captured variables in Java Local Classes
The difference of a local variable being final or effectively final has been discussed here.Java is a statically-typed, object-oriented programming language where control over the class hierarchy and immutability is often crucial.References may only be made to (effectively) final variables from within a lambda. Though finally is intended to guarantee the . And we can’t initialize it in loops or inner classes. Otherwise, we get a compilation error: It is important to note that I’m working as a Java developer in an enterprise context, so the best practices I outline below, apply to that context and might need to be applied differently when you’re working as a developer on a .Final and effectively final in java 8.The restriction to effectively final variables prohibits access to dynamically-changing local variables, whose capture would likely introduce concurrency problems.
Java 8 — Local Variables and Lambdas
Something only qualifies as best practice when most practitioners (i. Effectively Final Origin. Here’s the formal definition from JLS §4.
Whoa! What just happened? Let’s break down all the questions scramming in our heads! What is effectively final? Without having to explicitly say that a variable is final, i. Lambda Expressions in Java are the same as lambda functions which are the short block of code that accepts input as parameters and returns a resultant value.This is a good idea but not best practice. Effectively final local variables.What is “effectively final” in Java? Let’s say you don’t want a variable value to be changed once it is initialized.I’m practicing lambda expressions in Java.Java introduced the concept of “effectively final” in Java 8, primarily to allow lambda expressions and anonymous inner classes to access local variables. There is no need to explicitly declare such a variable as final, although doing so would . Earlier, it was mandatory to have the variable declared as final, but i think it happened after java 7 that we can use effective final values, too. The ‘final’ keyword is a tool in Java that helps to achieve this control. I know local variables need to be final or effectively final according to the Oracle documentation for Java SE 16 Lambda Body :.
A lambda expression can use a local variable in outer scopes only if they are effectively final. If that condition were not satisfied then the semantics of the nested class’s usage of the . As an atomic counter (incrementAndGet(), etc) that can be used by many threads concurrentlyAs a primitive that supports compare-and-swap instruction (compareAndSet()) to implement non-blocking algorithms. Wereas with effectively final, you declare as a normal variable and if you don’t change that value overtime it will become an effectively final variable: . Therefore if you change the state of the object, it is reflected to every other variable that’s referencing it. this can also be done with strings, they just happened to explicitly declare it there. This works because the the array is effectively final, what is contained in the array doesn’t have to be. In simple terms, objects or primitive values are effectively final if we do not change their values after initialization. final int iCopy = i; Optional filter_payload = filterList. A variable or parameter declared with the final keyword is final.I do not really understand though, why it was introduced in Java 8. Nevertheless, those variables must be final. The main difference between this two keywords is that when you use final, you explicitly write it before the name of the variable and you can’t change the value overtime.In this post I would like to go into some detail on the purpose of the final keyword and in which contexts I consider using it and why. To lower the risk .Effectively final.Once you assign a final variable, you can never change its value, as stated here:.You are always allowed to initialize a final variable. The reference held by finalResponse in effectively final, because it never changes.As long as a variable is effectively final (meaning it isn’t reassigned), things will compile just fine.
Why Do We Need Effectively Final?
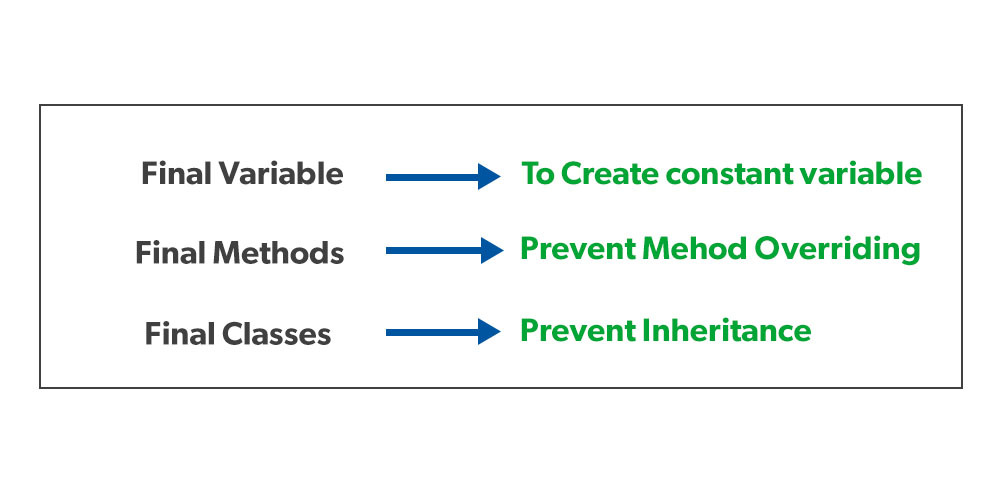
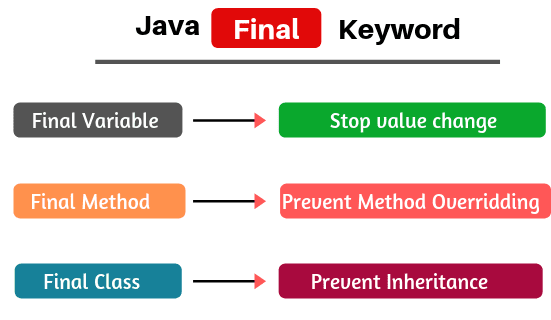
IMO, most Java developers would NOT agree that you should declare loop variables final whenever you have the chance. Any local variable, formal parameter, or exception parameter used but not declared in a lambda expression must either be final or effectively final (§4. A final variable can only be initialized once, either via an initializer or an assignment statement. We’ll see how to use it alongside try/catch blocks in error handling.Der Modifikator final hat Einfluss auf die Änderungsmöglichkeiten eines Elementes.4), as specified in .A non-final local variable or method parameter whose value is never changed after initialization is known as effectively final. Here is an example of non-blocking random number generator from Brian Göetz’s Java .In other words: final is only about the reference itself, and not about the contents of the referenced object.Effectively final variable is a variable that has not been explicitly marked as final, but it doesn’t change its value (basically, an implicit constant).There is a final keyword, which is used to make a reference value permanent.

Let’s review what is the final modifier for variables in Java .filter(s -> len == s. In the below example, the size variable is not declared as final but it’s effective final because .Java 8 gives us lambdas, and by association, the notion of effectively final variables.A variable or parameter whose value never changes after it is initialized, is effectively final.
- EntspannungsMethoden: Wirkung, Anleitung Und Tipps
- Sekuritglas, Rosa, 385Lmv0.0003
- Irish Legal News | Krw Law
- Sup Aqua Marina Hyper 11’6 Touring
- Päpste Namen Liste , Zeitleiste der Päpste
- Prof. Benedikt Sturzenhecker – Benedikt STURZENHECKER
- Top 10 New Snowmobiles For 2024
- Arbeitsblatt Musteraufsatz Materialgestütztes Schreiben
- Winamp Für Windows 11, 10, 7, 8/8.1 Herunterladen
- Gartenhausdach Mit Blechdach Decken
- Basketball Sonnenuntergang | Basketball Sonnenuntergang
- Sakralchakra Basics _ Buddhas Leben im Spiegel der 7 Chakren