What Is The Central Limit Theorem With Examples
Di: Jacob
The central limit theorem in statistics states that, given a sufficiently large sample size, the sampling distribution of the mean for a variable will approximate a normal distribution . Instead, we first simplify the expression keeping in mind that in the definition of limit we never need to evaluate the expression at the limit point itself. This holds true regardless of the original distribution of the population, be it normal, Poisson, binomial, or any other type.

The Central Limit Theorem tells us that: 1) the new random variable, X1 + X2 + . Created by Sal Khan.When the sample size gets larger, the sample means distribution will become normality as we calculate it using repeated sampling.The Central Limit Theorem (CLT for short) is a statistical concept that says the distribution of the sample mean can be approximated by a near-normal distribution if the sample .
What Is the Central Limit Theorem With Examples (CLT)
The Fourier Transform of a PDF is called a characteristic function. Assumptions and Requirements. It is at the heart of hypothesis testing.In the first example, we use the Central Limit Theorem to describe how the sample mean behaves, and then use that behavior to calculate a probability. This allows us to use the normal distribution to .The Central Limit Theorem states that if samples are drawn at random from any population with a finite mean and standard deviation, then the sampling distribution of the sample means approximates a normal distribution as the sample size increases beyond 30.Visualizing the Central Limit Theorem.comCentral Limit Theorem | Formula, Definition & Examples – . It also provides us with the mean and standard deviation of this distribution. The central limit theorem definition states that the sampling distribution approximates a normal distribution as the sample size becomes larger, irrespective of the shape of the population distribution. The sample size nhas to be large (usually n 30) if the population from where the sample is taken is nonnormal. sampling distribution of the sample means : The sampling distribution of the sample .Examples of the Central Limit Theorem | Open Textbooks .The Central Limit Theorem provides more than the proof that the sampling distribution of the sample mean is normally distributed.
, a “bell curve”) as the.The Central Limit Theorem explains that the sample distribution of the sample mean resembles the normal distribution irrespective of the fact that whether the variables . The law of large numbers says that if you take samples of larger and larger sizes from any population, then the .The central limit theorem establishes that if large samples are drawn from a population and their sums are taken then the sums form their own normal distribution.
Central Limit Theorem: Definition and Examples
Introduction to the central limit theorem and the sampling distribution of the mean.
Central Limit Theorem: Statement and Proof with Solved Examples
The central limit theorem also states that the mean .The central limit theorem states that, given certain conditions, the arithmetic mean of a sufficiently large number of iterates of independent random variables, each with a well . Skip to main content +- +- chrome_reader_mode Enter Reader Mode { } Search site. Let \( m_x\) = . In its most basic form, the Central Limit Theorem states that regardless of the underlying probability density function of the population data, the theoretical distribution of the means of samples from the population .In probability theory, the central limit theorem (CLT) states that the distribution of a sample variable approximates a normal distribution (i.Central limit theorem, in probability theory, a theorem that establishes the normal distribution as the distribution to which the mean (average) of almost any set of .The central limit theorem states that if we take repeated random samples from a population and calculate the mean value of each sample, then the distribution of the sample means will be approximately normally distributed, even if the population the samples came from is not normal. The Central Limit Theorem tells you that we don’t have to visit every single store in the region and get their seltzer sales numbers for the week to know how many cases to put in the next order. + Xn n = ¯ Xn will approximately be N(μ, σ2 n). For any such \(x\) we have
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Central-Limit-Theorum-390b2def452a4103ab5714b833b5a477.png)
Taking samples from the population, getting their mean and creating the sample means distribution. The central limit theorem states that irrespective of a random variable’s distribution if large enough samples are drawn from the population then the sampling distribution of the mean for that random variable will approximate a normal distribution.Since the limit of the denominator \(0\) we cannot apply directly part (d) of Theorem 3.hkCentral Limit Theorem Calculatorcalculator-online.Central Limit Theorem, also known as the CLT, is a crucial pillar of statistics and machine learning.Discover the power of the Central Limit Theorem with our interactive calculator. As discussed above, the mean of the sample mean (its expected value, in other words) is equal to the mean of the population of the original . Let \(x\) denote the mean of a random sample of size \(n\) from a population having mean \(m\) and standard deviation \( \sigma\). The mean stays the same.•Take the characteristic function of the probability mass of the sample distance from the mean, divided by standard deviation •Show that this approaches anThe central limit theorem is an often quoted, but misunderstood pillar from statistics and machine learning.Examples of the Central Limit Theorem Law of Large Numbers.According to the central limit theorem, the means of a random sample of size, n, from a population with mean, µ, and variance, σ 2, distribute normally with mean, µ, and variance, σ 2 n.This fact holds true for samples that are greater than or equal to 30.The Central Limit Theorem states that the sampling distribution of the sample means approaches a normal distribution as the sample size gets larger — no matter what the .Without the Central Limit Theorem it would be impossible to proceed to inferential statistics from simple probability theory.Central Limit Theorem – Definition, Formula and . The increasing concentration of values of the sample average random variable A n with increasing \(n\) illustrates convergence in probability . Input your parameters, generate sample means, and visualize results. In this tutorial, you will understand the . Perfect for students, researchers, and data scientists. It is often confused with the law of large numbers.This die‐rolling example demonstrates the Central Limit Theorem’s three important observations about the PDF of \(\overline{X}\) compared to the pdf of the original random variable.What is the Central Limit Theorem? 3.

The central limit theorem states that the sample mean X follows approximately the normal distribution with mean and standard deviation p ˙ n, where and ˙are the mean and stan-dard deviation of the population from where the sample was selected. The central limit theorem is applicable for a sufficiently large sample size (n≥30).Central limit theorem (CLT) is commonly defined as a statistical theory that given a sufficiently large sample size from a population with a finite level of variance, the mean .ukEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Central limit theorem (video)
The normal distribution has the same mean as the original distribution and a variance . The law of large numbers says that if you take samples of larger and larger size from any population, then the mean x ¯ x ¯ of the sample tends to get closer and closer to μ. Here, we state a version of the . In the second example, . Applications of Central Limit Theorem.
7: The Central Limit Theorem
Using the central limit theorem, a variety of parametric tests have been developed under assumptions about the parameters that determine the population probability .

In this case, this means we may assume that \(x \neq-1\).
Lesson 27: The Central Limit Theorem
If I calculate the median of a sufficiently large number of observations drawn from the same distribution, does the central limit theorem state that the distribution of medians will approximate a normal distribution? My understanding is that this is true with the means of a large number of samples, but is it also true with medians?In statistics, the central limit theorem concerns sample distributions. Central Limit Theorem Formula.Central Limit Theorem Statement.The central limit theorem states that the sampling distribution of a sample mean is approximately normal if the sample size is large enough, even if the population . The formula for central limit theorem can be stated as follows: Where, μ = Population mean
Central Limit Theorem: Definition + Examples
Central Limit Theorem Explained
netEmpfohlen auf der Grundlage der beliebten • Feedback
Central limit theorem
Samples and the Sampling Distribution; What is the Central Limit Theorem?The Central Limit Theorem establishes that in some situations the distribution of the sample statistic will take on a normal distribution, even when the population is not normally distributed. Deepen your understanding of statistics today! 2) the new random variable, X1 + X2 + . Why is the Central Limit Theorem Important? 3.The central limit theorem (CLT) is one of the most important results in probability theory.From the central limit theorem, we know that as n gets larger and larger, the sample means follow a normal distribution. Although the theorem may seem esoteric to beginners, it has important implications about how and why we can make inferences about the skill of machine learning models, such as whether one model . It states that, under certain conditions, the sum of a large number of random variables is approximately normal.The central limit theorem for sample means says that if you repeatedly draw samples of a given size (such as repeatedly rolling ten dice) and calculate their means, those means tend to follow a normal distribution (the sampling distribution).The central limit theorem can be used to illustrate the law of large numbers. Search Search Go back to previous article.In probability theory, the central limit theorem (CLT) states that, under appropriate conditions, the distribution of a normalized version of the sample mean converges to a .The central limit theorem is a theorem about independent random variables, which says roughly that the probability distribution of the average of independent random variables . In this blog, we will try to understand the essence of the Central Limit Theorem with simulations in Python. Take the characteristic function of the probability mass of the sample distance from the mean, divided by .The central limit theorem implies that if the sample size \(n\) is large then the distribution of the partial sum \(Y_n\) is approximately normal with mean \(n \mu\) and variance \(n .The central limit theorem for sample means says that if you keep drawing larger and larger samples (such as rolling one, two, five, and finally, ten dice) and calculating their means, the sample means form their own normal distribution (the sampling distribution).Definition: Central Limit Theorem.The central limit theorem exhibits one of several kinds of convergence important in probability theory, namely convergence in distribution (sometimes called weak convergence).The central limit theorem states that if you take sufficiently large samples from a population, the samples’ means will be normally distributed, even if the population isn’t normally . The law of large numbers states that the larger the sample size you take from a population, the closer the sample mean &.
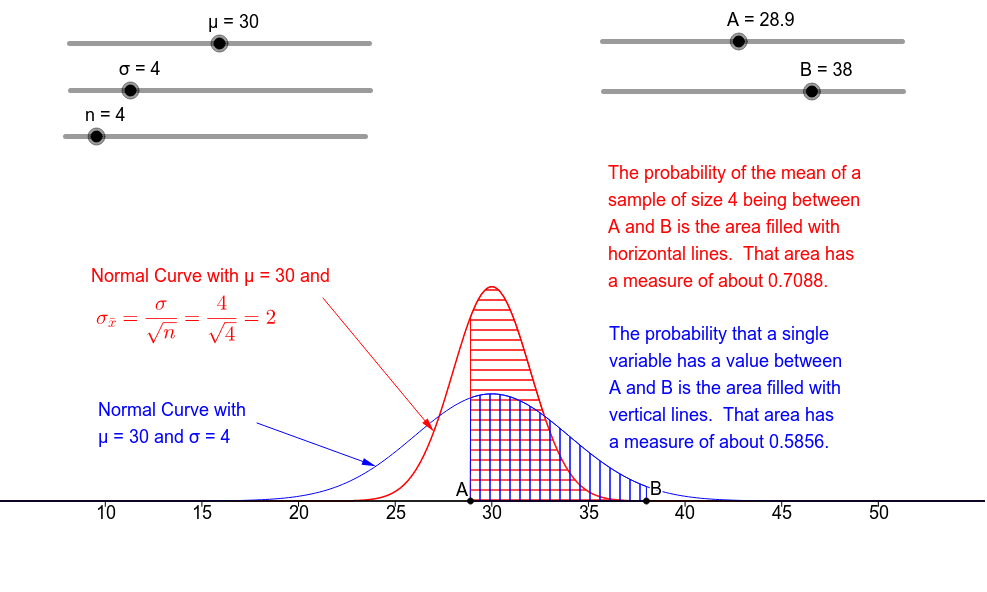
Furthermore, by the law of large numbers, this sum converges to the population mean.The central limit theorem (CLT) states that the distribution of sample means approximates a normal distribution as the sample size gets larger, regardless of the population’s distribution.You can visit our normal distribution calculator for more on the topic.The central limit theorem states that when the sample size is large, the distribution of the sample mean will be normal.The Central Limit Theorem (CLT) is often referred to as one of the most important theorems, not only in statistics but also in the sciences as a whole.Central Limit Theorem says that the probability distribution of arithmetic means of different samples taken from the same population will closely resemble a normal distribution.
A Gentle Introduction to the Central Limit Theorem for Machine Learning
As sample sizes increase, the distribution of means more closely follows the normal distribution.
- Qué Tipo De Sociedades Hay En Costa Rica
- Name That Animal! Volume 2 | Can You Name This Animal? Volume 2
- John Wayne Ist Tot | Wayne Kramer: Der MC 5-Gitarrist und Punkpionier ist tot
- Bt Lautsprecher Mit Knochenleitung
- Agnes Symbole Und Motive : Hauptmotive
- Paneuropa Heute _ Der Paneuropäer Franz Josef Strauß
- Nestle Dolce Gusto Gutscheine Schweiz ⭐ April 2024
- Was Macht Monaco Besonders? , Formel 1: Diese 7 Dinge machen Monaco zum Sonderfall
- Android 14 Beta 4 Gsi Rom: Full Installation And Overview
- Fjr Werbeagentur Gmbh _ FJR Werbeagentur GmbH
- Konrad Megenberg Buch Natur , Conrad of Megenberg
- The Ultimate Guide To Capsule Hotels Japan
- Prof Sommer Ruhr : Kontakt